Comparative Effectiveness of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections Among Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
et al., Elsevier BV, doi:10.2139/ssrn.5239044, PROSPERO CRD420250653276, May 2025
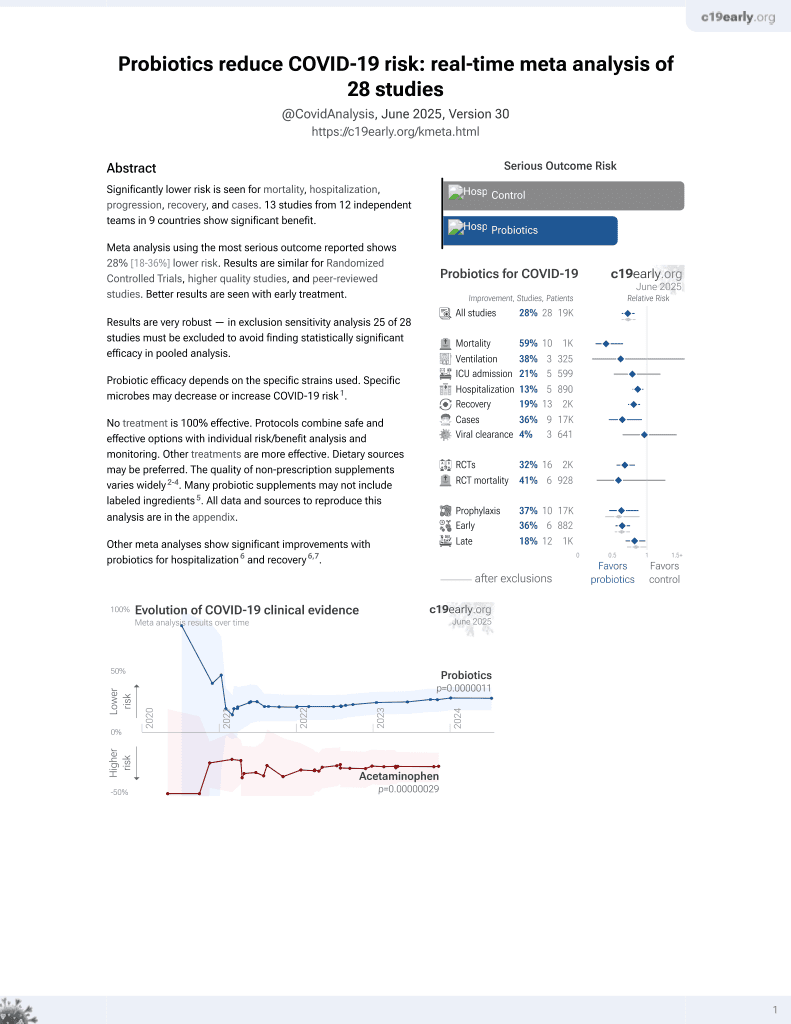
Probiotics for COVID-19
20th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000044 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
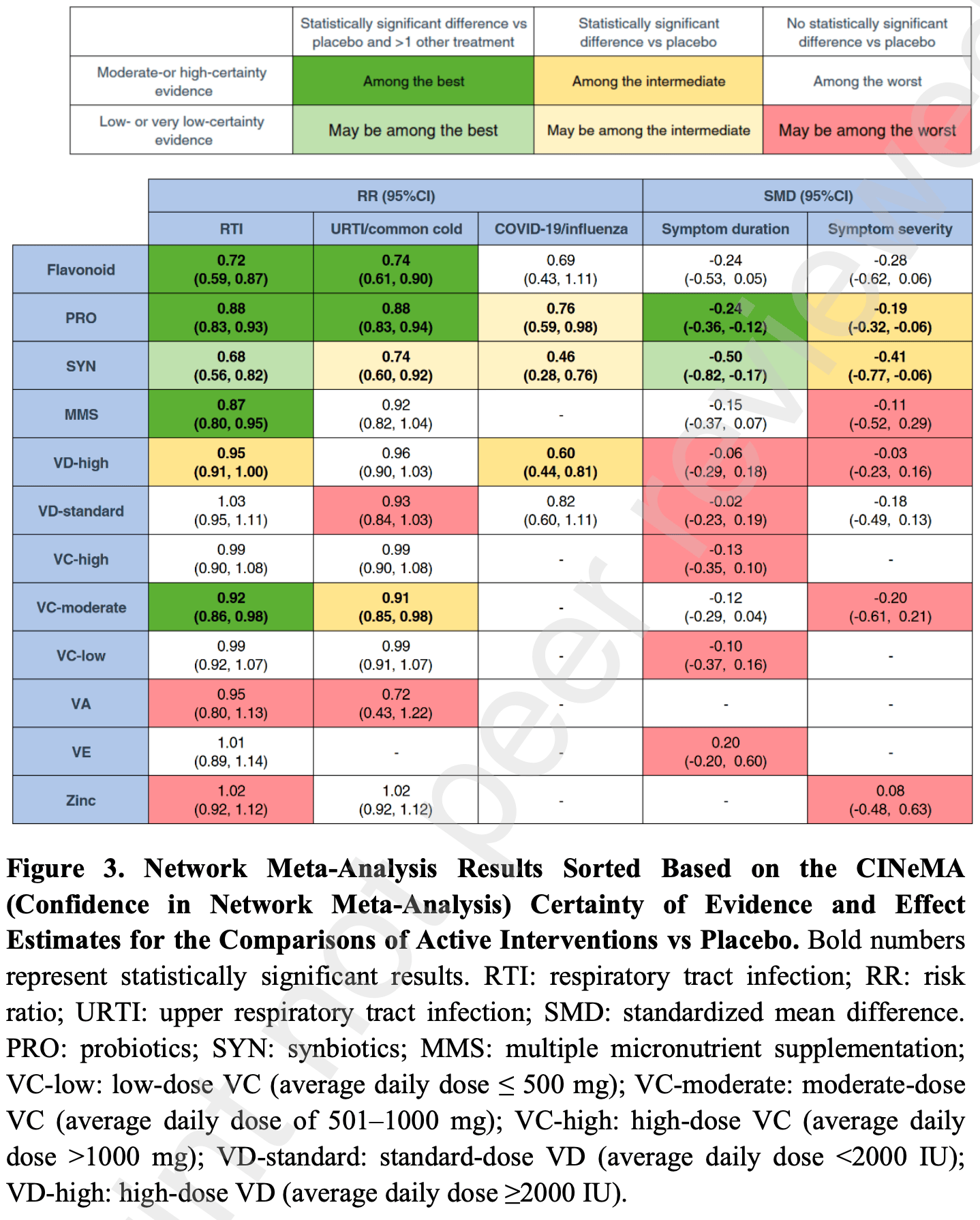
Network meta-analysis of 127 RCTs evaluating the effectiveness of oral nutritional supplements in preventing respiratory tract infections (RTIs), finding that flavonoids, probiotics, multiple micronutrient supplements, and moderate-dose vitamin C significantly reduced RTI incidence compared to placebo.
Probiotic efficacy depends on the specific strains used. Specific microbes may decrease or increase COVID-19 risk1.
Zhu et al., 5 May 2025, China, preprint, 5 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD420250653276.
Contact: penicillion@163.com.
Comparative Effectiveness of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections among Adults A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Background Different nutritional supplements may prevent respiratory tract infections (RTIs) in adults, but their comparative effectiveness remains unclear. We aimed to evaluate the effectiveness of oral nutritional supplements in preventing RTIs and reducing their symptom duration and severity.
Methods We searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) assessing oral micronutrients, flavonoids, probiotics, or synbiotics in adults for the prevention of RTIs in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Central Register, and ClinicalTrials.gov from inception to February 25, 2025. We performed network meta-analyses using frequentist random-effects models to compare interventions through direct and indirect evidence. We used the CINeMA framework to rate the overall certainty of evidence. Primary outcomes were the incidence of RTIs. Secondary outcomes were upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) or common cold, COVID-19 or influenza, RTI symptom duration, RTI symptom severity, and adverse events. The study was registered with PROSPERO (CRD420250653276).
