Screening and identification of host factors interacting with the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant using the yeast two-hybrid system
et al., BMC Microbiology, doi:10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7, Aug 2025
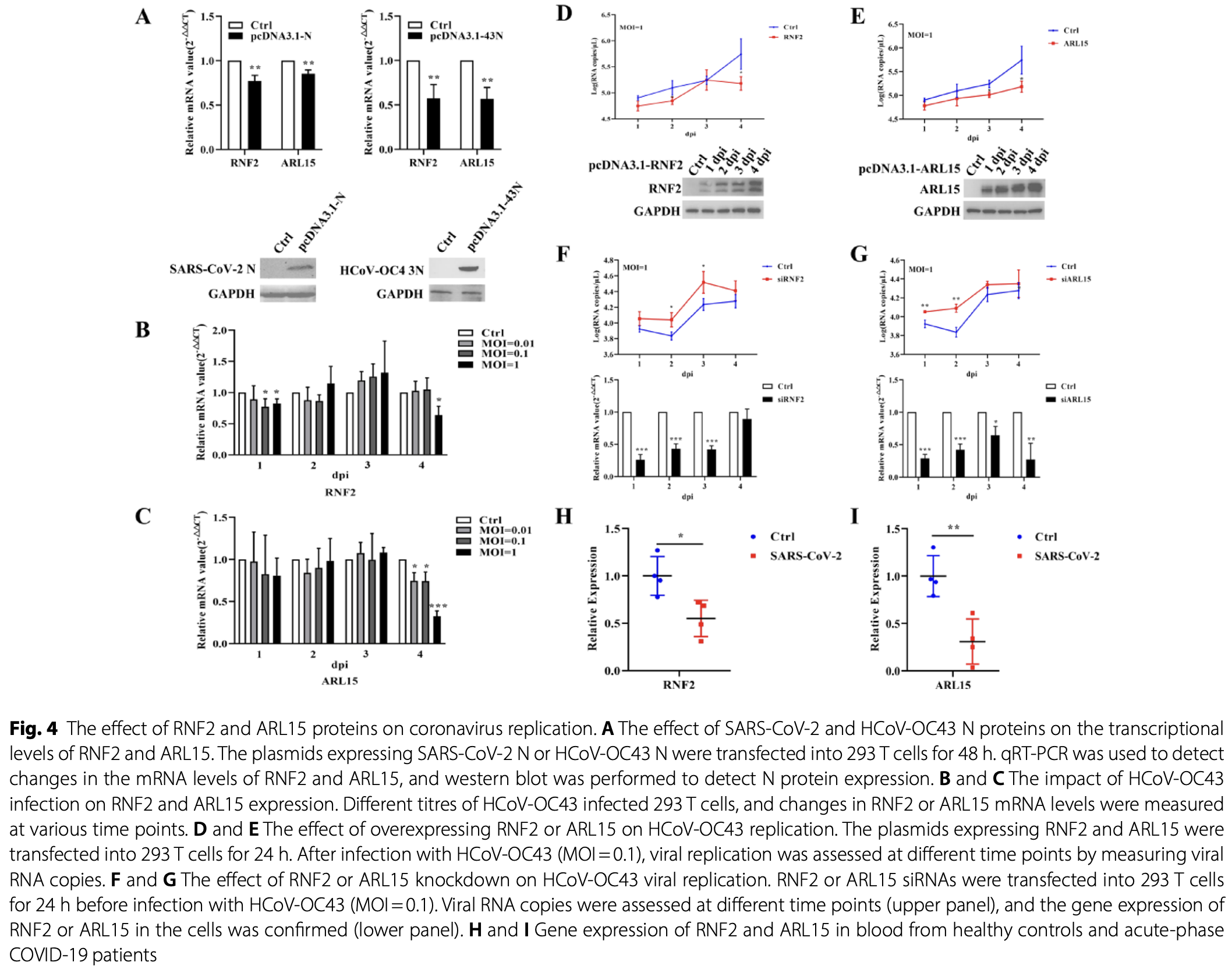
In vitro study showing that host proteins RNF2 and ARL15 interact with SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein and inhibit coronavirus replication in 293T cells. Authors used a yeast two-hybrid system to screen human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and identified 11 host proteins that potentially interact with the SARS-CoV-2 N protein, with RNF2 and ARL15 showing the highest positive clone rates.
