SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 binds Tollip and activates pro-inflammatory pathways while downregulating interferon-α and interferon-γ receptors
et al., mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01071-25, Aug 2025
In vitro study showing that SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 protein activates pro-inflammatory pathways while simultaneously downregulating interferon receptors, with the host protein Tollip serving as a potential regulator of these effects.
Thakur et al., 13 Aug 2025, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Contact: chris.basler@mssm.edu, joann.tufariello@mssm.edu.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 binds Tollip and activates pro-inflammatory pathways while downregulating interferon-α and interferon-γ receptors
mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01071-25
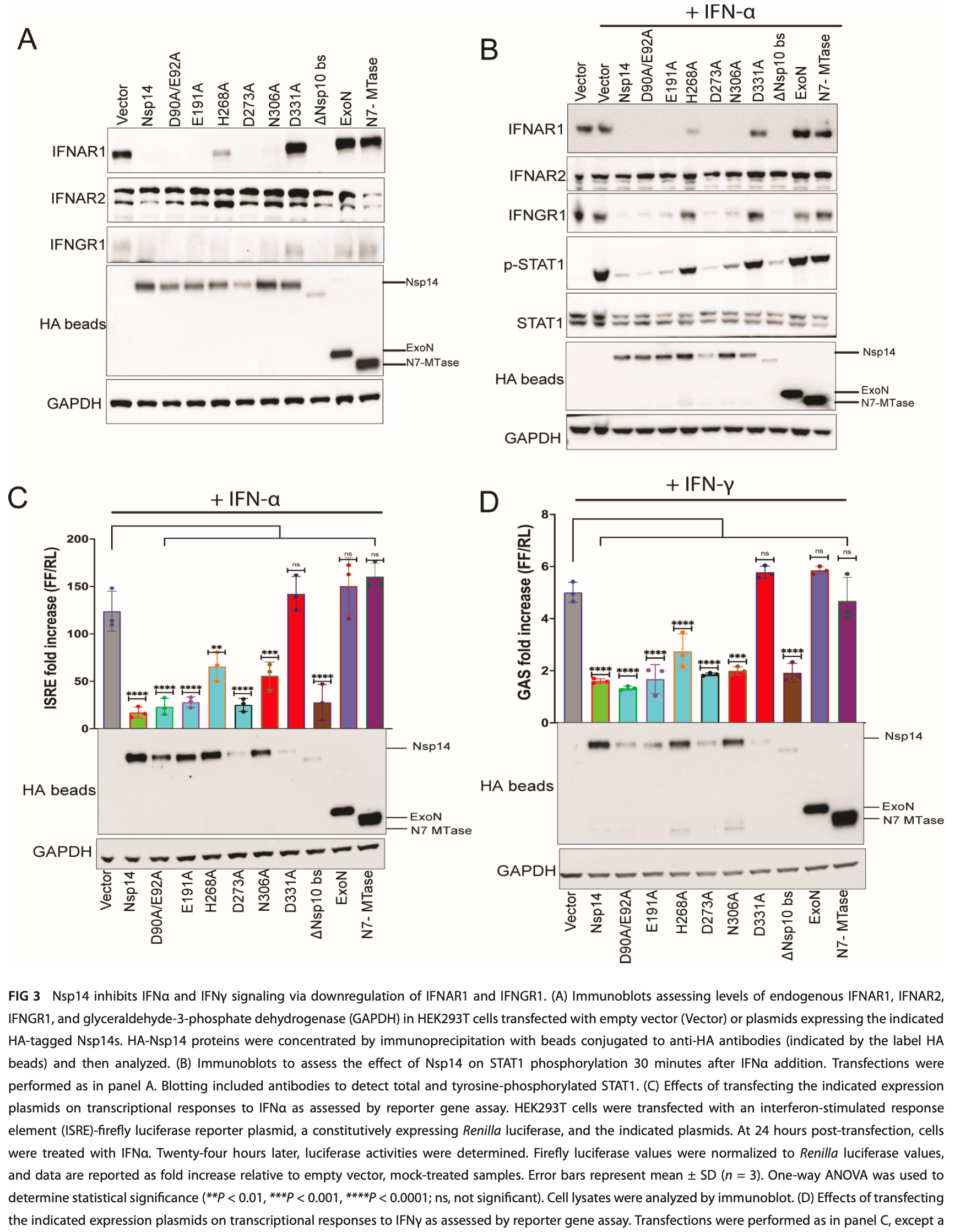
Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) non-struc tural protein 14 (Nsp14) possesses an N-terminal exonuclease (ExoN) domain that provides a proofreading function for the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and a C-terminal N7-methyltransferase (N7-MTase) domain that methylates viral mRNA caps. Nsp14 also modulates host functions. This includes the activation of NF-κB and downregulation of interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1). Here, we demonstrate that Nsp14 exerts broader effects, activating not only NF-κB responses but also extracellu lar-signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38, and Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-acti vated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling, promoting cytokine production. Furthermore, Nsp14 downregulates not only IFNAR1 but also IFN-γ receptor 1 (IFNGR1), impairing cellular responses to both IFNα and IFNγ. IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation is via a lysosomal pathway and occurs in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Analysis of a panel of Nsp14 mutants reveals a consistent pattern. Mutants that disable ExoN function remain largely active, whereas N7-MTase mutations impair both pro-inflammatory pathway activation and IFN receptor downregulation. Innate immune modulating