No association between use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, etravirine, or integrase-strand transfer inhibitors and acquisition or severe outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in people with HIV in the Netherlands
et al., AIDS, doi:10.1097/QAD.0000000000003577, Apr 2023
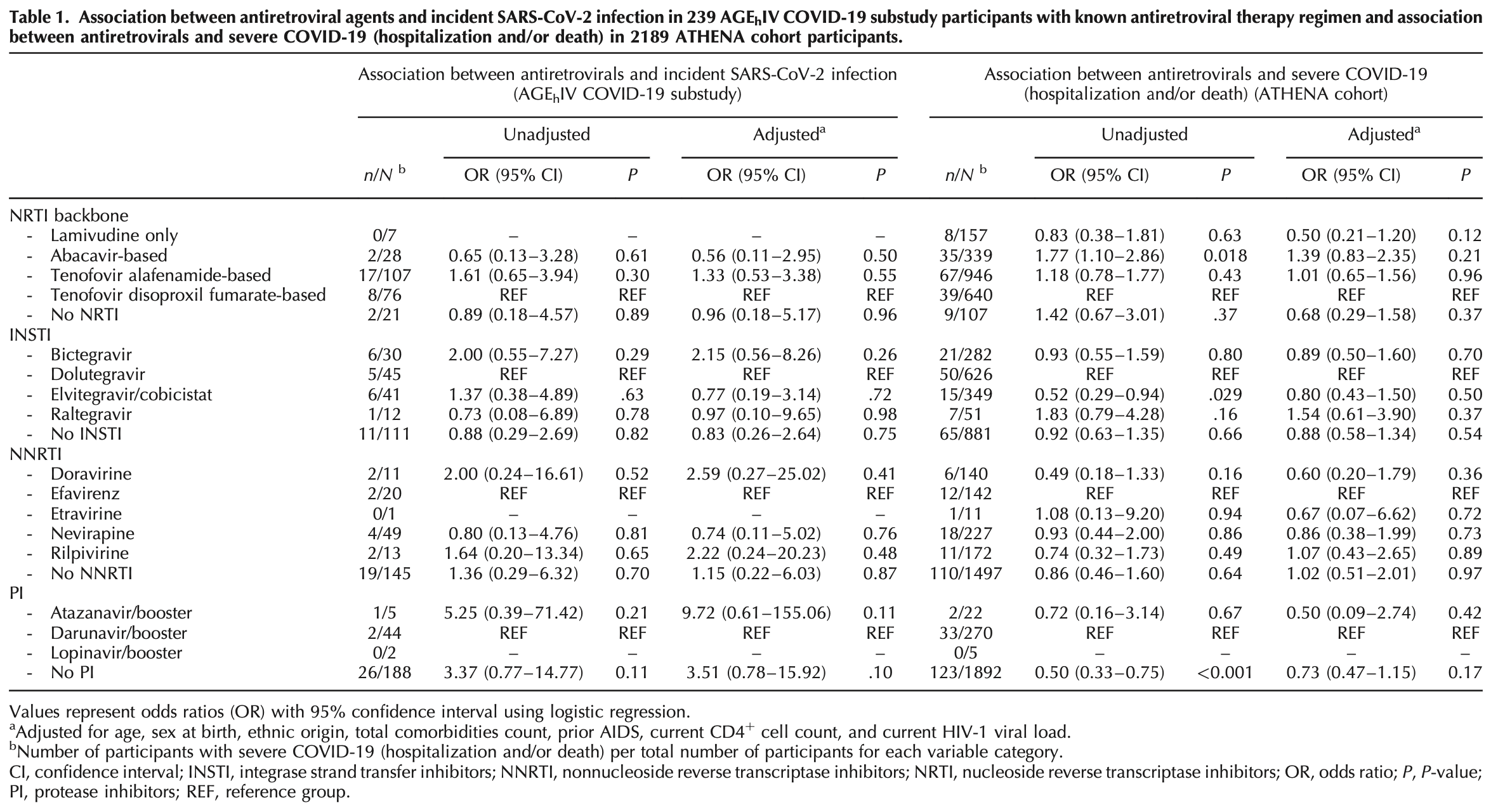
Analysis of two Dutch cohorts with HIV showing no association between tenofovir disoproxil fumarate (TDF), etravirine (ETR), or integrase-strand transfer inhibitors (INSTIs) use and either the risk of incident SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe COVID-19 outcomes.
|
risk of death/hospitalization, 13.6% higher, OR 1.14, p = 0.54, treatment 626, control 881, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, dolutegravir vs. no INSTI, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 20.5% higher, OR 1.20, p = 0.75, treatment 45, control 111, inverted to make OR<1 favor treatment, dolutegravir vs. no INSTI, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Verburgh et al., 13 Apr 2023, retrospective, Netherlands, peer-reviewed, median age 62.0, 5 authors, study period September 2020 - April 2021.
