Resveratrol and Pterostilbene Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Air–Liquid Interface Cultured Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells
et al., Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13071335, Jul 2021
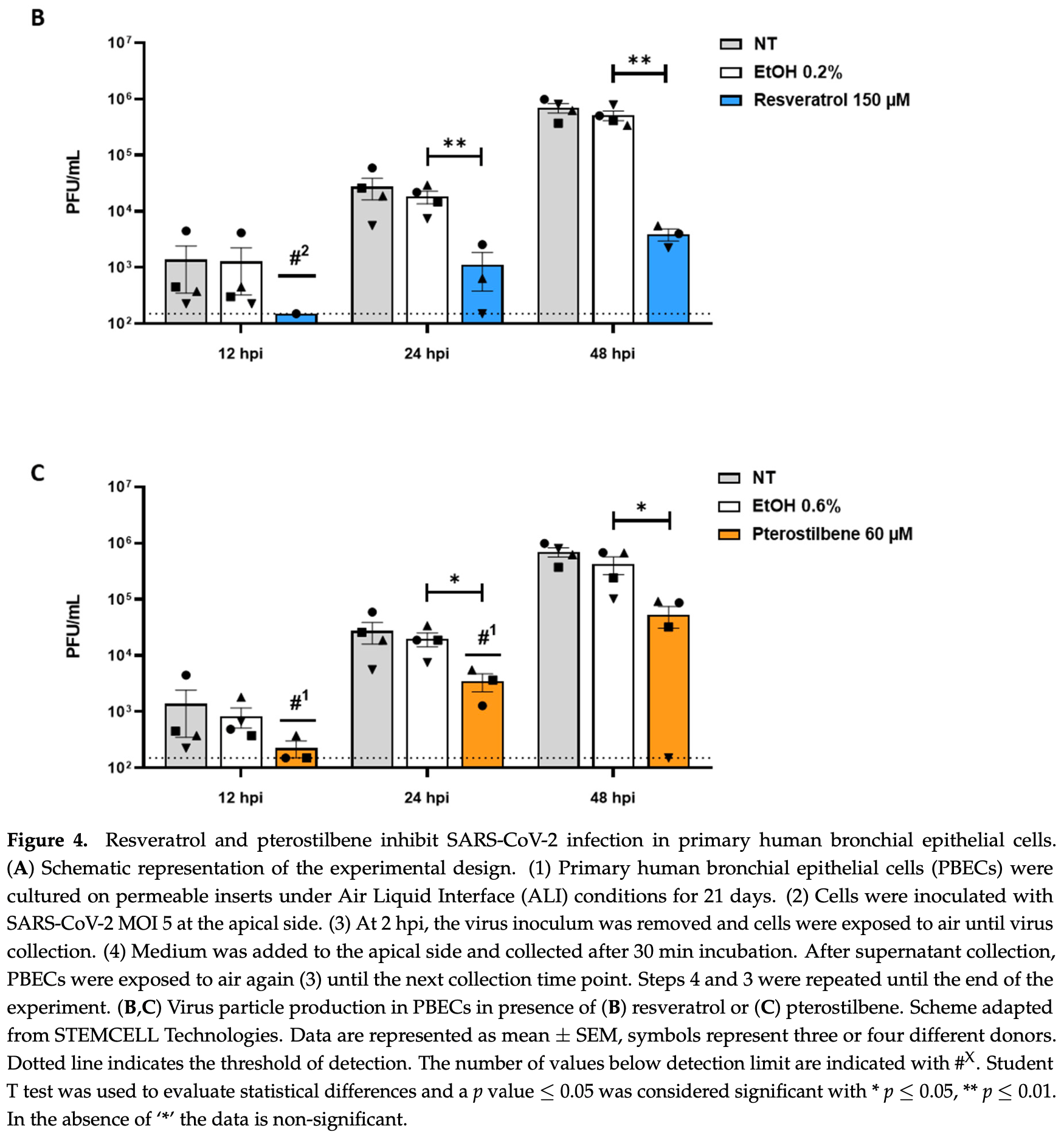
In vitro study showing resveratrol and pterostilbene inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication in Vero E6 cells and human bronchial epithelial cells. Both compounds had an antiviral effect when added post-infection, suggesting they interfere with viral RNA replication. Resveratrol reduced infected cells by 70% and drastically reduced intracellular RNA levels. In human bronchial cells, resveratrol and pterostilbene reduced viral titer by 99.3% and 87.5% respectively at 48 hours.