functions also require the presence of both the ExoN and N7-MTase domains, likely reflecting that the ExoN domain must be present to enable N7-MTase activity. We further identify multi-functional host protein Tollip as an Nsp14 interactor. Interaction requires the phosphoinositide-binding C2 domain of Tollip and sequences C-terminal to the C2 domain. Full-length Tollip or regions encompassing the Nsp14 interaction domain are sufficient to counteract both Nsp14-mediated and Nsp14-independent activation of NF-κB. Knockdown of Tollip partially reverses IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, suggesting the relevance of Nsp14-Tollip interaction for Nsp14 innate immune evasion functions. IMPORTANCE Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) non-struc tural protein 14 (Nsp14) both activates NF-κB, which promotes virus replication and inflammation, and downregulates interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1), which can render infected cells resistant to the antiviral effects of IFN-α/β. Our study demonstrates that Nsp14 also activates MAPK signaling and downregulates IFN-γ receptor 1 (IFNGR1), causing broader impacts than previously recognized. Data from a panel of Nsp14 mutants suggest that a common underlying effect of Nsp14 may be responsible for its multiple innate immune activities. We further describe a novel interaction between Nsp14 and Tollip, a selective autophagy receptor. We show that Tollip expression downregulates Nsp14 activation of NF-κB and that Tollip knockdown reverses IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation in SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that Tollip functions as a regulator of Nsp14 innate immune modulation.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS Naveen Thakur, Conceptualization, Investigation, Methodology, Writing -original draft, Writing -review and editing | Poushali Chakraborty, Formal analysis, Investigation | JoAnn M. Tufariello, Formal analysis, Methodology, Supervision, Writing -original draft, Writing -review and editing | Christopher F. Basler, Conceptualization, Formal analysis,
ADDITIONAL FILES The following material is available online.
Supplemental Material Supplemental material (mBio01071-25-s0001.pdf). Fig. S1-S5 ; Tables S1-S3 .