Wang et al., 1 Aug 2025, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: young@mail.sustech.edu.cn, shenliang.0829@163.com, xiaying0437@163.com.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Screening and identification of host factors interacting with the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant using the yeast two-hybrid system
BMC Microbiology, doi:10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7
Background The nucleocapsid protein (N protein) of SARS-CoV-2 is highly conserved in viral evolution and serves as the primary structural protein in viral infection, being the most abundant in viral particles. The N protein is highly immunogenic and plays a key role in the processes of viral infection and replication, making it of significant research value in both basic studies and clinical applications.
Results To further investigate the functions of SARS-CoV-2 N protein, the Matchmaker Gold Yeast Two-Hybrid System was used to identify potential interacting partners of the N protein in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs). Through this approach, we identified 11 host proteins that might interact with the SARS-CoV-2 N protein. We further validated the interaction between the N protein and two host proteins, RNF2 and ARL15, which showed the highest positive clone rates at the cellular level. We also predicted the critical amino acid residues mediating the interaction of the N protein with RNF2 or ARL15. Additionally, we explored the impact of these two host proteins on coronavirus replication. Functional analysis of all the 11 host proteins revealed their involvement in ribosome biogenesis, antigen processing and presentation, as well as various signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT.
Conclusions This study further enriches the understanding of interactions between the SARS-CoV-2 N protein and host, providing important theoretical insights for the deeper understanding of viral pathogenesis and the development of antiviral strategies.
Supplementary Information The online version contains supplementary material available at h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0 . 1 1 8 6 / s 1 2 8 6 6 -0 2 5 -0 4
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Xiangyang Central Hospital (2023-025-015). Before the study commenced, detailed discussions were made with the participants about the objective of the study and participants were enrolled after obtaining written informed consent and assent. All experiments were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Chunhua
References
Bai, Zhong, Gao, Overview of SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded proteins, Sci China Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s11427-021-1964-4
Bertoletti, SARS-CoV-2 immunity, Cell Mol Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41423-024-01128-y
Chen, Guan, Qiu, Xu, Bai et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein triggers hyperinflammation via protein-protein interaction-mediated intracellular Cl(-) accumulation in respiratory epithelium, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1038/s41392-022-01048-1
Chen, Wang, Feng, Chen, Comprehensive analysis of the host-virus interactome of SARS-CoV-2, h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g / 1 0, doi:10.1101/2020.12.31.424961
Chi, Yan, Zhang, Zhang, Zhang et al., A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abc6952
Cubuk, Alston, Incicco, Singh, Stuchell-Brereton et al., The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-21953-3
Das, Roy, Guzzi, Analyzing host-viral interactome of SARS-CoV-2 for identifying vulnerable host proteins during COVID-19 pathogenesis, Infect Genet Evol, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104921
Davis-Porada, George, Lam, Caron, Gray et al., Maintenance and functional regulation of immune memory to COVID-19 vaccines in tissues, Immunity, doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2024.10.003
Desforges, Miletti, Gagnon, Talbot, Activation of human monocytes after infection by human coronavirus 229E, Virus Res, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2007.06.016
Dong, Ouyang, Gao, Ma, Hou et al., PPP4C facilitates homologous recombination DNA repair by dephosphorylating PLK1 during early embryo development, Development, doi:10.1242/dev.200351
El-Maradny, Badawy, Mohamed, Ragab, Moharm et al., Unraveling the role of the nucleocapsid protein in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: from viral life cycle to vaccine development, Int J Biol Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135201
Flynn, Belk, Qi, Yasumoto, Wei et al., Discovery and functional interrogation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-host protein interactions, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.012
Gao, Gao, Liu, Nie, Sun et al., Identification and functional analysis of the SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein, BMC Microbiol, doi:10.1186/s12866-021-02107-3
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Hurst, Koetzner, Masters, Characterization of a critical interaction between the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 3 of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.01275-13
Kratzel, Kelly, Kovski, Portmann, Brüggemann et al., A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies interactors of the autophagy pathway as conserved coronavirus targets, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3001490
Lang, Chen, Li, Li, The nucleocapsid protein of zoonotic betacoronaviruses is an attractive target for antiviral drug discovery, Life Sci, doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118754
