Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19
et al., Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011, May 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
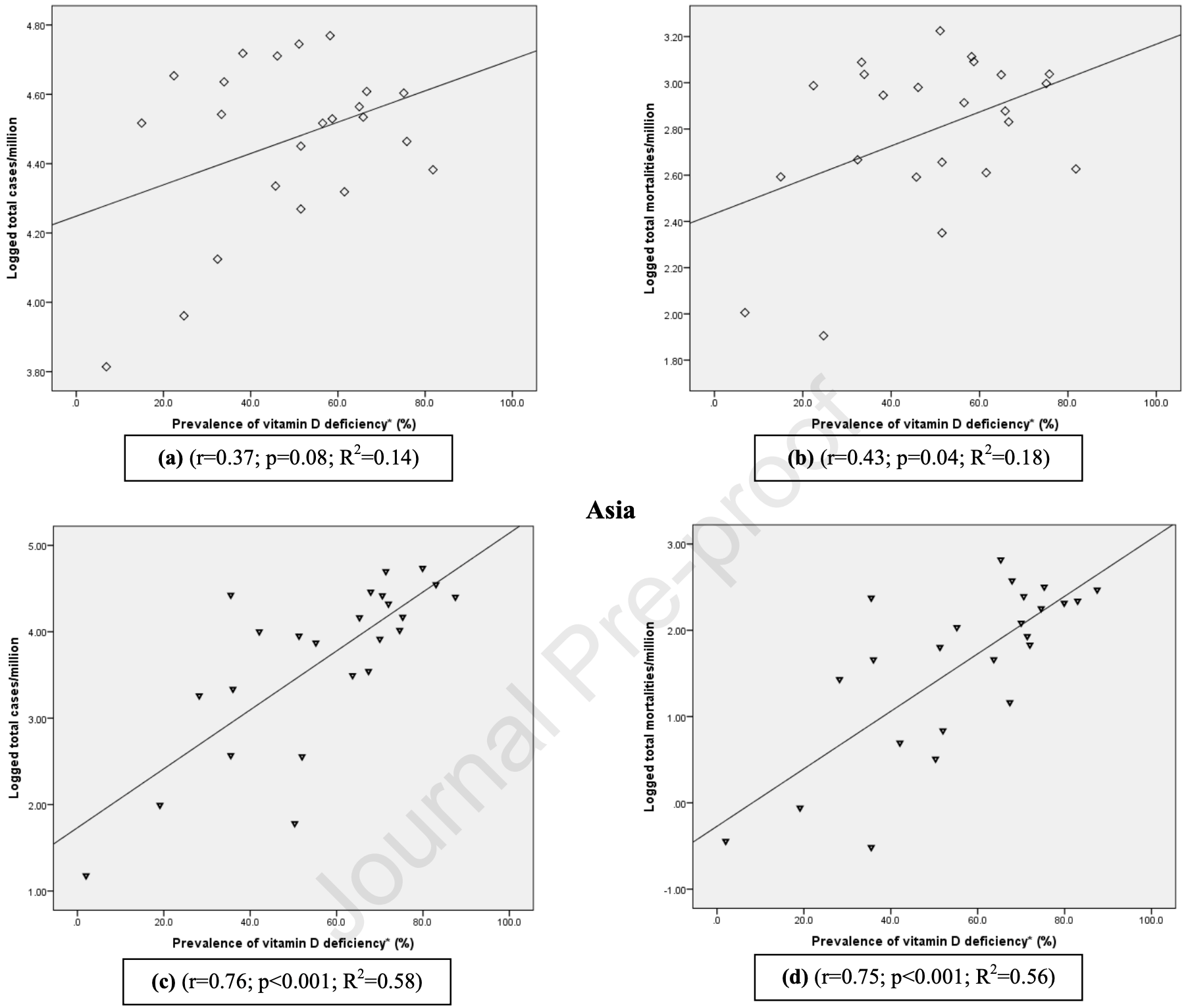
Analysis of vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 cases and deaths in 47 countries, showing vitamin D deficiency significantly associated with mortality.
