The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is important for replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic RNA viruses
et al., npj Viruses, doi:10.1038/s44298-024-00018-4, Feb 2024
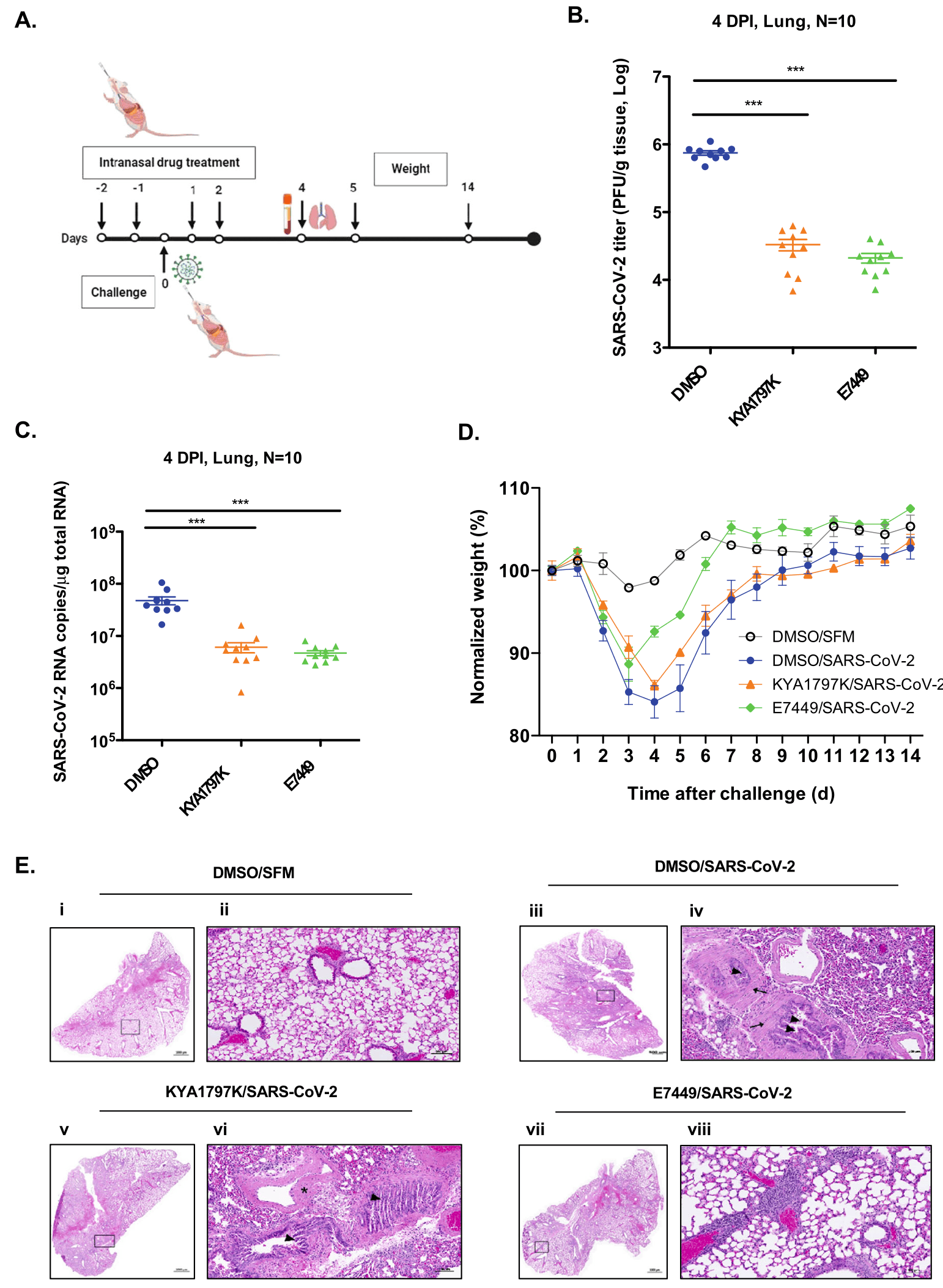
In vitro and mouse study showing that Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibitors reduce SARS-CoV-2 replication by increasing peroxisome formation and enhancing interferon response. Authors found that SARS-CoV-2 infection activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling, which suppresses peroxisome biogenesis, an organelle important for interferon production. Ten Wnt inhibitors were tested, with KYA1797K, Pyrvinium, and E7449 showing the most potent antiviral activity. These compounds increased peroxisome numbers by up to 50% and potentiated type I and III interferon production. In Calu-3 cells and primary human bronchial epithelial cells, the inhibitors reduced viral titers by 80-100%. The drugs were effective against multiple SARS-CoV-2 variants, including Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, and Omicron. In a mouse model, KYA1797K and E7449 reduced viral load by 23-36 fold and decreased inflammatory cytokines. E7449 was particularly effective in protecting mice from weight loss and lung injury. The compounds also showed broad-spectrum activity against other RNA viruses including seasonal coronaviruses, Zika virus, and Mayaro virus.