References
Acharya, Liu, Gack, Dysregulation of type I interferon responses in COVID-19, Nat Rev Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0346-x
Addetia, Lieberman, Phung, Hsiang, Xie et al., SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 disrupts bidirectional nucleocytoplasmic transport through interactions with Rae1 and Nup98, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.00065-21
Arya, Kumari, Pandey, Mistry, Bihani et al., Structural insights into SARS-CoV-2 proteins, J Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2020.11.024
Banerjee, Blanco, Bruce, Honson, Chen et al., SARS-CoV-2 disrupts splicing, translation, and protein trafficking to suppress host defenses, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Bouhaddou, Memon, Meyer, White, Rezelj et al., The global phosphorylation landscape of SARS-CoV-2 infection, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.034
Bouvet, Debarnot, Imbert, Selisko, Snijder et al., In vitro reconstitution of SARS-coronavirus mRNA cap methylation, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000863
Bouvet, Imbert, Subissi, Gluais, Canard et al., RNA 3'end mismatch excision by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus nonstructural protein nsp10/nsp14 exoribonuclease complex, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.1201130109
Brissoni, Agostini, Kropf, Martinon, Swoboda et al., Intracellular trafficking of interleukin-1 receptor I requires Tollip, Curr Biol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Bulut, Faure, Thomas, Equils, Arditi, Cooperation of tolllike receptor 2 and 6 for cellular activation by soluble tuberculosis factor and Borrelia burgdorferi outer surface protein A lipoprotein: role of Tollinteracting protein and IL-1 receptor signaling molecules in Toll-like receptor 2 signaling, J Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.987
Burns, Clatworthy, Martin, Martinon, Plumpton et al., Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the IL-1 receptor, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.1038/35014038
Capelluto, Tollip: a multitasking protein in innate immunity and protein trafficking, Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2011.08.018
Case, Ashbrook, Dermody, Denison, Mutagenesis of S-Adenosyl-l-methionine-binding residues in coronavirus nsp14 N7methyltransferase demonstrates differing requirements for genome translation and resistance to innate immunity, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.00542-16
Chan, Kok, Zhu, Chu, To et al., Genomic characterization of the 2019 novel human-pathogenic coronavirus isolated from a patient with atypical pneumonia after visiting Wuhan, Emerging Microbes Infect, doi:10.1073/pnas.1201130109
Chen, Tao, Sun, Wu, Su et al., Structure-function analysis of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus RNA cap guanine-N7-methyltransferase, J Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960
Chiale, Greene, Zuniga, Interferon induction, evasion, and paradoxical roles during SARS-CoV-2 infection, Immunol Rev, doi:10.1247/csf.23.33
Dharra, Sharma, Datta, Emerging aspects of cytokine storm in COVID-19: the role of proinflammatory cytokines and therapeutic prospects, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156287
Duan, Xing, Chu, Deng, Du et al., ACE2-dependent and -independent SARS-CoV-2 entries dictate viral replication and inflammatory response during infection, Nat Cell Biol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Eckerle, Becker, Halpin, Li, Venter et al., Infidelity of SARS-CoV Nsp14-exonuclease mutant virus replication is revealed by complete genome sequencing, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000896
Eckerle, Lu, Sperry, Choi, Denison, High fidelity of murine hepatitis virus replication is decreased in nsp14 exoribonuclease mutants, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01296-07
Finkel, Gluck, Nachshon, Winkler, Fisher et al., SARS-CoV-2 uses a multipronged strategy to impede host protein synthesis, Nature, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Hayashi, Takatori, Warsame, Tomita, Fujisawa et al., TOLLIP acts as a cargo adaptor to promote lysosomal degradation of aberrant ER membrane proteins, EMBO J, doi:10.15252/embj.2023114272
Hayn, Hirschenberger, Koepke, Nchioua, Straub et al., Systematic functional analysis of SARS-CoV-2 proteins uncovers viral innate immune antagonists and remaining vulnerabilities, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Higgins, Nilsson-Payant, Bonaventure, Kurland, Ye et al., SARS-CoV-2 hijacks p38β/MAPK11 to promote virus replication, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.01007-23
Hsu, Laurent-Rolle, Pawlak, Wilen, Cresswell, Translational shutdown and evasion of the innate immune response by SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 protein, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Hua, Hao, Wang, Song, Hasan et al., Linear ubiquitination mediates coronavirus NSP14-induced NF-κB activation, Cell Commun Signal, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Jin, He, Ma, Zhuang, Wang et al., Suppression of ACE2 SUMOylation protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection through TOLLIP-mediated selective autophagy, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-022-32957-y
Kamitani, Huang, Narayanan, Lokugamage, Makino, A two-pronged strategy to suppress host protein synthesis by SARS coronavirus Nsp1 protein, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1038/nsmb.1680
Katahira, Ohmae, Yasugi, Sasaki, Itoh et al., Nsp14 of SARS-CoV-2 inhibits mRNA processing and nuclear export by targeting the nuclear capbinding complex, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Kato, Ikliptikawati, Kobayashi, Kondo, Lim et al., Overexpression of SARS-CoV-2 protein ORF6 dislocates RAE1 and NUP98 from the nuclear pore complex, Biochem Biophys Res Commun, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.115
Kim, Lee, Yang, Kim, Kim et al., The architecture of SARS-CoV-2 transcriptome, Cell, doi:10.1073/pnas.1201130109