Li, Guo, Tian, Wang, Yang et al., Virus-Host Interactome and Proteomic Survey Reveal Potential Virulence Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis, Med, doi:10.1016/j.medj.2020.07.002
Liu, Huuskonen, Laitinen, Redchuk, Bogacheva et al., SARS-CoV-2-host proteome interactions for antiviral drug discovery, Mol Syst Biol, doi:10.15252/msb.202110396
López-Muñoz, Kosik, Holly, Yewdell, Cell surface SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein modulates innate and adaptive immunity, Res Sq, doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-1162804/v1
Ma, Zhu, Zhao, Shao, Yu et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid suppresses host pyroptosis by blocking Gasdermin D cleavage, Embo J, doi:10.15252/embj.2021108249
Nabeel-Shah, Lee, Ahmed, Burke, Farhangmehr et al., SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein binds host mRNAs and attenuates stress granules to impair host stress response, iScience, doi:10.1016/j.isci.2021.103562
Pan, Shen, Yu, Ge, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 N protein promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation to induce hyperinflammation, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-021-25015-6
Ren, Cai, Fang, Wang, Zhang et al., Multiplexed detection of viral antigen and RNA using nanopore sensing and encoded molecular probes, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-43004-9
Saini, Upadhyay, Dhiman, Manjhi, Kattuparambil et al., ARL15, a GTPase implicated in rheumatoid arthritis, potentially repositions its truncated N-terminus as a function of guanine nucleotide binding, Int J Biol Macromol, doi:10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127898
Sarkar, Runge, Russell, Movellan, Calero et al., Atomic-resolution structure of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein N-terminal domain, J Am Chem Soc, doi:10.1021/jacs.2c03320
Steiner, Kratzel, Barut, Lang, Moreira et al., SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z
Tai, Feng, Chai, Lu, Zhao et al., An mRNA-based T-cellinducing antigen strengthens COVID-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-38751-8
Tang, Tran, Wang, Horng, SARS-CoV-2 pandemics: An update of CRISPR in diagnosis and host-virus interaction studies, Biomed J, doi:10.1016/j.bj.2023.02.007
Tyl, Betsinger, Cristea, Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication, Curr Opin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016
Vandelli, Monti, Milanetti, Armaos, Rupert et al., Structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome and predictions of the human interactome, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkaa864
Vitiello, Zovi, Rezza, New emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and antiviral agents, Drug Resist Updat, doi:10.1016/j.drup.2023.100986
Wang, Chen, Yu, Lan, Signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein in viral infection, cell death and inflammation, Int J Biol Sci, doi:10.7150/ijbs.72663
Wang, Zhao, Yang, Yu, Li, E3 ligase RNF2 inhibits porcine circovirus type 3 replication by targeting its capsid protein for ubiquitinationdependent degradation, J Virol, doi:10.1128/jvi.00223-24
Yang, Johnson, Meliopoulos, Ju, Zhang et al., Interaction between host G3BP and viral nucleocapsid protein regulates SARS-CoV-2 replication, h t t p s : / / d o i . o r g, doi:10.1101/2023.06.29.546885
Yang, Li, Li, Zheng, Li et al., Engagement of the G3BP2-TRIM25 interaction by nucleocapsid protein suppresses the type i interferon response in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines10122042
Yao, Li, Jiang, Zhang, Li et al., RNF2 inhibits E-Cadherin transcription to promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via inducing histone mono-ubiquitination, Cell Death Dis, doi:10.1038/s41419-023-05785-1
Zhao, Syed, Khalid, Nguyen, Ciling et al., Assembly of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein with nucleic acid, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gkae256
Zheng, Sun, Yu, Shi, Zhu et al., Interactome analysis of the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 virus, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10091155
Zhou, Liu, Gupta, Paramo, Hou et al., A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interactome reveals COVID-19 pathobiology and potential host therapeutic targets, Nat Biotechnol, doi:10.1038/s41587-022-01474-0
Zhu, Blum, Bernareggi, Ask, Wu et al., Metabolic reprograming via deletion of CISH in human iPSC-derived NK cells promotes in vivo persistence and enhances anti-tumor activity, Cell Stem Cell, doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.05.008
Zolotarov, Ma, González-Recio, Hardy, Franken et al., ARL15 modulates magnesium homeostasis through N-glycosylation of CNNMs, Cell Mol Life Sci, doi:10.1007/s00018-021-03832-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2180"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7",
"alternative-id": [
"4226"
],
"article-number": "474",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "6 December 2024"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "14 July 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "1 August 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study was approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Xiangyang Central Hospital (2023–025-015). Before the study commenced, detailed discussions were made with the participants about the objective of the study and participants were enrolled after obtaining written informed consent and assent. All experiments were conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no conflict of interest."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wang",