Xu et al., 21 Feb 2024, peer-reviewed, 16 authors.
Contact: tom.hobman@ualberta.ca.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is important for replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic RNA viruses
npj Viruses, doi:10.1038/s44298-024-00018-4
Understanding how viruses affect cellular pathways during infection may facilitate development of host cell-targeted therapeutics with broad-spectrum antiviral activity. The interferon (IFN) response is critical for reducing replication and pathogenesis of many viruses including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19. Mounting evidence indicates that peroxisomes which are best known as metabolic organelles, function in the IFN response. Recently, we reported that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway strongly suppresses peroxisome biogenesis. Here, we show that SARS-CoV-2 infection activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and hypothesized that pharmacological inhibition of this pathway would result in increased peroxisome formation and enhanced IFN production. Indeed, Wnt/β-catenin signaling potently inhibits replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic RNA viruses in vitro and reduces viral load, inflammation and clinical symptoms in a mouse model of COVID-19. As such, targeting this cellular pathway may have prophylactic and/or therapeutic value in reducing the disease burden caused by emerging viral pathogens.
Statistical analyses The statistical significance of differences was assessed using the Student's t test or ANOVA. The mean ± standard error of the mean is shown in all bar and line graphs. The results shown are representative of at least three independent experiments. Significance was accepted at p < 0.05. Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism software.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION Supplementary information The online version contains supplementary material available at https://doi.org/10.1038/s44298-024-00018-4 . Correspondence and requests for materials should be addressed to Tom C. Hobman. Reprints and permission information is available at http://www.nature.com/ reprints Publisher's note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Albrecht, Tejeda-Munoz, De Robertis, Cell biology of canonical Wnt signaling, Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol
Andrews, Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant, N. Engl. J. Med
Baum, REGN-COV2 antibodies prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques and hamsters, Science
Bender, Activation of type I and III interferon response by mitochondrial and peroxisomal MAVS and inhibition by hepatitis C virus, PLoS Pathog
Biering, Screening a library of FDA-approved and bioactive compounds for antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2, ACS Infect. Dis
Braga, Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spikeinduced syncytia, Nature
Burke, Fish, Antiviral strategies: the present and beyond, Curr. Mol. Pharmacol
Cao, 2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection, Nature
Cha, Small-molecule binding of the axin RGS domain promotes betacatenin and Ras degradation, Nat. Chem. Biol
Chan, Tropism of and innate immune responses to the novel human betacoronavirus lineage C virus in human ex vivo respiratory organ cultures, J. Virol
Channappanavar, Dysregulated type I interferon and inflammatory monocyte-macrophage responses cause lethal pneumonia in SARS-CoV-infected mice, Cell Host Microbe
Chen, In vivo monoclonal antibody efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 variant strains, Nature
Choi, Wnt5a and Wnt11 as acute respiratory distress syndrome biomarkers for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 patients, Eur. Respir. J
Cinatl, Treatment of SARS with human interferons, Lancet
Desmyter, Melnick, Rawls, Defectiveness of interferon production and of rubella virus interference in a line of African green monkey kidney cells (Vero), J. Virol
Di Cara, Bulow, Simmonds, Rachubinski, Dysfunctional peroxisomes compromise gut structure and host defense by increased cell death and Tor-dependent autophagy, Mol. Biol. Cell
Di Cara, Peroxisomes in host defense, PLoS Pathog
Di Cara, Sheshachalam, Braverman, Rachubinski, Simmonds, Peroxisome-mediated metabolism is required for immune response to microbial infection, Immunity
Dittmar, Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-Cov-2, Cell Rep
Dixit, Peroxisomes are signaling platforms for antiviral innate immunity, Cell
Drayman, Masitinib is a broad coronavirus 3CL inhibitor that blocks replication of SARS-CoV-2, Science
Feikin, Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: results of a systematic review and metaregression, Lancet
Felgenhauer, Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by type I and type III interferons, J. Biol. Chem
Fujiki, Recent insights into peroxisome biogenesis and associated diseases, J. Cell Sci
Glasgow, Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
Gordon, Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNAdependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency, J. Biol. Chem
Group, A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N. Engl. J. Med
Gwak, Small molecule-based disruption of the Axin/beta-catenin protein complex regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation, Cell Res
Harvey, SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape, Nat. Rev. Microbiol
Ji, Li, Medicinal chemistry strategies toward host targeting antiviral agents, Med. Res. Rev
Kamel, Global analysis of protein-RNA interactions in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells reveals key regulators of infection, Mol. Cell
Kim, Huang, Park, Targeting Wnt signaling for gastrointestinal cancer therapy: present and evolving views, Cancers
Knoblach, Ishida, Hobman, Rachubinski, Peroxisomes exhibit compromised structure and matrix protein content in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, Mol. Biol. Cell
Kumar, SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 inhibits the interferon response by causing depletion of key host signaling factors, J. Virol
Lee, Koepke, Kirchhoff, Sparrer, Interferon antagonists encoded by SARS-CoV-2 at a glance, Med. Microbiol. Immunol
