Bromhexine, for Post Exposure COVID-19 Prophylaxis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Control Trial
et al., SSRN, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3989, Dec 2021
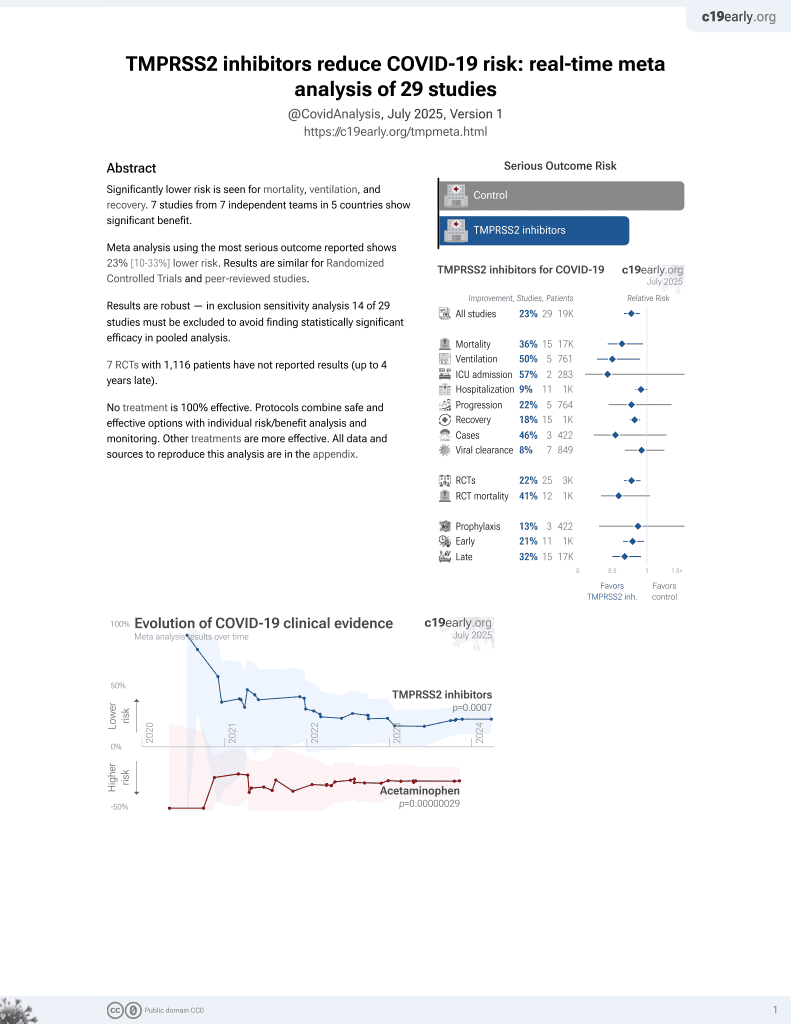
22nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
April 2021, now with p = 0.00063 from 29 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
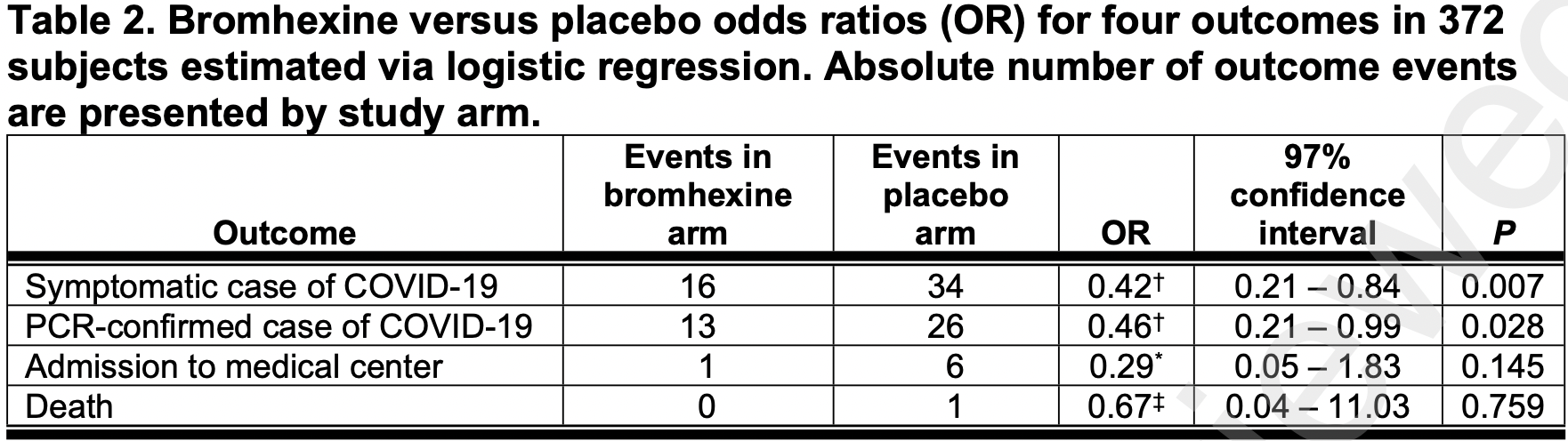
PEP RCT with 372 close contacts of COVID+ patients, 187 treated with bromhexine, showing significantly lower cases with treatment. IRCT20120703010178N22.