3 preclinical studies support the efficacy of resveratrol for COVID-19:
1.
Goc et al., Inhibitory effects of specific combination of natural compounds against SARS-CoV-2 and its Alpha, Beta, Gamma, Delta, Kappa, and Mu variants, European Journal of Microbiology and Immunology, doi:10.1556/1886.2021.00022.
ter Ellen et al., 10 Jul 2021, USA, peer-reviewed, 14 authors.
Contact: jolanda.smit@umcg.nl (corresponding author), b.m.ter.ellen@umcg.nl, n.dinesh.kumar@umcg.nl, e.m.bouma@umcg.nl, b.h.troost@umcg.nl, d.p.i.van.de.pol@umcg.nl, h.h.metselaar@umcg.nl, i.a.rodenhuis-zybert@umcg.nl, l.apperloo@umcg.nl, m.c.nawijn@umcg.nl, d.van.gosliga@umcg.nl, m.van.den.berge@umcg.nl, p.h.j.van.der.voort@umcg.nl, j.moser@umcg.nl.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Resveratrol and Pterostilbene Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Air–Liquid Interface Cultured Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells
Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13071335
The current COVID-19 pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and has an enormous impact on human health and economy. In search for therapeutic options, researchers have proposed resveratrol, a food supplement with known antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties as an advantageous antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, we provide evidence that both resveratrol and its metabolically more stable structural analog, pterostilbene, exhibit potent antiviral properties against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. First, we show that resveratrol and pterostilbene antiviral activity in African green monkey kidney cells. Both compounds actively inhibit virus replication within infected cells as reduced virus progeny production was observed when the compound was added at post-inoculation conditions. Without replenishment of the compound, antiviral activity was observed up to roughly five rounds of replication, demonstrating the long-lasting effect of these compounds. Second, as the upper respiratory tract represents the initial site of SARS-CoV-2 replication, we also assessed antiviral activity in air-liquid interface (ALI) cultured human primary bronchial epithelial cells, isolated from healthy volunteers. Resveratrol and pterostilbene showed a strong antiviral effect in these cells up to 48 h post-infection. Collectively, our data indicate that resveratrol and pterostilbene are promising antiviral compounds to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. Because these results represent laboratory findings in cells, we advocate evaluation of these compounds in clinical trials before statements are made whether these drugs are advantageous for COVID-19 treatment.
Institutional Review Board Statement: The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by The Medical Ethics Committee of the University Hospital of Groningen (Groningen, The Netherlands). Informed Consent Statement: Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest: The Authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Boocock, Faust, Patel, Schinas, Brown et al., Phase I Dose Escalation Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers of Resveratrol, a Potential Cancer Chemopreventive Agent, Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark, doi:10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0022
Braga, Kar, Berg, Carpaij, Pola Ński et al., A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0468-5
Brown, Patel, Viskaduraki, Crowell, Perloff et al., Repeat Dose Study of the Cancer Chemopreventive Agent Resveratrol in Healthy Volunteers: Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Effect on the Insulin-like Growth Factor Axis, Cancer Res, doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2364
Chan, Trinité, Levy, Potent Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication in Resting CD4 T Cells by Resveratrol and Pterostilbene, Antimicrob. Agents Chemother, doi:10.1128/AAC.00408-17
Chu, Chan, -W.; Yuen, Shuai, Yuan et al., Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: An observational study, Lancet Microbe, doi:10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30004-5
De Leo, Arena, Lacanna, Oliviero, Colavita et al., Resveratrol inhibits Epstein Barr Virus lytic cycle in Burkitt's lymphoma cells by affecting multiple molecular targets, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.09.003
Dhakar, Matencio, Caldera, Argenziano, Cavalli et al., Comparative Evaluation of Solubility, Cytotoxicity and Photostability Studies of Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol Loaded Nanosponges, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics11100545
Docherty, Fu, Stiffler, Limperos, Pokabla et al., Resveratrol inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication, Antivir. Res, doi:10.1016/S0166-3542(99)00042-X
Filardo, Di Pietro, Mastromarino, Sessa, Therapeutic potential of resveratrol against emerging respiratory viral infections, Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107613
Grant, Morales-Nebreda, Markov, Swaminathan, Guzman et al., Alveolitis in severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia is driven by self-sustaining circuits between infected alveolar macrophages and T cells, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.05.238188
He, Lau, Wu, Deng, Wang et al., Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5
Heijink, De Bruin, Dennebos, Jonker, Noordhoek et al., Cigarette smoke-induced epithelial expression of WNT-5B: Implications for COPD, Eur. Respir. J, doi:10.1183/13993003.01541-2015