Kim, Weller, Lin, Sheykhkarimli, Knapp et al., A proteome-scale map of the SARS-CoV-2-human contactome, Nat Biotechnol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Kimura, Konno, Uriu, Hopfensperger, Sauter et al., Sarbecovirus ORF6 proteins hamper induction of interferon signaling, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108916
Kopecky-Bromberg, Martinez-Sobrido, Palese, 7a protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus inhibits cellular protein synthesis and activates p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase, J Virol, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Kumar, Ishida, Strilets, Cole, Lopez-Orozco et al., SARS-CoV-2 nonstructural protein 1 inhibits the interferon response by causing depletion of key host signaling factors, J Virol, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Lamers, Haagmans, SARS-CoV-2 pathogenesis, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1247/csf.23.33
Lapointe, Grosely, Johnson, Wang, Fernández et al., Dynamic competition between SARS-CoV-2 NSP1 and mRNA on the human ribosome inhibits translation initiation, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2017715118
Lei, Dong, Ma, Xiao, Tian et al., Activation and evasion of type I interferon responses by SARS-CoV-2, Nat Commun, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Li, Goobie, Zhang, Toll-interacting protein impacts on inflammation, autophagy, and vacuole trafficking in human disease, J Mol Med (Berl), doi:10.1007/s00109-020-01999-4
Li, Hu, Li, Characterization of Tollip protein upon Lipopolysac charide challenge, Mol Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2004.03.009
Li, Kenney, Park, Fiches, Liu et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 protein associates with IMPDH2 and activates NF-κB signaling, Front Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Li, Wang, Peng, Shi, Wan et al., SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 induces AP-1 transcriptional activity via its interaction with MEK, Mol Immunol, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Liu, Shi, Becker, Schatz, Liu et al., Structural basis of mismatch recognition by a SARS-CoV-2 proofreading enzyme, Science, doi:10.1126/science.abi9310
Lu, Psakhye, Jentsch, Autophagic clearance of polyQ proteins mediated by ubiquitin-Atg8 adaptors of the conserved CUET protein family, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960
Minkoff, Innate immune evasion strategies of SARS-CoV-2, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-022-00839-1
Miorin, Kehrer, Sanchez-Aparicio, Zhang, Cohen et al., SARS-CoV-2 Orf6 hijacks Nup98 to block STAT nuclear import and antagonize interferon signaling, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2016650117
Mitra, Traughber, Brannon, Gomez, Capelluto, Ubiquitin interacts with the Tollip C2 and CUE domains and inhibits binding of Tollip to phosphoinositides, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M113.484170
Montazersaheb, Khatibi, Hejazi, Tarhriz, Farjami et al., COVID-19 infection: an overview on cytokine storm and related interventions, Virol J, doi:10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1
Morrison, MAP kinase pathways, Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960
Nilsson-Payant, Uhl, Grimont, Doane, Cohen et al., The NF-κB transcriptional footprint is essential for SARS-CoV-2 replication, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01257-21
Ogando, Kazzi, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Bontes, Decombe et al., Structure-function analysis of the nsp14 N7-guanine methyltransferase reveals an essential role in Betacoronavirus replication, Proc Natl Acad Sci, doi:10.1073/pnas.2108709118
Ogando, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Van Der Meer, Bredenbeek, Posthuma et al., The enzymatic activity of the nsp14 exoribonuclease is critical for replication of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV-2, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01246-20
Pan, Kindler, Cao, Zhou, Zhang et al., N7-methylation of the coronavirus RNA cap is required for maximal virulence by preventing innate immune recognition, mBio, doi:10.1128/mbio.03662-21
Park, Osinski, Hernandez, Eitson, Majumdar et al., The mechanism of RNA capping by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05185-z
Piao, Song, Chen, Diaz, Wahl et al., Endotoxin tolerance dysregulates MyD88-and Toll/ IL-1R domain-containing adapter inducing IFN-beta-dependent pathways and increases expression of negative regulators of TLR signaling, J Leukoc Biol, doi:10.1189/jlb.0309189
Riccio, Sullivan, Copeland, Activation of the SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 3'-5' exoribonuclease by NSP10 and response to antiviral inhibitors, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101518
Samuel, Interferon at the crossroads of SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19 disease, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960
Saramago, Bárria, Costa, Souza, Viegas et al., New targets for drug design: importance of nsp14/nsp10 complex formation for the 3'-5' exoribonucleolytic activity on SARS-CoV-2, FEBS J, doi:10.1111/febs.15815
Savellini, Anichini, Gandolfo, Cusi, Nucleopore traffic is hindered by SARS-CoV-2 ORF6 protein to efficiently suppress IFN-β and IL-6 secretion, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v14061273
Schubert, Karousis, Jomaa, Scaiola, Echeverria et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp1 binds the ribosomal mRNA channel to inhibit translation, Nat Struct Mol Biol, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Shannon, Selisko, Le, Huchting, Touret et al., Rapid incorporation of Favipiravir by the fast and permissive viral RNA polymerase complex results in SARS-CoV-2 lethal mutagenesis, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-18463-z
Smith, Blanc, Surdel, Vignuzzi, Denison, Coronavi ruses lacking exoribonuclease activity are susceptible to lethal mutagenesis: evidence for proofreading and potential therapeutics, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1003565
Song, Li, Xie, Hou, You, Cytokine storm induced by SARS-CoV-2, Clin Chim Acta, doi:10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.017
