Therapeutic effects of olfactory training and systemic vitamin A in patients with COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction: a double-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial
et al., Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451, Jun 2024
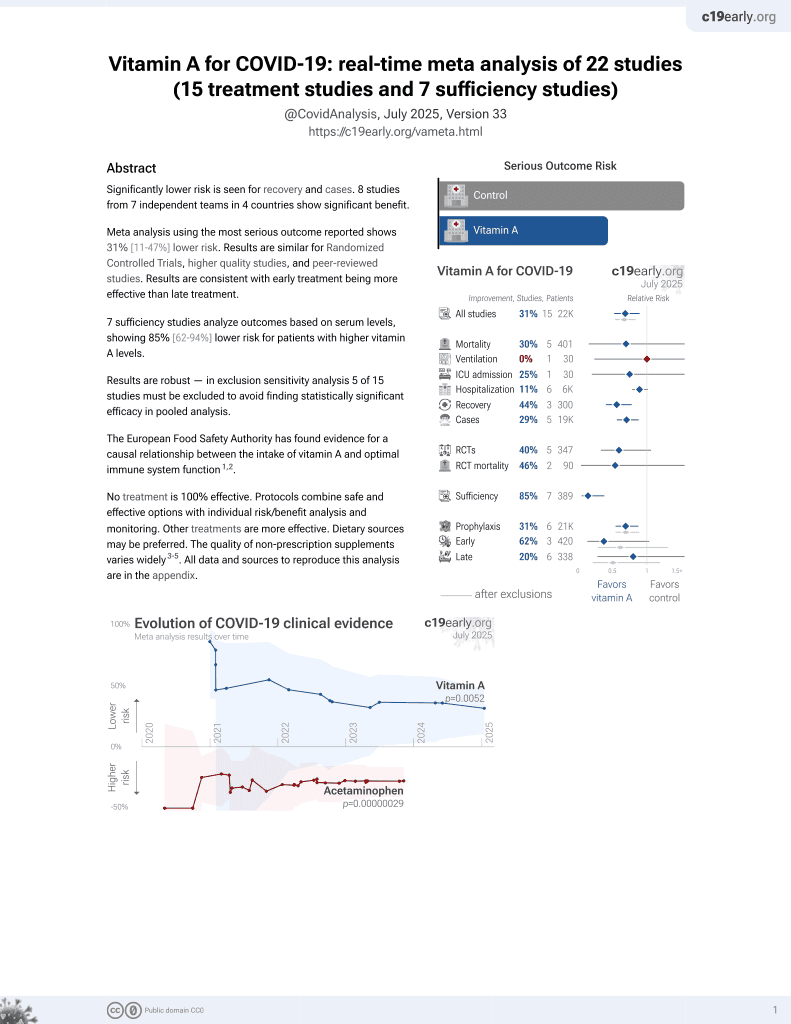
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
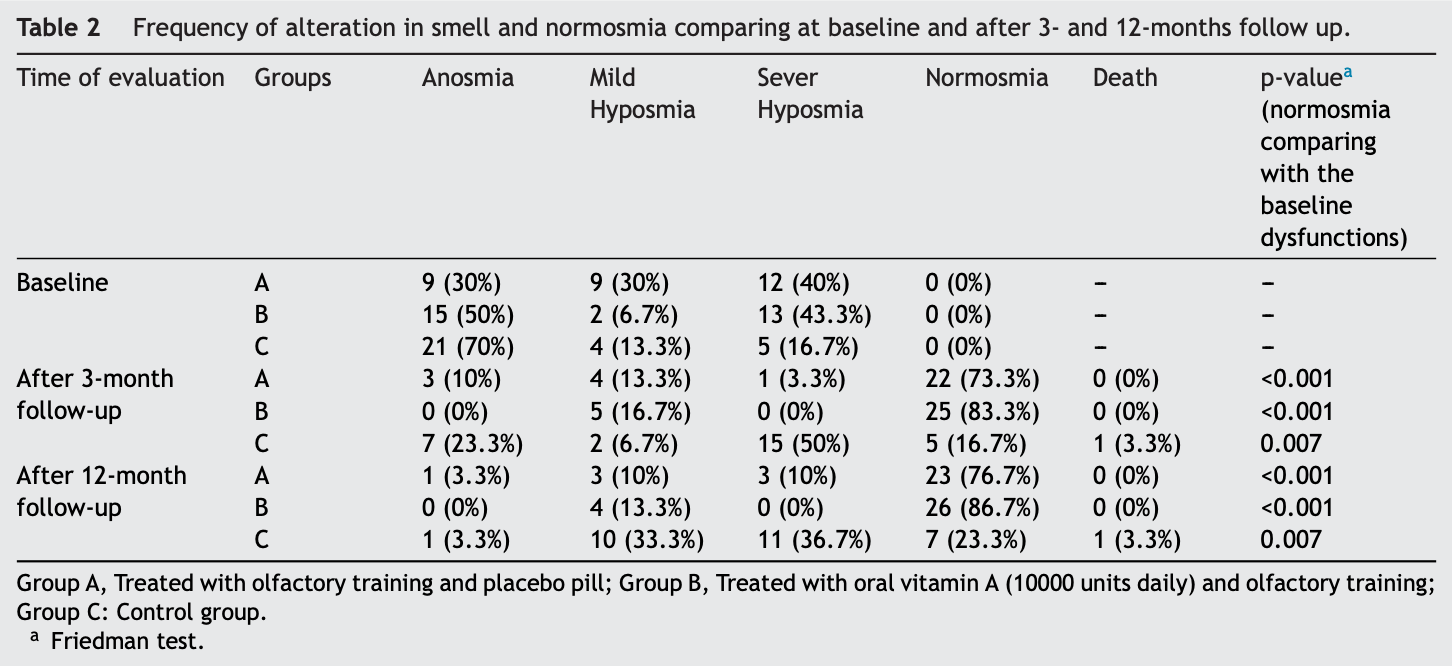
RCT 90 outpatients with post-COVID-19 anosmia showing significant improvements in smell alterations with olfactory training after 3 and 12 months. Adding oral vitamin A to olfactory training resulted in higher rates of improvement, but the difference was not statistically significant.
|
risk of no recovery, 37.5% lower, RR 0.62, p = 0.53, treatment 5 of 30 (16.7%), control 8 of 30 (26.7%), NNT 10.0, 12 months.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 42.9% lower, RR 0.57, p = 0.51, treatment 4 of 30 (13.3%), control 7 of 30 (23.3%), NNT 10.0, 3 months.
|
|
risk of anosmia, 66.7% lower, RR 0.33, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 1 of 30 (3.3%), NNT 30, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 12 months.
|
|
risk of anosmia, 85.7% lower, RR 0.14, p = 0.24, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 3 of 30 (10.0%), NNT 10.0, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 3 months.
|
|
risk of anosmia/severe hyposmia, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 4 of 30 (13.3%), NNT 7.5, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 12 months.
|
|
risk of anosmia/severe hyposmia, 88.9% lower, RR 0.11, p = 0.11, treatment 0 of 30 (0.0%), control 4 of 30 (13.3%), NNT 7.5, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), 3 months.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Taheri et al., 3 Jun 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, 6 authors, study period March 2020 - March 2021, post-COVID anosmia.
Contact: aborey110@gmail.com.
Therapeutic effects of olfactory training and systemic vitamin A in patients with COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction: a double-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial
Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, doi:10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451
Three-months olfactory training is effective to treat the COVID-19-related anosmia. • Daily oral vitamin A did not lead to better results in improving anosmia. • The intervention time was important in the final olfactory status of the patients.
Authors' contributions Dr. A. T is the main manager. He had the main rule in the of conceptualization and investigation in the research. Dr. M. N had the main role in data curation and writing the original draft of the manuscript. Dr. M. S helped in formal analysis. Dr. N. J. J and Dr. H. E. K were the project consultants and helped in methodology and data curation. Dr. R. A helped in validation, reviewing, and editing the manuscript.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Declarations Consent for publication: Not applicable.
