The Value of Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Severe COVID-19
et al., Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms12071269, Jun 2024
Retrospective 167 severe COVID-19 patients showing lower mortality with ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA). Timing and duration of treatment is unknown - UDCA patients may have been on UDCA since before COVID-19.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
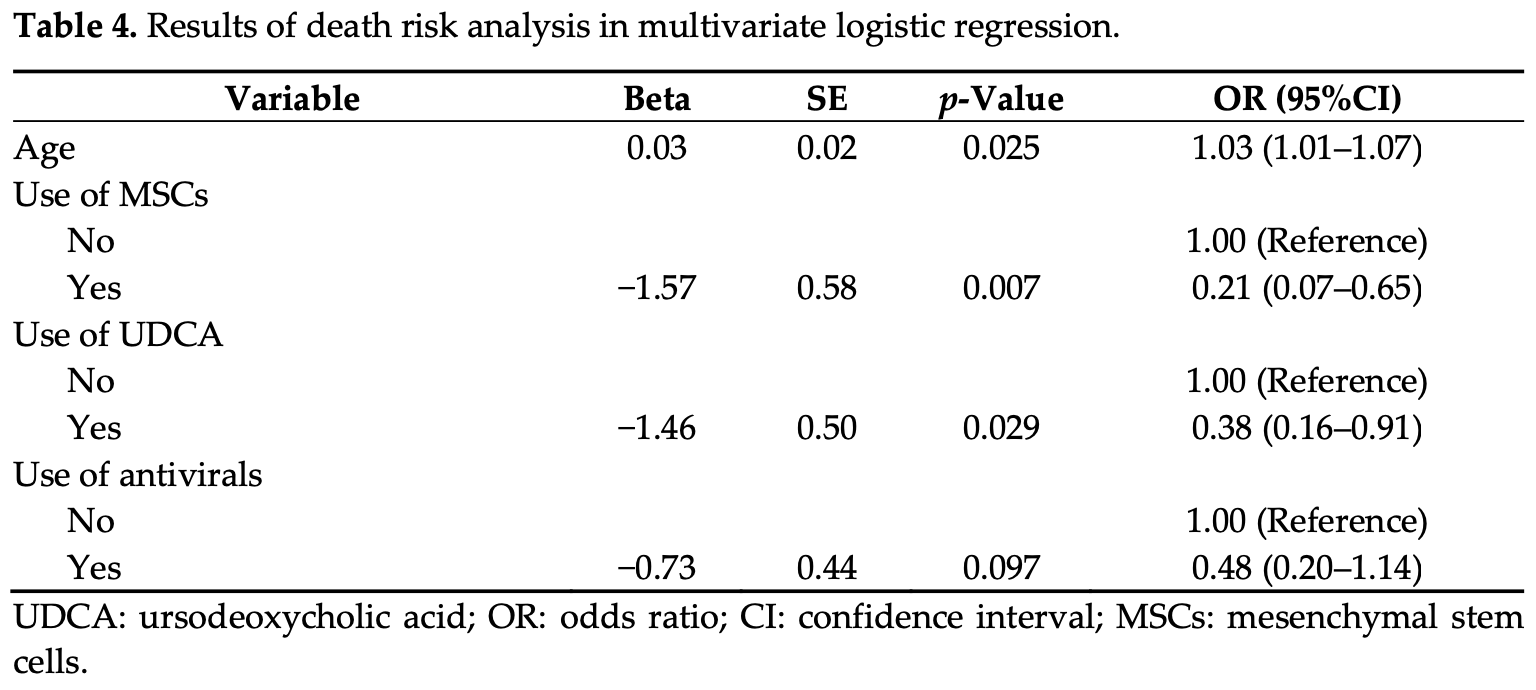
risk of death, 62.0% lower, OR 0.38, p = 0.03, treatment 42, control 125, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Zheng et al., 22 Jun 2024, retrospective, China, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
The Value of Ursodeoxycholic Acid and Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Treatment of Severe COVID-19
Microorganisms, doi:10.3390/microorganisms12071269
Objective: The objective of this study was to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in patients with severe COVID-19. Methods: We included severe COVID-19 patients hospitalized at Shulan (Hangzhou) Hospital between December 2022 and June 2023. We used a logistic regression model to compare the use of UDCA and MSCs in the two distinct groups of improved and poor outcomes. It is noteworthy that the deterioration group encompassed instances of both death and abandonment of treatment. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was plotted to assess the performance of the model. The aim was to assess the therapeutic effect of UDCA and MSCs on the outcome of severe COVID-19 patients. Results: A total of 167 patients with severe COVID-19 were included in this study. The analysis revealed that out of 42 patients (25.1%), 17 patients (10.2%) had taken UDCA, and 17 patients (10.2%) had used MSCs. Following a multivariable logistic regression, the results indicated a negative association between UDCA treatment (OR = 0.38 (0.16-0.91), p = 0.029), MSCs treatment (OR = 0.21 (0.07-0.65), p = 0.007), and the risk of severe COVID-19 mortality. Additionally, age showed a positive association with the risk of mortality (OR = 1.03 (1.01-1.07), p = 0.025). Conclusions: UDCA and MSCs have shown potential in improving the prognosis of severe COVID-19 patients and could be considered as additional treatments for COVID-19 in the future.