Thoms, Buschauer, Ameismeier, Koepke, Denk et al., Structural basis for translational shutdown and immune evasion by the Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2, Science, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Tidu, Janvier, Schaeffer, Sosnowski, Kuhn et al., The viral protein NSP1 acts as a ribosome gatekeeper for shutting down host translation and fostering SARS-CoV-2 translation, RNA, doi:10.1261/rna.078121.120
Tofaute, Weller, Graß, Halder, Dohai et al., SARS-CoV-2 NSP14 MTase activity is critical for inducing canonical NF-κB activation, Biosci Rep, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Toruń, Szymańska, Castanon, Wolińska-Nizioł, Bartosik et al., Endocytic adaptor protein Tollip inhibits canonical wnt signaling, PLoS One, doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960
Wu, Ma, Cai, Zhuang, Zhao et al., RNA-induced liquid phase separation of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein facilitates NF-κB hyper-activation and inflammation, Signal Transduct Target Ther, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Xia, Cao, Xie, Zhang, Chen et al., Evasion of type I interferon by SARS-CoV-2, Cell Rep, doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108234
Yamamoto, Tagawa, Yoshimori, Moriyama, Masaki et al., Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E cells, Cell Struct Funct, doi:10.1247/csf.23.33
Yin, Pu, Yuan, Pache, Churas et al., Global siRNA screen identifies human host factors critical for SARS-CoV-2 replication and late stages of infection, PLoS Biol, doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3002738
Yuan, Peng, Park, Hu, Devarkar et al., Nonstructural protein 1 of SARS-CoV-2 is a potent pathogenicity factor redirecting host protein synthesis machinery toward viral RNA, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Yuen, Lam, Wong, Mak, Wang et al., SARS-CoV-2 nsp13, nsp14, nsp15 and orf6 function as potent interferon antagonists, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Zaffagni, Harris, Patop, Pamudurti, Nguyen et al., SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 mediates the effects of viral infection on the host cell transcriptome, Elife, doi:10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062
Zhang, Ghosh, Negative regulation of toll-like receptormediated signaling by Tollip, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M109537200
Zhang, Miorin, Makio, Dehghan, Gao et al., Nsp1 protein of SARS-CoV-2 disrupts the mRNA export machinery to inhibit host gene expression, Sci Adv, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Zhou, Liu, Wang, Liu, Li et al., The nucleocap sid protein of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus inhibits cell cytokinesis and proliferation by interacting with translation elongation factor 1alpha, J Virol, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034
Zhu, Wang, Luo, Zhang, Ding et al., Tollip, an intracellular trafficking protein, is a novel modulator of the transforming growth factor-β signaling pathway, J Biol Chem, doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.388009
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01071-25",
"ISSN": [
"2150-7511"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1128/mbio.01071-25",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title/>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) non-structural protein 14 (Nsp14) possesses an N-terminal exonuclease (ExoN) domain that provides a proofreading function for the viral RNA-dependent RNA polymerase and a C-terminal N7-methyltransferase (N7-MTase) domain that methylates viral mRNA caps. Nsp14 also modulates host functions. This includes the activation of NF-κB and downregulation of interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1). Here, we demonstrate that Nsp14 exerts broader effects, activating not only NF-κB responses but also extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p38, and Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling, promoting cytokine production. Furthermore, Nsp14 downregulates not only IFNAR1 but also IFN-γ receptor 1 (IFNGR1), impairing cellular responses to both IFNα and IFNγ. IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation is via a lysosomal pathway and occurs in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells. Analysis of a panel of Nsp14 mutants reveals a consistent pattern. Mutants that disable ExoN function remain largely active, whereas N7-MTase mutations impair both pro-inflammatory pathway activation and IFN receptor downregulation. Innate immune modulating functions also require the presence of both the ExoN and N7-MTase domains, likely reflecting that the ExoN domain must be present to enable N7-MTase activity. We further identify multi-functional host protein Tollip as an Nsp14 interactor. Interaction requires the phosphoinositide-binding C2 domain of Tollip and sequences C-terminal to the C2 domain. Full-length Tollip or regions encompassing the Nsp14 interaction domain are sufficient to counteract both Nsp14-mediated and Nsp14-independent activation of NF-κB. Knockdown of Tollip partially reverses IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation in SARS-CoV-2-infected cells, suggesting the relevance of Nsp14-Tollip interaction for Nsp14 innate immune evasion functions.</jats:p>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>IMPORTANCE</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) non-structural protein 14 (Nsp14) both activates NF-κB, which promotes virus replication and inflammation, and downregulates interferon alpha/beta receptor 1 (IFNAR1), which can render infected cells resistant to the antiviral effects of IFN-α/β. Our study demonstrates that Nsp14 also activates MAPK signaling and downregulates IFN-γ receptor 1 (IFNGR1), causing broader impacts than previously recognized. Data from a panel of Nsp14 mutants suggest that a common underlying effect of Nsp14 may be responsible for its multiple innate immune activities. We further describe a novel interaction between Nsp14 and Tollip, a selective autophagy receptor. We show that Tollip expression downregulates Nsp14 activation of NF-κB and that Tollip knockdown reverses IFNAR1 and IFNGR1 downregulation in SARS-CoV-2 infection, suggesting that Tollip functions as a regulator of Nsp14 innate immune modulation.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n </jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1128/mbio.01071-25"
