Retrospective analysis of vitamin D status on ınflammatory markers and course of the disease in patients with COVID-19 infection
et al., Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9, Apr 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
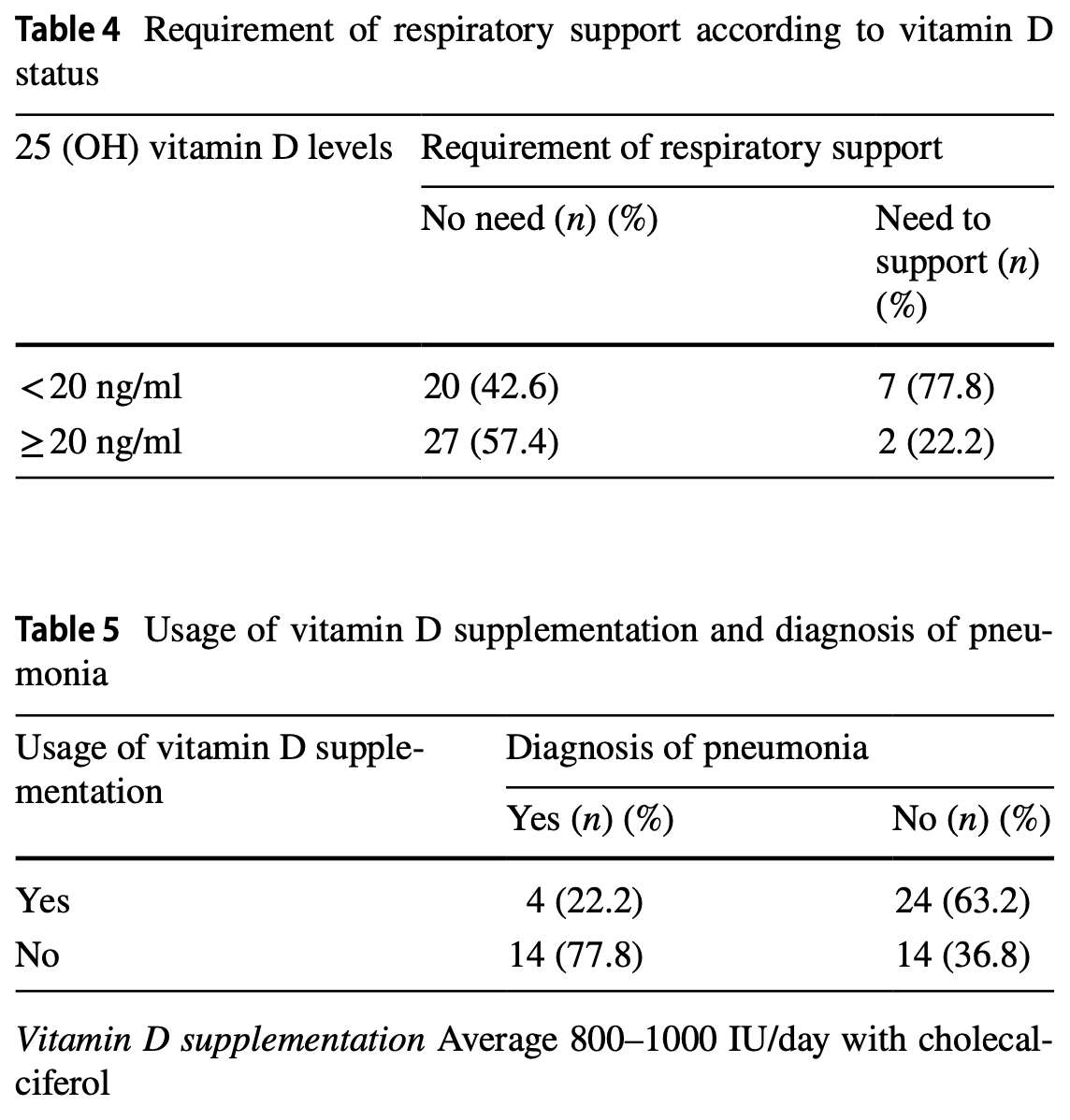
Retrospective 56 patients in Turkey showing greater need for oxygen therapy and higher mortality with vitamin D deficiency, and significantly lower risk of pneumonia with vitamin D supplementation.