Sooriyaarachchi et al., 29 May 2021, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN, doi:10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011
Background & aims: COVID-19 has emerged as a global pandemic affecting millions of people. Vitamin D deficiency is one of the risk factors for increased susceptibility to COVID-19. This study aimed to examine the correlation between the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 infection and mortality rates among the adult population in European and Asian continents. Methods: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in each country was retrieved through literature searching on PubMed® database for the last ten years. As of December, 31 st 2020, COVID-19 infections and mortalities per million population were extracted from the 'real time' statistics of the Worldometer website. The association between both vitamin D deficiency and COVID-19 infections and mortalities were explored. Results: Forty seven countries were included in the analysis. The prevalence of vitamin D deficiency ranged from 6.9 to 81.8% in European countries and 2.0e87.5% in Asian countries. Significantly positive correlations were observed for both COVID-19 infection (r ¼ 0.76; p < 0.001) and mortality rates (r ¼ 0.75; p < 0.001) in the Asian continent. The correlation values for the infections and mortality rates in the European continent were (r ¼ 0.37; p ¼ 0.08) and (r ¼ 0.43; p ¼ 0.04) respectively. When both the continents were combined, the correlation results for both infection (r ¼ 0.42; p ¼ 0.003) and mortality (r ¼ 0.35; p ¼ 0.016) rates with vitamin D deficiency values remained significant. Conclusion: Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was significantly associated with the mortality rate of COVID-19 in Europe and Asia. The association between the infection rate and prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was significant for Asia only. Both the associations were significant when the two continents were combined in the analysis. Therefore we suggest that vitamin D supplementation could play a key role in the prevention and/or treatment of the COVID-19 patients.
Authors' contributions RJ devised the conceptual idea. PS and DTJ searched databases. PS and DTJ were involved in retrieving data and analysis. PS and RJ drafted the manuscript. NK revised the manuscript. All authors provided critical feedback on the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics declarations Not applicable.
Declaration of competing interest The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
Abiaka, Delghandi, Kaur, Saleh, Vitamin D status and anthropometric indices of an Omani study population, Sultan Qaboos University Med J
Acherjya, Ali, Tarafder, Akhter, Chowdhury et al., Study of vitamin D deficiency among the apparently healthy population in Jashore, Bangladesh, Mymensingh Med J
Adebayo, Itkonen, Lilja, Jaaskelainen, Lundqvist et al., Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among three immigrant groups in Finland: evidence from a population-based study using standardised 25-hydroxyvitamin D data, Publ Health Nutr, doi:10.1017/s1368980019004312
Al-Hilali, Prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in adult Iraqi people including postmenopausal women, Sci Res J
Almesri, Das, Ali, Gumaa, Giha, Gender-dependent association of vitamin D deficiency with obesity and hypercholesterolemia (LDLC) in adults. Endocrine, metabolic & immune disorders-drug targets (formerly current drug targets-immune, Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders
Altowijri, Alloubani, Abdulhafiz, Saleh, Impact of nutritional and environmental factors on vitamin D deficiency. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP, Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP
Asakura, Etoh, Imamura, Michikawa, Nakamura et al., Vitamin D status in Japanese adults: relationship of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with simultaneously measured dietary vitamin D intake and ultraviolet ray exposure, Nutrients
Bae, Kim, The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19, Molecules
Benoit, Linear regression models with logarithmic transformations
Bi, Tey, Leong, Quek, Henry, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Singapore: its implications to cardiovascular risk factors, PloS One
Borissova, Shinkov, Vlahov, Dakovska, Todorov et al., Vitamin D status in Bulgaria-winter data, Arch Osteoporos
Bromage, Rich-Edwards, Tselmen, Baylin, Houghton et al., Seasonal epidemiology of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations among healthy adults living in rural and urban areas in Mongolia, Nutrients
Cannell, Vieth, Umhau, Holick, Grant et al., Epidemic influenza and vitamin D, Epidemiol Infect
Cantorna, Snyder, Lin, Yang, Vitamin D and 1, 25 (OH) 2D regulation of T cells, Nutrients
Castillo, Costa, Barrios, Díaz, Miranda et al., Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Chaudhry, Dranitsaris, Mubashir, Bartoszko, Riazi, A country level analysis measuring the impact of government actions, country preparedness and socioeconomic factors on COVID-19 mortality and related health outcomes, EClinicalMedicine
Coli C Bari C, Keser, Bituh, Rumbak, Samarin et al., Vitamin D status and prevalence of inadequacy in Croatian population
Danai, Sinha, Moss, Haber, Martin, Seasonal variation in the epidemiology of sepsis, Crit Care Med
Deplanque, Wullens, Norberciak, Prevalence and risk factors of vitamin D deficiency in healthy adults aged 18-65 years in northern France, Rev Med Interne
Dimakopoulos, Magriplis, Mitsopoulou, Karageorgou, Bakogianni et al., Association of serum vitamin D status with dietary intake and sun exposure in adults, Clin Nutr ESPEN
Dimitrov, Barbier, Ismailova, Wang, Dmowski et al., Vitamin D-regulated gene expression profiles: species-specificity and cellspecific effects on metabolism and immunity, Endocrinology
Duarte, Carvalheiro, Rodrigues, Dias, Marques et al., Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its predictors in the Portuguese population: a nationwide population-based study, Arch Osteoporos