],
"article-number": "e01071-25",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2025-04-15"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-05-29"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-06-25"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/04a9tmd77",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai",
"place": [
"New York, USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Thakur",
"given": "Naveen",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/04a9tmd77",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai",
"place": [
"New York, USA"
]
}
],
"family": "Chakraborty",
"given": "Poushali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2785-1572",
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/04a9tmd77",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai",
"place": [
"New York, USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tufariello",
"given": "JoAnn M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-4195-425X",
"affiliation": [
{
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "https://ror.org/04a9tmd77",
"id-type": "ROR"
}
],
"name": "Department of Microbiology, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai",
"place": [
"New York, USA"
]
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Basler",
"given": "Christopher F.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "mBio",
"container-title-short": "mBio",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.asm.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-06-25T09:02:51Z",
"timestamp": 1750842171000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-13T13:04:49Z",
"timestamp": 1755090289000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lednicky",
"given": "John A.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"AI161104"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000060",
"award": [
"AI164080"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000060",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-15T02:39:24Z",
"timestamp": 1755225564127,
"version": "3.43.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1755043200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/non-commercial-tdm-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-13T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1755043200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01071-25",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/pdf/10.1128/mbio.01071-25",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "235",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1128",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
13
]
]
},
"publisher": "American Society for Microbiology",
"reference": [
{
"key": "e_1_3_5_2_2",
"unstructured": "World Health Organization. 2024. WHO COVID-19 dashboard. Available from: https://data.who.int/dashboards/covid19/deaths. Retrieved 11 June 2024."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_3_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1719902",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_4_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.1201130109",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_5_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2020.11.024",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_6_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.15815",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_7_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2021.101518",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_8_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-18463-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_9_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000896",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_10_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01296-07",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_11_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1003565",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_12_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1000863",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_13_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05185-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_14_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2108709118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_15_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.03662-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_16_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00542-16",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_17_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01257-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_18_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_19_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mbio.01007-23",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_20_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156287",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_21_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cca.2020.06.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_22_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01814-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_23_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00839-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_24_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nsmb.1680",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_25_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-0511-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_26_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abc8665",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_27_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.80.2.785-793.2006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_28_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00133-08",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_29_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00266-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_30_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abe7386",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_31_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03610-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_32_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.10.