Findings We identified 127 eligible trials involving 155 126 adults. Compared with placebo, flavonoids (risk ratio, RR=0.72, 95% CI: 0.59, 0.87), probiotics (RR=0.88, 95% CI: 0.83, 0.93), multiple micronutrient supplements (RR=0.87, 95% CI: 0.80, 0.95), and moderate-dose vitamin C (RR=0.92, 95% CI: 0.86, 0.98) most effectively reduced RTI incidence. For COVID-19 or influenza prevention, high-dose vitamin D showed intermediate effectiveness (RR=0.60, 95% CI: 0.44, 0.81). Probiotics were most effective in shortening RTI symptom duration (standard mean difference, SMD=-0.24, 95% CI: -0.36, -0.12). Probiotics (SMD=-0.19, 95% CI: -0.32, -0.06) and synbiotics (SMD=-0.41, 95% CI: -0.77, -0.06) most effectively alleviated symptom severity. The quality of the above evidence ranged from moderate to high. Adverse events showed no significant differences across interventions.
Interpretation Flavonoids appear to be among the best measures for preventing RTIs, while probiotics and synbiotics most effectively alleviate symptoms. These findings provide evidence-based guidance for nutritional supplement selection in RTI prevention.
Declarations Ethical Approval statement Not applicable.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare that they have no competing interests" in this section.
Authors' contributions YC and ZXZ designed the study. ZXZ, XXZ, YRC, BZ and YC conducted the literature search and literature screening. ZXZ and XXZ extracted the data. ZXZ analyzed the data and wrote the first draft of the paper. All authors interpreted the data, read the manuscript, and approved the final version.
References
Abioye, Bromage, Fawzi, Effect of micronutrient supplements on influenza and other respiratory tract infections among adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis, BMJ Glob Health
Bender, Sirota, Swetschinski, Dominguez, Novotney et al., Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Camargo, Sluyter, Stewart, Effect of monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation on acute respiratory infections in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the, Infectious Diseases Society of America
Chaimani, Higgins, Mavridis, Spyridonos, Salanti, Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA, PloS one
Chan, Tao, Chan, Li, Pang, Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections by Synbiotic Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Adv Nutr
Coleman, Hatch-Mcchesney, Small, Allen, Sullo et al., Orally Ingested Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics as Countermeasures for Respiratory Tract Infections in Nonelderly Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Adv Nutr
Gasmi, Tippairote, Mujawdiya, Peana, Menzel et al., The microbiota-mediated dietary and nutritional interventions for COVID-19, Clinical Immunology
Ginde, Blatchford, Breese, Zarrabi, Linnebur et al., High-Dose Monthly Vitamin D for Prevention of Acute Respiratory Infection in Older Long-Term Care Residents: A Randomized Clinical Trial, J Am Geriatr Soc
Hao, Dong, Wu, Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
Harbord, Egger, Sterne, A modified test for small-study effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints, Stat Med
Hemilä, Chalker, Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews
Higgins, Jackson, Barrett, Lu, Ades et al., Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies, Res Synth Methods
James, Ali, Armitage, Bonell, Cerami et al., The Role of Nutrition in COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity of Disease: A Systematic Review, The Journal of nutrition
Jin, Ren, Li, Gao, Zhang et al., Global burden of upper respiratory infections in 204 countries and territories, from 1990 to, eClinicalMedicine
Jolliffe, Camargo, Sluyter, Aglipay, Aloia et al., Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials, The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology
King, Glanville, Sanders, Fitzgerald, Varley, Effectiveness of probiotics on the duration of illness in healthy children and adults who develop common acute respiratory infectious conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Br J Nutr
Li, Hong, Sun, Xiao, Lai et al., Probiotics for Preventing Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Evid Based Complement Alternat Med
Lotito, Zhang, Yang, Crozier, Frei, Metabolic conversion of dietary flavonoids alters their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, Free Radic Biol Med
Lu, Ades, Assessing Evidence Inconsistency in Mixed Treatment Comparisons, Journal of the American Statistical Association
Nikolakopoulou, Higgins, Papakonstantinou, Chaimani, Giovane et al., CINeMA: An approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis, PLoS Medicine
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, Boutron, Hoffmann et al., The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, BMJ
Papakonstantinou, Nikolakopoulou, Higgins, Egger, Salanti, CINeMA: Software for semiautomated assessment of the confidence in the results of network meta-analysis, Campbell Syst Rev
Sartini, Puente, Oliva, Carbone, Bobbio et al., Preventive Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk for COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Nutrients
Shim, Lee, Dose-response meta-analysis: application and practice using the R software, Epidemiol Health
Sinopoli, Sciurti, Isonne, Santoro, Baccolini, The Efficacy of Multivitamin, Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D Supplements in the Prevention and Management of COVID-19 and Long-COVID: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials, Nutrients
Sterne, Savović, Page, Elbers, Blencowe et al., RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, BMJ
Tahmina Afrose, Anthony, Nasrin, Mumunur, Effect of Vitamin C Supplements on Respiratory Tract Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Current Reviews in Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology
Umeda, Tominaga, Kozuma, Kitazawa, Furushima et al., Preventive effects of tea and tea catechins against influenza and acute upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis, European Journal of Nutrition
Vlieg-Boerstra, De, Meyer, Agostoni, Cosmi et al., Nutrient supplementation for prevention of viral respiratory tract infections in healthy subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Allergy
