Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
et al., Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1177/2515690x241258403, PROSPERO CRD42023422779, Jun 2024
41st treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2022, now with p = 0.00028 from 6 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
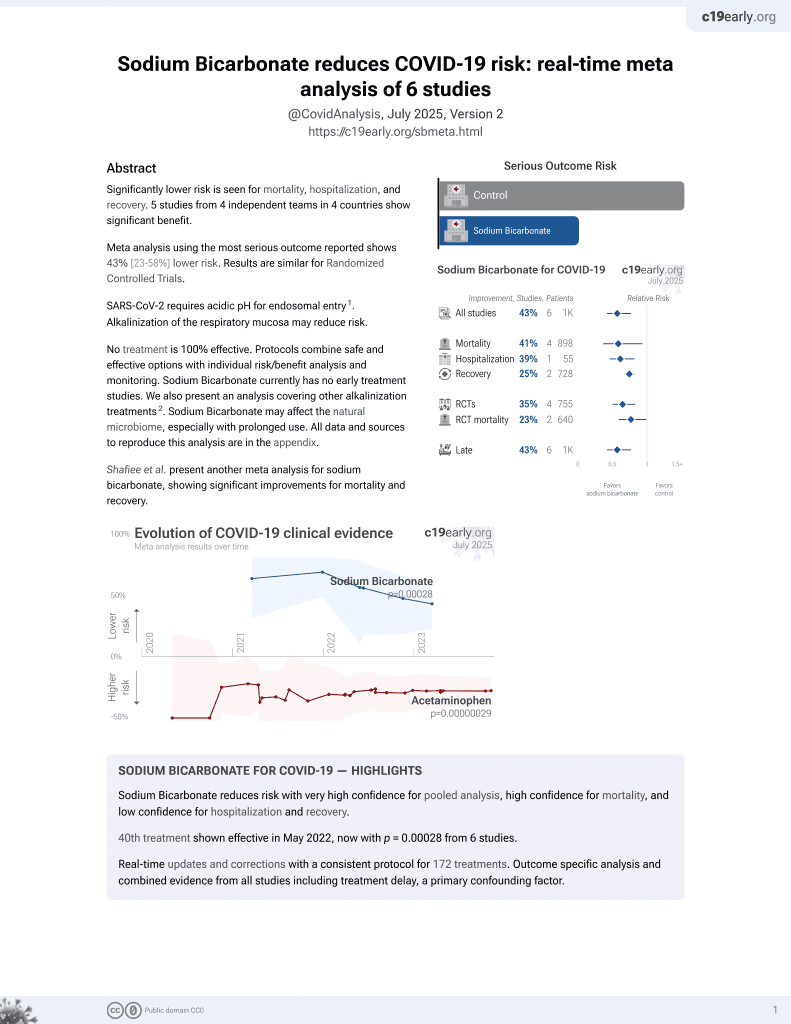
Meta analysis of 7 studies showing significantly lower mortality, shorter hospitalization, and higher recovery with alkalinization using sodium bicarbonate for COVID-19.
Currently there are 6 sodium bicarbonate studies and meta-analysis shows:
| Outcome | Improvement |
|---|---|
| Mortality | 41% lower [6‑63%] |
| Hospitalization | 39% lower [18‑54%] |
|
risk of death, 27.0% lower, RR 0.73, p = 0.02.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 39.0% lower, RR 0.61, p = 0.30.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 53.1% lower, RR 0.47, p < 0.001, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Shafiee et al., 3 Jun 2024, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, trial PROSPERO CRD42023422779.
Contact: hamidrezamozhgani@gmail.com.
Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine, doi:10.1177/2515690x241258403
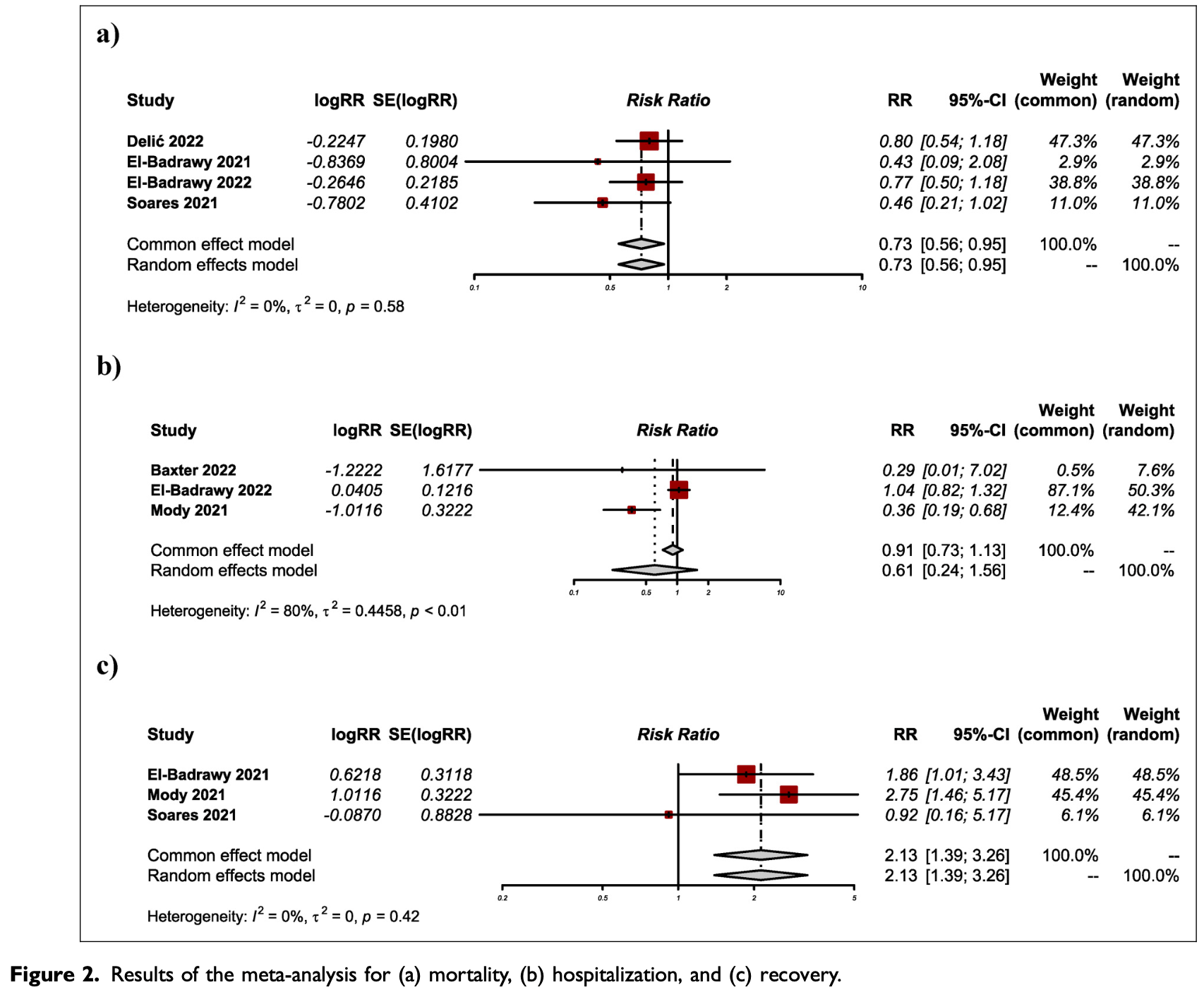
Background: A systematic review and meta-analysis have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of alkalinization for COVID-19 patients based on current evidence to determine the impact of alkalinization on COVID-19 outcomes. Methods: We searched MEDLINE (Pubmed), Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinicaltrials.gov for studies evaluating the efficacy of alkalinization up to 30 April 2023. Based on the PRISMA 2020 statement criteria a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies were performed. Results: The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in mortality rate in the alkalinization group compared to controls (RR 0.73, 95% CI: 0.56-0.95; I2 = 0%). However, our subgroup analysis showed no significant improvement in RCT-only studies (RR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.59-1.05; I2 = 0%), the recovery rate was significantly higher in the alkalinization group (RR 2.13, 95% CI: 1.39-3.26; I2 = 0%), duration of recovery also has improved in alkalinization group (SMD 0.76, 95% CI: 0.33-1.18; I2 = 0%). The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in the duration of hospitalization in the alkalinization group compared to controls with very low certainty of evidence (SMD -0.66, 95% CI: -0.97 to -0.35; I2 = 36%). Conclusion: With low certainty of evidence, alkalinization (by sodium bicarbonate) can be an efficient and safe adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 patients. Future randomized controlled trials are needed to strengthen the available evidence.
