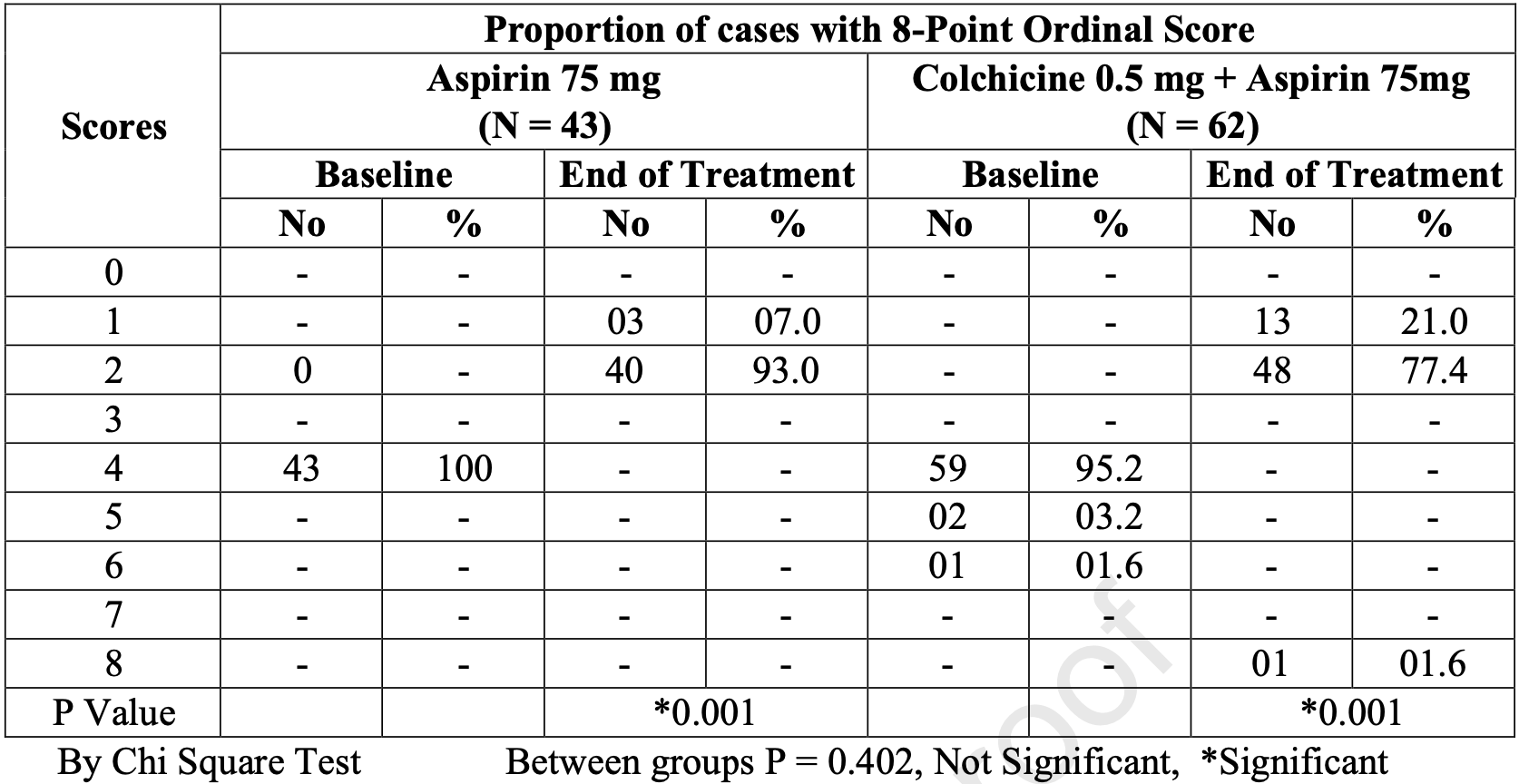
Effect of colchicine and aspirin given together in patients with moderate COVID-19
et al., Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070, CTRI/2021/03/032060, Jan 2023
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 122 hospitalized patients in India, showing improved recovery with colchicine treatment. All patients received aspirin. There was one death and higher progression in the colchicine arm, however 3 patients in the colchicine arm had baseline ordinal scores ≥5, while no patients in the control arm did.
|
risk of death, 169.4% higher, RR 2.69, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 62 (1.6%), control 0 of 43 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of progression, 108.1% higher, RR 2.08, p = 0.64, treatment 3 of 62 (4.8%), control 1 of 43 (2.3%).
|
|
recovery, 7.3% lower, RR 0.93, p = 0.21, treatment 62, control 43, relative improvement in ordinal score.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 15.0% lower, RR 0.85, p = 0.06, treatment 49 of 62 (79.0%), control 40 of 43 (93.0%), NNT 7.1, ordinal score ≤1.
|
|
recovery, 24.3% lower, RR 0.76, p = 0.02, treatment 62, control 43, relative improvement in CT score.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Sunil Naik et al., 21 Jan 2023, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 3 authors, trial CTRI/2021/03/032060.
Contact: rmg.trial21@gmail.com.