Esmaeili, Mohammadian, Radbakhsh, Momtazi-Borojeni, Parizi et al., Evaluation of vitamin D3 deficiency: a population-based study in northeastern Iran, J Cell Biochem
Fraser, Vitamin D-deficiency in Asia, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Giuliani, Barbieri, Pierro, Rossi, Widmann et al., LCeMS/MS based 25 (OH) D status in a large Southern European outpatient cohort: gender-and age-specific differences, Eur J Nutr
Gonz Alez-Molero, Morcillo, Vald Es, Erez-Valero, Botas et al., Vitamin D deficiency in Spain: a population-based cohort study, Eur J Clin Nutr
Grant, Lahore, Mcdonnell, Baggerly, French et al., Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths, Nutrients
Grant, Variations in vitamin D production could possibly explain the seasonality of childhood respiratory infections in Hawaii, Pediatr Infect Dis J
Griffin, Wall, Blake, Griffin, Robinson et al., Higher risk of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency for rural than urban dwellers, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Gromova, Doschanova, Lokshin, Tuletova, Grebennikova et al., Vitamin D deficiency in Kazakhstan: cross-sectional study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Guessous, Dudler, Glatz, Theler, Zoller et al., Vitamin D levels and associated factors: a population-based study in Switzerland, Swiss Med Wkly
G€ Oktas, Ersoy, Ercan, Can, Vitamin D status in the adult population of Bursa-Turkey, Eur J Gen Pract
Hansen, Tjønneland, Køster, Brot, Andersen et al., Vitamin D status and seasonal variation among Danish children and adults: a descriptive study, Nutrients
Ho-Pham, Nguyen, Lai, Eisman, Nguyen, Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone in a urban population in Vietnam, Osteoporos Int
Hoge, Donneau, Streel, Kolh, Chapelle et al., Vitamin D deficiency is common among adults in Wallonia (Belgium, 51 30' North): findings from the Nutrition, Environment and Cardio-Vascular Health study, Nutr Res
Hribar, Hristov, Gregori C M, Blaznik, Zaletel et al., Nutrihealth study: seasonal variation in vitamin D status among the slovenian adult and elderly population, Nutrients
Jayawardena, Jeyakumar, Francis, Misra, Impact of the vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 infection and morality in Asian countries, Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review. Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome, Clin Res Rev
Jiang, Wu, Xiao, Ding, Chen, An epidemiology survey of vitamin D deficiency and its influencing factors, Med Clínica
Jin, Agarwala, Kundu, Harvey, Zhang et al., Assessment of individual-and community-level risks for COVID-19 mortality in the US and implications for vaccine distribution, medRxiv
Jolliffe, Hanifa, Witt, Venton, Rowe et al., Environmental and genetic determinants of vitamin D status among older adults in London, UK, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Kandhro, Dahot, Naqvi, Ujjan, Study of Vitamin D deficiency and contributing factors in the population of Hyderabad, Pakistan, Pak J Pharm Sci
Karonova, Andreeva, Nikitina, Belyaeva, Mokhova et al., Prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in the North-West region of Russia: a cross-sectional study, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Khasawneh, Hiari, Khalaileh, Khasawneh, Alzghoul et al., Frequency of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in a Jordanian cohort: a hospital based study, J Royal Med Services
Kull, Kallikorm, Tamm, Lember, Seasonal variance of 25-(OH) vitamin D in the general population of Estonia, a Northern European country, BMC Publ Health
La, Alzoughool, Atoum, The human coronavirus disease COVID-19: its origin, characteristics, and insights into potential drugs and its mechanisms, Pathogens
Laird, Rhodes, Kenny, Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19, Ir Med J
Leong, Yakob, Fung, Pande, High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in a mixed sample of patients in Brunei Darussalam, Brunei Int Med J
Lips, Cashman, Lamberg-Allardt, Bischoff-Ferrari, Obermayer-Pietsch et al., Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society, Eur J Endocrinol
Lips, Vitamin D status and nutrition in Europe and Asia, J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol
Liu, Zhu, Zhang, Li, Peng, Intravenous high-dose vitamin C for the treatment of severe COVID-19: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial, BMJ open
Maggini, Wintergerst, Beveridge, Hornig, Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses, Br J Nutr
Mallapaty, Vaccines are curbing COVID: data from Israel show drop in infections, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-00316-4
Mechenro, Venugopal, Kumar, Balakrishnan, Ramakrishna, Vitamin D status in kancheepuram district, Tamil nadu, India, BMC Publ Health
Niculescu, Capatina, Dusceac, Caragheorgheopol, Ghemigian et al., Seasonal variation of serum vitamin D levels in Romania, Arch Osteoporosis
N€ Als En, Becker, Pearson, Ridefelt, Lindroos et al., Vitamin D status in children and adults in Sweden: dietary intake and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in children aged 10-12 years and adults aged 18-80 years, J Nutr Sci
Olliver, Spelmink, Hiew, Meyer-Hoffert, Henriques-Normark et al., Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae, J Infect Dis
Petrenya, Lamberg-Allardt, Melhus, Broderstad, Brustad, Vitamin D status in a multi-ethnic population of northern Norway: the SAMINOR 2 clinical survey, Publ Health Nutr
Povoroznyuk, Balatska, Muts, Klymovytsky, Synenky, Vitamin D deficiency in Ukraine: a demographic and seasonal analysis, Gerontol
Pugach, Pugach, Strong correlation between prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency and population mortality rate from COVID-19 in Europe, Wien Klin Wochenschr, doi:10.1007/s00508-021-01833-y
Płudowski, Ducki, Konstantynowicz, Jaworski, Vitamin D status in Poland, Pol Arch Med Wewn
Rabenberg, Scheidt-Nave, Busch, Thamm, Rieckmann et al., Implications of standardization of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data for the evaluation of vitamin D status in Germany, including a temporal analysis, BMC Publ Health