Author Contributions: Q.Z., L.L. and G.S.: Conception and design of the study. Q.Z. and Y.L.: Data collection, data analysis, and writing of this article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
References
Abdulrab, Al-Maweri, Halboub, Ursodeoxycholic acid as a candidate therapeutic to alleviate and/or prevent COVID-19-associated cytokine storm, Med. Hypotheses
Brevini, Maes, Webb, John, Fuchs et al., FXR inhibition may protect from SARS-CoV-2 infection by reducing ACE2, Nature
Cabrera, Arab, Arrese, Udca, NorUDCA, and TUDCA in Liver Diseases: A Review of Their Mechanisms of Action and Clinical Applications, Handb. Exp. Pharmacol
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Wang et al., A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Chen, Hu, Chen, Tang, Zhu et al., Clinical Study of Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment for Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Induced by Epidemic Influenza A (H7N9) Infection: A Hint for COVID-19 Treatment, Engineering
Colapietro, Angelotti, Masetti, Shiffer, Pugliese et al., Ursodeoxycholic Acid Does Not Improve COVID-19 Outcome in Hospitalized Patients, Viruses
Couto, Al-Arawe, Filgueiras, Fonseca, Hinterseher et al., Systematic review and meta-analysis of cell therapy for COVID-19: Global clinical trial landscape, published safety/efficacy outcomes, cell product manufacturing and clinical delivery, Front. Immunol
Ding, Shyu, Lin, Mesenchymal stem cells, Cell Transplant
Donovan-Banfield, Penrice-Randal, Goldswain, Rzeszutek, Pilgrim et al., Characterisation of SARS-CoV-2 genomic variation in response to molnupiravir treatment in the AGILE Phase IIa clinical trial, Nat. Commun
Ehianeta, Mzee, Adebisi, Ehianeta, Recent SARS-CoV-2 Outlook and Implications in a COVID-19 Vaccination Era, Infect. Microbes Dis
Ferretti, Martinkova, Biskup, Benke, Gialdini et al., Sex and gender differences in Alzheimer's disease: Current challenges and implications for clinical practice: Position paper of the Dementia and Cognitive Disorders Panel of the European Academy of Neurology, Eur. J. Neurol
Fonseca-González, Alamilla-Sánchez, García-Macas, Herrera-Acevedo, Villalobos-Brito et al., Impact of plasmapheresis on severe COVID-19, Sci. Rep
John, Bastaich, Webb, Brevini, Moon et al., Ursodeoxycholic acid is associated with a reduction in SARS-CoV-2 infection and reduced severity of COVID-19 in patients with cirrhosis, J. Intern. Med
Lan, Neilsen, Slack, Cantara, Castaner et al., Nirmatrelvir Resistance in SARS-CoV-2 Omicron_BA.1 and WA1 Replicons and Escape Strategies, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.31.522389
Lanzoni, Linetsky, Correa, Messinger Cayetano, Alvarez et al., Umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for COVID-19 acute respiratory distress syndrome: A doubleblind, phase 1/2a, randomized controlled trial, Stem Cells Transl. Med
Leng, Zhu, Hou, Feng, Yang et al., Transplantation of ACE2(-) Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improves the Outcome of Patients with COVID-19 Pneumonia, Aging Dis
Li, Niu, Guo, Gao, Wang et al., Stem cell therapy for COVID-19, ARDS and pulmonary fibrosis, Cell Prolif
Lin, Abi Fadel, Huang, Milinovich, Sacha et al., Nirmatrelvir or Molnupiravir Use and Severe Outcomes From Omicron Infections, JAMA Netw. Open
Luo, He, Wei, Lu, Yi, Paxlovid-tacrolimus drug-drug interaction caused severe diarrhea that induced combined diabetic ketoacidosis and a hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state in a kidney transplant patient: A case report, J. Med. Case Rep
Montori, Baroni, Santori, Di Giampaolo, Ponziani et al., Liver Damage and COVID-19: At Least a "Two-Hit" Story in Systematic Review, Curr. Issues Mol. Biol
Ngo, Marik, Kory, Shapiro, Thomadsen et al., The time to offer treatments for COVID-19, Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs
Rahman, Montero, Rowe, Kirton, Kunik et al., Epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentations, diagnosis and treatment of COVID-19: A review of current evidence, Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol
Singla, Goyal, Antiviral activity of molnupiravir against COVID-19: A schematic review of evidences, Bull. Natl. Res. Cent
Subramanian, Iles, Ikramuddin, Steer, Merit of an Ursodeoxycholic Acid Clinical Trial in COVID-19 Patients, Vaccines
Thuy, Bao, Moon, Ursodeoxycholic acid ameliorates cell migration retarded by the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in BEAS-2B human bronchial epithelial cells, Biomed. Pharmacother
Tong, Keung, Arnold, Stevens, Pruijssers et al., Evaluation of in vitro antiviral activity of SARS-CoV-2 M(pro) inhibitor pomotrelvir and cross-resistance to nirmatrelvir resistance substitutions, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Vegivinti, Evanson, Lyons, Akosman, Barrett et al., Efficacy of antiviral therapies for COVID-19: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials, BMC Infect. Dis
Vitiello, Troiano, La Porta, What will be the role of molnupiravir in the treatment of COVID-19 infection?, Drugs Ther. Perspect
Wecht, Rojas, Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of chronic lung disease, Respirology