Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hainan, China
et al., medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539, Mar 2020
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
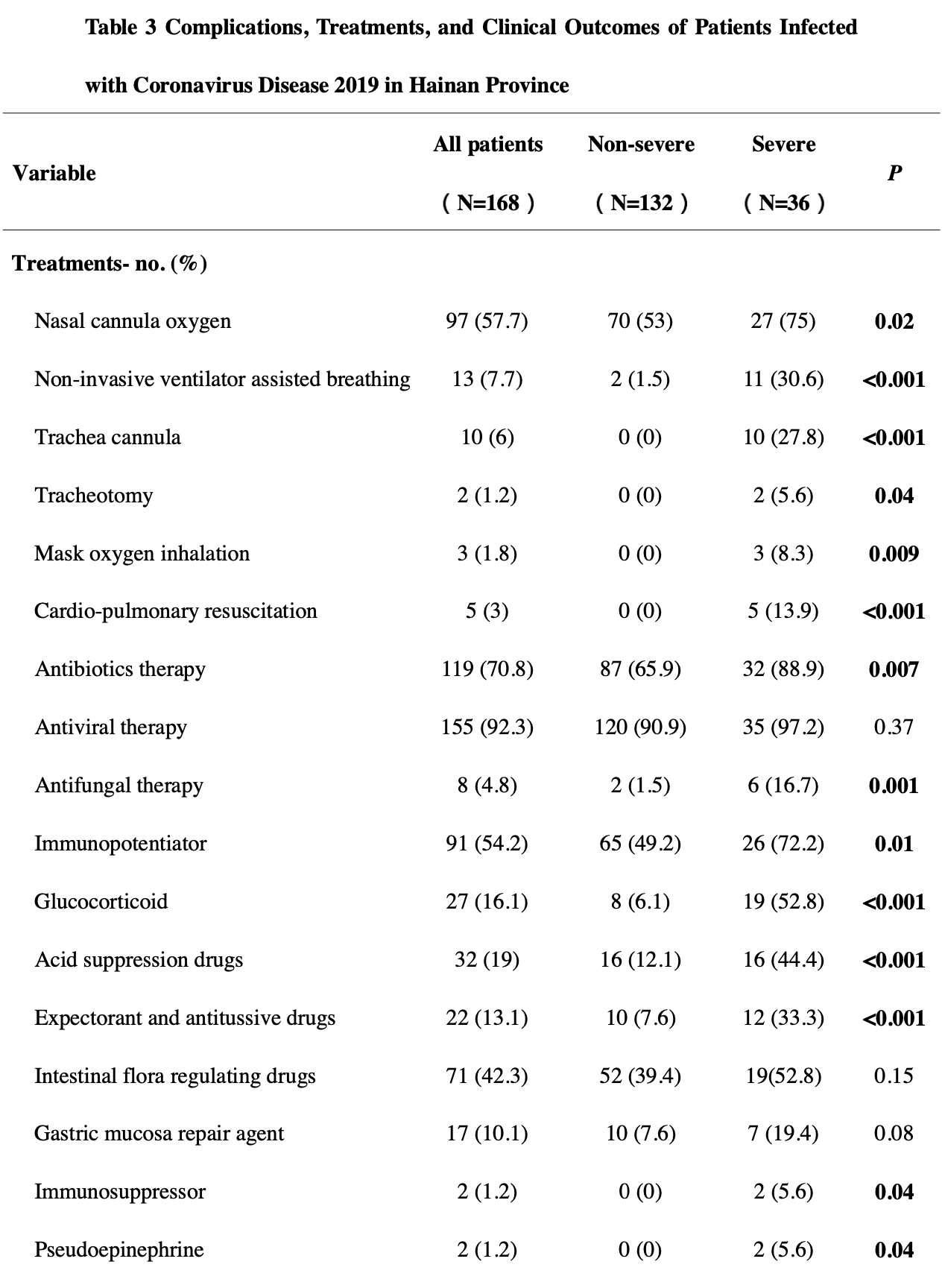
Retrospective 168 hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China showing higher risk of severe cases with acid suppression drugs.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
China, is average with moderate efficacy for approved treatments1.
|
risk of severe case, 240.0% higher, RR 3.40, p < 0.001, treatment 16 of 32 (50.0%), control 20 of 136 (14.7%).
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Yan et al., 23 Mar 2020, retrospective, China, preprint, median age 51.0, 17 authors, study period 22 January, 2020 - 13 March, 2020.