This is the 61st of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of death, 80.6% lower, RR 0.19, p = 0.23, high D levels 0 of 29 (0.0%), low D levels 2 of 27 (7.4%), NNT 14, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), ≥20ng/mL.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 73.4% lower, RR 0.27, p = 0.07, high D levels 2 of 29 (6.9%), low D levels 7 of 27 (25.9%), NNT 5.3, ≥20ng/mL.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ünsal et al., 5 Apr 2021, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 10 authors.
Retrospective analysis of vitamin D status on ınflammatory markers and course of the disease in patients with COVID-19 infection
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation, doi:10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9
Purpose The aim of the study was to investigate the association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D status within the last 6 months prior to COVID-19 infection and parameters of immune function and clinical outcomes. Methods Fifty-six patients, who were admitted to the emergency clinic and diagnosed with COVID-19 infection, were included in the study. Data on clinical characteristics, inflammatory parameters and vitamin D status were recorded for each patient. All the participants had data on 25-hydroxyvitamin D status within the last 6 months prior to COVID-19 infection.
Results The patients were stratified as those with vitamin D status less than 20 ng/mL and higher than 20 ng/mL. A group with vitamin D status less than 20 ng/mL had lower lymphocyte counts and lower haemoglobin levels that was statistically significant (respectively; p = 0.021, p = 0.035). Higher C-reactive protein (CRP) levels were seen in the vitamin D-deficient group (p = 0.013). It was observed that vitamin D status of the patients who required oxygen therapy were lower than those who did not require oxygen therapy, not statistically significant (p = 0.05). Patients who did not use vitamin D supplementation within 6 months prior to COVID-19 infection had more likely to be diagnosed with pneumonia (p = 0.004). Conclusion Cases with lower vitamin D status had increased inflammatory markers and worse clinical outcomes than patients with higher vitamin D status. This study suggests that vitamin D status can be used as a prognostic factor in COVID-19 patients, and vitamin D supplementation can be recommended to improve the clinical outcomes in COVID-19 infection.
Declarations Conflict of interest On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest. Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Adami, Giollo, Fassio, Benini, Bertoldo et al., Vitamin D and disease severity in coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19), Reumatismo
Ahmed, Siman-Tov, Hall, Bhalla, Narayanan, Human antimicrobial peptides as therapeutics for viral infections, Viruses
Algassim, Elghazaly, Alnahdi, Prognostic significance of hemoglobin level and autoimmune hemolytic anemia in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Ann Hematol
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity, J Infect Public Health
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus
Barlow, Svoboda, Mackellar, Nash, York et al., Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin, PLoS ONE
Bodnar, Krohn, Simhan, Maternal vitamin D deficiency is associated with bacterial vaginosis in the first trimester of pregnancy, J Nutr
Bouillon, Marcocci, Carmeliet, Bikle, White et al., Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions, Endocrine Rev
Burton, Fort, Seoane, Hospitalization and Mortality among Black Patients and White Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Cannell, Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol, Infect
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1, 25 (OH) 2D regulation of T cells, Nutrients
Chan, Yuan, Kok, A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster, Lancet
Dankers, Colin, Van Hamburg, Lubberts, Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential, Front Immunol
Dawson-Hughes, Mithal, Bonjour, IOF position statement: vitamin D recommendations for older adults, Osteoporos Int
Ginde, Mansbach, Camargo, Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, Arch Intern Med
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Guan, Ni, Hu, China medical treatment expert group for C. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2002032
Holick, Binkley, Bischoff-Ferrari, Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline, J Clin Endocrinol Metab
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China Lancet
Hughes, Norton, Vitamin D and respiratory health, Clin Exp Immunol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x
Infante, Ricordi, Sanchez, Salzler, Padilla et al., Influence of vitamin d on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes, Nutrients
Jain, Chaurasia, Sengar, Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers, Sci Rep
Khademvatani, Seyyed-Mohammadzad, Akbari, Rezaei, Eskandari et al., The relationship between vitamin D status and idiopathic lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis, Int J Gen Med
Kragholm, Andersen, Gerds, Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) -a Danish nationwide, register-based study, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa924.