Radujkovic, Hippchen, Tiwari-Heckler, Dreher, Boxberger, Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients, Nutrients
Rajatanavin, Kanokrungsee, Aekplakorn, Vitamin D status in Thai dermatologists and working-age Thai population, J Dermatol
Saad, Akiki, Rahme, Ajjour, Assaad et al., Time trends and predictors of hypovitaminosis D across the life course: 2009e2016, Metabolism
Scharla, Prevalence of subclinical vitamin D deficiency in different European countries, Osteoporos Int
Sebekova, Krivosikova, Gajdos, Podracka, Vitamin D status in apparently healthy medication-free Slovaks: association to blood pressure, body mass index, self-reported smoking status and physical activity, Bratisl Lek Listy
Shafinaz, Moy, Vitamin D level and its association with adiposity among multi-ethnic adults in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: a cross sectional study, BMC Publ Health
Sherchand, Sapkota, Chaudhari, Khan, Baranwal et al., Association between vitamin D deficiency and depression in Nepalese population, Psychiatr Res
Sokolovic, Alimanovic-Alagic, Dzananovic, Cavaljuga, Beslic et al., Vitamin D status in Bosnia and Herzegovina: the cross-sectional epidemiological analysis, Osteoporos Int
Sooriyaarachchi, Jeyakumar, King, None, Clinical Nutrition ESPEN
Spiro, Buttriss, Vitamin D: an overview of vitamin D status and intake in E urope, Nutr Bull
Tsiaras, Weinstock, Factors influencing vitamin D status, Acta Derm Venereol
Van Schoor, Lips, Global overview of vitamin D status, Endocrinol Metabol Clin
Van Schoor, Lips, Worldwide vitamin D status, Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metabol
Vj, Hormeño-Holgado, Enez, Benitez-Agudelo, Enez et al., Dynamics of population immunity due to the herd effect in the COVID-19 pandemic, Vaccines
Worldometer, COVID-19 coronovirus pandemic
Zainel, Qotba, Nuaimi, Syed, Vitamin D status among adults (18e65 years old) attending primary healthcare centres in Qatar: a crosssectional analysis of the Electronic Medical Records for the year 2017, BMJ Open
Zarooni, Marzouqi, Darmaki, Prinsloo, Nagelkerke, Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and associated comorbidities among Abu Dhabi Emirates population, BMC Res Notes
Zhang, Hooti, Zenki, Alomirah, Jamil et al., Vitamin D deficiency is associated with high prevalence of diabetes in Kuwaiti adults: results from a national survey, BMC Publ Health
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011",
"ISSN": [
"2405-4577"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011",
"alternative-id": [
"S2405457721001911"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 European Society for Clinical Nutrition and Metabolism. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9570-2344",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sooriyaarachchi",
"given": "Piumika",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3849-1795",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Jeyakumar",
"given": "Dhanushya T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "King",
"given": "Neil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayawardena",
"given": "Ranil",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"container-title-short": "Clinical Nutrition ESPEN",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalnutritionespen.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-05-30T00:23:04Z",
"timestamp": 1622334184000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-23T07:44:31Z",
"timestamp": 1658562271000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-23T23:30:13Z",
"timestamp": 1711236613683
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 18,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1627776000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721001911?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2405457721001911?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "372-378",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens9050331",
"article-title": "The human coronavirus disease COVID-19: its origin, characteristics, and insights into potential drugs and its mechanisms",
"author": "Alanagreh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "331",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Pathogens",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Worldometer",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib2",
"series-title": "COVID-19 coronovirus pandemic",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/vaccines8020236",
"article-title": "Dynamics of population immunity due to the herd effect in the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Clemente-Suárez",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "236",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Vaccines",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib3",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2020.100464",
"article-title": "A country level analysis measuring the impact of government actions, country preparedness and socioeconomic factors on COVID-19 mortality and related health outcomes",
"author": "Chaudhry",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100464",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib4",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Jin",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib5",
"series-title": "Assessment of individual-and community-level risks for COVID-19 mortality in the US and implications for vaccine distribution",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ecl.2017.07.002",
"article-title": "Global overview of vitamin D status",
"author": "Van Schoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "845",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Endocrinol Metabol Clin",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib6",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2340/00015555-0980",
"article-title": "Factors influencing vitamin D status",
"author": "Tsiaras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "115",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Acta Derm Venereol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib7",