"given": "Chunhua",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yu",
"given": "Tingyu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xie",
"given": "Moyue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhan",
"given": "Dongang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Shuaijie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chai",
"given": "Wenqi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhao",
"given": "Jianzhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yin",
"given": "Lijuan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shen",
"given": "Liang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xia",
"given": "Ying",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Microbiology",
"container-title-short": "BMC Microbiol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T09:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1754038832000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T09:00:32Z",
"timestamp": 1754038832000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"2022YZ04"
],
"name": "Scientific research project of Xiangyang Central Hospital"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T09:40:03Z",
"timestamp": 1754041203232,
"version": "3.41.2"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7",
"author": "B Hu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "141",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "4226_CR1",
"unstructured": "Hu B, Guo H, Zhou P, Shi ZL. Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2021;19(3):141–54. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-024-01128-y",
"author": "A Bertoletti",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "101",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Immunol",
"key": "4226_CR2",
"unstructured": "Bertoletti A. SARS-CoV-2 immunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024;21(2):101–2. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41423-024-01128-y.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2024.10.003",
"author": "J Davis-Porada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "4226_CR3",
"unstructured": "Davis-Porada J, George AB, Lam N, Caron DP, Gray JI, Huang J, et al. Maintenance and functional regulation of immune memory to COVID-19 vaccines in tissues. Immunity. 2024. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2024.10.003.",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-38751-8",
"author": "W Tai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2962",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "4226_CR4",
"unstructured": "Tai W, Feng S, Chai B, Lu S, Zhao G, Chen D, et al. An mRNA-based T-cell-inducing antigen strengthens COVID-19 vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):2962. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-38751-8.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.drup.2023.100986",
"author": "A Vitiello",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100986",
"journal-title": "Drug Resist Updat",
"key": "4226_CR5",
"unstructured": "Vitiello A, Zovi A, Rezza G. New emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants and antiviral agents. Drug Resist Updat. 2023;70:100986. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.drup.2023.100986.",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkaa864",
"author": "A Vandelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "11270",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "4226_CR6",
"unstructured": "Vandelli A, Monti M, Milanetti E, Armaos A, Rupert J, Zacco E, et al. Structural analysis of SARS-CoV-2 genome and predictions of the human interactome. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020;48(20):11270–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa864.",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-21953-3",
"author": "J Cubuk",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1936",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "4226_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cubuk J, Alston JJ, Incicco JJ, Singh S, Stuchell-Brereton MD, Ward MD, et al. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is dynamic, disordered, and phase separates with RNA. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):1936. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21953-3.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.01275-13",
"author": "KR Hurst",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "9159",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "4226_CR8",
"unstructured": "Hurst KR, Koetzner CA, Masters PS. Characterization of a critical interaction between the coronavirus nucleocapsid protein and nonstructural protein 3 of the viral replicase-transcriptase complex. J Virol. 2013;87(16):9159–72. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.01275-13.",
"volume": "87",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.72663",
"author": "W Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4704",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Sci",
"key": "4226_CR9",
"unstructured": "Wang W, Chen J, Yu X, Lan HY. Signaling mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid protein in viral infection, cell death and inflammation. Int J Biol Sci. 2022;18(12):4704–13. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.72663.",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/jacs.2c03320",