Leist, A mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 induces acute lung injury and mortality in standard laboratory mice, Cell
Limonta, Nodosome inhibition as a novel broad-spectrum antiviral strategy against arboviruses, enteroviruses and SARS-CoV-2, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother
Livak, Schmittgen, Analysis of relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method, Methods
Lokugamage, Type I interferon susceptibility distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 from SARS-CoV, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01410-20
Lopez-Orozco, The RNA interference effector protein argonaute 2 functions as a restriction factor against SARS-CoV-2, J. Mol. Biol
Lowery, Sariol, Perlman, Innate immune and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2: Implications for COVID-19, Cell Host Microbe
Mahlakoiv, Combined action of type I and type III interferon restricts initial replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the lung but fails to inhibit systemic virus spread, J. Gen. Virol
Mcgonigle, a dual inhibitor of PARP1/2 and tankyrase1/2 inhibits growth of DNA repair deficient tumors and antagonizes Wnt signaling, Oncotarget
Mirabelli, Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
Moghadasi, Transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors, Sci. Adv
Odendall, Diverse intracellular pathogens activate type III interferon expression from peroxisomes, Nat. Immunol
Plummer, First-in-human study of the PARP/tankyrase inhibitor E7449 in patients with advanced solid tumours and evaluation of a novel drug-response predictor, Br. J. Cancer
Ramasamy, Subbian, Critical determinants of cytokine storm and type I interferon response in COVID-19 pathogenesis, Clin. Microbiol. Rev
Richtsmeier, Human interferon production in tonsil and adenoid tissue cultures, Am. J. Otolaryngol
Roczkowsky, COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and suppresses peroxisomes in the brain, Ann. Neurol
Rosenke, Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model, Nat. Commun
Sallard, Lescure, Yazdanpanah, Mentre, Peiffer-Smadja, Type 1 interferons as a potential treatment against COVID-19, Antiviral Res
Sheahan, An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice, Sci. Transl. Med
Shrestha, Foster, Rawlinson, Tedla, Bull, Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants BA.1 to BA.5: Implications for immune escape and transmission, Rev. Med. Virol
Sleijfer, Bannink, Van Gool, Kruit, Stoter, Side effects of interferon-alpha therapy, Pharm. World Sci
Spiegel, Pichlmair, Mühlberger, Haller, Weber, The antiviral effect of interferon-beta against SARS-coronavirus is not mediated by MxA protein, J. Clin. Virol
Sun, In vivo structural characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome identifies host proteins vulnerable to repurposed drugs, Cell
Szemiel, In vitro selection of Remdesivir resistance suggests evolutionary predictability of SARS-CoV-2, PLoS Pathog
Vanblargan, An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies, Nat. Med
Vanderheiden, Type I and type III interferons restrict SARS-CoV-2 infection of human airway epithelial cultures, J. Virol
Vuong, Feline coronavirus drug inhibits the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 and blocks virus replication, Nat. Commun
Wahl, SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801, Nature
Wang, Genetic screens identify host factors for SARS-CoV-2 and common cold coronaviruses, Cell
Wang, Histopathological changes caused by inflammation and oxidative stress in diet-induced-obese mouse following experimental lung injury, Sci. Rep
Wei, Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal host factors critical for SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell
Weston, The SKI complex is a broad-spectrum, host-directed antiviral drug target for coronaviruses, influenza, and filoviruses, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA
Wong, Interplay between Zika Virus and Peroxisomes during Infection, Cells
Wong, Xu, Power, Hobman, Targeted elimination of peroxisomes during viral infection: lessons from HIV and other viruses, DNA Cell Biol
Xie, Engineering SARS-CoV-2 using a reverse genetic system, Nat. Protoc
Xu, Lodge, Power, Cohen, Hobman, The HIV-1 accessory protein VPU downregulates peroxisome biogenesis, mBio
Xu, MicroRNAs upregulated during HIV infection target peroxisome biogenesis factors: Implications for virus biology, disease mechanisms and neuropathology, PLoS Pathog
You, Flavivirus infection impairs peroxisome biogenesis and early antiviral signaling, J. Virol
Zhang, Ke, Blikslager, Fujita, Yoo, Type III interferon restriction by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and the role of viral protein nsp1 in IRF1 signaling, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01677-17
Zielecki, Human cell tropism and innate immune system interactions of human respiratory coronavirus EMC compared to those of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J. Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s44298-024-00018-4",
"ISSN": [
"2948-1767"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s44298-024-00018-4",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>Understanding how viruses affect cellular pathways during infection may facilitate development of host cell-targeted therapeutics with broad-spectrum antiviral activity. The interferon (IFN) response is critical for reducing replication and pathogenesis of many viruses including Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), the causative agent of COVID-19. Mounting evidence indicates that peroxisomes which are best known as metabolic organelles, function in the IFN response. Recently, we reported that the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway strongly suppresses peroxisome biogenesis. Here, we show that SARS-CoV-2 infection activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling and hypothesized that pharmacological inhibition of this pathway would result in increased peroxisome formation and enhanced IFN production. Indeed, Wnt/β-catenin signaling potently inhibits replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic RNA viruses in vitro and reduces viral load, inflammation and clinical symptoms in a mouse model of COVID-19. As such, targeting this cellular pathway may have prophylactic and/or therapeutic value in reducing the disease burden caused by emerging viral pathogens.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"18"