"volume": "91",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.beem.2011.06.007",
"article-title": "Worldwide vitamin D status",
"author": "van Schoor",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "671",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metabol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib8",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.CCM.0000253405.17038.43",
"article-title": "Seasonal variation in the epidemiology of sepsis",
"author": "Danai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "410",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib9",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/INF.0b013e3181817bc1",
"article-title": "Variations in vitamin D production could possibly explain the seasonality of childhood respiratory infections in Hawaii",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "853",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Infect Dis J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib10",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0950268806007175",
"article-title": "Epidemic influenza and vitamin D",
"author": "Cannell",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Epidemiol Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib11",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1210/endocr/bqaa218",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-regulated gene expression profiles: species-specificity and cell-specific effects on metabolism and immunity",
"author": "Dimitrov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "bqaa218",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Endocrinology",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib12",
"volume": "162",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jit355",
"article-title": "Immunomodulatory effects of vitamin D on innate and adaptive immune responses to Streptococcus pneumoniae",
"author": "Olliver",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1474",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib13",
"volume": "208",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12040988",
"article-title": "Evidence that vitamin D supplementation could reduce risk of influenza and COVID-19 infections and deaths",
"author": "Grant",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "988",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0007114507832971",
"article-title": "Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses",
"author": "Maggini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S29",
"issue": "S1",
"journal-title": "Br J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib15",
"volume": "98",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25225346",
"article-title": "The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19",
"author": "Bae",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "22",
"journal-title": "Molecules",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib16",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2020-039519",
"article-title": "Intravenous high-dose vitamin C for the treatment of severe COVID-19: study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Liu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "BMJ open",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib17",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu7043011",
"article-title": "Vitamin D and 1, 25 (OH) 2D regulation of T cells",
"author": "Cantorna",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3011",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib18",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"author": "Benoit",
"first-page": "23",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib19",
"volume": "vol. 22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2015.06.005",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is common among adults in Wallonia (Belgium, 51°30' North): findings from the Nutrition, Environment and Cardio-Vascular Health study",
"author": "Hoge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "716",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nutr Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib20",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-016-3831-0",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Bosnia and Herzegovina: the cross-sectional epidemiological analysis",
"author": "Sokolovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1021",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib21",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-013-0133-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Bulgaria--winter data",
"author": "Borissova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "133",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporos",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib22",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib23",
"series-title": "Vitamin D status and prevalence of inadequacy in Croatian population",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu10111801",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and seasonal variation among Danish children and adults: a descriptive study",
"author": "Hansen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1801",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib24",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980019004312",
"article-title": "Prevalence and determinants of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency among three immigrant groups in Finland: evidence from a population-based study using standardised 25-hydroxyvitamin D data",
"author": "Adebayo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1254",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Publ Health Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib25",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.revmed.2016.12.013",
"article-title": "Prevalence and risk factors of vitamin D deficiency in healthy adults aged 18-65 years in northern France",