Heijink, Kies, Kauffman, Postma, Van Oosterhout et al., Down-Regulation of E-Cadherin in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Leads to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent Th2 Cell-Promoting Activity, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7678
Heijink, Postma, Noordhoek, Broekema, Kapus, House Dust Mite-Promoted Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Bronchial Epithelium, Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol, doi:10.1165/rcmb.2008-0449OC
Hopkins, None
Horne, Vohl, Biological plausibility for interactions between dietary fat, resveratrol, ACE2, and SARS-CoV illness severity, Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00150.2020
Kim, Yoo, Lee, Byeon, Lee et al., The TRIF/TBK1/IRF-3 activation pathway is the primary inhibitory target of resveratrol, contributing to its broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects, Pharmazie, doi:10.1691/ph.2011.0798
Lin, Ho, Chuo, Li, Wang et al., Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol, BMC Infect. Dis, doi:10.1186/s12879-017-2253-8
Liu, Ren, Chen, Huang, Li et al., Resveratrol Protects against Cigarette Smoke-Induced Oxidative Damage and Pulmonary Inflammation, J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol, doi:10.1002/jbt.21586
Liu, Zang, Zhou, Li, Xie et al., Resveratrol Inhibits the TRIF-Dependent Pathway by Upregulating Sterile Alpha and Armadillo Motif Protein, Contributing to Anti-Inflammatory Effects after Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection, J. Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.03637-13
Lv, Zhang, Shen, Preliminary Clinical Effect Evaluation of Resveratrol in Adults with Allergic Rhinitis, Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol, doi:10.1159/000486959
Marinella, Indomethacin and resveratrol as potential treatment adjuncts for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13535
Mccormack, Mcfadden, A Review of Pterostilbene Antioxidant Activity and Disease Modification, Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev, doi:10.1155/2013/575482
Nagao, Jinnouchi, Kai, Yanagita, Pterostilbene, a dimethylated analog of resveratrol, promotes energy metabolism in obese rats, J. Nutr. Biochem, doi:10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.02.009
Ogando, Dalebout, Zevenhoven-Dobbe, Limpens, Van Der Meer et al., SARS-coronavirus-2 replication in Vero E6 cells: Replication kinetics, rapid adaptation and cytopathology, J. Gen. Virol, doi:10.1099/jgv.0.001453
Palamara, Nencioni, Aquilano, De Chiara, Hernandez et al., Inhibition of Influenza a Virus Replication by Resveratrol, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1086/429694
Pasquereau, Nehme, Ahmad, Daouad, Van Assche et al., Resveratrol Inhibits HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Replication In Vitro, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v13020354
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Zhang, Yang et al., Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China, Clin. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciaa248
Ravindra, Alfajaro, Gasque, Habet, Wei et al., Single-cell longitudinal analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human airway epithelium, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.05.06.081695
Riche, Mcewen, Riche, Sherman, Wofford et al., Analysis of Safety from a Human Clinical Trial with Pterostilbene, J. Toxicol, doi:10.1155/2013/463595
Sahakijpijarn, Moon, Koleng, Christensen, Williams, Development of Remdesivir as a Dry Powder for Inhalation by Thin Film Freezing, Pharmaceutics, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics12111002
Szkudelska, Nogowski, Szkudelski, The inhibitory effect of resveratrol on leptin secretion from rat adipocytes, Eur. J. Clin. Investig, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02188.x
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nat. Rev. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
Tellez, Willemse, Brouwer, Nijboer-Brinksma, Vandepoele et al., Protocadherin-1 Localization and Cell-Adhesion Function in Airway Epithelial Cells in Asthma, PLoS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163967
Troost, Mulder, Diosa-Toro, Van De Pol, Rodenhuis-Zybert et al., a natural steroidal alkaloid shows antiviral activity towards chikungunya virus in vitro, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/s41598-020-63397-7
Trotta, Lee, Loo, Young, Traini et al., Co-spray dried resveratrol and budesonide inhalation formulation for reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in rat alveolar macrophages, Eur. J. Pharm. Sci, doi:10.1016/j.ejps.2016.02.018
Tsai, Ho, Chen, Biological actions and molecular effects of resveratrol, pterostilbene, and 3 -hydroxypterostilbene, J. Food Drug Anal, doi:10.1016/j.jfda.2016.07.004
Van Der Voort, Moser, Zandstra, Kobold, Knoester et al., Leptin levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection related respiratory failure: A cross-sectional study and a pathophysiological framework on the role of fat tissue, Heliyon, doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04696
Walle, Hsieh, Delegge, Oatis, Walle, High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans, Drug Metab. Dispos, doi:10.1124/dmd.104.000885
Wang, Li, Li, Miao, Xiao, The Effects of Resveratrol on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules22091529
Wang, Sang, Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and pterostilbene, BioFactors, doi:10.1002/biof.1410
Wong, Lam, Wu, Ip, Lee et al., Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome, Clin. Exp. Immunol, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x