Contact: m.l.verburgh@amsterdamumc.nl.
Abstract: Research Letters
AIDS 2023, 37:1481–1489
No association between use of tenofovir disoproxil
fumarate, etravirine, or integrase-strand transfer
inhibitors and acquisition or severe outcomes of
SARS-CoV-2 infection in people with HIV in
the Netherlands
Myrthe L. Verburgha,b,c,d, Marc van der Valka,b,e,
Bart J.A. Rijndersf, Peter Reissa,b,d,g
and Ferdinand W.N.M. Wita,b,e
See related paper on page 1473
In two Dutch observational cohorts of people with
HIV, the use of TDF, ETR, or INSTIs was not
independently associated with either the risk
of incident SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe
COVID-19 outcomes, as was suggested by previous
observational and molecular docking studies. Our
findings do not support a strategy of modifying
antiretroviral therapy to include these agents to
protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe
COVID-19 outcomes.
Since the start of the COVID-19 pandemic, several studies
have tried to determine factors associated with acquisition
of and clinical outcome of SARS-CoV-2 infection in
people with HIV (PWH). Recent observational studies
have suggested a protective effect of tenofovir disoproxil
fumarate (TDF) against acquisition of SARS-CoV-2 [1,2]
and severe COVID-19 outcomes [1,3,4], whereas other
studies found no benefit of TDF or tenofovir alafenamide
(TAF) in PWH [5,6] or adults without HIV [7,8].
Etravirine (ETR) and the integrase-strand transfer
inhibitors (INSTIs) – specifically raltegravir (RAL) and
dolutegravir (DTG) – were proposed as potential
inhibitors of two major SARS-CoV-2 proteins in a
molecular docking [9] and molecular dynamics simulation
study [10]. One recent study showed that in-vitro docking
by SARS-CoV-2 to the ACE2 receptor is inhibited by
DTG and ETR [11]. Thus far, no studies in PWH have
reported epidemiological evidence for a protective effect
of the use of INSTIs or ETR against acquiring SARSCoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes.
We investigated the association between the abovementioned antiretrovirals and incident SARS-CoV-2
infection and COVID-19-associated hospitalization and/
or death in two Dutch observational cohorts of PWH.
First, we used data from the COVID-19 substudy of the
AGEhIV cohort collected from September 2020 until
April 2021 [12]. PWH and participants without HIV
were assessed every 6 months for incident SARS-CoV-2
infection. Incident SARS-CoV-2 infection was defined
as positive combined IgA/IgM/IgG SARS-CoV-2
nucleocapsid (N) antibody assay or a self-reported
positive PCR test in participants without detectable
N-antibodies. We previously reported that younger age
and sub-Saharan African origin, but not HIV-status, were
independently associated with higher risk of incident
SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, we did not investigate
the association with specific antiretrovirals in PWH.
Second, we used data from the Dutch national observational HIV cohort (ATHENA), containing data of more
than 95% of PWH in care in one of the 24 HIV-treatment
centers in the Netherlands [13]. Within this cohort, we
recently reported that the risk of severe COVID-19
outcomes was increased in individuals with uncontrolled
HIV replication, low CD4þ cell count and prior AIDS,
independently of general risk factors such as age,
comorbidity burden, and non-Western origin (F.W.N.
M. Wit, P. Reiss, B. Rijnders, M. van der Valk, in
preparation), but potential associations with specific
antiretrovirals were not extensively analyzed.