Levi, Van Der, Coagulation and sepsis, Thromb Res
Liu, Liu, Xiang, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts critical illness patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in the early stage, J Transl Med
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/ mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS ONE
Maghbooli, Sahraian, Ebrahimi, Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/ mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection, PLoS ONE
Merzon, Tworowski, Gorohovski, Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15495
Murai, Fernandes, Sales, Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D 3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Onder, Rezza, Brusaferro, Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy, JAMA
Ortega, Serrano, Pujol, Rangel, Role of changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the interaction with the human ACE2 receptor: An in silico analysis, EXCLI J
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study, BMJ
Rezaei, Aslani, Marashi, Rezaei, Sharif-Paghaleh, Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D in influenza infection, Curr Immunol Rev
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Ross, Taylor, Yaktine, Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin . Institute of medicine (US) committee to review dietary reference intakes for vitamin D and calcium
Tan, Ho, Kalimuddin, Cherng, Teh et al., A cohort study to evaluate the effect of combination vitamin D. Magnesium and vitamin B12 (DMB) on progression to severe outcome in older COVID-19 patients, Infect Dis (except HIV/AIDS)
Tang, Li, Wang, Sun, Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia, J Thrombosis Haemostasis: JTH
Tripodi, D-dimer testing in laboratory practice, Clin Chem
Villamor, A potential role for vitamin D on HIV infection?, Nutr Rev, doi:10.1301/nr.2006.may
Wacker, Holick, Vitamin D: effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation, Nutrients
Weiss, Ganz, Goodnough, Anemia of inflammation, Blood
Wu, He, Low vitamin D levels are associated with the development of deep venous thromboembolic events in patients with ischemic stroke, Clin Appl Thromb Hemost
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of aReport of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.2648
Xu, Yang, Chen, Luo, Zhang et al., Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin-angiotensin system, Mol Med Rep
Yang, Yu, Xu, Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study, Lancet Respir Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9",
"ISSN": [
"1720-8386"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9",
"alternative-id": [
"1566"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "28 December 2020"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "29 March 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "5 April 2021"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest."
},
{
"label": "Free to read",
"name": "free",
"value": "This content has been made available to all."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1566-3099",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ünsal",
"given": "Y. A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1332-4165",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Gül",
"given": "Ö. Ö.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-6303-7896",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cander",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4672-7681",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ersoy",
"given": "C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4300-2965",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aydemir",
"given": "E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4565-9848",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ateş",
"given": "C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1363-2966",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uzun",
"given": "Z.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-4641-9873",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Armağan",
"given": "E.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3215-8457",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ünsal",
"given": "O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2399-6608",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ertürk",
"given": "E.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Endocrinological Investigation",
"container-title-short": "J Endocrinol Invest",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-05T11:02:44Z",
"timestamp": 1617620564000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
11,
6
]
],
"date-time": "2021-11-06T21:13:30Z",
"timestamp": 1636233210000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-19T17:05:22Z",
"timestamp": 1692464722909
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issue": "12",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "12",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1617580800000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.springer.com/tdm",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2021-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1617580800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"page": "2601-2607",
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"key": "1566_CR1",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. Director-General’s remarks at the media briefing on 2019-nCoV on 11 February 2020. (Accessed on February 12, 2020). http://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-remarks-at-the-media-briefing-on-2019-ncov-on-11-february-2020."