"author": "Deplanque",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "368",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Rev Med Interne",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib26",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-018-5769-y",
"article-title": "Implications of standardization of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D data for the evaluation of vitamin D status in Germany, including a temporal analysis",
"author": "Rabenberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Publ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib27",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.09.008",
"article-title": "Association of serum vitamin D status with dietary intake and sun exposure in adults",
"author": "Dimakopoulos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Clin Nutr ESPEN",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib28",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105547",
"article-title": "Higher risk of vitamin D insufficiency/deficiency for rural than urban dwellers",
"author": "Griffin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105547",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib29",
"volume": "197",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00394-018-1803-1",
"article-title": "LC–MS/MS based 25 (OH) D status in a large Southern European outpatient cohort: gender-and age-specific differences",
"author": "Giuliani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2511",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Eur J Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib30",
"volume": "58",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S1368980018003816",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in a multi-ethnic population of northern Norway: the SAMINOR 2 clinical survey",
"author": "Petrenya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1186",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Publ Health Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib31",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Poland",
"author": "Płudowski",
"first-page": "530",
"issue": "7–8",
"journal-title": "Pol Arch Med Wewn",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib32",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-020-0695-x",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its predictors in the Portuguese population: a nationwide population-based study",
"author": "Duarte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporos",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib33",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11657-017-0407-3",
"article-title": "Seasonal variation of serum vitamin D levels in Romania",
"author": "Niculescu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Arch Osteoporosis",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib34",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.03.026",
"article-title": "Prevalence of Vitamin D deficiency in the North-West region of Russia: a cross-sectional study",
"author": "Karonova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "230",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib35",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in apparently healthy medication-free Slovaks: association to blood pressure, body mass index, self-reported smoking status and physical activity",
"author": "Sebekova",
"first-page": "702",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Bratisl Lek Listy",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib36",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061838",
"article-title": "Nutrihealth study: seasonal variation in vitamin D status among the slovenian adult and elderly population",
"author": "Hribar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib37",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ejcn.2010.265",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Spain: a population-based cohort study",
"author": "González-Molero",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "321",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Nutr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib38",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/jns.2020.40",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in children and adults in Sweden: dietary intake and 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations in children aged 10-12 years and adults aged 18-80 years",
"author": "Nälsén",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e47",
"journal-title": "J Nutr Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib39",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D levels and associated factors: a population-based study in Switzerland",
"author": "Guessous",
"journal-title": "Swiss Med Wkly",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib40",
"volume": "142",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Ukraine: a demographic and seasonal analysis",
"author": "Povoroznyuk",
"first-page": "191",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Gerontol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib41",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2016.01.005",
"article-title": "Environmental and genetic determinants of vitamin D status among older adults in London, UK",
"author": "Jolliffe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "30",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib42",
"volume": "164",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Gender-dependent association of vitamin D deficiency with obesity and hypercholesterolemia (LDLC) in adults. Endocrine, metabolic & immune disorders-drug targets (formerly current drug targets-immune",
"author": "Almesri",
"first-page": "425",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Endocrine & Metabolic Disorders)",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib43",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Study of vitamin D deficiency among the apparently healthy population in Jashore, Bangladesh",
"author": "Acherjya",