"author": "S Sarkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "10543",
"issue": "23",
"journal-title": "J Am Chem Soc",
"key": "4226_CR10",
"unstructured": "Sarkar S, Runge B, Russell RW, Movellan KT, Calero D, Zeinalilathori S, et al. Atomic-resolution structure of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein N-terminal domain. J Am Chem Soc. 2022;144(23):10543–55. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.2c03320.",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkae256",
"author": "H Zhao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6647",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "4226_CR11",
"unstructured": "Zhao H, Syed AM, Khalid MM, Nguyen A, Ciling A, Wu D, et al. Assembly of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein with nucleic acid. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024;52(11):6647–61. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae256.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11427-021-1964-4",
"author": "C Bai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "280",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Sci China Life Sci",
"key": "4226_CR12",
"unstructured": "Bai C, Zhong Q, Gao GF. Overview of SARS-CoV-2 genome-encoded proteins. Sci China Life Sci. 2022;65(2):280–94. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-021-1964-4.",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12866-021-02107-3",
"author": "T Gao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "58",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Microbiol",
"key": "4226_CR13",
"unstructured": "Gao T, Gao Y, Liu X, Nie Z, Sun H, Lin K, et al. Identification and functional analysis of the SARS-COV-2 nucleocapsid protein. BMC Microbiol. 2021;21(1):58. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-021-02107-3.",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016",
"author": "MD Tyl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "135",
"journal-title": "Curr Opin Virol",
"key": "4226_CR14",
"unstructured": "Tyl MD, Betsinger CN, Cristea IM. Virus-host protein interactions as footprints of human cytomegalovirus replication. Curr Opin Virol. 2022;52:135–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coviro.2021.11.016.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104921",
"author": "JK Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "104921",
"journal-title": "Infect Genet Evol",
"key": "4226_CR15",
"unstructured": "Das JK, Roy S, Guzzi PH. Analyzing host-viral interactome of SARS-CoV-2 for identifying vulnerable host proteins during COVID-19 pathogenesis. Infect Genet Evol. 2021;93:104921. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meegid.2021.104921.",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medj.2020.07.002",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "99",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Med",
"key": "4226_CR16",
"unstructured": "Li J, Guo M, Tian X, Wang X, Yang X, Wu P, et al. Virus-Host Interactome and Proteomic Survey Reveal Potential Virulence Factors Influencing SARS-CoV-2 Pathogenesis. Med. 2021;2(1):99-112.e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.medj.2020.07.002.",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10091155",
"author": "X Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "4226_CR17",
"unstructured": "Zheng X, Sun Z, Yu L, Shi D, Zhu M, Yao H, et al. Interactome analysis of the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 virus. Pathogens. 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens10091155.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z",
"author": "S Steiner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "206",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Microbiol",
"key": "4226_CR18",
"unstructured": "Steiner S, Kratzel A, Barut GT, Lang RM, Aguiar Moreira E, Thomann L, et al. SARS-CoV-2 biology and host interactions. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2024;22(4):206–25. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41579-023-01003-z.",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-1162804/v1",
"author": "AD López-Muñoz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Res Sq",
"key": "4226_CR19",
"unstructured": "López-Muñoz AD, Kosik I, Holly J, Yewdell JW. Cell surface SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein modulates innate and adaptive immunity. Res Sq. 2021. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1162804/v1.",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-022-01474-0",
"author": "Y Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "128",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Biotechnol",
"key": "4226_CR20",
"unstructured": "Zhou Y, Liu Y, Gupta S, Paramo MI, Hou Y, Mao C, et al. A comprehensive SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interactome reveals COVID-19 pathobiology and potential host therapeutic targets. Nat Biotechnol. 2023;41(1):128–39. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-022-01474-0.",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25015-6",
"author": "P Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4664",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "4226_CR21",
"unstructured": "Pan P, Shen M, Yu Z, Ge W, Chen K, Tian M, et al. SARS-CoV-2 N protein promotes NLRP3 inflammasome activation to induce hyperinflammation. Nat Commun. 2021;12(1):4664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-25015-6.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2023.06.29.546885",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "4226_CR22",