Conclusion Alkalinization using sodium bicarbonate in COVID-19 patients showed possible advantages through reducing the risk of mortality, and improving recovery rates. Although the results of the current study suggest the positive effect of alkalinization on COVID-19 outcomes, but higher-quality studies should concentrate on the investigation of alkalinization in COVID-19.
CRediT Author Statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests The authors declare that they have no known competing interests.
Ethical Approval This study was approved by the ethics committee of Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Alborz, Karaj, Iran (IR.ABZUMS.REC.1402.154).
Informed Consent
Not applicable
Supplemental material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
Abdullah, Periasamy, Ismail, Nasal irrigation as treatment in sinonasal symptoms relief: a review of its efficacy and clinical applications, Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg
Balduzzi, Rücker, Schwarzer, How to perform a meta-analysis with R: a practical tutorial, Evid Based Ment Health
Baxter, Schwartz, Johnson, Rapid initiation of nasal saline irrigation to reduce severity in high-risk COVID + outpatients, Ear Nose Throat J
Browning, Pharmacology of chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine Chloroquine Retinopathy, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-0597-3_2
Cadegiani, Wambier, Goren, Spironolactone: an antiandrogenic and anti-hypertensive drug that may provide protection against the novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) induced acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in COVID-19, Front Med, doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00453
Cardenas, Rifas-Shiman, Sordillo, DNA Methylation architecture of the ACE2 gene in nasal cells of children, Sci Rep
Carrouel, Valette, Gadea, Use of an antiviral mouthwash as a barrier measure in the SARS-CoV-2 transmission in adults with asymptomatic to mild COVID-19: a multicentre, randomized, double-blind controlled trial, Clin Microbiol Infect
Ceramella, Iacopetta, Sinicropi, Drugs for COVID-19: An Update, Molecules
Cheema, Rehman, Elrashedy, Antiandrogens for the treatment of COVID-19 patients: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Med Virol
Chen, Shen, Rowan, Elevated ACE-2 expression in the olfactory neuroepithelium: Implications for anosmia and upper respiratory SARS-CoV-2 entry and replication, Eur Respir J
Chu, Mcelroy, Chu, Bauman, Whittaker, The avian coronavirus infectious bronchitis virus undergoes direct low-pH-dependent fusion activation during entry into host cells, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.80.7.3180-3188.2006
Delic, Matetic, Domjanovic, Effects of different inhalation therapy on ventilator-associated pneumonia in ventilated COVID-19 patients: a randomized controlled trial, Microorganisms
El-Badrawy, Elmorsey, El-Hadidy, El-Badrawy, Shokeir, A randomized controlled trial of adjuvant inhalable sodium bicarbonate role in treatment of COVID-19
El-Badrawy, Saleh, El-Badrawy, Role of sodium bicarbonate as adjuvant treatment of nonsevere computed tomography-identified COVID-19 pneumonia: a preliminary report, Indian J Respir Care
Guyatt, Oxman, Vist, GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations, Br Med J
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor, Cell
Huijghebaert, Hoste, Vanham, Correction to: essentials in saline pharmacology for nasal or respiratory hygiene in times of COVID-19, Eur J Clin Pharmacol
Kraut, Cheetham-Wilkinson, Swan, Stagi, Kurtz, Impact of various buffers and weak bases on lysosomal and intracellular pH: implications for infectivity of SARS-CoV-2, FASEB bioAdvances
Kreutzberger, Sanyal, Saminathan, SARS-CoV-2 requires acidic pH to infect cells, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A
Liu, Xia, Ji, Sodium bicarbonate sub-diaphragmatic irrigation relieves shoulder pain after total laparoscopic hysterectomy: a randomized controlled trial, J Pain Res, doi:10.2147/JPR.S338716
Luchini, Stubbs, Solmi, Veronese, Assessing the quality of studies in meta-analyses: advantages and limitations of the Newcastle Ottawa scale, World J Meta-Anal
Marois, Cloutier, Meunier, Weingartl, Cantin et al., Inhibition of influenza virus replication by targeting broad host cell pathways, PLOS ONE
Misra, Gasparyan, Zimba, Benefits and adverse effects of hydroxychloroquine, methotrexate and colchicine: searching for repurposable drug candidates, Rheumatol Int
Mody, Effect of 8.4% soda-bicarbonate steam inhalation on the course of disease in mild to moderate cases of COVID-19, Acta Sci Orthop
Mousa, Prevention and treatment of influenza, influenzalike illness, and common cold by herbal, complementary, and natural therapies, J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med