"first-page": "214",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Mymensingh Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib44",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency and deficiency in a mixed sample of patients in Brunei Darussalam",
"author": "Leong",
"first-page": "134",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Brunei Int Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib45",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.medcli.2019.03.019",
"article-title": "An epidemiology survey of vitamin D deficiency and its influencing factors",
"author": "Jiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "7",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Med Clínica",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib46",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-018-6244-5",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in kancheepuram district, Tamil nadu, India",
"author": "Mechenro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Publ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib47",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcb.28317",
"article-title": "Evaluation of vitamin D3 deficiency: a population-based study in northeastern Iran",
"author": "Esmaeili",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10337",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Cell Biochem",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib48",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in adult Iraqi people including postmenopausal women",
"author": "Al-Hilali",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Sci Res J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib49",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12030743",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Japanese adults: relationship of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with simultaneously measured dietary vitamin D intake and ultraviolet ray exposure",
"author": "Asakura",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "743",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib50",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Frequency of vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in a Jordanian cohort: a hospital based study",
"author": "Khasawneh",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "5938",
"journal-title": "J Royal Med Services",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib51",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2019.105565",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency in Kazakhstan: cross-sectional study",
"author": "Gromova",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105565",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib52",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-016-2758-x",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency is associated with high prevalence of diabetes in Kuwaiti adults: results from a national survey",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Publ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib53",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.metabol.2020.154138",
"article-title": "Time trends and predictors of hypovitaminosis D across the life course: 2009–2016",
"author": "Saad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "154138",
"journal-title": "Metabolism",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib54",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12889-016-2924-1",
"article-title": "Vitamin D level and its association with adiposity among multi-ethnic adults in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia: a cross sectional study",
"author": "Shafinaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Publ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib55",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu8100592",
"article-title": "Seasonal epidemiology of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations among healthy adults living in rural and urban areas in Mongolia",
"author": "Bromage",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "592",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib56",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.psychres.2018.06.018",
"article-title": "Association between vitamin D deficiency and depression in Nepalese population",
"author": "Sherchand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "266",
"journal-title": "Psychiatr Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib57",
"volume": "267",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12816/0003227",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and anthropometric indices of an Omani study population",
"author": "Abiaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Sultan Qaboos University Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib58",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"article-title": "Study of Vitamin D deficiency and contributing factors in the population of Hyderabad, Pakistan",
"author": "Kandhro",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Pak J Pharm Sci",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib59",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjopen-2019-029334",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status among adults (18–65 years old) attending primary healthcare centres in Qatar: a cross-sectional analysis of the Electronic Medical Records for the year 2017",
"author": "Zainel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "BMJ Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib60",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of nutritional and environmental factors on vitamin D deficiency",
"author": "Altowijri",
"first-page": "2569",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP: Asian Pac J Cancer Prev APJCP",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib61",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0147616",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency in Singapore: its implications to cardiovascular risk factors",