References
Bagheri, Asghari, Farhadi, Coincidence of COVID-19 epidemic and olfactory dysfunction outbreak in Iran, Med J Islam Repub Iran
Bon, Konopnicki, Pisarski, Prunier, Lechien et al., Efficacy and safety of oral corticosteroids and olfactory training in the management of COVID-19-related loss of smell, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Chan, Wong, Tang, COVID-19: an update on the epidemiological, clinical, preventive and therapeutic evidence and guidelines of integrative Chinese---Western medicine for the management of 2019 novel coronavirus disease, Am J Chin Med
Cheng, Huang, Zhang, Liu, Li et al., Epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia in Henan
Chinazzi, Davis, Ajelli, Gioannini, Litvinova et al., The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak, Science
Choi, Jeong, Noh, Park, Cho et al., Effects of olfactory training in patients with postinfectious olfactory dysfunction, Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol
Colclasure, Gross, Kountakis, Endoscopic sinus surgery in patients older than sixty, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Duncan, Briggs, Treatment of uncomplicated anosmia by vitamin A, Arch Otolaryngol
Henning, Geruch, None, II. Zeitschrift für Psychologie
Hummel, Rissom, Reden, Hähner, Weidenbecher et al., Effects of olfactory training in patients with olfactory loss, Laryngoscope
Hummel, Whitcroft, Rueter, Haehner, Intranasal vitamin A is beneficial in post-infectious olfactory loss, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Langarizadeh, Tavakoli, Abiri, Ghasempour, Rezaei et al., A review on function and side effects of systemic corticosteroids used in high-grade COVID-19 to prevent cytokine storms, EXCLI J
Lechien, Chiesa-Estomba, Siati, Horoi, Bon et al., Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study, Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol
Lozada-Nur, Chainani-Wu, Fortuna, Dysgeusia in COVID-19: possible mechanisms and implications, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol
Machado, Gutierrez, Anosmia and ageusia as initial or unique symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 virus infection, doi:10.20944/preprints202004.0272.v1
Mao, Wang, Hu, Chen, He, Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China, JAMA Neurol
Mynzhanova, Baesheva, Omarova, Analysis of the implementation of clinical manifestations of COVID-19 in contact persons
Rawal, Hoffman, Bainbridge, Huedo-Medina, Duffy, Prevalence and risk factors of self-reported smell and taste alterations: results from the 2011---2012 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), Chem Senses
Reden, Lill, Zahnert, Haehner, Hummel, Olfactory function in patients with postinfectious and posttraumatic smell disorders before and after treatment with vitamin A: a double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial, Laryngoscope
Stockman, Bellamy, Garner, SARS: systematic review of treatment effects, PLoS Med
Taherkhani, Moztarzadeh, Seraj, Nazari, Taherkhani et al., Iran smell iden-Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology xxxx;xxx(xx):xxx tification test (Iran-SIT): a modified version of the University of Pennsylvania smell identification test (UPSIT) for the Iranian population, Chemosens Percept
Tyrrell, Bynoe, Cultivation of a novel type of commoncold virus in organ cultures, Br Med J
Wang, Wysocki, Gold, Induction of olfactory receptor sensitivity in mice, Science
Wang, Zhou, Liu, Reasons for healthcare workers becoming infected with novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China, J Hosp Infect
Whicroft, Hummel, Cummings otolaryngology head and neck surgery
Yousefifard, Ali, Aghaei, Zali, Neishaboori et al., Corticosteroids on the management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systemic review and meta-analysis, Iran J Public Health
Zheng, Feng, Liu, Targher, Byrne et al., Extrapulmonary complications of COVID-19: a multisystem disease?, J Med Virol
İs ¸lek, Balcı, Phantosmia with COVID-19 related olfactory dysfunction: report of nine case, Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451",
"ISSN": [
"1808-8694"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451",
"alternative-id": [
"S1808869424000661"
],
"article-number": "101451",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Therapeutic effects of olfactory training and systemic vitamin A in patients with COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction: a double-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2024 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier España, S.L.U."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1960-7251",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Taheri",
"given": "Abolfazl",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-8598-6694",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Naderi",
"given": "Maryam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6006-7771",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jafari",
"given": "Nematollah Jonaidi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1139-1276",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Koochak",
"given": "Hamid Emadi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3455-7013",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Esfeedvajani",
"given": "Mohsen Saberi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2481-6536",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Abolghasemi",
"given": "Reyhaneh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology",
"container-title-short": "Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-03T16:54:36Z",
"timestamp": 1717433676000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-03T16:54:53Z",
"timestamp": 1717433693000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-04T00:26:16Z",
"timestamp": 1717460776892
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717200000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1717200000000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2024-05-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1716508800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1808869424000661?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1808869424000661?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101451",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.1.5448.1467",
"article-title": "Cultivation of a novel type of common-cold virus in organ cultures",
"author": "Tyrrell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1467",
"journal-title": "Br Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0005",
"volume": "1",
"year": "1965"
},
{
"article-title": "Analysis of the implementation of clinical manifestations of COVID-19 in contact persons",
"author": "Mynzhanova",
"first-page": "5",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0010",
"series-title": "Hаука и здравоохранение",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0015",
"unstructured": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptoms of coronavirus. [Accessed 25 December 2023]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/symptoms-testing/symptoms.html."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.aba9757",
"article-title": "The effect of travel restrictions on the spread of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID-19) outbreak",
"author": "Chinazzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "395",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0020",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhin.2020.03.002",
"article-title": "Reasons for healthcare workers becoming infected with novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in China",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100",
"journal-title": "J Hosp Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0025",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Coincidence of COVID-19 epidemic and olfactory dysfunction outbreak in Iran",
"author": "Bagheri",
"first-page": "62",
"journal-title": "Med J Islam Repub Iran",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0030",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.otohns.2004.06.710",
"article-title": "Endoscopic sinus surgery in patients older than sixty",