Ohishi, Nukuzuma, Seki, Alkalization of blood pH is responsible for survival of cancer patients by mild hyperthermia, Biomed Res
Ou, Liu, Lei, Characterization of spike glycoprotein of SARS-CoV-2 on virus entry and its immune cross-reactivity with SARS-CoV, Nat Commun
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, Br Med J
Shafiee, Athar, Gargari, Jafarabady, Siahvoshi et al., Ivermectin under scrutiny: a systematic review and meta-analysis of efficacy and possible sources of controversies in COVID-19 patients, Virol J
Soares, Da Silva, Soares, Preliminary observation of the use of sodium bicarbonate solution as an adjunct in the treatment of coronavirus 2019 disease (COVID-19): Prognosis improvement in patients requiring intensive care / observação preliminar do uso de solução de bicarbonato de sódio como coadjuvante no tratamento da doença coronavírus 2019 (COVID-19): melhora do prognóstico na necessidade de terapia intensiva, Braz J Dev
Sterne, Savovic, Page, Rob 2: a revised tool for assessing risk of bias in randomised trials, Br Med J
Sturman, Ricard, Holmes, Conformational change of the coronavirus peplomer glycoprotein at pH 8.0 and 37 °C correlates with virus aggregation and virus-induced cell fusion, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.64.6.3042-3050.1990
Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Efficacy of nasal irrigation and oral rinse with sodium bicarbonate solution on virus clearance for COVID-19 patients, Front Public Health
Wang, Zhang, Zhang, Efficacy of nasal irrigation and oral rinse with sodium bicarbonate solution on virus clearance for COVID-19 patients, Front Public Health
Widuri, Rianto, Indrawati, Nugraha, Wahab, Nasal irrigation with various solutions for adults with allergic rhinitis: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials, Medicine
Yang, Shen, Targeting the endocytic pathway and autophagy process as a novel therapeutic strategy in COVID-19, Int J Biol Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2515690x241258403",
"ISSN": [
"2515-690X",
"2515-690X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/2515690x241258403",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Background</jats:title><jats:p> A systematic review and meta-analysis have been conducted to evaluate the efficacy of alkalinization for COVID-19 patients based on current evidence to determine the impact of alkalinization on COVID-19 outcomes. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Methods</jats:title><jats:p> We searched MEDLINE (Pubmed), Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinicaltrials.gov for studies evaluating the efficacy of alkalinization up to 30 April 2023. Based on the PRISMA 2020 statement criteria a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies were performed. </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p> The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in mortality rate in the alkalinization group compared to controls (RR 0.73, 95% CI: 0.56-0.95; I2 = 0%). However, our subgroup analysis showed no significant improvement in RCT-only studies (RR 0.78, 95% CI: 0.59-1.05; I2 = 0%), the recovery rate was significantly higher in the alkalinization group (RR 2.13, 95% CI: 1.39-3.26; I2 = 0%), duration of recovery also has improved in alkalinization group (SMD 0.76, 95% CI: 0.33-1.18; I2 = 0%). The results of our meta-analysis showed a significant reduction in the duration of hospitalization in the alkalinization group compared to controls with very low certainty of evidence (SMD −0.66, 95% CI: −0.97 to −0.35; I2 = 36%). </jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p> With low certainty of evidence, alkalinization (by sodium bicarbonate) can be an efficient and safe adjuvant treatment for COVID-19 patients. Future randomized controlled trials are needed to strengthen the available evidence. </jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/2515690X241258403"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Shafiee",
"given": "Arman",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Jafarabady",
"given": "Kyana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Moltazemi",
"given": "Hassan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Amini",
"given": "Mohammad Javad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rafiei",
"given": "Mohammad Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Student Research Committee, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Akhondi",
"given": "Amirhossein",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4570-2252",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Non-communicable Diseases Research Center, Alborz University of Medical Sciences, Karaj, Iran"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mozhgani",