],
"article-number": "6",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "26 September 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "10 January 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "21 February 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "T.C.H., Z.X. and C.P.W. are co-inventors on US patent application (PCT/CA2021/051077) entitled: Use of WNT/BETA-Catenin Pathway Inhibitors to Block Replication of SARS-COV-2 and other pathogenic viruses tonix pharmaceuticals had no role in design or interpretation of the experiments described in this study."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Zaikun",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Elaish",
"given": "Mohamed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wong",
"given": "Cheung Pang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hassan",
"given": "Bardes B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopez-Orozco",
"given": "Joaquin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Felix-Lopez",
"given": "Alberto",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ogando",
"given": "Natacha S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nagata",
"given": "Les",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mahal",
"given": "Lara K.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Anil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wilson",
"given": "Joyce A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Noyce",
"given": "Ryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayers",
"given": "Irv",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Power",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Evans",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hobman",
"given": "Tom C.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "npj Viruses",
"container-title-short": "npj Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T11:03:49Z",
"timestamp": 1708513429000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T11:05:21Z",
"timestamp": 1708513521000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-08T05:55:45Z",
"timestamp": 1723096545780
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708473600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2024-02-21T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1708473600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00018-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00018-4",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00018-4.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
2,
21
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2119451",
"author": "N Andrews",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1532",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "18_CR1",
"unstructured": "Andrews, N. et al. Covid-19 vaccine effectiveness against the omicron (B.1.1.529) Variant. N. Engl. J. Med. 386, 1532–1546 (2022).",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)00152-0",
"author": "DR Feikin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "18_CR2",
"unstructured": "Feikin, D. R. et al. Duration of effectiveness of vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease: results of a systematic review and meta-regression. Lancet 399, 924–944 (2022).",
"volume": "399",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-021-00573-0",
"author": "WT Harvey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "409",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Microbiol.",
"key": "18_CR3",
"unstructured": "Harvey, W. T. et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 409–424 (2021).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04980-y",
"author": "Y Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "18_CR4",
"unstructured": "Cao, Y. et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 608, 593–602 (2022).",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2381",
"author": "LB Shrestha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2381",
"journal-title": "Rev. Med. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR5",
"unstructured": "Shrestha, L. B., Foster, C., Rawlinson, W., Tedla, N. & Bull, R. A. Evolution of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variants BA.1 to BA.5: Implications for immune escape and transmission. Rev. Med. Virol. 32, e2381 (2022).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01678-y",
"author": "LA VanBlargan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "18_CR6",
"unstructured": "VanBlargan, L. A. et al. An infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.529 Omicron virus escapes neutralization by therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 28, 490–495 (2022).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.ade8778",
"author": "SA Moghadasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eade8778",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "18_CR7",
"unstructured": "Moghadasi, S. A. et al. Transmissible SARS-CoV-2 variants with resistance to clinical protease inhibitors. Sci. Adv. 9, eade8778 (2023).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1009929",
"author": "AM Szemiel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1009929",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "18_CR8",
"unstructured": "Szemiel, A. M. et al. In vitro selection of Remdesivir resistance suggests evolutionary predictability of SARS-CoV-2. PLoS Pathog. 17, e1009929 (2021).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03312-w",
"author": "A Wahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "451",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "18_CR9",
"unstructured": "Wahl, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection is effectively treated and prevented by EIDD-2801. Nature 591, 451–457 (2021).",
"volume": "591",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abb5883",
"author": "TP Sheahan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabb5883",