},
{
"key": "1566_CR2",
"unstructured": "WHO Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection when Novel coronavirus (nCoV) infection is suspected: interim guidance. (2020). https://www.who.int/internal-publications-detail/clinical-management-of severe-acute-respiratory-infection-when-novel-coronavirus-(ncov)- infection-is-suspected."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9",
"author": "JF Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "514",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "1566_CR3",
"unstructured": "Chan JF, Yuan S, Kok KH et al (2020) A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: a study of a family cluster. Lancet 395:514–523",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30079-5",
"author": "X Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "475",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "1566_CR4",
"unstructured": "Yang X, Yu Y, Xu J et al (2020) Clinical course and outcomes of critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a single-centered, retrospective, observational study. Lancet Respir Med 8:475–481",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.2648",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1566_CR5",
"unstructured": "Wu Z, McGoogan JM. Characteristics of and Important Lessons From the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Outbreak in China: Summary of a\nReport of 72 314 Cases From the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention. JAMA. 2020;323(13):1239–1242. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2020.2648"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m1966",
"author": "CM Petrilli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1966",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "1566_CR6",
"unstructured": "Petrilli CM, Jones SA, Yang J et al (2020) Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease 2019 in New York City: prospective cohort study. BMJ 369:1966",
"volume": "369",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.6775",
"author": "S Richardson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2052",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1566_CR7",
"unstructured": "Richardson S, Hirsch JS, Narasimhan M et al (2020) Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area. JAMA 323:2052–2059",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "G Onder",
"first-page": "1775",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1566_CR8",
"unstructured": "Onder G, Rezza G, Brusaferro S (2020) Case-fatality rate and characteristics of patients dying in relation to COVID-19 in Italy. JAMA 323:1775–1776",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa924.",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1566_CR9",
"unstructured": "Kragholm K, Andersen MP, Gerds TA, et al (2020) Association between male sex and outcomes of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (Covid-19) - a Danish nationwide, register-based study.\nClin Infect Dis 8:ciaa924. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciaa924."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsa2011686",
"author": "EG Price-Haywood",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2534",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1566_CR10",
"unstructured": "Price-Haywood EG, Burton J, Fort D, Seoane L (2020) Hospitalization and Mortality among Black Patients and White Patients with Covid-19. N Engl J Med 382:2534–2543",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine",
"first-page": "250",
"key": "1566_CR11",
"unstructured": "Food and Nutrition Board of the Institute of Medicine (1997) Vitamin D . Dietary reference intakes for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D, fluoride. National Academies Press, Washington, DC, p 250",
"volume-title": "Dietary reference intakes for calcium, phosphorus, magnesium, vitamin D, fluoride",
"year": "1997"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/jc.2011-0385",
"author": "MF Holick",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1911",
"journal-title": "J Clin Endocrinol Metab",
"key": "1566_CR12",
"unstructured": "Holick MF, Binkley NC, Bischoff-Ferrari HA et al (2011) Evaluation, treatment, and prevention of vitamin D deficiency: an endocrine society clinical practice guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 96:1911–1930",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-010-1285-3",
"author": "B Dawson-Hughes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1151",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "1566_CR13",
"unstructured": "Dawson-Hughes B, Mithal A, Bonjour JP et al (2010) IOF position statement: vitamin D recommendations for older adults. Osteoporos Int 21:1151",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"author": "AC Ross",
"key": "1566_CR14",
"unstructured": "Ross AC, Taylor CL, Yaktine AL et al (2011) Dietary reference intakes for calcium and vitamin . Institute of medicine (US) committee to review dietary reference intakes for vitamin D and calcium. National Academies Press",
"volume-title": "Institute of medicine (US) committee to review dietary reference intakes for vitamin D and calcium",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu5010111",
"author": "M Wacker",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "111",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1566_CR15",
"unstructured": "Wacker M, Holick MF (2013) Vitamin D: effects on skeletal and extraskeletal health and the need for supplementation. Nutrients 5(1):111–148",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1301/nr.2006.may",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1566_CR16",
"unstructured": "Villamor E (2006) A potential role for vitamin D on HIV infection? Nutr Rev 64(5 Pt 1):226–233. https://doi.org/10.1301/nr.2006.may"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archinternmed.2008.560",
"author": "AA Ginde",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "384",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Arch Intern Med",
"key": "1566_CR17",
