Identification and validation of programmed cell death related biomarkers for the treatment and prevention COVID-19
et al., Annals of Medicine, doi:10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830, Apr 2025
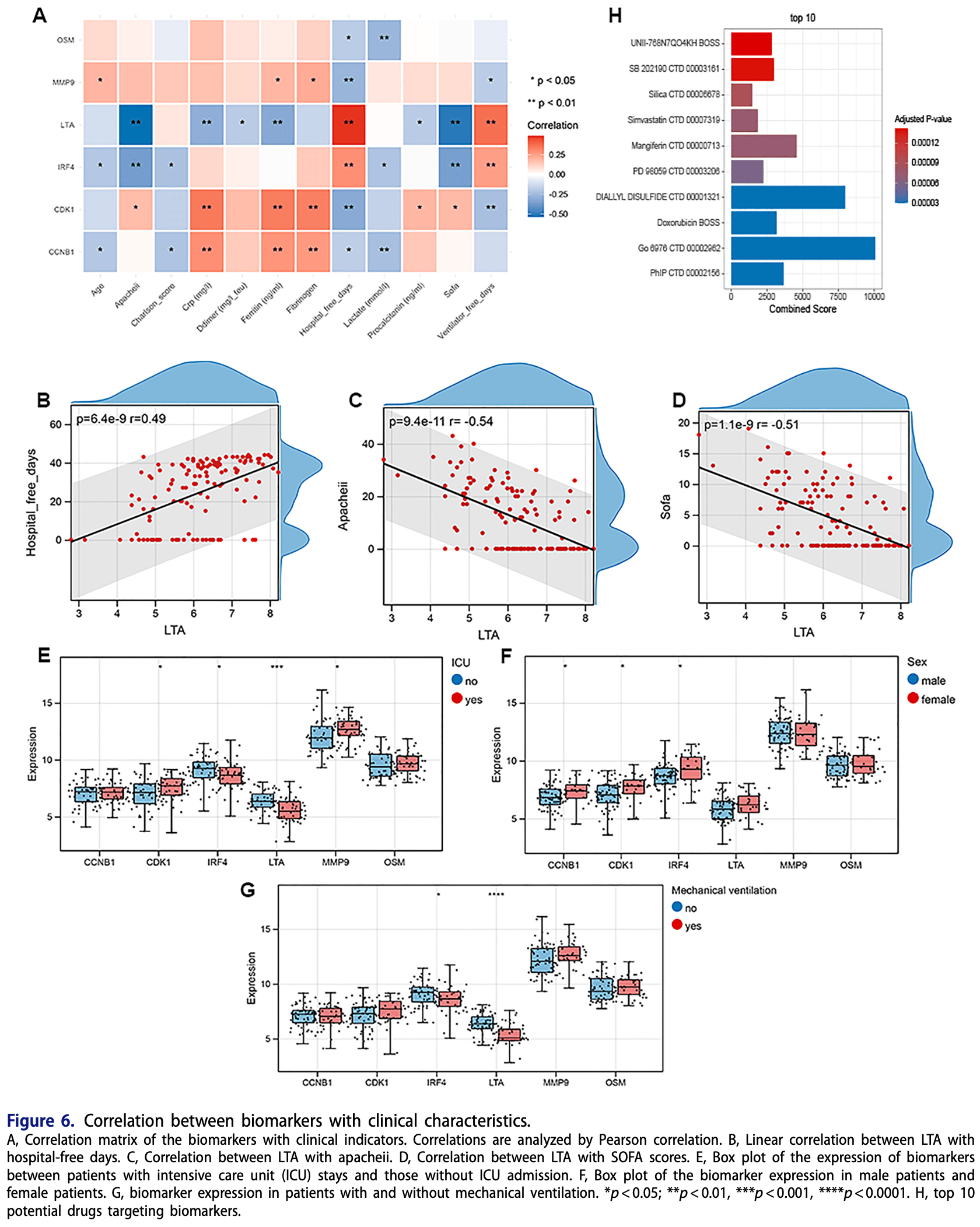
Bioinformatic study analyzing gene expression data from COVID-19 patients to identify six programmed cell death (PCD) related biomarkers (CCNB1, CDK1, IRF4, LTA, MMP9, and OSM) for COVID-19 diagnosis and severity prediction. Through analysis of three GEO datasets and validation with RT-qPCR in clinical samples, authors found these biomarkers were differentially expressed in COVID-19 patients compared to controls and correlated with clinical features including ICU admission and mechanical ventilation.