"journal-title": "Sci. Transl. Med.",
"key": "18_CR10",
"unstructured": "Sheahan, T. P. et al. An orally bioavailable broad-spectrum antiviral inhibits SARS-CoV-2 in human airway epithelial cell cultures and multiple coronaviruses in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 12, eabb5883 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.RA120.013679",
"author": "CJ Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6785",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "18_CR11",
"unstructured": "Gordon, C. J. et al. Remdesivir is a direct-acting antiviral that inhibits RNA-dependent RNA polymerase from severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 with high potency. J. Biol. Chem. 295, 6785–6797 (2020).",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22580-8",
"author": "K Rosenke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "18_CR12",
"unstructured": "Rosenke, K. et al. Orally delivered MK-4482 inhibits SARS-CoV-2 replication in the Syrian hamster model. Nat. Commun. 12, 2295 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18096-2",
"author": "W Vuong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "18_CR13",
"unstructured": "Vuong, W. et al. Feline coronavirus drug inhibits the main protease of SARS-CoV-2 and blocks virus replication. Nat. Commun. 11, 4282 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abg5827",
"author": "N Drayman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "931",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "18_CR14",
"unstructured": "Drayman, N. et al. Masitinib is a broad coronavirus 3CL inhibitor that blocks replication of SARS-CoV-2. Science 373, 931–936 (2021).",
"volume": "373",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03720-y",
"author": "RE Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "18_CR15",
"unstructured": "Chen, R. E. et al. In vivo monoclonal antibody efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 variant strains. Nature 596, 103–108 (2021).",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe2402",
"author": "A Baum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1110",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "18_CR16",
"unstructured": "Baum, A. et al. REGN-COV2 antibodies prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques and hamsters. Science 370, 1110–1115 (2020).",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2033130",
"author": "A-TL-CS Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "905",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "18_CR17",
"unstructured": "Group, A.-T. L.-C. S. et al. A neutralizing monoclonal antibody for hospitalized patients with Covid-19. N. Engl. J. Med. 384, 905–914 (2021).",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2016093117",
"author": "A Glasgow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "28046",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "18_CR18",
"unstructured": "Glasgow, A. et al. Engineered ACE2 receptor traps potently neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117, 28046–28055 (2020).",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00491-21",
"author": "D Limonta",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0049121",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.",
"key": "18_CR19",
"unstructured": "Limonta, D. et al. Nodosome inhibition as a novel broad-spectrum antiviral strategy against arboviruses, enteroviruses and SARS-CoV-2. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 65, e0049121 (2021).",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2021.05.023",
"author": "W Kamel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2851",
"journal-title": "Mol. Cell",
"key": "18_CR20",
"unstructured": "Kamel, W. et al. Global analysis of protein-RNA interactions in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells reveals key regulators of infection. Mol. Cell 81, 2851–2867.e2857 (2021).",
"volume": "81",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.028",
"author": "J Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "18_CR21",
"unstructured": "Wei, J. et al. Genome-wide CRISPR screens reveal host factors critical for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Cell 184, 76–91.e13 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2012939117",
"author": "S Weston",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "30687",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "18_CR22",
"unstructured": "Weston, S. et al. The SKI complex is a broad-spectrum, host-directed antiviral drug target for coronaviruses, influenza, and filoviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 117, 30687–30698 (2020).",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.12.004",
"author": "R Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "106",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "18_CR23",
"unstructured": "Wang, R. et al. Genetic screens identify host factors for SARS-CoV-2 and common cold coronaviruses. Cell 184, 106–119.e114 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.008",
"author": "L Sun",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1865",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "18_CR24",
"unstructured": "Sun, L. et al. In vivo structural characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA genome identifies host proteins vulnerable to repurposed drugs. Cell 184, 1865–1883.e1820 (2021).",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsinfecdis.1c00017",
"author": "SB Biering",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2337",
"journal-title": "ACS Infect. Dis.",
"key": "18_CR25",
"unstructured": "Biering, S. B. et al. Screening a library of FDA-approved and bioactive compounds for antiviral activity against SARS-CoV-2. ACS Infect. Dis. 7, 2337–2351 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2105815118",
"author": "C Mirabelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e2105815118",
"journal-title": "Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA",
"key": "18_CR26",
"unstructured": "Mirabelli, C. et al. Morphological cell profiling of SARS-CoV-2 infection identifies drug repurposing candidates for COVID-19. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 118, e2105815118 (2021).",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03491-6",
