Use of distinct anti‐hypertensive drugs and risk for COVID‐19 among hypertensive people: A population‐based cohort study in Southern Catalonia, Spain
et al., The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, doi:10.1111/jch.13948, Jul 2020
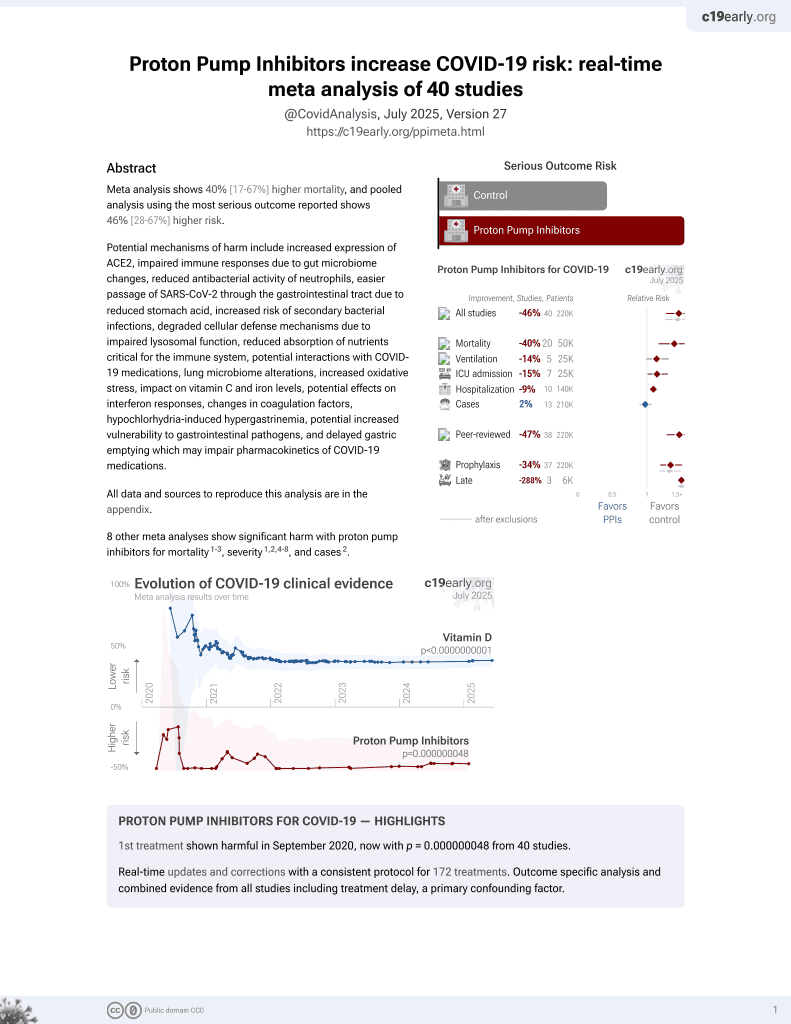
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
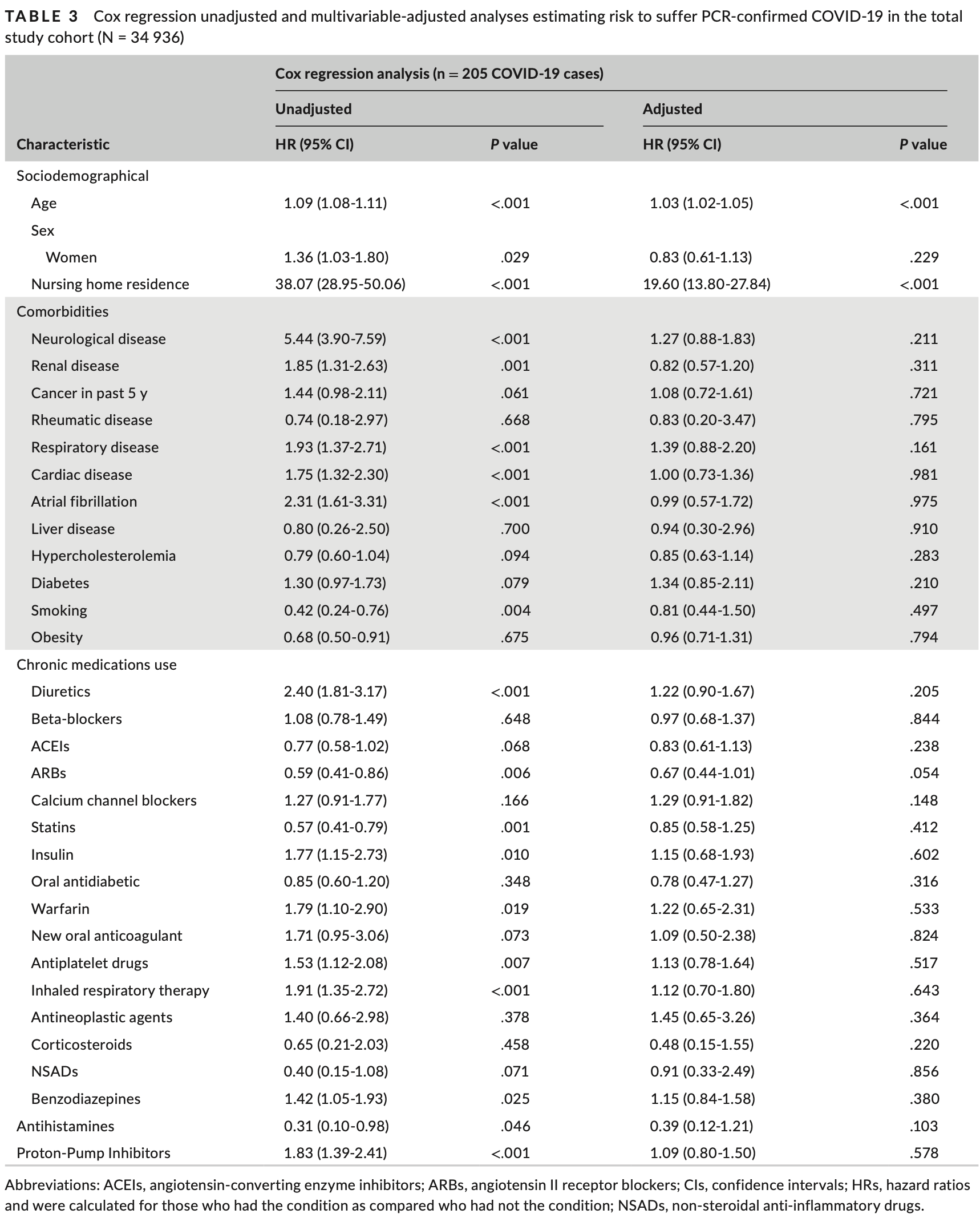
Retrospective 34,936 hypertensive outpatients in Spain showing no significant difference in COVID-19 cases with PPIs and antihistamine H1RAs.
Study covers proton pump inhibitors and antihistamine H1RAs.
|
risk of case, 9.0% higher, HR 1.09, p = 0.58, treatment 11,807, control 23,129, adjusted per study, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Vila-Corcoles et al., 25 Jul 2020, retrospective, Spain, peer-reviewed, mean age 70.9, 11 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 30 April, 2020.
Contact: oochoa.tgn.ics@gencat.cat.
Use of distinct anti‐hypertensive drugs and risk for COVID‐19 among hypertensive people: A population‐based cohort study in Southern Catalonia, Spain
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension, doi:10.1111/jch.13948
The use of some anti-hypertensive drugs in the current COVID-19 pandemic has become controversial. This study investigated possible relationships between antihypertensive medications use and COVID-19 infection risk in the ambulatory hypertensive population. This is a population-based retrospective cohort study involving 34 936 hypertensive adults >50 years in Tarragona (Southern Catalonia, Spain)
| 1387 VILA-CORCOLES Et AL.
E TH I C S A PPROVA L A N D CO N S E NT TO PA RTI CI PATE The study was approved by the ethical committee of the Institution (ethic committee IDIAP Jordi Gol, Barcelona, file 20/065-PCV) and was conducted in accordance with the general principles for observational studies. Given this is a non-interventional study, an informed consent for all 2 025 730 study participants was not required. Data were anonymized, and risk of identification was null.