Yang et al., 29 Apr 2025, China, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: llxx1110806@163.com.
Identification and validation of programmed cell death related biomarkers for the treatment and prevention COVID-19
Annals of Medicine, doi:10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830
Purpose: Programmed cell death (PCD) plays a key role in the progression of coronavirus disease 2019 . However, PCD-relevant biomarkers have not been fully discovered. The aim of this study was to explore the PCD-relevant biomarkers for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19. Methods: Bioinformatic analyses were performed to explore the clinical relevant PCD genes with differential expression (DE) in COVID-19 compared with matched controls. PPI network was used for hub genes screening and machine learning methods were employed for filtering feature genes. The biomarker genes were screened by Venn diagram. The correlations between biomarkers with clinical features and immune microenvironment were further explored. Biomarker validation was performed in clinical samples by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Results: In total, 118 clinically relevant and PCD associated differential expressed genes (DEGs) were screened, which were mainly related with apoptosis related pathways, among which six biomarkers (Cyclin B1 (CCNB1), cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1), interferon regulatory factor 4 (IRF4), lipoteichoic acid (LTA), matrix metallopeptidase 9 (MMP9) and Oncostatin M (OSM)) were identified. The excellent or good diagnostic performance of biomarkers was determined by receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis. The biomarkers showed diverse correlations with clinical indicators, such as age, sex and Intensive Care Unit (ICU) admission. Total 14 types of immune cells exerted differential infiltration between COVID-19 and controls. Biomarkers were correlated with immune cells at varying levels. COVID-19 was classified in three clusters, which showed differential expression of biomarker genes and significant associations with clinical information, such as sex, age and ICU admission. The DEGs of biomarkers were determined in COVID-19 patients relative to controls.
Conclusion: The six biomarkers (CCNB1, CDK1, IRF4, LTA, MMP9 and OSM) can be served as the biomarkers for the treatment and prevention of COVID-19.
Author contributions statement Jie Yang: Conceptualization, Data Curation and Writing -Original Draft Preparation. YaoXi Tan: Conceptualization and Formal Analysis. Xing Liu: Conceptualization, Data Curation and Writing -Review & Editing. All authors agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Database ethics statement Based on the database is publicly available, the ethics application was exempted by the Affiliated Wuxi Fifth Hospital of Jiangnan University.
Disclosure statement No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
References
Ablamunits, Lepsy, Blocking TNF signaling may save lives in COVID-19 infection, Mol Biol Rep, doi:10.1007/s11033-022-07166-x
Bader, Cooney, Pellegrini, Programmed cell death: the pathways to severe COVID-19?, Biochem J, doi:10.1042/BCJ20210602
Belgiu, Drăguţ, Random forest in remote sensing: a review of applications and future directions, ISPRS J Photogramm Remote Sens, doi:10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.01.011
Cascella, Rajnik, Aleem, Features, Evaluation, and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19)
Chen, Yang, Luo, Identification of key regulatory genes in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and sepsis: an observational study, Medicine, doi:10.1097/md.0000000000038378
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7
Chutipongtanate, Morrow, Newburg, Human milk oligosaccharides: potential applications in COVID-19, Biomedicines, doi:10.3390/biomedicines10020346
Ciaccio, Agnello, Biochemical biomarkers alterations in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Diagnosis (Berl), doi:10.1515/dx-2020-0057
Croft, The role of TNF superfamily members in T-cell function and diseases, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri2526
Desai, Lavelle, Boursiquot, Long-term complications of COVID-19, Am J Physiol Cell Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2021
Dimitriadou, Hornik, Fpackage, R Software package
Gibellini, Moro, Programmed cell death in health and disease, MDPI, doi:10.3390/cells10071765
Gillot, Favresse, Mullier, NETosis and the immune system in COVID-19: mechanisms and potential treatments, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.708302
González, Programmed cell death. Review and its impact in covid-19, Clinical Research and Trials
Hahn, Hamilton, Wangen, Development of a PROTAC-based targeting strategy provides a mechanistically unique mode of anti-cytomegalovirus activity, Int J Mol Sci, doi:10.3390/ijms222312858