"unstructured": "Yang Z, Johnson BA, Meliopoulos VA, Ju X, Zhang P, Hughes MP, et al. Interaction between host G3BP and viral nucleocapsid protein regulates SARS-CoV-2 replication. bioRxiv. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.06.29.546885."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118754",
"author": "Y Lang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "118754",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "4226_CR23",
"unstructured": "Lang Y, Chen K, Li Z, Li H. The nucleocapsid protein of zoonotic betacoronaviruses is an attractive target for antiviral drug discovery. Life Sci. 2021;282:118754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118754.",
"volume": "282",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc6952",
"author": "X Chi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "650",
"issue": "6504",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "4226_CR24",
"unstructured": "Chi X, Yan R, Zhang J, Zhang G, Zhang Y, Hao M, et al. A neutralizing human antibody binds to the N-terminal domain of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Science. 2020;369(6504):650–5. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc6952.",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-43004-9",
"author": "R Ren",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7362",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "4226_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ren R, Cai S, Fang X, Wang X, Zhang Z, Damiani M, et al. Multiplexed detection of viral antigen and RNA using nanopore sensing and encoded molecular probes. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):7362. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-43004-9.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135201",
"author": "YA El-Maradny",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "135201",
"issue": "Pt 2",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "4226_CR26",
"unstructured": "El-Maradny YA, Badawy MA, Mohamed KI, Ragab RF, Moharm HM, Abdallah NA, et al. Unraveling the role of the nucleocapsid protein in SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis: from viral life cycle to vaccine development. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;279(Pt 2):135201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2024.135201.",
"volume": "279",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2021108249",
"author": "J Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e108249",
"issue": "18",
"journal-title": "Embo J",
"key": "4226_CR27",
"unstructured": "Ma J, Zhu F, Zhao M, Shao F, Yu D, Ma J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid suppresses host pyroptosis by blocking Gasdermin D cleavage. Embo J. 2021;40(18):e108249. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2021108249.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.103562",
"author": "S Nabeel-Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103562",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "iScience.",
"key": "4226_CR28",
"unstructured": "Nabeel-Shah S, Lee H, Ahmed N, Burke GL, Farhangmehr S, Ashraf K, et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein binds host mRNAs and attenuates stress granules to impair host stress response. iScience. 2022;25(1):103562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103562.",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines10122042",
"author": "Z Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "4226_CR29",
"unstructured": "Yang Z, Li J, Li J, Zheng H, Li H, Lai Q, et al. Engagement of the G3BP2-TRIM25 interaction by nucleocapsid protein suppresses the type i interferon response in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Vaccines. 2022. https://doi.org/10.3390/vaccines10122042.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-022-01048-1",
"author": "L Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "255",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct Target Ther",
"key": "4226_CR30",
"unstructured": "Chen L, Guan WJ, Qiu ZE, Xu JB, Bai X, Hou XC, et al. SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein triggers hyperinflammation via protein-protein interaction-mediated intracellular Cl(-) accumulation in respiratory epithelium. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022;7(1):255. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01048-1.",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41419-023-05785-1",
"author": "L Yao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "261",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Death Dis",
"key": "4226_CR31",
"unstructured": "Yao L, Li J, Jiang B, Zhang Z, Li X, Ouyang X, et al. RNF2 inhibits E-Cadherin transcription to promote hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis via inducing histone mono-ubiquitination. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(4):261. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-023-05785-1.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127898",
"author": "M Saini",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "127898",
"issue": "Pt 2",
"journal-title": "Int J Biol Macromol",
"key": "4226_CR32",
"unstructured": "Saini M, Upadhyay N, Dhiman K, Manjhi SK, Kattuparambil AA, Ghoshal A, et al. ARL15, a GTPase implicated in rheumatoid arthritis, potentially repositions its truncated N-terminus as a function of guanine nucleotide binding. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024;254(Pt 2):127898. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.127898.",