"unstructured": "Ginde AA, Mansbach JM, Camargo CA Jr (2009) Association between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and upper respiratory tract infection in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Arch Intern Med 169(4):384–390",
"volume": "169",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"author": "JJ Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect",
"key": "1566_CR18",
"unstructured": "Cannell JJ et al (2006) Epidemic influenza and vitamin D. Epidemiol Infect 134(6):1129–1140",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3945/jn.108.103168",
"author": "LM Bodnar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1157",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Nutr",
"key": "1566_CR19",
"unstructured": "Bodnar LM, Krohn MA, Simhan HN (2009) Maternal vitamin D deficiency is associated with bacterial vaginosis in the first trimester of pregnancy. J Nutr 139(6):1157–1161",
"volume": "139",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1573395513666171031162100",
"author": "R Rezaei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "40",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Curr Immunol Rev",
"key": "1566_CR20",
"unstructured": "Rezaei R, Aslani S, Marashi M, Rezaei F, Sharif-Paghaleh E (2018) Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D in influenza infection. Curr Immunol Rev 14(1):40–49",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v11080704",
"author": "A Ahmed",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "704",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1566_CR21",
"unstructured": "Ahmed A, Siman-Tov G, Hall G, Bhalla N, Narayanan A (2019) Human antimicrobial peptides as therapeutics for viral infections. Viruses 11:704",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0025333",
"author": "PG Barlow",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "25333",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1566_CR22",
"unstructured": "Barlow PG, Svoboda P, Mackellar A, Nash AA, York IA, Pohl J, Davidson DJ, Donis RO (2011) Antiviral activity and increased host defense against influenza infection elicited by the human cathelicidin. PLoS ONE 6:25333",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1566_CR23",
"unstructured": "Hughes DA, Norton R (2009) Vitamin D and respiratory health. Clin Exp Immunol 158(1):20–25. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2249.2009.04001.x"
},
{
"author": "JT Ortega",
"first-page": "410",
"journal-title": "EXCLI J",
"key": "1566_CR24",
"unstructured": "Ortega JT, Serrano ML, Pujol FH, Rangel HR (2020) Role of changes in SARS-CoV-2 spike protein in the interaction with the human ACE2 receptor: An in silico analysis. EXCLI J 19:410–417",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/mmr.2017.7546",
"author": "J Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "7432",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Mol Med Rep",
"key": "1566_CR25",
"unstructured": "Xu J, Yang J, Chen J, Luo Q, Zhang Q, Zhang H (2017) Vitamin D alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via regulation of the renin–angiotensin system. Mol Med Rep 16(5):7432–7438",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1566_CR26",
"unstructured": "Merzon E, Tworowski D, Gorohovski A et al (2020) Low plasma 25(OH) vitamin D level is associated with increased risk of COVID-19 infection: an Israeli population-based study. FEBS J 287:3693. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15495"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"author": "Z Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0239799",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1566_CR27",
"unstructured": "Maghbooli Z, Sahraian MA, Ebrahimi M et al (2020) Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE 15:e0239799",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.06.021",
"author": "N Ali",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1373",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "1566_CR28",
"unstructured": "Ali N (2020) Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity. J Infect Public Health 13(10):1373–1380",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2016.00697",
"author": "W Dankers",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "697",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "1566_CR29",
"unstructured": "Dankers W, Colin EM, van Hamburg JP, Lubberts E (2017) Vitamin D in autoimmunity: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Front Immunol 7:697",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092185",
"author": "M Infante",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2185",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1566_CR30",
"unstructured": "Infante M, Ricordi C, Sanchez J, Clare-Salzler MJ, Padilla N, Fuenmayor V (2019) Influence of vitamin d on islet autoimmunity and beta-cell function in type 1 diabetes. Nutrients 11:2185",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/er.2018-00126",
"author": "R Bouillon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1109",
"journal-title": "Endocrine Rev",
"key": "1566_CR31",
"unstructured": "Bouillon R, Marcocci C, Carmeliet G, Bikle D, White JH, Dawson-Hughes B (2019) Skeletal and extraskeletal actions of vitamin D: current evidence and outstanding questions. Endocrine Rev 40:1109–1151",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"author": "WB Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "988",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1566_CR32",
"unstructured": "Grant WB, Lahore H, McDonnell SL, Baggerly CA, French CB, Aliano JL (2020) Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths. Nutrients 12:988",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"author": "MT Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3011",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "1566_CR33",
"unstructured": "Cantorna MT, Snyder L, Lin Y-D, Yang L (2015) Vitamin D and 1, 25 (OH) 2D regulation of T cells. Nutrients 7:3011–3021",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "China Lancet",
"key": "1566_CR34",