Huang, Hung, SVM-RFE based feature selection and Taguchi parameters optimization for multiclass SVM classifier, The Scientific World Journal, doi:10.1155/2014/795624
Jorgensen, Rayamajhi, Miao, Programmed cell death as a defence against infection, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/nri.2016.147
Karki, Sharma, Tuladhar, Synergism of TNF-α and IFN-γ triggers inflammatory cell death, tissue damage, and mortality in SARS-CoV-2 infection and cytokine shock syndromes, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025
Kim, Witwit, Cubitt, Inhibitors of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins exhibit potent and broad-spectrum anti-mammarenavirus activity via cell cycle arrest at G0/G1 phase, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi
Knoll, Schultze, Schulte-Schrepping, Monocytes and macrophages in COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.720109
Koupenova, Corkrey, Vitseva, SARS-CoV-2 initiates programmed cell death in platelets, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319117
Lakbar, Luque-Paz, Mege, COVID-19 gender susceptibility and outcomes: a systematic review, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0241827
Langfelder, Horvath, WGCNA: an R package for weighted correlation network analysis, BMC Bioinf, doi:10.1186/1471-2105-9-559
Luo, Xie, Zheng, Comprehensive insights on pivotal prognostic signature involved in clear cell renal cell carcinoma microenvironment using the ESTIMATE algorithm, Cancer Med, doi:10.1002/cam4.2983
Marone, Mozzetti, Ritis, Semiquantitative RT-PCR analysis to assess the expression levels of multiple transcripts from the same sample, Biol Proced Online, doi:10.1251/bpo20
Mceligot, Poynor, Sharma, Logistic LASSO Regression for Dietary Intakes and Breast Cancer, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12092652
Merad, Martin, Pathological inflammation in patients with COVID-19: a key role for monocytes and macrophages, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4
Mozaffarian, Brewer, Trueblood, Mechanisms of oncostatin M-induced pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7243
Paces, Strizova, Smrz, COVID-19 and the immune system, Physiol Res, doi:10.33549/physiolres.934492
Pijls, Jolani, Atherley, Demographic risk factors for COVID-19 infection, severity, ICU admission and death: a meta-analysis of 59 studies, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044640
Qin, Abulaiti, Maimaiti, Integrated machine learning survival framework develops a prognostic model based on inter-crosstalk definition of mitochondrial function and cell death patterns in a large multicenter cohort for lower-grade glioma, J Transl Med, doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04468-x
Robin, Turck, Hainard, pROC: an open-source package for R and S + to analyze and compare ROC curves, BMC Bioinf, doi:10.1186/1471-2105-12-77
Sasso, Agnello, Giglio, Longitudinal analysis of anti-SARS-CoV-2 S-RBD IgG antibodies before and after the third dose of the BNT162b2 vaccine, Sci Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-022-12750-z
Shannon, Markiel, Ozier, Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks, Genome Res, doi:10.1101/gr.1239303
Song, Zhang, Li, Significance of neutrophil extracellular traps-related gene in the diagnosis and classification of atherosclerosis, Apoptosis, doi:10.1007/s10495-023-01923-4
Strobl, Boulesteix, Zeileis, Bias in random forest variable importance measures: illustrations, sources and a solution, BMC Bioinf, doi:10.1186/1471-2105-8-25
Suykens, Vandewalle, Least squares support vector machine classifiers, Neural Processing Letters
Wilkerson, Waltman, Wilkerson, Package 'ConsensusClusterPlus
Wolf, Pruett, Lighter, The clinical relevance of OSM in inflammatory diseases: a comprehensive review, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239732
Xiao, Liu, Li, Identification and verification of immune-related gene prognostic signature based on ssGSEA for osteosarcoma, Front Oncol, doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.607622
Yoo, Shin, Kim, DSigDB: drug signatures database for gene set analysis, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btv313
Yu, Wang, Han, clusterProfiler: an R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters, OMICS, doi:10.1089/omi.2011.0118
Zaim, Chong, Sankaranarayanan, COVID-19 and multiorgan response, Curr Probl Cardiol, doi:10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618
Zhou, Gao, Xu, Implications of different cell death patterns for prognosis and immunity in lung adenocarcinoma, NPJ Precis Oncol, doi:10.1038/s41698-023-00456-y
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830",
"ISSN": [
"0785-3890",
"1365-2060"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "Peer Review Statement",
"name": "peerreview_statement",
"order": 1,
"value": "The publishing and review policy for this title is described in its Aims & Scope."