Xie, Zang, Li, Wang, Deng et al., Resveratrol Inhibits Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Induced IL-6 Production, Decreases Viral Replication, and Downregulates TRIF Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells, Inflammation, doi:10.1007/s10753-012-9452-7
Yang, Wei, Huang, Lei, Shen et al., Resveratrol inhibits the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 ( SARS-CoV -2) in cultured Vero cells, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6916
Yiu, Chen, Chang, Chiu, Lin, Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol on the Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Cycle, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules15107115
Youn, Lee, Fitzgerald, Young, Akira et al., Specific Inhibition of MyD88-Independent Signaling Pathways of TLR3 and TLR4 by Resveratrol: Molecular Targets Are TBK1 and RIP1 in TRIF Complex, J. Immunol, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3339
Zainal, Chang, Cheng, Wu, Anderson et al., Resveratrol treatment reveals a novel role for HMGB1 in regulation of the type 1 interferon response in dengue virus infection, Sci. Rep, doi:10.1038/srep42998
Zhu, Lei, Dong, Resveratrol as a potential therapeutic drug for respiratory system diseases, Drug Des. Dev. Ther, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S148868
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13071335",
"ISSN": [
"1999-4915"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/v13071335",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The current COVID-19 pandemic is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and has an enormous impact on human health and economy. In search for therapeutic options, researchers have proposed resveratrol, a food supplement with known antiviral, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties as an advantageous antiviral therapy for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Here, we provide evidence that both resveratrol and its metabolically more stable structural analog, pterostilbene, exhibit potent antiviral properties against SARS-CoV-2 in vitro. First, we show that resveratrol and pterostilbene antiviral activity in African green monkey kidney cells. Both compounds actively inhibit virus replication within infected cells as reduced virus progeny production was observed when the compound was added at post-inoculation conditions. Without replenishment of the compound, antiviral activity was observed up to roughly five rounds of replication, demonstrating the long-lasting effect of these compounds. Second, as the upper respiratory tract represents the initial site of SARS-CoV-2 replication, we also assessed antiviral activity in air–liquid interface (ALI) cultured human primary bronchial epithelial cells, isolated from healthy volunteers. Resveratrol and pterostilbene showed a strong antiviral effect in these cells up to 48 h post-infection. Collectively, our data indicate that resveratrol and pterostilbene are promising antiviral compounds to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection. Because these results represent laboratory findings in cells, we advocate evaluation of these compounds in clinical trials before statements are made whether these drugs are advantageous for COVID-19 treatment.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"v13071335"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "ter Ellen",
"given": "Bram M.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
},
{
"name": "Department of Biomedical Sciences of Cells & Systems, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Dinesh Kumar",
"given": "Nilima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Bouma",
"given": "Ellen M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Troost",
"given": "Berit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van de Pol",
"given": "Denise P.I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van der Ende-Metselaar",
"given": "Heidi H.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology and Medical Biology, GRIAC Research Institute, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Apperloo",
"given": "Leonie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pediatrics, Beatrix Children’s Hospital, GRIAC Research Institute, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van Gosliga",
"given": "Djoke",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pulmonary Diseases, GRIAC Research Institute, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van den Berge",
"given": "Maarten",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology and Medical Biology, GRIAC Research Institute, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Nawijn",
"given": "Martijn C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "van der Voort",
"given": "Peter H.J.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Critical Care, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Moser",
"given": "Jill",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Rodenhuis-Zybert",
"given": "Izabela A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medical Microbiology and Infection Prevention, University Medical Center Groningen, University of Groningen, 9700 RB Groningen, The Netherlands"
}
],
"family": "Smit",
"given": "Jolanda M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Viruses",
"container-title-short": "Viruses",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-12T02:16:48Z",
"timestamp": 1626056208000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-15T07:25:36Z",
"timestamp": 1721028336000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001826",
"award": [
"10430012010006"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100001826",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "ZonMw"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100010665",