Study covers TMPRSS2 inhibitors and bromhexine.
|
risk of death, 32.9% lower, RR 0.67, p = 0.76, treatment 0 of 187 (0.0%), control 1 of 185 (0.5%), odds ratio converted to relative risk, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 70.3% lower, RR 0.30, p = 0.14, treatment 1 of 187 (0.5%), control 6 of 185 (3.2%), adjusted per study, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of symptomatic case, 53.0% lower, RR 0.47, p = 0.007, treatment 16 of 187 (8.6%), control 34 of 185 (18.4%), NNT 10, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
|
risk of case, 50.2% lower, RR 0.50, p = 0.03, treatment 13 of 187 (7.0%), control 26 of 185 (14.1%), NNT 14, odds ratio converted to relative risk.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Tolouian et al., 20 Dec 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, preprint, 16 authors, study period 21 December, 2020 - 25 July, 2021.
Bromhexine, for post exposure COVID-19 prophylaxis: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Control Trial
Background: Limited number of medications are available for the post-exposure prophylaxis of COVID-19 infection. Whether bromhexine can prevent or mitigate symptomatic infection after virus exposure is undetermined.
Methods: A multi-center randomized; double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted. The 372 adults (≥18 years) who had close contact within 4 days with a household member with confirmed COVID-19 were randomly assigned to receive bromhexine (n=187) or placebo (n=185) three times a day for two weeks. The primary outcome was the incidence of symptomatic COVID-19. Secondary outcomes included the incidence of hospitalization or death, the incidence of confirmed COVID-19 detection by PCR in symptomatic patients and presence of adverse drug reactions.
Findings: The incidence of symptomatic COVID-19 was significantly lower in individuals who received bromhexine than in those who received the placebo (16 [8.6%] vs 34 [18.4%], relative risk=0.47, p=0.005). PCRconfirmation was reported in 13 (7.0%) and 26 (14.1%) of the individuals in the bromhexine and placebo groups, respectively (p=0.025), with a relative risk reduction of 50%. The hospitalization rate, death and medication side effects did not vary significantly between the bromhexine or placebo arms. Interpretation: Bromhexine is an effective, non-invasive, and affordable agent with a low side-effect profile to prevent symptomatic COVID-19. Early use of bromhexine potentially provides another layer of protection and hence it can play a prominent role in ending the pandemic especially given the emergence of new variants and the vaccination challenges faced by developing countries.
References
Anand, Puranik, Aravamudan, Venkatakrishnan, Soundararajan, SARS-CoV-2 strategically mimics proteolytic activation of human ENaC, Elife
Ansarin K, Tolouian, Ardalan, Taghizadeh, Varshochi, Teimouri, Effect of bromhexine on clinical outcomes and mortality in COVID-19 patients: A randomized clinical trial, BioImpacts
Bartoszko, Siemieniuk, Kum, Qasim, Zeraatkar et al., Prophylaxis against covid-19: living systematic review and network meta-analysis, BMJ
Bernal, Andrews, Gower, Gallagher, Simmons et al., Effectiveness of Covid-19 Vaccines against the B.1.617.2 (Delta) Variant, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Andrews, Gower, Robertson, Stowe et al., Effectiveness of the Pfizer-BioNTech and Oxford-AstraZeneca vaccines on covid-19 related symptoms, hospital admissions, and mortality in older adults in England: test negative case-control study, BMJ
Boulware, Pullen, Bangdiwala, Pastick, Lofgren et al., A Randomized Trial of Hydroxychloroquine as Postexposure Prophylaxis for Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Fernandez, Mulla, Avoiding sparse data bias: an example from gynecologic oncology, Journal of registry management
Garten, Braden, Arendt, Peitsch, Baron et al., Influenza virus activating host proteases: Identification, localization and inhibitors as potential therapeutics, Eur J Cell Biol
Greenland, Modeling and variable selection in epidemiologic analysis, Am J Public Health
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, Krüger, Herrler et al., SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 entry into cells, Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol
Jahromi, Mazloom, Ballard, What the European and American health care systems can learn from China COVID-19 epidemic; action planning using purpose designed medical telecommunication, courier services, home-based quarantine, and COVID-19 walk-in-centers, Immunopathol Persa
Mikhaylov, Vakhrushev, Stepanov, Lebedev, Vasilieva, Bromhexine Hydrochloride Prophylaxis of COVID-19 for Medical Personnel: A Randomized Open-Label Study2021
O'brien, Forleo-Neto, Musser, Chan, Sarkar, Subcutaneous REGEN-COV Antibody Combination to Prevent Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Ou, Mou, Zhang, Ojha, Choe et al., Hydroxychloroquine-mediated inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 entry is attenuated by TMPRSS2, PLoS Pathog
Pocock, Clinical Trials: A Practical Approach
Rossier, Stutts, Activation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by serine proteases, Annu Rev Physiol
Shei, Peabody, Kaza, Rowe, The epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) as a therapeutic target for cystic fibrosis, Curr Opin Pharmacol
Tolouian, Tolouian, Ardalan, Blocking serine protease (TMPRSS2) by Bromhexine; looking at potential treatment to prevent COVID-19 infection, Marshall Journal of Medicine
Vahed, Ghiyasvand, Tolouian, Noshad, Tolouian et al., The footprint of androgen sensitive serine protease (TMPRSS2) in gender mortality with COVID-19, Immunopathol Persa
Wiersinga, Rhodes, Cheng, Peacock, Prescott, Pathophysiology, Transmission, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA
Zanasi, Mazzolini, Kantar, A reappraisal of the mucoactive activity and clinical efficacy of bromhexine, Multidisciplinary respiratory medicine
Zumla, Chan, Azhar, Hui, Yuen, Coronaviruses -drug discovery and therapeutic options, Nat Rev Drug Discov