"author": "L Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "18_CR27",
"unstructured": "Braga, L. et al. Drugs that inhibit TMEM16 proteins block SARS-CoV-2 spike-induced syncytia. Nature 594, 88–93 (2021).",
"volume": "594",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108959",
"author": "M Dittmar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108959",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "18_CR28",
"unstructured": "Dittmar, M. et al. Drug repurposing screens reveal cell-type-specific entry pathways and FDA-approved drugs active against SARS-Cov-2. Cell Rep. 35, 108959 (2021).",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/med.21664",
"author": "X Ji",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1519",
"journal-title": "Med. Res. Rev.",
"key": "18_CR29",
"unstructured": "Ji, X. & Li, Z. Medicinal chemistry strategies toward host targeting antiviral agents. Med. Res. Rev. 40, 1519–1557 (2020).",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1874467210902010032",
"author": "JD Burke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "32",
"journal-title": "Curr. Mol. Pharmacol.",
"key": "18_CR30",
"unstructured": "Burke, J. D. & Fish, E. N. Antiviral strategies: the present and beyond. Curr. Mol. Pharmacol. 2, 32–39 (2009).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01410-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "18_CR31",
"unstructured": "Lokugamage, K. G. et al. Type I interferon susceptibility distinguishes SARS-CoV-2 from SARS-CoV. J. Virol. 94. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01410-20 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00430-022-00734-9",
"author": "JH Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Med. Microbiol. Immunol.",
"key": "18_CR32",
"unstructured": "Lee, J. H., Koepke, L., Kirchhoff, F. & Sparrer, K. M. J. Interferon antagonists encoded by SARS-CoV-2 at a glance. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 212, 125–131 (2023).",
"volume": "212",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2021.05.004",
"author": "SA Lowery",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1052",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "18_CR33",
"unstructured": "Lowery, S. A., Sariol, A. & Perlman, S. Innate immune and inflammatory responses to SARS-CoV-2: Implications for COVID-19. Cell Host Microbe 29, 1052–1062 (2021).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2020.104791",
"author": "E Sallard",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104791",
"journal-title": "Antiviral Res.",
"key": "18_CR34",
"unstructured": "Sallard, E., Lescure, F. X., Yazdanpanah, Y., Mentre, F. & Peiffer-Smadja, N. Type 1 interferons as a potential treatment against COVID-19. Antiviral Res. 178, 104791 (2020).",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1005264",
"author": "S Bender",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1005264",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "18_CR35",
"unstructured": "Bender, S. et al. Activation of type I and III interferon response by mitochondrial and peroxisomal MAVS and inhibition by hepatitis C virus. PLoS Pathog. 11, e1005264 (2015).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.E21-02-0074",
"author": "B Knoblach",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1273",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "18_CR36",
"unstructured": "Knoblach, B., Ishida, R., Hobman, T. C. & Rachubinski, R. A. Peroxisomes exhibit compromised structure and matrix protein content in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 32, 1273–1282 (2021).",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ana.26679",
"author": "A Roczkowsky",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "531",
"journal-title": "Ann. Neurol.",
"key": "18_CR37",
"unstructured": "Roczkowsky, A. et al. COVID-19 induces neuroinflammation and suppresses peroxisomes in the brain. Ann. Neurol. 94, 531–546 (2023).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01677-17",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "18_CR38",
"unstructured": "Zhang, Q., Ke, H., Blikslager, A., Fujita, T. & Yoo, D. Type III interferon restriction by porcine epidemic diarrhea virus and the role of viral protein nsp1 in IRF1 signaling. J. Virol. 92, https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.01677-17 (2018).."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01365-15",
"author": "J You",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "12349",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR39",
"unstructured": "You, J. et al. Flavivirus infection impairs peroxisome biogenesis and early antiviral signaling. J. Virol. 89, 12349–12361 (2015).",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1006360",
"author": "Z Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1006360",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "18_CR40",
"unstructured": "Xu, Z. et al. MicroRNAs upregulated during HIV infection target peroxisome biogenesis factors: Implications for virus biology, disease mechanisms and neuropathology. PLoS Pathog. 13, e1006360 (2017).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells8070725",
"author": "CP Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "725",
"journal-title": "Cells",
"key": "18_CR41",
"unstructured": "Wong, C. P. et al. Interplay between Zika Virus and Peroxisomes during Infection. Cells 8, 725 (2019).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.03395-19",
"author": "Z Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e03395",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "18_CR42",
"unstructured": "Xu, Z., Lodge, R., Power, C., Cohen, E. A. & Hobman, T. C. The HIV-1 accessory protein VPU downregulates peroxisome biogenesis. mBio 11, e03395–19 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01531-2020",
"author": "EY Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2001531",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "18_CR43",
"unstructured": "Choi, E. Y. et al. Wnt5a and Wnt11 as acute respiratory distress syndrome biomarkers for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 patients. Eur. Respir. J. 56, 2001531 (2020).",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cancers12123638",