"award": [
"713660"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100010665",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "H2020 Marie Skłodowska-Curie Actions"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-02-21T16:36:08Z",
"timestamp": 1740155768235,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 56,
"issue": "7",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "7",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625875200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/7/1335/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1335",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref_1",
"unstructured": "(2021, February 07). John Hopkins University and Medicine. Available online: https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/map.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19: Immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_2",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2249.2004.02415.x",
"article-title": "Plasma inflammatory cytokines and chemokines in severe acute respiratory syndrome",
"author": "Wong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "95",
"journal-title": "Clin. Exp. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_3",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.05.238188",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_4",
"unstructured": "Grant, R.A., Morales-Nebreda, L., Markov, N.S., Swaminathan, S., Guzman, E.R., Abbott, D.A., Donnelly, H.K., Donayre, A., Goldberg, I.A., and Klug, Z.M. (2020). Alveolitis in severe SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia is driven by self-sustaining circuits between infected alveolar macrophages and T cells. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/biof.1410",
"article-title": "Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of resveratrol and pterostilbene",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "16",
"journal-title": "BioFactors",
"key": "ref_5",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jfda.2016.07.004",
"article-title": "Biological actions and molecular effects of resveratrol, pterostilbene, and 3′-hydroxypterostilbene",
"author": "Tsai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "J. Food Drug Anal.",
"key": "ref_6",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00408-17",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_7",
"unstructured": "Chan, C.N., Trinité, B., and Levy, D.N. (2017). Potent Inhibition of HIV-1 Replication in Resting CD4 T Cells by Resveratrol and Pterostilbene. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother., 61."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/429694",
"article-title": "Inhibition of Influenza a Virus Replication by Resveratrol",
"author": "Palamara",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1719",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_8",
"volume": "191",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10753-012-9452-7",
"article-title": "Resveratrol Inhibits Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Induced IL-6 Production, Decreases Viral Replication, and Downregulates TRIF Expression in Airway Epithelial Cells",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1392",
"journal-title": "Inflammation",
"key": "ref_9",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-017-2253-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_10",
"unstructured": "Lin, S.-C., Ho, C.-T., Chuo, W.-H., Li, S., Wang, T.T., and Lin, C.-C. (2017). Effective inhibition of MERS-CoV infection by resveratrol. BMC Infect. Dis., 17."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6916",
"article-title": "Resveratrol inhibits the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 ( SARS-CoV -2) in cultured Vero cells",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1127",
"journal-title": "Phytother. Res.",
"key": "ref_11",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13020354",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_12",
"unstructured": "Pasquereau, S., Nehme, Z., Ahmad, S.H., Daouad, F., Van Assche, J., Wallet, C., Schwartz, C., Rohr, O., Morot-Bizot, S., and Herbein, G. (2021). Resveratrol Inhibits HCoV-229E and SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Replication In Vitro. Viruses, 13."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107613",
"article-title": "Therapeutic potential of resveratrol against emerging respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Filardo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107613",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol. Ther.",
"key": "ref_13",
"volume": "214",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/DDDT.S148868",
"article-title": "Resveratrol as a potential therapeutic drug for respiratory system diseases",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3591",
"journal-title": "Drug Des. Dev. Ther.",
"key": "ref_14",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajpendo.00150.2020",
"article-title": "Biological plausibility for interactions between dietary fat, resveratrol, ACE2, and SARS-CoV illness severity",
"author": "Horne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "E830",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.",
"key": "ref_15",
"volume": "318",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13535",
"article-title": "Indomethacin and resveratrol as potential treatment adjuncts for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19",
"author": "Marinella",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e13535",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Clin. Pract.",