"author": "Colclasure",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "946",
"journal-title": "Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0035",
"volume": "131",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/archotol.1962.00740040122008",
"article-title": "Treatment of uncomplicated anosmia by vitamin A",
"author": "Duncan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "116",
"journal-title": "Arch Otolaryngol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0040",
"volume": "75",
"year": "1962"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0045",
"unstructured": "American Academy of Otolaryngology- Head and Neck Surgery. COVID-19 anosmia reporting tool open to all clinicians. [Accessed 25 December 2023]. Available from: https://www.entnet.org/."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12078-015-9192-9",
"article-title": "Iran smell identification test (Iran-SIT): a modified version of the University of Pennsylvania smell identification test (UPSIT) for the Iranian population",
"author": "Taherkhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "183",
"journal-title": "Chemosens Percept",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0050",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Der Geruch. II",
"author": "Henning",
"first-page": "305",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0055",
"volume": "vol. 74",
"year": "1916"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127",
"article-title": "Neurologic manifestations of hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Mao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "683",
"journal-title": "JAMA Neurol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0060",
"volume": "77",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Epidemiological characteristics of novel coronavirus pneumonia in Henan",
"author": "Cheng",
"first-page": "327",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0065",
"series-title": "Zhonghua jie he he hu xi za zhi",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1",
"article-title": "Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study",
"author": "Lechien",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2251",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0070",
"volume": "277",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.8493539",
"article-title": "Induction of olfactory receptor sensitivity in mice",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "998",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0075",
"volume": "260",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/lary.20101",
"article-title": "Effects of olfactory training in patients with olfactory loss",
"author": "Hummel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"journal-title": "Laryngoscope",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0080",
"volume": "119",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1142/S0192415X20500378",
"article-title": "COVID-19: an update on the epidemiological, clinical, preventive and therapeutic evidence and guidelines of integrative Chinese–Western medicine for the management of 2019 novel coronavirus disease",
"author": "Chan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "737",
"journal-title": "Am J Chin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0085",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21053/ceo.2020.00143",
"article-title": "Effects of olfactory training in patients with postinfectious olfactory dysfunction",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "88",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0090",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/lary.23405",
"article-title": "Olfactory function in patients with postinfectious and posttraumatic smell disorders before and after treatment with vitamin A: a double‐blind, placebo‐controlled, randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Reden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1906",
"journal-title": "Laryngoscope",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0095",
"volume": "122",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-017-4576-x",
"article-title": "Intranasal vitamin A is beneficial in post-infectious olfactory loss",
"author": "Hummel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2819",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0100",
"volume": "274",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26294",
"article-title": "Extrapulmonary complications of COVID‐19: a multisystem disease?",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "323",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0105",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20944/preprints202004.0272.v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0110",
"unstructured": "Machado C, Gutierrez JV. Anosmia and ageusia as initial or unique symptoms after SARS-CoV-2 virus infection. doi: https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202004.0272.v1. (preprints)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.oooo.2020.06.016",
"article-title": "Dysgeusia in COVID-19: possible mechanisms and implications",
"author": "Lozada-Nur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0115",
"volume": "130",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/chemse/bjv057",
"article-title": "Prevalence and risk factors of self-reported smell and taste alterations: results from the 2011–2012 US National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES)",
"author": "Rawal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "69",
"journal-title": "Chem Senses",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0120",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12070-021-02505-z",
"article-title": "Phantosmia with COVID-19 related olfactory dysfunction: report of nine case",
"author": "İşlek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2891",
"issue": "Suppl 2",
"journal-title": "Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0125",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pmed.0030343",
"article-title": "SARS: systematic review of treatment effects",
"author": "Stockman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e343",
"journal-title": "PLoS Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0130",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"article-title": "Corticosteroids on the management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): a systemic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Yousefifard",
"first-page": "1411",
"journal-title": "Iran J Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0135",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "World Health Organization",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0140",
"series-title": "Clinical management of severe acute respiratory infection (SARI) when COVID-19 disease is suspected: interim guidance, 13 March 2020",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "A review on function and side effects of systemic corticosteroids used in high-grade COVID-19 to prevent cytokine storms",
"author": "Langarizadeh",
"first-page": "339",
"journal-title": "EXCLI J",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0145",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Cummings otolaryngology head and neck surgery",
"author": "Whicroft",
"first-page": "599",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0150",
"series-title": "Philadelphia",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00405-020-06520-8",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of oral corticosteroids and olfactory training in the management of COVID-19-related loss of smell",
"author": "Le Bon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3113",
"journal-title": "Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol",
"key": "10.1016/j.bjorl.2024.101451_bib0155",
"volume": "278",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 31,
"references-count": 31,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1808869424000661"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Therapeutic effects of olfactory training and systemic vitamin A in patients with COVID-19-related olfactory dysfunction: a double-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}