"author": "MJ Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3638",
"journal-title": "Cancers",
"key": "18_CR44",
"unstructured": "Kim, M. J., Huang, Y. & Park, J. I. Targeting Wnt signaling for gastrointestinal cancer therapy: present and evolving views. Cancers 12, 3638 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/cr.2011.127",
"author": "J Gwak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Cell Res.",
"key": "18_CR45",
"unstructured": "Gwak, J. et al. Small molecule-based disruption of the Axin/beta-catenin protein complex regulates mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cell Res. 22, 237–247 (2012).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1242/jcs.236943",
"author": "Y Fujiki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "jcs236943",
"journal-title": "J. Cell Sci.",
"key": "18_CR46",
"unstructured": "Fujiki, Y. et al. Recent insights into peroxisome biogenesis and associated diseases. J. Cell Sci. 133, jcs236943 (2020).",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0196-0709(83)80019-2",
"author": "WJ Richtsmeier",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "325",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Otolaryngol.",
"key": "18_CR47",
"unstructured": "Richtsmeier, W. J. Human interferon production in tonsil and adenoid tissue cultures. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 4, 325–333 (1983).",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1983"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.2.10.955-961.1968",
"author": "J Desmyter",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "955",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR48",
"unstructured": "Desmyter, J., Melnick, J. L. & Rawls, W. E. Defectiveness of interferon production and of rubella virus interference in a line of African green monkey kidney cells (Vero). J. Virol. 2, 955–961 (1968).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1968"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1146/annurev-cellbio-120319-023657",
"author": "LV Albrecht",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "369",
"journal-title": "Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol.",
"key": "18_CR49",
"unstructured": "Albrecht, L. V., Tejeda-Munoz, N. & De Robertis, E. M. Cell biology of canonical Wnt signaling. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 37, 369–389 (2021).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.09.050",
"author": "SR Leist",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1070",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "18_CR50",
"unstructured": "Leist, S. R. et al. A mouse-adapted SARS-CoV-2 induces acute lung injury and mortality in standard laboratory mice. Cell 183, 1070–1085.e1012 (2020).",
"volume": "183",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41416-020-0916-5",
"author": "R Plummer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "525",
"journal-title": "Br. J. Cancer",
"key": "18_CR51",
"unstructured": "Plummer, R. et al. First-in-human study of the PARP/tankyrase inhibitor E7449 in patients with advanced solid tumours and evaluation of a novel drug-response predictor. Br. J. Cancer 123, 525–533 (2020).",
"volume": "123",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "S Ramasamy",
"first-page": "e00299",
"journal-title": "Clin. Microbiol. Rev.",
"key": "18_CR52",
"unstructured": "Ramasamy, S. & Subbian, S. Critical determinants of cytokine storm and type I interferon response in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 34, e00299–20 (2021).",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.018",
"author": "E Dixit",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "668",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "18_CR53",
"unstructured": "Dixit, E. et al. Peroxisomes are signaling platforms for antiviral innate immunity. Cell 141, 668–681 (2010).",
"volume": "141",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/dna.2018.4153",
"author": "CP Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "417",
"journal-title": "DNA Cell Biol",
"key": "18_CR54",
"unstructured": "Wong, C. P., Xu, Z., Power, C. & Hobman, T. C. Targeted elimination of peroxisomes during viral infection: lessons from HIV and other viruses. DNA Cell Biol 37, 417–421 (2018).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni.2915",
"author": "C Odendall",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "717",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "18_CR55",
"unstructured": "Odendall, C. et al. Diverse intracellular pathogens activate type III interferon expression from peroxisomes. Nat. Immunol. 15, 717–726 (2014).",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1008636",
"author": "F Di Cara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e1008636",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathog.",
"key": "18_CR56",
"unstructured": "Di Cara, F. Peroxisomes in host defense. PLoS Pathog. 16, e1008636 (2020).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1091/mbc.E18-07-0434",
"author": "F Di Cara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2766",
"journal-title": "Mol. Biol. Cell",
"key": "18_CR57",
"unstructured": "Di Cara, F., Bulow, M. H., Simmonds, A. J. & Rachubinski, R. A. Dysfunctional peroxisomes compromise gut structure and host defense by increased cell death and Tor-dependent autophagy. Mol. Biol. Cell 29, 2766–2783 (2018).",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2017.06.016",
"author": "F Di Cara",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "93",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "18_CR58",
"unstructured": "Di Cara, F., Sheshachalam, A., Braverman, N. E., Rachubinski, R. A. & Simmonds, A. J. Peroxisome-mediated metabolism is required for immune response to microbial infection. Immunity 47, 93–106.e107 (2017).",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.AC120.013788",
"author": "U Felgenhauer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13958",
"journal-title": "J. Biol. Chem.",
"key": "18_CR59",
"unstructured": "Felgenhauer, U. et al. Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by type I and type III interferons. J. Biol. Chem. 295, 13958–13964 (2020).",