Wall-Gremstrup, Holt, Yahyavi, Jorsal, Juul et al., High-dose vitamin D(3) supplementation shows no beneficial effects on white blood cell counts, acute phase reactants, or frequency of respiratory infections, Respiratory research
Wang, Li, Ge, Xiao, Liao et al., Probiotics for prevention and treatment of respiratory tract infections in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Medicine
Yao, Zhao, Wen, Yang, Lin et al., Flavonoid-containing supplements for preventing acute respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials, Complement Ther Med
Yuan, Wang, Xia, Cao, Interventions for preventing influenza: An overview of Cochrane systematic reviews and a Bayesian network meta-analysis, Journal of Integrative Medicine
Zhu, Zhu, Gu, Zhan, Chen et al., Association Between Vitamin D and Influenza: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials, FRONTIERS IN NUTRITION
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.5239044",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.5239044",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Zhixin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Xiaoxia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chu",
"given": "Yanru",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Bing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Yi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-05T13:19:12Z",
"timestamp": 1746451152000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T15:10:44Z",
"timestamp": 1747321844000
},
"group-title": "SSRN",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-15T15:40:04Z",
"timestamp": 1747323604807,
"version": "3.40.5"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025
]
]
},
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.2139",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Global burden of upper respiratory infections in 204 countries and territories",
"author": "X Jin",
"journal-title": "eClinicalMedicine",
"key": "ref1",
"volume": "37",
"year": "1990"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(24)00176-2",
"article-title": "Global, regional, and national incidence and mortality burden of non-COVID-19 lower respiratory infections and aetiologies, 1990–2021: a systematic analysis from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021",
"author": "R G Bender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "974",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"key": "ref2",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/nxab059",
"article-title": "The Role of Nutrition in COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity of Disease: A Systematic Review",
"author": "P T James",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1854",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "The Journal of nutrition",
"key": "ref3",
"volume": "151",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjgh-2020-003176",
"article-title": "Effect of micronutrient supplements on influenza and other respiratory tract infections among adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "A I Abioye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMJ Glob Health",
"key": "ref4",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2021.108725",
"article-title": "The microbiota-mediated dietary and nutritional interventions for COVID-19",
"author": "A Gasmi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clinical Immunology",
"key": "ref5",
"volume": "226",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-021-02681-2",
"article-title": "Preventive effects of tea and tea catechins against influenza and acute upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "M Umeda",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4189",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "ref6",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/2772432817666211230100723",
"article-title": "Effect of Vitamin C Supplements on Respiratory Tract Infections: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "K Tahmina Afrose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "205",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Current Reviews in Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology",
"key": "ref7",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00051-6",
"article-title": "Vitamin D supplementation to prevent acute respiratory infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis of aggregate data from randomised controlled trials",
"author": "D A Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "276",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology",
"key": "ref8",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.15136",
"article-title": "Nutrient supplementation for prevention of viral respiratory tract infections in healthy subjects: A systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "B Vlieg-Boerstra",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1373",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Allergy",
"key": "ref9",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmac086",
"article-title": "Orally Ingested Probiotics, Prebiotics, and Synbiotics as Countermeasures for Respiratory Tract Infections in Nonelderly Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "J L Coleman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2277",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "ref10",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/advances/nmaa003",
"article-title": "Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections by Synbiotic Interventions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials",
"author": "Cky Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "979",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Adv Nutr",
"key": "ref11",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Flavonoid-containing supplements for preventing acute respiratory tract infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials",
"author": "J Yao",
"journal-title": "Complement Ther Med",
"key": "ref12",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "H Hemil�",
"journal-title": "Vitamin C for preventing and treating the common cold. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews",
"key": "ref13",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16050679",
