Comparison between Vitamin D Level of Asymptomatic Confirmed Covid-19 Patients with Symptomatic Confirmed Covid-19 Patients in Makassar
et al., Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 25:6, May 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 135 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
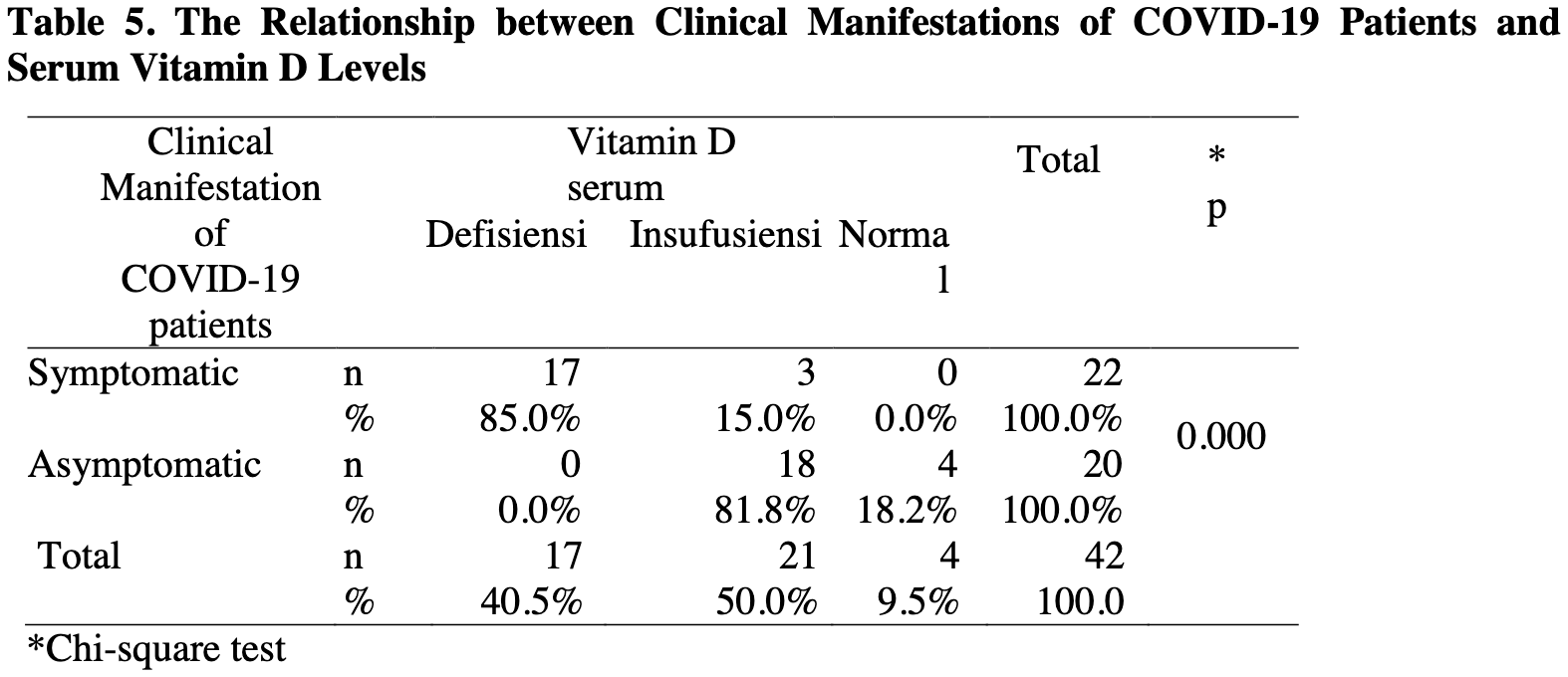
Retrospective 42 PCR+ patients in Indonesia, showing significantly higher risk of symptomatic cases with vitamin D deficiency.
This is the 63rd of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
|
risk of symptomatic case, 88.0% lower, RR 0.12, p < 0.001, high D levels 3 of 25 (12.0%), low D levels 17 of 17 (100.0%), NNT 1.1, >20ng/ml.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Savitri et al., 8 May 2021, retrospective, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
Comparison between Vitamn D Level of Asymptomatic Confirmed Covid-19 Patients with Symptomatic Confirmed Covid-19 Patients in Makassar
Vitamin D shows an important role in immune function. However,there is still little analysis regarding the role of vitamin D inpreventing infection and death fromCOVID-19.This researchaimed todetermine vitamin D levels inpatients with confirmed COVID-19. A crosssectional study was conducted. Researcher collected blood fromthemedian cubital vein of COVID-19 patients and examined the vitamin D levels in patients using the ELISA method.This research showed a comparison of serum vitaminD based on clinical manifestations of COVID-19 patients in all subjects. In20 patients with symptomatic COVID-19 clinical manifestations there were 17 patients (85 %) with vitamin Ddeficiency, 3 patients (15 %) with vitamin D insufficiency; To the contrary, there were noasymptomatic COVID-19 patientswith vitamin D deficiency, 18 patients with vitamin D insufficiency, and 4 patients with normal vitamin D levels.There was a significant relationship between the clinicalmanifestations of patients with COVID-19 and the patient's serum vitamin D levels where asymptomatic patientshad higher levels than that of symptomatic patients (p-value with the Chi-square test was 0.000 with p <0.001).In addition, there was a significant difference between vitamin D levels in asymptomatic and symptomatic patients whereserum vitamin D levels were obtained to be higher in the asymptomatic patient group than in thesymptomaticgroup.
References
Ahn, Current Status of Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Therapeutics and Vaccines for Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Page
Ali, Role of vitamin D in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity
Alipio, Vitamin D Supplementation Could Possibly Improve Clinical Outcomes of Patients Infected with Coronavirus, doi:10.2139/ssrn.3571484
Carpagno, Vitamin D defciency as a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with acute respiratory failure due to COVID-19, Journal of Endocrinological Investigation
Cui, Vitamin D receptor activation regulates microglia polarization and oxidative stress in spontaneously hypertensive rats and angiotensin II-exposed microglial cells: role of renin-angiotensin system, Redox Biol, doi:10.1016/j.redox.2019.101295
Ebadi, Montana, Perspective: improving vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19, Eur J ClinNutr
Gruber-Bzura, Vitamin D and influenza-prevention or therapy?, Int J MolSci, doi:10.3390/ijms19082419
Horani, Nationality, Gender, Age, and Body Mass Index Influences on Vitamin D Concentration among Elderly Patients and Young Iraqi and Jordanian in Jordan, Biochemistry Research International