References
De Abajo, Rodríguez-Martín, Lerma, Use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: a case-population study, Lancet
Deng, Yin, Chen, Zeng, Clinical determinants for fatality of 44,672 patients with COVID-19, Crit Care
Esler, Esler, Can angiotensin receptor-blockingdrugsperhaps be harmful in the COVID-19 pandemic?, J Hypertens
Grasselli, Zangrillo, Zanella, Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy Region, Italy, JAMA
Hosmer, Lemeshow, Applied Survival Analysis. Regression Modeling of Time to Event Data
Jarcho, Ingelfinger, Hamel, Agostino, Harrington, Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system and Covid-19 [published online ahead of print, N Engl J Med
Kai, Kai, Interactions of coronaviruses with ACE2, angiotensin II, and RAS inhibitors-lessons from available evidence and insights into COVID-19, Hypertens Res
Kreutz, Algharably, Azizi, Hypertension, the reninangiotensin system, and the risk of lower respiratory tract infections and lung injury: implications for COVID-19, Cardiovasc Res
Lieberman, Pepper, Naccache, Comparison of commercially available and laboratory developed assays for in vitro detection of sars-cov-2 in clinical laboratories, J Clin Microbiol
Lopes, Macedo, De Barros, Continuing versus suspending angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: impact on adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), Am Heart J, doi:10.1016/j.ahj.2020.05.002
Mancia, Rea, Ludergnani, Renin-angiotensinaldosterone system blockers and the risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Park, Lee, Cho, Is the use of RAS inhibitors safe in the current era of COVID-19 pandemic?, Clin Hypertens
Reiner, Hatamipour, Banach, Statins and the COVID-19 main protease: in silico evidence on direct interaction, Arch Med Sci
Reynolds, Adhikari, Pulgarin, Renin-Angiotensinaldosterone system inhibitors and risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Testa, Prandoni, Paoletti, Direct oral anticoagulant plasma levels' striking increase in severe COVID-19 respiratory syndrome patients treated with antiviral agents: the Cremona experience, J Thromb Haemost
Versmissen, Verdonk, Lafeber, Angiotensin-converting enzyme-2 in SARS-CoV-2 infection: goodorbad?, J Hypertens
Vila-Corcoles, Hospital-Guardiola, Ochoa-Gondar, Rationale and design of the CAPAMIS study: effectiveness of pneumococcal vaccination against community-acquired pneumonia, acute myocardial infarction and stroke, BMC Public Health
Wan, Shang, Graham, Receptor recognition by the novel coronavirus from Wuhan: an analysis based on decade-long structural studies of SARS coronavirus, J Virol
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Yang, Zheng, Gou, Prevalence of comorbidities and its effects in patients infected with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Zhang, Zhu, Cai, Association of inpatient use of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors and Angiotensin II receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jch.13948",
"ISSN": [
"1524-6175",
"1751-7176"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jch.13948",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>The use of some anti‐hypertensive drugs in the current COVID‐19 pandemic has become controversial. This study investigated possible relationships between anti‐hypertensive medications use and COVID‐19 infection risk in the ambulatory hypertensive population. This is a population‐based retrospective cohort study involving 34 936 hypertensive adults >50 years in Tarragona (Southern Catalonia, Spain) who were retrospectively followed through pandemic period (from 01/03/2020 to 30/04/2020). Two data sets including demographic/clinical characteristics (comorbidities and cardiovascular medications use) and laboratory PCR codes for COVID‐19 were linked to construct an anonymized research database. Cox regression was used to calculate multivariable hazard ratios (HRs) and estimate the risk of suffering COVID‐19 infection. Across study period, 205 PCR‐confirmed COVID‐19 cases were observed, which means an overall incidence of 586.8 cases per 100 000 persons‐period. In multivariable analyses, only age (HR: 1.03; 95% CI: 1.02‐1.05; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < .001) and nursing home residence (HR: 19.60; 95% CI: 13.80‐27.84; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> < .001) appeared significantly associated with increased risk of COVID‐19. Considering anti‐hypertensive drugs, receiving diuretics (HR: 1.22; 95% CI: 0.90‐1.67; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .205), calcium channel blockers (HR: 1.29; 95%CI: 0.91‐1.82; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .148), beta‐blockers (HR: 0.97; 95% CI: 0.68‐1.37; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .844), and angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors (HR: 0.83; 95% CI: 0.61‐1.13; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .238) did not significantly alter the risk of PCR‐confirmed COVID‐19, whereas receiving angiotensin II receptor blockers was associated with an almost statistically significant reduction risk (HR: 0.67; 95% CI: 0.44‐1.01; <jats:italic>P</jats:italic> = .054). In conclusion, our data support that receiving renin‐angiotensin‐aldosterone system inhibitors does not predispose for suffering COVID‐19 infection in ambulatory hypertensive people. Conversely, receiving angiotensin II receptor blockers could be related with a reduced risk.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/jch.13948"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2020-06-02"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2020-07-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2020-07-25"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Primary Health Care Service Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
},
{
"name": "Unitat de Suport a la Recerca Tarragona‐Reus IDIAP Jordi Gol Barcelona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Vila‐Corcoles",
"given": "Angel",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Primary Health Care Service Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
},
{
"name": "Unitat de Suport a la Recerca Tarragona‐Reus IDIAP Jordi Gol Barcelona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Satue‐Gracia",
"given": "Eva",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7015-0018",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Primary Health Care Service Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
},
{
"name": "Unitat de Suport a la Recerca Tarragona‐Reus IDIAP Jordi Gol Barcelona Spain"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ochoa‐Gondar",
"given": "Olga",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Information and Communication Technologies DAP Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Torrente‐Fraga",
"given": "Cristina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology Hospital Universitari Joan XXIII Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Gomez‐Bertomeu",
"given": "Frederic",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unitat de Suport a la Recerca Tarragona‐Reus IDIAP Jordi Gol Barcelona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Vila‐Rovira",
"given": "Angel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Primary Health Care Service Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Hospital‐Guardiola",