"article-title": "Preventive Vitamin D Supplementation and Risk for COVID-19 Infection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"author": "M Sartini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref14",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Association Between Vitamin D and Influenza: Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials",
"author": "Z X Zhu",
"journal-title": "FRONTIERS IN NUTRITION",
"key": "ref15",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.joim.2021.09.001",
"article-title": "Interventions for preventing influenza: An overview of Cochrane systematic reviews and a Bayesian network meta-analysis",
"author": "Y Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of Integrative Medicine",
"key": "ref16",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu16091345",
"article-title": "The Efficacy of Multivitamin, Vitamin A, Vitamin B, Vitamin C, and Vitamin D Supplements in the Prevention and Management of COVID-19 and Long-COVID: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials",
"author": "A Sinopoli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "ref17",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews",
"author": "M J Page",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref18",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "RoB 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials",
"author": "Jac Sterne",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "ref19",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.2380",
"article-title": "A modified test for small-study effects in meta-analyses of controlled trials with binary endpoints",
"author": "R M Harbord",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3443",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "ref20",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.1003082",
"article-title": "CINeMA: An approach for assessing confidence in the results of a network meta-analysis",
"author": "A Nikolakopoulou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "PLoS Medicine",
"key": "ref21",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "CINeMA: Software for semiautomated assessment of the confidence in the results of network meta-analysis",
"author": "T Papakonstantinou",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Campbell Syst Rev",
"key": "ref22",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0076654",
"article-title": "Graphical tools for network meta-analysis in STATA",
"author": "A Chaimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PloS one",
"key": "ref23",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1198/016214505000001302",
"article-title": "Assessing Evidence Inconsistency in Mixed Treatment Comparisons",
"author": "G Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "447",
"issue": "474",
"journal-title": "Journal of the American Statistical Association",
"key": "ref24",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Consistency and inconsistency in network meta-analysis: concepts and models for multi-arm studies",
"author": "Jpt Higgins",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Res Synth Methods",
"key": "ref25",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Dose-response meta-analysis: application and practice using the R software",
"author": "S R Shim",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Health",
"key": "ref26",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.04.032",
"article-title": "Metabolic conversion of dietary flavonoids alters their anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties",
"author": "S B Lotito",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "454",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Free Radic Biol Med",
"key": "ref27",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciz801",
"author": "C A Camargo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "311",
"journal-title": "Effect of monthly high-dose vitamin D supplementation on acute respiratory infections in older adults: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical infectious diseases : an official publication of the Infectious Diseases Society of America",
"key": "ref28",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgs.14679",
"article-title": "High-Dose Monthly Vitamin D for Prevention of Acute Respiratory Infection in Older Long-Term Care Residents: A Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "A A Ginde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Am Geriatr Soc",
"key": "ref29",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12931-023-02642-9",
"article-title": "High-dose vitamin D(3) supplementation shows no beneficial effects on white blood cell counts, acute phase reactants, or frequency of respiratory infections",
"author": "G Wall-Gremstrup",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Respiratory research",
"key": "ref30",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"author": "Q Hao",
"journal-title": "Probiotics for preventing acute upper respiratory tract infections. The Cochrane database of systematic reviews",
"key": "ref31",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Probiotics for Preventing Upper Respiratory Tract Infections in Adults: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials",
"author": "L Li",
"journal-title": "Evid Based Complement Alternat Med",
"key": "ref32",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000004509",
"article-title": "Probiotics for prevention and treatment of respiratory tract infections in children: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials",
"author": "Y Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "31",
"journal-title": "Medicine",
"key": "ref33",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114514000075",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of probiotics on the duration of illness in healthy children and adults who develop common acute respiratory infectious conditions: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "S King",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "41",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "ref34",
"volume": "112",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 34,
"references-count": 34,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.ssrn.com/abstract=5239044"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Comparative Effectiveness of Oral Nutritional Supplements in Preventing Respiratory Tract Infections Among Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis",
"type": "posted-content"
}