Contact: lvchuanzhu677@126.com.
Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hainan, China
doi:10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539
Background: Since January 2020, coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) has spread rapidly and developing the pandemic model around the world. Data have been needed on the clinical characteristics of the affected patients in an imported cases as model in island outside Wuhan. Methods: We conducted a retrospective study included all 168 confirmed cases of Covid-19 in Hainan province from 22 January 2020 to 13 March 2020. Cases were confirmed by real-time RT-PCR and were analysed for demographic, clinical, radiological and laboratory data. Results: Of 168 patients, 160 have been discharged, 6 have died and 2 remain hospitalized. The median age was 51.0 years and 51.8% were females. 129 (76.8%) patients were imported cases, and 118 (70.2%), 51 (30.4%) and 52 (31%) of patients lived in Wuhan or traveled to Wuhan, had contact with Covid-19 patients, or had contact with Wuhan residents, respectively. The most common symptoms at onset of illness were fever (65.5%), dry cough (48.8%) and expectoration (32.1%). On admission, ground-glass opacity was the most common radiologic finding on chest computed tomography (60.2%). The elderly people with diabetes, hypertension and CVD are more likely to develop severe cases. Follow-up of 160 discharged patients found that 20 patients (12.5%) had a positive RT-PCR test results of pharyngeal swabs or anal swabs or fecal. Conclusions: In light of the rapid spread of Covid-19 around the world, early diagnosis and quarantine is important to curb the spread of Covid-19 and intensive
Course-Median (IQR), days Time from onset of symptoms to first hospital visit (N=168)
References
Chan, Kok, Zhu, Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan, Emerg Microbes Infect
Chen, Zhou, Dong, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study, Lancet
Force, Ranieri, Rubenfeld, Acute respiratory distress syndrome: the Berlin Definition, JAMA
Gao, Wang, Gu, Association Between Cardiac Injury and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Infected With Avian Influenza A (H7N9) Virus, Crit Care
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Holshue, Debolt, Lindquist, First Case of 2019 Novel Coronavirus in the United States, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Khwaja, KDIGO clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney injury, Nephron Clinical practice
Li, Guan, Wu, Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Lin, Fong, Zhu, Karlberg, Environmental factors on the SARS epidemic: air temperature, passage of time and multiplicative effect of hospital infection, Epidemiol Infect
Lu, Stratton, Tang, Outbreak of pneumonia of unknown etiology in Wuhan, China: The mystery and the miracle, J Med Virol
Phan, Nguyen, Luong, Importation and Human-to-Human Transmission of a Novel Coronavirus in Vietnam, N Engl J Med
Rothe, Schunk, Sothmann, Transmission of 2019-nCoV Infection from an Asymptomatic Contact in Germany, N Engl J Med
Singer, Granger, Inflammatory responses underlying the microvascular dysfunction associated with obesity and insulin resistance, Microcirculation
Van Den Oever, Raterman, Nurmohamed, Simsek, Endothelial dysfunction, inflammation, and apoptosis in diabetes mellitus, Mediators Inflamm
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA
Xu, Li, Zhu, Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding, Nature Medicine
Xu, Wu, Jiang, Clinical findings in a group of patients infected with the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-Cov-2) outside of Wuhan, China: retrospective case series, BMJ
Yang, Cao, Qin, Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19):A multi-center study in Wenzhou city, Zhejiang, China, J Infect
Yang, Yu, Xu, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, The Lancet Respiratory Medicine
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy
Zhou, Yang, Wang, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature
Zhu, Zhang, Wang, A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539",
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p>Since January 2020, coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) has spread rapidly and developing the pandemic model around the world. Data have been needed on the clinical characteristics of the affected patients in an imported cases as model in island outside Wuhan.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p>We conducted a retrospective study included all 168 confirmed cases of Covid-19 in Hainan province from 22 January 2020 to 13 March 2020. Cases were confirmed by real-time RT-PCR and were analysed for demographic, clinical, radiological and laboratory data.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>Of 168 patients, 160 have been discharged, 6 have died and 2 remain hospitalized. The median age was 51.0 years and 51.8% were females. 129 (76.8%) patients were imported cases, and 118 (70.2%), 51 (30.4%) and 52 (31%) of patients lived in Wuhan or traveled to Wuhan, had contact with Covid-19 patients, or had contact with Wuhan residents, respectively. The most common symptoms at onset of illness were fever (65.5%), dry cough (48.8%) and expectoration (32.1%). On admission, ground-glass opacity was the most common radiologic finding on chest computed tomography (60.2%). The elderly people with diabetes, hypertension and CVD are more likely to develop severe cases. Follow-up of 160 discharged patients found that 20 patients (12.5%) had a positive RT-PCR test results of pharyngeal swabs or anal swabs or fecal.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title><jats:p>In light of the rapid spread of Covid-19 around the world, early diagnosis and quarantine is important to curb the spread of Covid-19 and intensive treatments in early stage is to prevent patients away from critical condition.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"accepted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
23
]
]
},
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yan",
"given": "Shijiao",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Xingyue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Feng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Haiyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Xiaozhi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Li",
"given": "Min",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ruan",
"given": "Jianwen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Changfeng",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Xiaoran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wu",