"key": "ref_16",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e04696",
"article-title": "Leptin levels in SARS-CoV-2 infection related respiratory failure: A cross-sectional study and a pathophysiological framework on the role of fat tissue",
"author": "Moser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e04696",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "ref_17",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-019-0468-5",
"article-title": "A cellular census of human lungs identifies novel cell states in health and in asthma",
"author": "Braga",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_18",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.178.12.7678",
"article-title": "Down-Regulation of E-Cadherin in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells Leads to Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor-Dependent Th2 Cell-Promoting Activity",
"author": "Heijink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7678",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_19",
"volume": "178",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1165/rcmb.2008-0449OC",
"article-title": "House Dust Mite–Promoted Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in Human Bronchial Epithelium",
"author": "Heijink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol.",
"key": "ref_20",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1099/jgv.0.001453",
"article-title": "SARS-coronavirus-2 replication in Vero E6 cells: Replication kinetics, rapid adaptation and cytopathology",
"author": "Ogando",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "925",
"journal-title": "J. Gen. Virol.",
"key": "ref_21",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-020-63397-7",
"article-title": "Tomatidine, a natural steroidal alkaloid shows antiviral activity towards chikungunya virus in vitro",
"author": "Troost",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6364",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_22",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2666-5247(20)30004-5",
"article-title": "Comparative tropism, replication kinetics, and cell damage profiling of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV with implications for clinical manifestations, transmissibility, and laboratory studies of COVID-19: An observational study",
"author": "Chu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e14",
"journal-title": "Lancet Microbe",
"key": "ref_23",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-0869-5",
"article-title": "Temporal dynamics in viral shedding and transmissibility of COVID-19",
"author": "He",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "672",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "ref_24",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01541-2015",
"article-title": "Cigarette smoke-induced epithelial expression of WNT-5B: Implications for COPD",
"author": "Heijink",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "504",
"journal-title": "Eur. Respir. J.",
"key": "ref_25",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.05.06.081695",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_26",
"unstructured": "Ravindra, N.G., Alfajaro, M.M., Gasque, V., Habet, V., Wei, J., Filler, R.B., Huston, N.C., Wan, H., Szigeti-Buck, K., and Wang, B. (2020). Single-cell longitudinal analysis of SARS-CoV-2 infection in human airway epithelium. bioRxiv."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0163967",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_27",
"unstructured": "Tellez, G.F., Willemse, B.W.M., Brouwer, U., Nijboer-Brinksma, S., Vandepoele, K., Noordhoek, J.A., Heijink, I., de Vries, M., Smithers, N.P., and Postma, D.S. (2016). Protocadherin-1 Localization and Cell-Adhesion Function in Airway Epithelial Cells in Asthma. PLoS ONE, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/575482",
"article-title": "A Review of Pterostilbene Antioxidant Activity and Disease Modification",
"author": "Mccormack",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "575482",
"journal-title": "Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev.",
"key": "ref_28",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0166-3542(99)00042-X",
"article-title": "Resveratrol inhibition of herpes simplex virus replication",
"author": "Docherty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "145",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_29",
"volume": "43",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules15107115",
"article-title": "Inhibitory Effects of Resveratrol on the Epstein-Barr Virus Lytic Cycle",
"author": "Yiu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7115",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "ref_30",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2012.09.003",
"article-title": "Resveratrol inhibits Epstein Barr Virus lytic cycle in Burkitt’s lymphoma cells by affecting multiple molecular targets",
"author": "Arena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "196",
"journal-title": "Antivir. Res.",
"key": "ref_31",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa248",
"article-title": "Dysregulation of Immune Response in Patients With Coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Qin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "762",
"journal-title": "Clin. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "ref_32",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "ref_33",