Extending our earlier analyses, we now assessed whether
use of..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/qad.0000000000003577",
"ISSN": [
"0269-9370",
"1473-5571"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/QAD.0000000000003577",
"abstract": "<jats:sec>\n <jats:title/>\n <jats:p>In two Dutch observational cohorts of people with HIV, the use of TDF, ETR, or INSTIs was not independently associated with either the risk of incident SARS-CoV-2 infection or severe COVID-19 outcomes, as was suggested by previous observational and molecular docking studies. Our findings do not support a strategy of modifying antiretroviral therapy to include these agents to protect against SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe COVID-19 outcomes.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Amsterdam UMC location University of Amsterdam"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Public Health, Global Health"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Global Health and Development"
}
],
"family": "Verburgh",
"given": "Myrthe L.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Amsterdam UMC location University of Amsterdam"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"name": "HIV Monitoring Foundation, Amsterdam"
}
],
"family": "van der Valk",
"given": "Marc",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Erasmus Medical Center, Departments of Internal Medicine & Medical Microbiology, Rotterdam"
}
],
"family": "Rijnders",
"given": "Bart J.A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Amsterdam UMC location University of Amsterdam"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Global Health and Development"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam UMC location University of Amsterdam, Global Health, Amsterdam, The Netherlands."
}
],
"family": "Reiss",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Amsterdam UMC location University of Amsterdam"
},
{
"name": "Amsterdam Institute for Infection and Immunity, Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"name": "HIV Monitoring Foundation, Amsterdam"
}
],
"family": "Wit",
"given": "Ferdinand W.N.M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "AIDS",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"lww.com",
"ovid.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-03T10:23:10Z",
"timestamp": 1688379790000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-15T18:44:06Z",
"timestamp": 1723747446000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
8,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2024-08-16T00:15:57Z",
"timestamp": 1723767357453
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 3,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2023-04-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1681344000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/QAD.0000000000003577",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1481-1486",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
13
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
4,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
15
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1097/QAD.0000000000003314",
"article-title": "Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate and COVID-19 outcomes in men with HIV",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1689",
"journal-title": "AIDS",
"key": "R1-20240815",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.06.023",
"article-title": "Prevalence and factors associated with SARS-CoV-2 seropositivity in the Spanish HIV Research Network Cohort",
"author": "Berenguer",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1678",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "R2-20240815",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-3689",
"article-title": "Incidence and severity of COVID-19 in HIV-positive persons receiving antiretroviral therapy: a cohort study",
"author": "Del Amo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "536",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "R3-20240815",
"volume": "173",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1198",
"article-title": "Risk factors for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) death in a population cohort study from the Western Cape Province, South Africa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2005",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R4-20240815",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkac177",
"article-title": "Impact of tenofovir on SARS-CoV-2 infection and severe outcomes among people living with HIV: a propensity score-matched study",
"author": "Nomah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2265",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "R5-20240815",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "MO43 Prevalence, risk factors and the impact of antiretroviral treatment in SARS-CoV-2 infection in people with HIV: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "De Lazzari",
"first-page": "e26009",
"issue": "(Suppl 6)",
"journal-title": "J Int AIDS Soc",
"key": "R6-20240815",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac628",
"article-title": "Tenofovir disoproxil fumarate/emtricitabine and baricitinib for patients at high risk of severe COVID-19: the PANCOVID Randomized Clinical Trial",
"author": "Montejano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e116",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R7-20240815",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaa455",
"article-title": "Preventive efficacy of tenofovir/emtricitabine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 among pre-exposure prophylaxis users",
"author": "Ayerdi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "ofaa455",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "R8-20240815",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.10.015",
"article-title": "Raltegravir, Indinavir, Tipranavir, Dolutegravir, and Etravirine against main protease and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of SARS-CoV-2: a molecular docking and drug repurposing approach",
"author": "Indu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1856",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "R9-20240815",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1753577",
"article-title": "Targeting SARS-CoV-2: a systematic drug repurposing approach to identify promising inhibitors against 3C-like proteinase and 2’-O-ribose methyltransferase",
"author": "Khan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2679",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "R10-20240815",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms23074050",
"article-title": "Identification of entry inhibitors against Delta and Omicron variants of SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4050",
"journal-title": "Int J Mol Sci",
"key": "R11-20240815",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab616",
"article-title": "Similar risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection and similar nucleocapsid antibody levels in people with well controlled human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) and a comparable cohort of people without HIV",
"author": "Verburgh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1937",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "R12-20240815",
"volume": "225",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2018-022516",
"article-title": "AIDS Therapy Evaluation in the Netherlands (ATHENA) national observational HIV cohort: cohort profile",
"author": "Boender",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e022516",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "R13-20240815",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
}
],
"reference-count": 13,
"references-count": 13,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/QAD.0000000000003577"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "No association between use of tenofovir disoproxil fumarate, etravirine, or integrase-strand transfer inhibitors and acquisition or severe outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection in people with HIV in the Netherlands",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/lww.0000000000001000",
"volume": "37"
}