"given": "Qiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Luo",
"given": "Zhiqian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Wenning",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chen",
"given": "Song",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yuan",
"given": "Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Shengxing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yao",
"given": "Jinjian",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lv",
"given": "Chuanzhu",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2020-03-23T17:55:18Z",
"timestamp": 1584986118000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
11,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2020-11-17T19:15:34Z",
"timestamp": 1605640534000
},
"group-title": "Infectious Diseases (except HIV/AIDS)",
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-29T18:05:59Z",
"timestamp": 1706551559330
},
"institution": [
{
"name": "medRxiv"
}
],
"is-referenced-by-count": 20,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
23
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "246",
"original-title": [],
"posted": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
23
]
]
},
"prefix": "10.1101",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
3,
23
]
]
},
"publisher": "Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25678",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902",
"article-title": "Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Emerg Microbes Infect",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.2",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.3"
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.4",
"unstructured": "Zhou P , Yang XL , Wang XG , et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature 2020."
},
{
"article-title": "An update on the epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia (COVID-19)",
"author": "Special Expert Group for Control of the Epidemic of Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia of the Chinese Preventive Medicine Association",
"first-page": "139",
"journal-title": "Chinese Journal of Epidemiology",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.5",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.6",
"unstructured": "Li Q , Guan X , Wu P , et al. Early Transmission Dynamics in Wuhan, China, of Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia. N Engl J Med 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMc2001468",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001191",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.10"
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.11",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report-53. March 13, 2020 (https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/20200313-sitrep-53-Covid-19.pdf?sfvrsn=adb3f72_2)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.02.016",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.12",
"unstructured": "Yang W , Cao Q , Qin L , et al. Clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of the 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19):A multi-center study in Wenzhou city, Zhejiang, China. J Infect 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m606",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30211-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.1585",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.15",
"unstructured": "Wang D , Hu B , Hu C , et al. Clinical Characteristics of 138 Hospitalized Patients With 2019 Novel Coronavirus-Infected Pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268805005054",
"article-title": "Environmental factors on the SARS epidemic: air temperature, passage of time and multiplicative effect of hospital infection",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "223",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.16",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.17",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) infection is suspected: interim guidance. March 5, 2020 (https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/clinical-management-of-novel-cov.pdf)."
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.18",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment of new coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 3).March 13, 2020 (http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202001/f492c9153ea9437bb587ce2ffcbee1fa/files/39e7578d85964dbe81117736dd789d8f.pdf)."
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.19",
"unstructured": "National Health Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Diagnosis and treatment of new coronavirus pneumonia (trial version 7). March 13, 2020 (http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7653p/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb1989/files/ce3e6945832a438eaae415350a8ce964.pdf)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2012.5669",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000339789",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCM.0000000000004207",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.22",
"unstructured": "Gao C , Wang Y , Gu X , et al. Association Between Cardiac Injury and Mortality in Hospitalized Patients Infected With Avian Influenza A (H7N9) Virus. Crit Care 2020."
},
{
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.23",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ , Ni ZY , Hu Y , et al. Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2010/792393",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10739680701283158",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0817-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.26",
"unstructured": "Xu Y , Li X , Zhu B , et al. Characteristics of pediatric SARS-CoV-2 infection and potential evidence for persistent fecal viral shedding. Nature Medicine 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.27",
"unstructured": "Yang X , Yu Y , Xu J , et al. Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14238",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "2020111711150685000_2020.03.19.20038539v1.28",
"unstructured": "Zhang JJ , Dong X , Cao YY , et al. Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China. Allergy 2020."
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://medrxiv.org/lookup/doi/10.1101/2020.03.19.20038539"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"subtype": "preprint",
"title": "Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Hainan, China",
"type": "posted-content"
}