"given": "Imma",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Primary Health Care Service Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "de Diego‐Cabanes",
"given": "Cinta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Farmacology DAP Camp de Tarragona Institut Catala de la Salut Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Bejarano‐Romero",
"given": "Ferran",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Laboral Medicine ACTIVA Mutua Tarragona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Rovira‐Veciana",
"given": "Dolors",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Fundació Institut Universitari per a la recerca a l'Atenció Primària de Salut Jordi Gol i Gurina (IDIAPJGol) Barcelona Spain"
}
],
"family": "Basora‐Gallisa",
"given": "Josep",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Journal of Clinical Hypertension",
"container-title-short": "J of Clinical Hypertension",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-25T15:53:36Z",
"timestamp": 1595692416000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-05T19:59:50Z",
"timestamp": 1693943990000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004587",
"award": [
"COV20/00852"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Instituto de Salud Carlos III"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-13T13:25:53Z",
"timestamp": 1715606753396
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 31,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1595635200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.wiley.com/onlinelibrary/tdm/v1/articles/10.1111%2Fjch.13948",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/jch.13948",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1111/jch.13948",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/jch.13948",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1379-1388",
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
25
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_2_1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization.Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19): situation report‐87 https://www.who.int/docs/default‐source/coronaviruse/situation‐reports/20200416‐sitrep‐87‐covid‐19.pdf?sfvrsn=9523115a_2(2020 [accessed 10 May 2020]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_4_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Continuing versus suspending angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers: impact on adverse outcomes in hospitalized patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS‐CoV‐2) [published online ahead of print, 2020 May 13]",
"author": "Lopes RD",
"first-page": "49",
"journal-title": "Am Heart J",
"key": "e_1_2_10_5_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0000000000002450",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_6_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/HJH.0000000000002472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_7_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00127-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_8_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2006923",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_9_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31030-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2008975",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_11_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_12_1",
"unstructured": "World Medical Association.WMA Declaration of Helsinki – Ethical Principles for Medical Research Involving Human Subjects. Available at:https://www.wma.net/policies‐post/wma‐declaration‐of‐helsinki‐ethical‐principles‐for‐medical‐research‐involving‐human‐subjects/. [Accessed May 14 2020]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2458-10-25",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_13_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_14_1",
"unstructured": "Generalitat de Catalunya.Sub‐direcció General de Vigilància i Resposta a Emergències de Salut Pública. Procediment d’actuació enfront de casos d’infecció pel nou coronavirus SARS‐CoV‐2. Available at:https://canalsalut.gencat.cat/web/.content/_A‐Z/C/coronavirus‐2019‐ncov/material‐divulgatiu/procediment‐actuacio‐coronavirus.pdf[Accessed May 16 2020]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.00821-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_15_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_16_1",
"unstructured": "Who Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology.ATC/DDD Index 2020 Available at:https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/[Accessed May 12 2020]."
},
{
"author": "Hosmer DW",
"key": "e_1_2_10_17_1",
"volume-title": "Applied Survival Analysis. Regression Modeling of Time to Event Data",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_18_1",
"unstructured": "Consumo. Dirección General de Salud Pública Calidad e innovación. Centro de Coordinación de Alertas y Emergencias Sanitarias.Información científica‐técnica. Enfermedad por coronavirus COVID19. Actualización 17 de abril Available at:https://www.mscbs.gob.es/profesionales/saludPublica/ccayes/alertasActual/nCov‐China/documentos/20200417_ITCoronavirus.pdf[Accessed May 5 2020]."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-02902-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.03.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_20_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Hypertension, the renin–angiotensin system, and the risk of lower respiratory tract infections and lung injury: implications for COVID‐19",
"author": "Kreutz R",
"first-page": "cvaa097",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Res",
"key": "e_1_2_10_21_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41440-020-0455-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5114/aoms.2020.94655",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_24_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14871",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_25_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMe2012924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40885-020-00144-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_10_27_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_28_1",
"unstructured": "European Society of Cardiology.Position Statement of the ESC Council on Hypertension on ACE‐Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers Available at:https://www.escardio.org/Councils/Council‐on‐Hypertension‐(CHT)/News/position‐statement‐of‐the‐esc‐council‐on‐hypertension‐on‐ace‐inhibitors‐and‐ang[Accessed May 15 2020]."
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_10_29_1",
"unstructured": "American Heart Association.HFSA/ACC/AHA statement addresses concerns re: using RAAS antagonists in COVID‐19 Available at:https://professional.heart.org/professional/ScienceNews/UCM_505836_HFSAACCAHA‐statement‐addresses‐concerns‐re‐using‐RAAS‐antagonists‐in‐COVID‐19.jsp[Accessed May 15 2020]."
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jch.13948"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Use of distinct anti‐hypertensive drugs and risk for COVID‐19 among hypertensive people: A population‐based cohort study in Southern Catalonia, Spain",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "22"
}