Antiplatelet therapy and outcome in patients with COVID-19. Results from a multi-center international prospective registry (HOPE-COVID19)
et al., European Heart Journal, doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.3002, Oct 2021
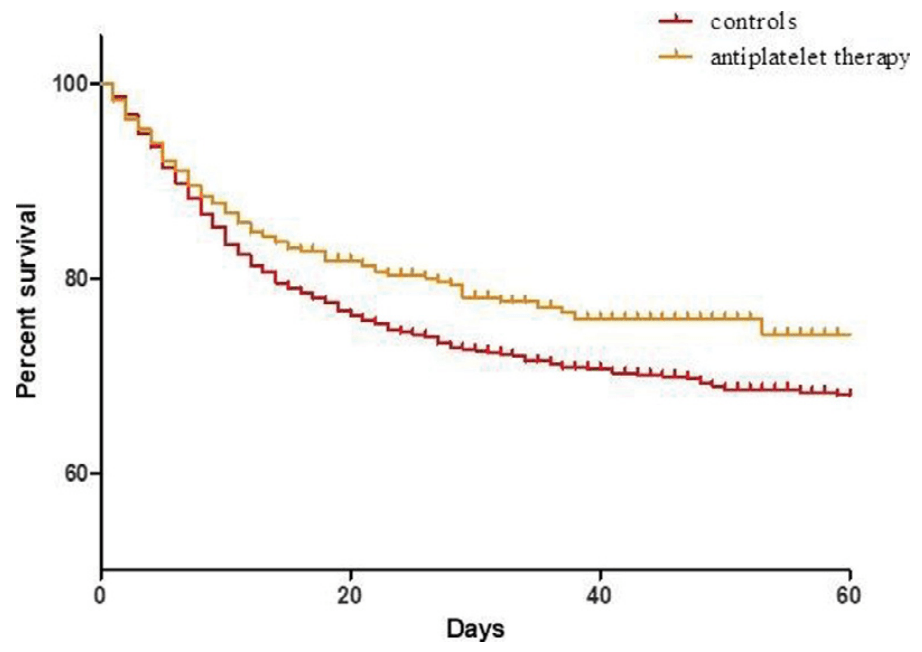
Retrospective database analysis of 7,824 patients in the HOPE-COVID19 registry, 730 receiving antiplatelet therapy including aspirin, showing lower mortality with treatment. Authors do not provide results restricted to aspirin.
|
risk of death, 71.0% lower, RR 0.29, p < 0.001, treatment 730, control 7,094, antiplatelet therapy, multivariable.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Santoro et al., 14 Oct 2021, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 6 authors.
Antiplatelet therapy and outcome in patients with COVID-19. Results from a multi-center international prospective registry (HOPE-COVID19)
Background: No standard therapy is currently recommended for . Autopsy studies showed high prevalence of platelet-fibrin rich micro-thrombi in several organs. Aim of the study was to evaluate safety and efficacy of antiplatelet therapy (APT) in COVID-19 hospitalized patients and its impact on survival. Methods: 7824 consecutive patients with COVID-19 were enrolled in a multicenter-international prospective registry (HOPE-COVID19). Clinical data and in-hospital complications were recorded. AP regimen, including aspirin and other antiplatelet drugs, was obtained for each patient. Results: During hospitalization 730 (9.3%) patients received AP drugs with single (93%, n=680) or dual APT (7%, n=50). Patients treated with APT were older (73±12 vs 62±17 years, p<0.01), more frequently male (70% vs 64%, p<0.01) and had higher prevalence of diabetes (39.5% vs 17%, p<0.01).
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.3002",
"ISSN": [
"0195-668X",
"1522-9645"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.3002",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>No standard therapy is currently recommended for Corona-virus-19 disease (COVID-19). Autopsy studies showed high prevalence of platelet-fibrin rich micro-thrombi in several organs. Aim of the study was to evaluate safety and efficacy of antiplatelet therapy (APT) in COVID-19 hospitalized patients and its impact on survival.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>7824 consecutive patients with COVID-19 were enrolled in a multicenter-international prospective registry (HOPE-COVID19). Clinical data and in-hospital complications were recorded. AP regimen, including aspirin and other antiplatelet drugs, was obtained for each patient.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>During hospitalization 730 (9.3%) patients received AP drugs with single (93%, n=680) or dual APT (7%, n=50). Patients treated with APT were older (73±12 vs 62±17 years, p&lt;0.01), more frequently male (70% vs 64%, p&lt;0.01) and had higher prevalence of diabetes (39.5% vs 17%, p&lt;0.01).</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Patients treated with APT showed no differences in terms of in-hospital mortality (18% vs 19%, p=0.64, Log Rank p=0.23), need of invasive ventilation (8.7% vs 8.5%, p=0.88) and bleeding (2.1% vs 2.4%, p=0.43); However, after excluding patients treated only with anticoagulation, APT was associated with lower mortality rates (Log Rank p&lt;0.01, relative risk 0.79, 95% CI 0.70–0.94) (Figure 1).</jats:p>\n <jats:p>At multivariable analysis including age, gender, diabetes, hypertension, respiratory failure, pre-hospital therapy with antiplatelet drugs, in-hospital APT, and anticoagulation therapy, in-hospital APT was associated with a lower mortality risk (relative risk 0.29, 95% CI 0.22–0.38, p&lt;0.001).</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>APT during hospitalization for COVID-19 could be associated with lower mortality risk without increased risk of bleeding. Randomized trials are needed to confirm these preliminary data.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Funding Acknowledgement</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Type of funding sources: None. Figure 1</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Foggia, Department of Cardiology, Foggia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Santoro",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Foggia, Department of Cardiology, Foggia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Vitale",
"given": "E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Clinico San Carlos, Deparment of Cardiology, Madrid, Spain"
}
],
"family": "Nunez Gil",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Hospital Riuniti of Ancona, Deparment of Cardiology, Ancona, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Guerra",
"given": "F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Medical Centre of Mannheim, Deparment of Cardiology, Mannheim, Germany"
}
],
"family": "El-Battrawy",
"given": "I",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University of Foggia, Department of Cardiology, Foggia, Italy"
}
],
"family": "Brunetti",
"given": "N D",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "European Heart Journal",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-20T19:41:36Z",
"timestamp": 1634758896000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-04T05:59:07Z",
"timestamp": 1641275947000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-01T09:23:37Z",
"timestamp": 1648805017036
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/journals/pages/open_access/funder_policies/chorus/standard_publication_model",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633046400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article-pdf/42/Supplement_1/ehab724.3002/41050914/ehab724.3002.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article-pdf/42/Supplement_1/ehab724.3002/41050914/ehab724.3002.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
14
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/eurheartj/article/doi/10.1093/eurheartj/ehab724.3002/6394238"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Antiplatelet therapy and outcome in patients with COVID-19. Results from a multi-center international prospective registry (HOPE-COVID19)",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "42"
}