Targeting the coronavirus membrane protein: A promising novel therapeutic strategy
et al., Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029, Aug 2025
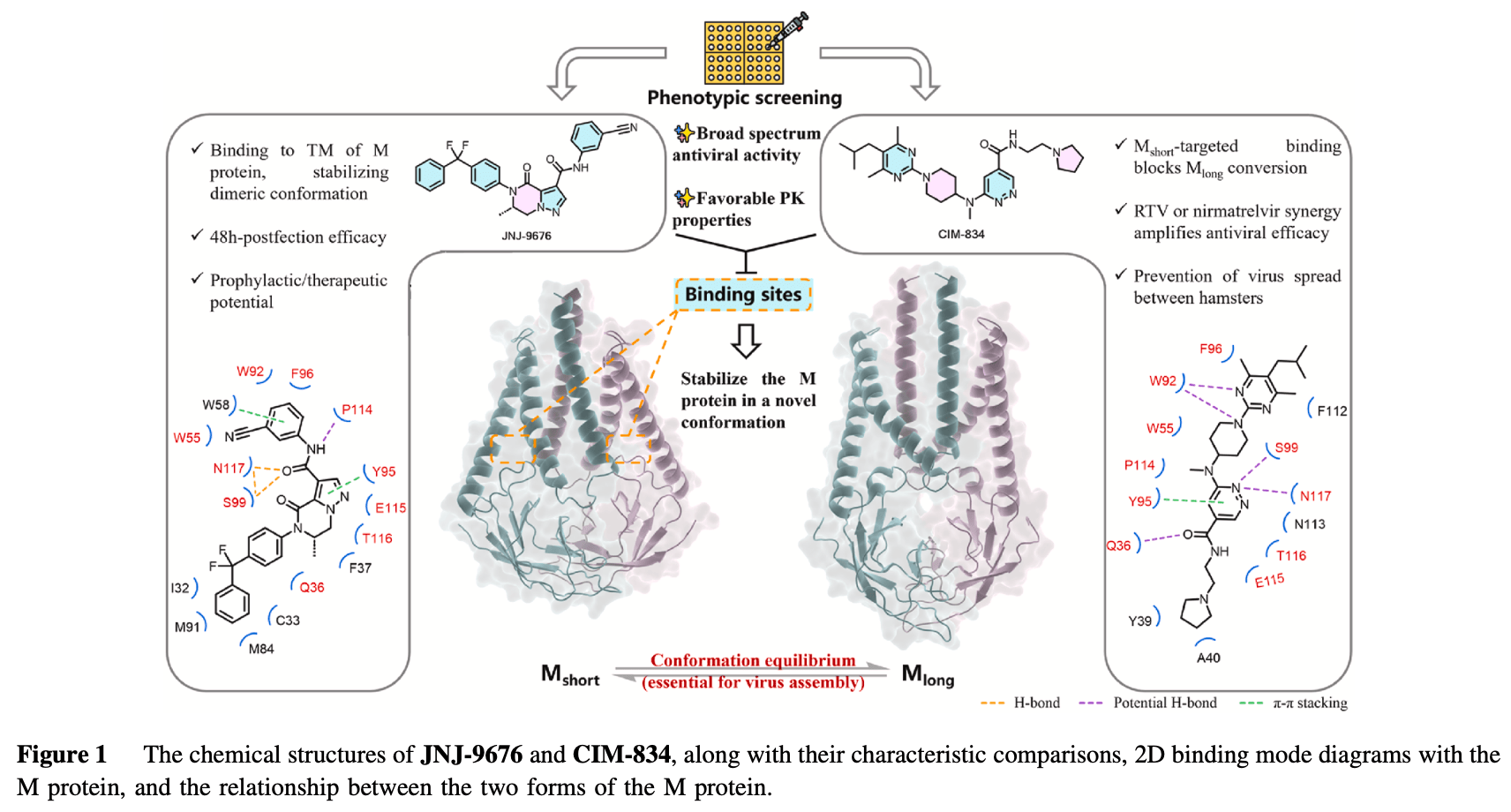
Review of preclinical research on two small-molecule inhibitors (JNJ-9676 and CIM-834) targeting the SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein, showing promising antiviral activity in cell culture and animal models.
Shi et al., 31 Aug 2025, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
Targeting the coronavirus membrane protein: A promising novel therapeutic strategy
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029
Coronavirus membrane protein; JNJ-9676; CIM-834; M protein The past two decades have witnessed multiple severe outbreaks caused by betacoronaviruses, including severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS), Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS), and coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Among these, the global pandemic of COVID-19 caused by SARS-CoV-2 has placed unprecedented pressure on public health systems worldwide. Current therapeutic options primarily include remdesivir, molnupiravir (targeting RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, RdRp), nirmatrelvir/ritonavir, and ensitrelvir (targeting main protease, M pro ). However, these drugs are limited by challenges such as drug resistance, drug-drug interactions, and reduced efficacy in specific clinical contexts. Consequently, there is an urgent need to develop novel antiviral agents targeting underexplored stages of the coronavirus replication cycle. In this context, two recent studies published in Nature have garnered significant attention by identifying small-molecule inhibitors that target the SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein (M protein) 1,2 . Specifically, JNJ-9676 and CIM-834 were shown to interfere with viral assembly, offering promising insights into the development of next-generation anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapeutics (Fig. 1 ). These findings highlight the potential of targeting the M protein as a novel strategy to address existing gaps in antiviral treatment. The coronavirus M protein is the most abundant viral structural protein and serves as a critical driver of viral assembly and morphogenesis. M protein exists in two distinct conformational states, M short and M long , and conformation equilibrium between these states are essential for the assembly process. By interacting with key viral components, including the nucleocapsid protein and genomic RNA, the M protein induces membrane curvature, a critical step in facilitating viral particle formation and maturation 3 . Due to its central role in viral assembly and its high degree of conservation across sarbecoviruses, the M protein emerges as a promising therapeutic target. However, current anti-SARS-CoV-2 therapies predominantly target the RdRp and the M pro , while the development of small-molecule inhibitors targeting M protein remains underexplored. This gap highlights the urgent need for novel therapeutic strategies targeting the M protein, which could offer substantial clinical benefits in the treatment of coronavirus infections. The identification of potential antiviral compounds targeting SARS-CoV-2 and related coronaviruses has been advanced through phenotypic screening and medicinal chemistry optimization. JNJ-9676 was identified by Van Loock and Draghia-Akli's team through high throughput-based phenotypic screening of the Janssen proprietary compound library 1 , while CIM-834 was discovered by Neyts and Chaltin's group following an imagingbased high-throughput, high-content phenotypic screening against SARS-CoV-2, coupled with medicinal chemistry..