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_33_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2020.10.034",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_34_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2017715118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_35_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1261/rna.078121.120",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_36_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108234",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_37_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_38_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.11.115",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_39_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00065-21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_40_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2016650117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_41_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108916",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_42_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v14061273",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_43_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2101161118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_44_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkad483",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_45_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.71945",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_46_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.1007089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_47_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41556-024-01388-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_48_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/BSR20231418",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_49_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-022-01475-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_50_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12964-024-01949-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_51_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00575-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_52_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molimm.2024.09.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_53_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2020.1780953",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_54_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17665-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_55_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109126",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_56_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00109-020-01999-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_57_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abi9310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_58_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.01246-20",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_59_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M112.388009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_60_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cub.2006.09.062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_61_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/embj.2023114272",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_62_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micinf.2011.08.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_63_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M113.484170",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_64_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/35014038",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_65_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M109537200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_66_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.167.2.987",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_67_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.048",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_68_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0130818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_69_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/cshperspect.a011254",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_70_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.00061-13",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_71_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jbc.2023.104960",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_72_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0346-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_73_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41579-022-00713-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_74_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/imr.13113",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_75_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1247/csf.23.33",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_76_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3002738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_77_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1189/jlb.0309189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_78_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molimm.2004.03.009",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_79_2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32957-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_3_5_80_2"
}
],
"reference-count": 79,
"references-count": 79,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/mbio.01071-25"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "SARS-CoV-2 Nsp14 binds Tollip and activates pro-inflammatory pathways while downregulating interferon-α and interferon-γ receptors",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1128/asmj-crossmark-policy-page",
"volume": "16"
}