"given": "Sayed-Hamidreza",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Evidence-Based Integrative Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Evid Based Complementary Altern Med",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-03T07:02:23Z",
"timestamp": 1717398143000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-03T07:02:28Z",
"timestamp": 1717398148000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2024-06-04T00:21:52Z",
"timestamp": 1717460512426
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2515690X241258403",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/2515690X241258403",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/2515690X241258403",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
6,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"author": "Cheema HA",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol.",
"key": "bibr1-2515690X241258403",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12985-022-01829-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr2-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules27238562",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/ijbs.45498",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2209514119",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jvi.64.6.3042-3050.1990",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.80.7.3180-3188.2006",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2021.05.028",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000031884",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"author": "Page MJ",
"journal-title": "Br Med J.",
"key": "bibr10-2515690X241258403",
"volume": "372",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13105/wjma.v5.i4.80",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"author": "Sterne JA",
"journal-title": "Br Med J.",
"key": "bibr12-2515690X241258403",
"volume": "366",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.39489.470347.AD",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/ebmental-2019-300117",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"author": "Baxter AL",
"first-page": "145561322112373",
"journal-title": "Ear Nose Throat J.",
"key": "bibr15-2515690X241258403",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/microorganisms10061118",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.21203/rs.3.rs-2214180/v1",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr17-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4103/ijrc.ijrc_48_21",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31080/ASOR.2021.04.0290",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.34117/bjdv7n12-039",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"author": "Wang T",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health",
"key": "bibr21-2515690X241258403",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr22-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-15562-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr23-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0110631",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr24-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2156587216641831",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr25-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.00453",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr26-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01948-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr27-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-86494-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr28-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00228-021-03141-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr29-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"author": "Wang T",
"journal-title": "Front Public Health.",
"key": "bibr30-2515690X241258403",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12070-017-1070-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr31-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/JPR.S338716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr32-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1096/fba.2022-00062",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr33-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2220/biomedres.30.95",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr34-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-0597-3_2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr35-2515690X241258403"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00296-020-04694-2",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr36-2515690X241258403"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/2515690X241258403"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Alkalinization Using Sodium Bicarbonate for COVID-19 Treatment: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy",
"volume": "29"
}
shafiee3