"unstructured": "Kim, M.H., Yoo, D.S., Lee, S.Y., Byeon, S.E., Lee, Y.G., Min, T., Rho, H.S., Rhee, M.H., Lee, J., and Cho, J.Y. (2011). The TRIF/TBK1/IRF-3 activation pathway is the primary inhibitory target of resveratrol, contributing to its broad-spectrum anti-inflammatory effects. Pharmazie."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.03637-13",
"article-title": "Resveratrol Inhibits the TRIF-Dependent Pathway by Upregulating Sterile Alpha and Armadillo Motif Protein, Contributing to Anti-Inflammatory Effects after Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4229",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "ref_34",
"volume": "88",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.175.5.3339",
"article-title": "Specific Inhibition of MyD88-Independent Signaling Pathways of TLR3 and TLR4 by Resveratrol: Molecular Targets Are TBK1 and RIP1 in TRIF Complex",
"author": "Youn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3339",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol.",
"key": "ref_35",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jbt.21586",
"article-title": "Resveratrol Protects against Cigarette Smoke-Induced Oxidative Damage and Pulmonary Inflammation",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "465",
"journal-title": "J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_36",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules22091529",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_37",
"unstructured": "Wang, X.-L., Li, T., Li, J.-H., Miao, S.-Y., and Xiao, X.-Z. (2017). The Effects of Resveratrol on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in a Rat Model of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Molecules, 22."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/srep42998",
"article-title": "Resveratrol treatment reveals a novel role for HMGB1 in regulation of the type 1 interferon response in dengue virus infection",
"author": "Zainal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42998",
"journal-title": "Sci. Rep.",
"key": "ref_38",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/j.1365-2362.2009.02188.x",
"article-title": "The inhibitory effect of resveratrol on leptin secretion from rat adipocytes",
"author": "Szkudelska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "899",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Clin. Investig.",
"key": "ref_39",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2017.02.009",
"article-title": "Pterostilbene, a dimethylated analog of resveratrol, promotes energy metabolism in obese rats",
"author": "Nagao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"journal-title": "J. Nutr. Biochem.",
"key": "ref_40",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2364",
"article-title": "Repeat Dose Study of the Cancer Chemopreventive Agent Resveratrol in Healthy Volunteers: Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Effect on the Insulin-like Growth Factor Axis",
"author": "Brown",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "9003",
"journal-title": "Cancer Res.",
"key": "ref_41",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2013/463595",
"article-title": "Analysis of Safety from a Human Clinical Trial with Pterostilbene",
"author": "Riche",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "463595",
"journal-title": "J. Toxicol.",
"key": "ref_42",
"volume": "2013",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/dmd.104.000885",
"article-title": "High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans",
"author": "Walle",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Drug Metab. Dispos.",
"key": "ref_43",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-07-0022",
"article-title": "Phase I Dose Escalation Pharmacokinetic Study in Healthy Volunteers of Resveratrol, a Potential Cancer Chemopreventive Agent",
"author": "Boocock",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1246",
"journal-title": "Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark.",
"key": "ref_44",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejps.2016.02.018",
"article-title": "Co-spray dried resveratrol and budesonide inhalation formulation for reducing inflammation and oxidative stress in rat alveolar macrophages",
"author": "Trotta",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Eur. J. Pharm. Sci.",
"key": "ref_45",
"volume": "86",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pharmaceutics11100545",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_46",
"unstructured": "Dhakar, N.K., Matencio, A., Caldera, F., Argenziano, M., Cavalli, R., Dianzani, C., Zanetti, M., López-Nicolás, J.M., and Trotta, F. (2019). Comparative Evaluation of Solubility, Cytotoxicity and Photostability Studies of Resveratrol and Oxyresveratrol Loaded Nanosponges. Pharmaceutics, 11."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000486959",
"article-title": "Preliminary Clinical Effect Evaluation of Resveratrol in Adults with Allergic Rhinitis",
"author": "Lv",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "231",
"journal-title": "Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol.",
"key": "ref_47",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.07.26.222109",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "ref_48",
"unstructured": "Sahakijpijarn, S., Moon, C., Koleng, J., Christensen, D., and Williams, R. (2020). Development of Remdesivir as a Dry Powder for Inhalation by Thin Film Freezing. Pharmaceutics, 12."
}
],
"reference-count": 48,
"references-count": 48,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/1999-4915/13/7/1335"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Resveratrol and Pterostilbene Inhibit SARS-CoV-2 Replication in Air–Liquid Interface Cultured Human Primary Bronchial Epithelial Cells",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "13"
}