},
{
"URL": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=iann20",
"label": "Aim & Scope",
"name": "aims_and_scope_url",
"order": 2,
"value": "http://www.tandfonline.com/action/journalInformation?show=aimsScope&journalCode=iann20"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-09-05"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Revised",
"name": "revised",
"order": 1,
"value": "2024-12-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-01-07"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-04-29"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated hospital of Jiangnan University",
"place": [
"Wuxi, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Jie",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Diseases, Affiliated hospital of Jiangnan University",
"place": [
"Wuxi, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Tan",
"given": "YaoXi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Emergency, Affiliated Wuxi Fifth Hospital of Jiangnan University",
"place": [
"Wuxi, China"
]
}
],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xing",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Annals of Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Annals of Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"www.tandfonline.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-29T21:13:21Z",
"timestamp": 1745961201000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-29T21:13:23Z",
"timestamp": 1745961203000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-30T04:22:59Z",
"timestamp": 1745986979062,
"version": "3.40.4"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
31
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-04-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1745884800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/pdf/10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "301",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1080",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
4,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Informa UK Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2020.100618",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0331-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_3_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_6_4_1",
"unstructured": "Cascella M Rajnik M Aleem A et al. Features Evaluation and Treatment of Coronavirus (COVID-19). 2023 Aug 18. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10071765",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_5_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri.2016.147",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BCJ20210602",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_7_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Programmed cell death. Review and its impact in covid-19",
"author": "González A.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clinical Research and Trials",
"key": "e_1_3_6_8_1",
"unstructured": "González A. Programmed cell death. Review and its impact in covid-19. Clinical Research and Trials. 2020;7:1–11.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.708302",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-9-559",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41698-023-00456-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-023-04468-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/omi.2011.0118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.1239303",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1023/A:1018628609742",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-8-25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2014/795624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092652",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2016.01.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_19_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_6_20_1",
"unstructured": "Dimitriadou E Hornik K Leisch FPackage ‘e1071’. R Software package avaliable at et al. ; 2009http://cran rproject org/web/packages/e1071/index html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-12-77",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_21_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btv313",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10495-023-01923-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fonc.2020.607622",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_24_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_3_6_25_1",
"unstructured": "Wilkerson M Waltman P Wilkerson MM. 2013. Package ‘ConsensusClusterPlus’"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cam4.2983",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1251/bpo20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/dx-2020-0057",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.121.319117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpcell.00375.2021",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nri2526",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.11.025",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11033-022-07166-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_34_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_35_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms222312858",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/md.0000000000038378",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1239732",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_38_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.181.10.7243",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_39_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/biomedicines10020346",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0241827",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-044640",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33549/physiolres.934492",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_43_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.720109",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_44_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-022-12750-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_6_45_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 44,
"references-count": 44,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/07853890.2025.2492830"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Identification and validation of programmed cell death related biomarkers for the treatment and prevention COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1080/tandf_crossmark_01",
"volume": "57"
}