Author contributions Dazhou Shi: Writing -original draft, review & editing. Chunhua Ma: Funding acquisition, Validation. Shujing Xu: Writing -review & editing, Conceptualization. Peng Zhan: Writing-review & editing, supervision, funding acquisition, conceptualization.
Conflicts of interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
Dai, Zhang, Jiang, Su, Li et al., Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease, Sci Technol Humanit
Du, Liu, Hu, Zhan, Targeting novel sites represents an effective strategy for combating drug resistance, Chin Chem Lett
Duan, Zhou, Liu, Iketani, Lin et al., Molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir, Nature
Laporte, Jochmans, Bardiot, Desmarets, Antoniak et al., A coronavirus assembly inhibitor that targets the viral membrane protein, Nature
Van Damme, Abeywickrema, Yin, Xie, Jacobs et al., A small-molecule SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor targeting the membrane protein, Nature
Vernuccio, Martı ´nez Leo ´n, Poojari, Buchrieser, Selverian et al., Structural insights into tecovirimat antiviral activity and poxvirus resistance, Nat Microbiol
Wu, Xu, Zhou, Shi, Wang et al., Harnessing molecular proximity for antiviral innovations: advances in proximity-inducing modalities against viral infections, Sci China Chem
Xu, Wang, Shi, Wang, Qiao et al., Discovery and mechanism verification of first-in-class hydrophobic tagging-based degraders of HBV core protein, Acta Pharm Sin B
Yang, Kim, Zhan, Jun12682, a potent SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitor with exceptional antiviral efficacy in mice, Acta Pharm Sin B
Zhang, Nomura, Muramoto, Ekimoto, Uemura et al., Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly, Nat Commun
Zhang, Yang, Wang, Yu, Huang et al., Artificial intelligence in drug development, Nat Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029",
"ISSN": [
"2211-3835"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029",
"alternative-id": [
"S2211383525003636"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Targeting the coronavirus membrane protein: A promising novel therapeutic strategy"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2025 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Chinese Pharmaceutical Association and Institute of Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Dazhou",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ma",
"given": "Chunhua",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Xu",
"given": "Shujing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-7168-613X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Zhan",
"given": "Peng",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"container-title-short": "Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-30T16:21:20Z",
"timestamp": 1748622080000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-19T17:06:53Z",
"timestamp": 1755623213000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-21T17:59:34Z",
"timestamp": 1755799174116,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/legal/tdmrep-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2025-08-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1754006400000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1748304000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383525003636?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2211383525003636?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "4309-4312",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-025-08651-6",
"article-title": "A small-molecule SARS-CoV-2 inhibitor targeting the membrane protein",
"author": "Van Damme",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "506",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib1",
"volume": "640",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-025-08773-x",
"article-title": "A coronavirus assembly inhibitor that targets the viral membrane protein",
"author": "Laporte",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "514",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib2",
"volume": "640",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-32019-3",
"article-title": "Structure of SARS-CoV-2 membrane protein essential for virus assembly",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4399",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib3",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Structure-based design of antiviral drug candidates targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease",
"author": "Dai",
"first-page": "1331",
"journal-title": "Sci Technol Humanit",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib4",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cclet.2024.110378",
"article-title": "Targeting novel sites represents an effective strategy for combating drug resistance",
"author": "Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110378",
"journal-title": "Chin Chem Lett",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib5",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2024.07.001",
"article-title": "Jun12682, a potent SARS-CoV-2 papain-like protease inhibitor with exceptional antiviral efficacy in mice",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4189",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib6",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.02.033",
"article-title": "Discovery and mechanism verification of first-in-class hydrophobic tagging-based degraders of HBV core protein",
"author": "Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2170",
"journal-title": "Acta Pharm Sin B",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib7",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"article-title": "Harnessing molecular proximity for antiviral innovations: advances in proximity-inducing modalities against viral infections",
"author": "Wu",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Sci China Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib8",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-024-03434-4",
"article-title": "Artificial intelligence in drug development",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "45",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib9",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06609-0",
"article-title": "Molecular mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 resistance to nirmatrelvir",
"author": "Duan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "376",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib10",
"volume": "622",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-025-01936-6",
"article-title": "Structural insights into tecovirimat antiviral activity and poxvirus resistance",
"author": "Vernuccio",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "734",
"journal-title": "Nat Microbiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.apsb.2025.05.029_bib11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2025"
}
],
"reference-count": 11,
"references-count": 11,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S2211383525003636"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Targeting the coronavirus membrane protein: A promising novel therapeutic strategy",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "15"
}