"author": "Bi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PloS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib62",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/1346-8138.14742",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in Thai dermatologists and working-age Thai population",
"author": "Rajatanavin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "J Dermatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib63",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/13814788.2020.1846712",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status in the adult population of Bursa-Turkey",
"author": "Göktaş",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "156",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gen Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib64",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13104-019-4536-1",
"article-title": "Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and associated comorbidities among Abu Dhabi Emirates population",
"author": "Al Zarooni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Res Notes",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib65",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00198-010-1207-4",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and parathyroid hormone in a urban population in Vietnam",
"author": "Ho-Pham",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "241",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib66",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"article-title": "Vitamin D and inflammation: potential implications for severity of Covid-19",
"author": "Laird",
"first-page": "81",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Ir Med J",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib67",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12092757",
"article-title": "Vitamin D deficiency and outcome of COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Radujkovic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2757",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib68",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "Jayawardena",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib69",
"series-title": "Impact of the vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19 infection and morality in Asian countries",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00508-021-01833-y",
"article-title": "Strong correlation between prevalence of severe vitamin D deficiency and population mortality rate from COVID-19 in Europe",
"author": "Pugach",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "403",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Wien Klin Wochenschr",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib70",
"volume": "133",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/nbu.12108",
"article-title": "Vitamin D: an overview of vitamin D status and intake in E urope",
"author": "Spiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "322",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutr Bull",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib71",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2004.03.057",
"article-title": "Vitamin D-deficiency in Asia",
"author": "Fraser",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "491",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib72",
"volume": "89",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2006.12.076",
"article-title": "Vitamin D status and nutrition in Europe and Asia",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "620",
"issue": "3–5",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib73",
"volume": "103",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/PL00022726",
"article-title": "Prevalence of subclinical vitamin D deficiency in different European countries",
"author": "Scharla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S7",
"journal-title": "Osteoporos Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib74",
"volume": "8",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2458-9-22",
"article-title": "Seasonal variance of 25-(OH) vitamin D in the general population of Estonia, a Northern European country",
"author": "Kull",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Publ Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib75",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-00316-4",
"article-title": "Vaccines are curbing COVID: data from Israel show drop in infections",
"author": "Mallapaty",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "197",
"issue": "7845",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib76",
"volume": "590",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"article-title": "Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: a review",
"author": "Jayawardena",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clin Res Rev",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib77",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1530/EJE-18-0736",
"article-title": "Current vitamin D status in European and Middle East countries and strategies to prevent vitamin D deficiency: a position statement of the European Calcified Tissue Society",
"author": "Lips",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "P23",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Eur J Endocrinol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib78",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsbmb.2020.105751",
"article-title": "Effect of calcifediol treatment and best available therapy versus best available therapy on intensive care unit admission and mortality among patients hospitalized for COVID-19: a pilot randomized clinical study",
"author": "Castillo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "105751",
"journal-title": "J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol",
"key": "10.1016/j.clnesp.2021.05.011_bib79",
"volume": "203",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 79,
"references-count": 79,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2405457721001911"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Impact of vitamin D deficiency on COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "44"
}