Effect of colchicine and aspirin given together in patients with moderate COVID-19
Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications, doi:10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
Declaration of interests ☐ The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. ☒The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests: The study has been funded by ROMEG therapeutics LLC n but there is no financial interest to disclose related to trial results and manuscript writing/reviewing/publishing. J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Anesthesia, None, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292J
Arif, Aggarwal, Salicylic Acid (Aspirin)
Bester, Matshailwe, Pretorius, Simultaneous presence of hypercoagulation and increased clot lysis time due to IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8, Cytokine, doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2018.01.007
Bianconiv, Violi, Fallarino, Pignatelli, Sahebkara et al., Is Acetylsalicylic Acid a Safe and Potentially Useful Choice for Adult Patients with COVID-19?, Drugs, doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01365-1
Cao, Wang, Wen, A Trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Adults Hospitalized with Severe Covid-19, New England Journal of Medicine, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Chandwani, Shuter, Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: a review, Ther Clin Risk Manag, doi:10.2147/tcrm.s3285
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Aspirin Use is Associated with Decreased Mechanical Ventilation, ICU Admission
Cui, Chen, Li, Liu, Wang, Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia, J ThrombHaemost, doi:10.1111/jth.14830
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatisda, Effect of Colchicine vs Standard Care on Cardiac and Inflammatory Biomarkers and Clinical Outcomes in Patients Hospitalized With Coronavirus Disease, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136
Giannis, Ziogasia, Gianni, Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past, J Clin Virol, doi:10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104362
Godino, Scotti, Maugeri, Antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19? -Rationale and Evidence, International Journal of Cardiology, doi:10.1016/j.ijcard.2020.09.064
Healio, FDA approves ticagrelor-aspirin DAPT to reduce MI, stroke in CAD
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
J O U R N A L P R E, -p r o o f
Leung, Hui, Kraus, Colchicine--Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses, Semin Arthritis Rheum, doi:10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: an interim analysis of a randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled clinical trial. medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.08.06.20169573
Marotta, FDA: Center for Drug Evaluation and Research; Labelling of Aspirin. Food and Drug Administration
Schlesinger, Firestein, Brunetti, Colchicine in COVID-19: an Old Drug, NewUse. CurrPharmacol Rep, doi:10.1007/s40495-020-00225-
Sriram, Insel Inflammation and thrombosis in COVID-19 pathophysiology: proteinase-activated and purinergic receptors as drivers and candidate therapeutic targets, Physiological Reviews
Tardif, Kouz, Waters, Efficacy and Safety of Low-Dose Colchicine after Myocardial Infarction, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1912388
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19:immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nature Reviews Immunology, doi:10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070",
"ISSN": [
"2451-8654"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070",
"alternative-id": [
"S2451865423000169"
],
"article-number": "101070",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Effect of colchicine and aspirin given together in patients with moderate COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Published by Elsevier Inc."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sunil Naik",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Andhalkar",
"given": "Niranjan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pendse",
"given": "Sohal",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications",
"container-title-short": "Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-21T16:36:53Z",
"timestamp": 1674319013000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-21T16:37:03Z",
"timestamp": 1674319023000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-22T05:47:52Z",
"timestamp": 1674366472638
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 13,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673654400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451865423000169?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2451865423000169?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101070",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2001282",
"article-title": "A trial of lopinavir–ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe covid-19",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1787",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib2",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID-19:immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat. Rev. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Antithrombotic therapy in patients with COVID-19? - rationale and evidence-",
"author": "Godino",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Cardiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cyto.2018.01.007",
"article-title": "Simultaneous presence of hypercoagulation and increased clot lysis time due to IL-1β, IL-6 and IL-8",
"author": "Bester",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "237",
"journal-title": "Cytokine",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib5",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40265-020-01365-1",
"article-title": "Is acetylsalicylic acid a safe and potentially useful choice for adult patients with COVID-19?",
"author": "BianconiV",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1383",
"issue": "14",
"journal-title": "Drugs",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib6",
"volume": "80",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jth.14830",
"article-title": "Prevalence of venous thromboembolism in patients with severe novel coronavirus pneumonia",
"author": "Cui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1421",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J ThrombHaemost",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib7",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104362",
"article-title": "Coagulation disorders in coronavirus infected patients: COVID-19, SARS-CoV-1, MERS-CoV and lessons from the past",
"author": "Giannis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib8",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/physrev.00035.2020",
"article-title": "Insel Inflammation and thrombosis in COVID-19 pathophysiology: proteinase-activated and purinergic receptors as drivers and candidate therapeutic targets",
"author": "Sriram",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "545",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Physiol. Rev.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib9",
"volume": "101",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Lopinavir/ritonavir in the treatment of HIV-1 infection: a review",
"author": "Chandwani",
"first-page": "1023",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Therapeut. Clin. Risk Manag.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib10",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.semarthrit.2015.06.013",
"article-title": "Colchicine-Update on mechanisms of action and therapeutic uses",
"author": "Leung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "341",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Semin. Arthritis Rheum.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib11",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"article-title": "Salicylic acid (aspirin)",
"author": "Arif",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib12",
"series-title": "StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Colchicine in COVID-19: an old drug, NewUse",
"author": "Schlesinger",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "CurrPharmacol Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa1912388",
"article-title": "Efficacy and safety of low-dose colchicine after myocardial infarction",
"author": "Tardif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2497",
"issue": "26",
"journal-title": "N. Engl. J. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib14",
"volume": "381",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "FDA: center for drug evaluation and Research; labelling of aspirin",
"journal-title": "Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib15",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "New aspirin formulation nabs FDA approval",
"author": "Marotta",
"journal-title": "Pharmacy Times. Published2015.",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Healio",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019",
"author": "Deftereos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw. Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib18",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: an interim analysis of a randomized, double-blinded, placebo controlled clinical trial",
"author": "Lopes",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Chow",
"key": "10.1016/j.conctc.2023.101070_bib20",
"series-title": "Aspirin Use Is Associated with Decreased Mechanical Ventilation, ICU Admission, and In-Hospital Mortality in Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 19,
"references-count": 19,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2451865423000169"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Pharmacology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Effect of colchicine and aspirin given together in patients with moderate COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