"unstructured": "Huang C, Wang Y, Li X, Ren L, Zhao J, Hu Y et al (2020) Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan. China Lancet 395(10223):497–506",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02374-0",
"author": "J Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "206",
"journal-title": "J Transl Med",
"key": "1566_CR35",
"unstructured": "Liu J, Liu Y, Xiang P et al (2020) Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts critical illness patients with 2019 coronavirus disease in the early stage. J Transl Med 18:206",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1182/blood-2018-06-856500",
"author": "G Weiss",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "40",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Blood",
"key": "1566_CR36",
"unstructured": "Weiss G, Ganz T, Goodnough LT (2019) Anemia of inflammation. Blood 133(1):40–50",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00277-020-04256-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1566_CR37",
"unstructured": "Algassim, A.A., Elghazaly, A.A., Alnahdi, A.S. et al. Prognostic significance of hemoglobin level and autoimmune hemolytic anemia in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Ann Hematol. 2020."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-77093-z",
"author": "A Jain",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "20191",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "1566_CR38",
"unstructured": "Jain A, Chaurasia R, Sengar NS et al (2020) Analysis of vitamin D level among asymptomatic and critically ill COVID-19 patients and its correlation with inflammatory markers. Sci Rep 10:20191",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4081/reumatismo.2020.1333",
"author": "G Adami",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "189",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Reumatismo",
"key": "1566_CR39",
"unstructured": "Adami G, Giollo A, Fassio A, Benini C, Bertoldo E, Bertoldo F, Orsolini G, Idolazzi L, Viapiana O, Giannini S, Passeri G, Tacconelli E, Micheletto C, Gatti D, Rossini M (2021) Vitamin D and disease severity in coronavirus disease 19 (COVID-19). Reumatismo 72(4):189–196",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.thromres.2016.11.007",
"author": "M Levi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "38",
"journal-title": "Thromb Res",
"key": "1566_CR40",
"unstructured": "Levi M, van der Poll T (2017) Coagulation and sepsis. Thromb Res 149:38–44",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1373/clinchem.2011.166249",
"author": "A Tripodi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1256",
"journal-title": "Clin Chem",
"key": "1566_CR41",
"unstructured": "Tripodi A (2011) D-dimer testing in laboratory practice. Clin Chem 57:1256–1262",
"volume": "57",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"author": "WJ Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1566_CR42",
"unstructured": "Guan WJ, Ni ZY, Hu Y et al (2020) China medical treatment expert group for C. Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2002032 (Epub ahead of print)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14768",
"author": "N Tang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "844",
"journal-title": "J Thrombosis Haemostasis: JTH",
"key": "1566_CR43",
"unstructured": "Tang N, Li D, Wang X, Sun Z (2020) Abnormal coagulation parameters are associated with poor prognosis in patients with novel coronavirus pneumonia. J Thrombosis Haemostasis: JTH 18:844–847",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "K Khademvatani",
"first-page": "303",
"journal-title": "Int J Gen Med",
"key": "1566_CR44",
"unstructured": "Khademvatani K, Seyyed-Mohammadzad MH, Akbari M, Rezaei Y, Eskandari R, Rostamzadeh A (2014) The relationship between vitamin D status and idiopathic lower-extremity deep vein thrombosis. Int J Gen Med 7:303–309",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1076029618786574",
"author": "WX Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Clin Appl Thromb Hemost",
"key": "1566_CR45",
"unstructured": "Wu WX, He DR (2018) Low vitamin D levels are associated with the development of deep venous thromboembolic events in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost 24:69–75",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2139/ssrn.3571484",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "1566_CR46",
"unstructured": "Alipio M.Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus-2019 (COVID-19) (April 9, 2020). Available at SSRN: https://ssrn.com/abstract=3571484."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0239799",
"author": "Z Maghbooli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e0239799",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "PLoS ONE",
"key": "1566_CR47",
"unstructured": "Maghbooli Z, Sahraian MA, Ebrahimi M et al (2020) Vitamin D sufficiency, a serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D at least 30 ng/mL reduced risk for adverse clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19 infection. PLoS ONE 15(9):e0239799",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "CW Tan",
"first-page": "111017",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis (except HIV/AIDS)",
"key": "1566_CR48",
"unstructured": "Tan CW, Ho LP, Kalimuddin S, Cherng BPZ, Teh YE, Thien SY (2020) A cohort study to evaluate the effect of combination vitamin D. Magnesium and vitamin B12 (DMB) on progression to severe outcome in older COVID-19 patients. Infect Dis (except HIV/AIDS) 79–80:111017 (preprint)",
"volume": "79–80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.26848",
"author": "IH Murai",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1053",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1566_CR49",
"unstructured": "Murai IH, Fernandes AL, Sales LP et al (2021) Effect of a single high dose of vitamin D3 on hospital length of stay in patients with moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial. JAMA 325:1053",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40618-021-01566-9"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Retrospective analysis of vitamin D status on ınflammatory markers and course of the disease in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "44"
}