"volume": "254",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1242/dev.200351",
"author": "MZ Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Development",
"key": "4226_CR33",
"unstructured": "Dong MZ, Ouyang YC, Gao SC, Ma XS, Hou Y, Schatten H, et al. PPP4C facilitates homologous recombination DNA repair by dephosphorylating PLK1 during early embryo development. Development. 2022. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.200351.",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.stem.2020.05.008",
"author": "H Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "224",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell Stem Cell",
"key": "4226_CR34",
"unstructured": "Zhu H, Blum RH, Bernareggi D, Ask EH, Wu Z, Hoel HJ, et al. Metabolic reprograming via deletion of CISH in human iPSC-derived NK cells promotes in vivo persistence and enhances anti-tumor activity. Cell Stem Cell. 2020;27(2):224-37.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2020.05.008.",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.00223-24",
"author": "D Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0022324",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "4226_CR35",
"unstructured": "Wang D, Zhao J, Yang X, Ji Y, Yu J, Li Z, et al. E3 ligase RNF2 inhibits porcine circovirus type 3 replication by targeting its capsid protein for ubiquitination-dependent degradation. J Virol. 2024;98(8):e0022324. https://doi.org/10.1128/jvi.00223-24.",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00018-021-03832-8",
"author": "Y Zolotarov",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5427",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol Life Sci",
"key": "4226_CR36",
"unstructured": "Zolotarov Y, Ma C, González-Recio I, Hardy S, Franken GAC, Uetani N, et al. ARL15 modulates magnesium homeostasis through N-glycosylation of CNNMs. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2021;78(13):5427–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-021-03832-8.",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.12.31.424961",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "4226_CR37",
"unstructured": "Chen Z, Wang C, Feng X, Chen J. Comprehensive analysis of the host-virus interactome of SARS-CoV-2. bioRxiv. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.12.31.424961."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "7816",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "4226_CR38",
"unstructured": "Gordon DE, Jang GM, Bouhaddou M, Xu J, Obernier K, White KM, et al. A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing. Nature. 2020;583(7816):459–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9.",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/msb.202110396",
"author": "X Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e10396",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Mol Syst Biol",
"key": "4226_CR39",
"unstructured": "Liu X, Huuskonen S, Laitinen T, Redchuk T, Bogacheva M, Salokas K, et al. SARS-CoV-2-host proteome interactions for antiviral drug discovery. Mol Syst Biol. 2021;17(11):e10396. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.202110396.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.012",
"author": "RA Flynn",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2394",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "4226_CR40",
"unstructured": "Flynn RA, Belk JA, Qi Y, Yasumoto Y, Wei J, Alfajaro MM, et al. Discovery and functional interrogation of SARS-CoV-2 RNA-host protein interactions. Cell. 2021;184(9):2394-411.e16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.012.",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3001490",
"author": "A Kratzel",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e3001490",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol",
"key": "4226_CR41",
"unstructured": "Kratzel A, Kelly JN, V’Kovski P, Portmann J, Brüggemann Y, Todt D, et al. A genome-wide CRISPR screen identifies interactors of the autophagy pathway as conserved coronavirus targets. PLoS Biol. 2021;19(12):e3001490. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3001490.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bj.2023.02.007",
"author": "WF Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100587",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Biomed J",
"key": "4226_CR42",
"unstructured": "Tang WF, Tran AT, Wang LY, Horng JT. SARS-CoV-2 pandemics: An update of CRISPR in diagnosis and host-virus interaction studies. Biomed J. 2023;46(2):100587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bj.2023.02.007.",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2007.06.016",
"author": "M Desforges",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "228",
"issue": "1–2",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "4226_CR43",
"unstructured": "Desforges M, Miletti TC, Gagnon M, Talbot PJ. Activation of human monocytes after infection by human coronavirus 229E. Virus Res. 2007;130(1–2):228–40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2007.06.016.",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2007"
}
],
"reference-count": 43,
"references-count": 43,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcmicrobiol.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12866-025-04226-7"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Screening and identification of host factors interacting with the nucleocapsid protein of SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant using the yeast two-hybrid system",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "25"
}