"volume": "295",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00985-20",
"author": "A Vanderheiden",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00985",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR60",
"unstructured": "Vanderheiden, A. et al. Type I and type III interferons restrict SARS-CoV-2 infection of human airway epithelial cultures. J. Virol. 94, e00985–20 (2020).",
"volume": "94",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(03)13973-6",
"author": "J Cinatl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "293",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "18_CR61",
"unstructured": "Cinatl, J. et al. Treatment of SARS with human interferons. Lancet 362, 293–294 (2003).",
"volume": "362",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2016.01.007",
"author": "R Channappanavar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "181",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "18_CR62",
"unstructured": "Channappanavar, R. et al. Dysregulated type I interferon and inflammatory monocyte-macrophage responses cause lethal pneumonia in SARS-CoV-infected mice. Cell Host Microbe 19, 181–193 (2016).",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/vir.0.046284-0",
"author": "T Mahlakoiv",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2601",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR63",
"unstructured": "Mahlakoiv, T. et al. Combined action of type I and type III interferon restricts initial replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus in the lung but fails to inhibit systemic virus spread. J. Gen. Virol. 93, 2601–2605 (2012).",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00009-13",
"author": "RW Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6604",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR64",
"unstructured": "Chan, R. W. et al. Tropism of and innate immune responses to the novel human betacoronavirus lineage C virus in human ex vivo respiratory organ cultures. J. Virol. 87, 6604–6614 (2013).",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2003.11.013",
"author": "M Spiegel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "211",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR65",
"unstructured": "Spiegel, M., Pichlmair, A., Mühlberger, E., Haller, O. & Weber, F. The antiviral effect of interferon-beta against SARS-coronavirus is not mediated by MxA protein. J. Clin. Virol. 30, 211–213 (2004).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03496-12",
"author": "F Zielecki",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5300",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR66",
"unstructured": "Zielecki, F. et al. Human cell tropism and innate immune system interactions of human respiratory coronavirus EMC compared to those of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus. J. Virol. 87, 5300–5304 (2013).",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11096-005-1319-7",
"author": "S Sleijfer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "423",
"journal-title": "Pharm. World Sci.",
"key": "18_CR67",
"unstructured": "Sleijfer, S., Bannink, M., Van Gool, A. R., Kruit, W. H. & Stoter, G. Side effects of interferon-alpha therapy. Pharm. World Sci. 27, 423–431 (2005).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nchembio.2103",
"author": "PH Cha",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Nat. Chem. Biol.",
"key": "18_CR68",
"unstructured": "Cha, P. H. et al. Small-molecule binding of the axin RGS domain promotes beta-catenin and Ras degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 12, 593–600 (2016).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.18632/oncotarget.5846",
"author": "S McGonigle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "41307",
"journal-title": "Oncotarget",
"key": "18_CR69",
"unstructured": "McGonigle, S. et al. E7449: a dual inhibitor of PARP1/2 and tankyrase1/2 inhibits growth of DNA repair deficient tumors and antagonizes Wnt signaling. Oncotarget 6, 41307–41323 (2015).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2023.168170",
"author": "J Lopez-Orozco",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "168170",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "18_CR70",
"unstructured": "Lopez-Orozco, J. et al. The RNA interference effector protein argonaute 2 functions as a restriction factor against SARS-CoV-2. J. Mol. Biol. 435, 168170 (2023).",
"volume": "435",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41596-021-00491-8",
"author": "X Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1761",
"journal-title": "Nat. Protoc.",
"key": "18_CR71",
"unstructured": "Xie, X. et al. Engineering SARS-CoV-2 using a reverse genetic system. Nat. Protoc. 16, 1761–1784 (2021).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00266-21",
"author": "A Kumar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0026621",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "18_CR72",
"unstructured": "Kumar, A. et al. SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 inhibits the interferon response by causing depletion of key host signaling factors. J. Virol. 95, e0026621 (2021).",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1006/meth.2001.1262",
"author": "KJ Livak",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "402",
"journal-title": "Methods",
"key": "18_CR73",
"unstructured": "Livak, K. J. & Schmittgen, T. D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408 (2001).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-32420-3",
"author": "F Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "18_CR74",
"unstructured": "Wang, F. et al. Histopathological changes caused by inflammation and oxidative stress in diet-induced-obese mouse following experimental lung injury. Sci. Rep. 8, 14250 (2018).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 74,
"references-count": 74,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s44298-024-00018-4"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The Wnt/β-catenin pathway is important for replication of SARS-CoV-2 and other pathogenic RNA viruses",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "2"
}