A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of nitazoxanide for treatment of mild or moderate COVID-19
et al., eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310, NCT04486313, Apr 2021 (preprint)
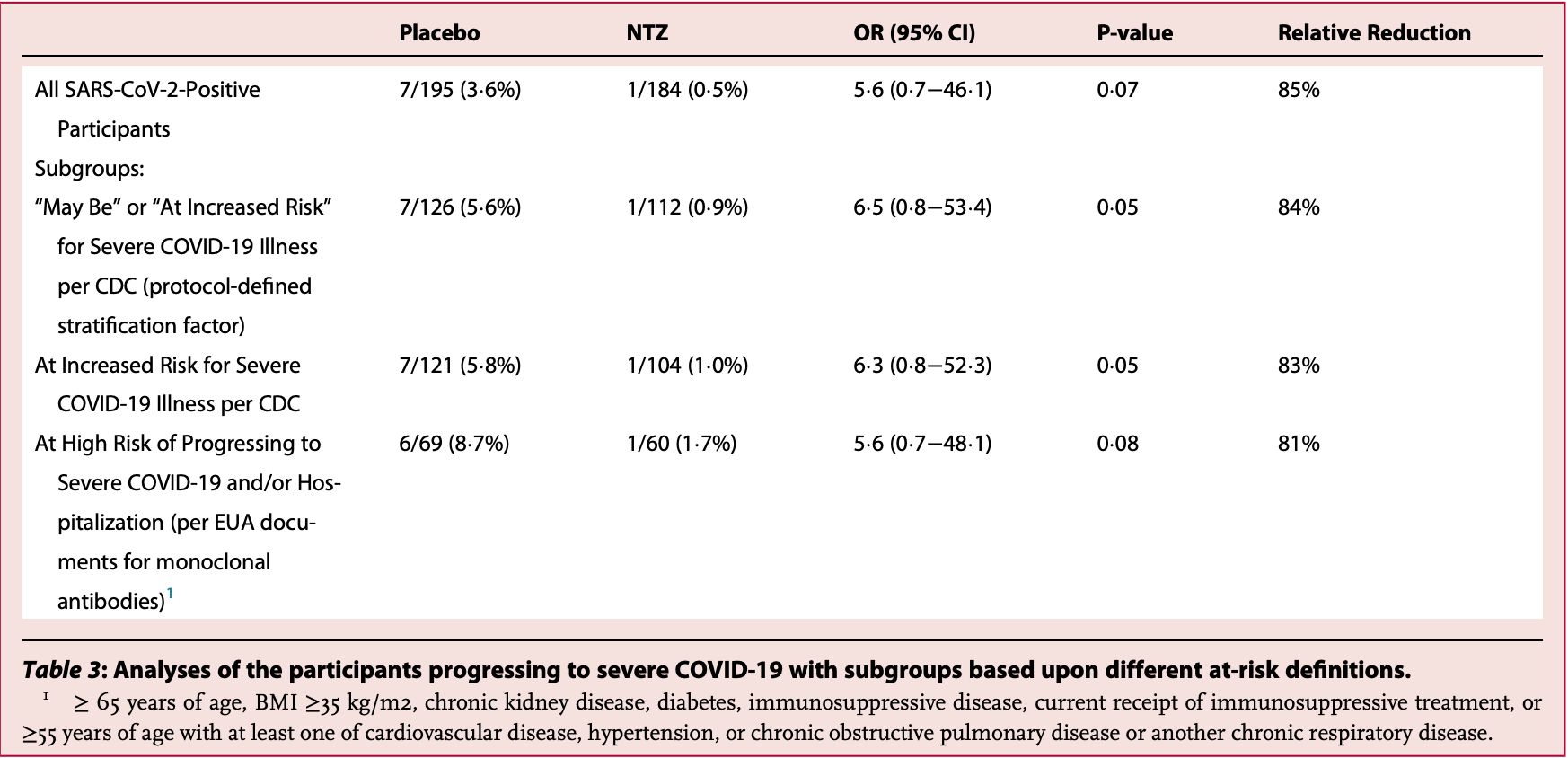
RCT with 184 outpatients treated with an extended release formulation of nitazoxanide, and 195 controls, showing lower hospitalization and progression to severe disease with treatment. There was one COVID-19 related death in the treatment arm. 600mg twice daily for five days.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 206.0% higher, RR 3.06, p = 0.49, treatment 1 of 184 (0.5%), control 0 of 195 (0.0%), continuity correction due to zero event (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), COVID-19 deaths.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 78.8% lower, RR 0.21, p = 0.22, treatment 1 of 184 (0.5%), control 5 of 195 (2.6%), NNT 49.
|
|
risk of severe case, 84.9% lower, RR 0.15, p = 0.07, treatment 1 of 184 (0.5%), control 7 of 195 (3.6%), NNT 33.
|
|
risk of severe case, 83.9% lower, RR 0.16, p = 0.07, treatment 1 of 112 (0.9%), control 7 of 126 (5.6%), NNT 21, high-risk subgroup.
|
|
time to sustained recovery, 7.3% higher, relative time 1.07, p = 0.88, treatment 184, control 195, primary outcome.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rossignol et al., 20 Apr 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, USA, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period August 2020 - February 2021, average treatment delay 1.83 days, trial NCT04486313 (history).
A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of nitazoxanide for treatment of mild or moderate COVID-19
eClinicalMedicine, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310
Background There is an urgent need for treatments of mild or moderate COVID-19 in an outpatient setting. Methods A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial in 36 centers in the U.S. between August 2020 and February 2021 investigated the safety and effectiveness of oral nitazoxanide 600 mg twice daily for five days in outpatients with symptoms of mild or moderate COVID-19 enrolled within 72 h of symptom onset (ClinicalTrials. gov NCT04486313). Efficacy endpoints were time to sustained clinical recovery (TSR, a novel primary endpoint) and proportion of participants progressing to severe illness within 28 days (key secondary). Findings 1092 participants were enrolled. 379 with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were analyzed. In the primary analysis, median (IQR) TSR were 13¢3 (6¢3, >21) and 12¢4 (7¢2, >21) days for the nitazoxanide and placebo groups, respectively (p = 0¢88). 1 of 184 (0¢5%) treated with nitazoxanide progressed to severe illness compared to 7 of 195 (3¢6%) treated with placebo (key secondary analysis, odds ratio 5¢6 [95% CI 0¢7 -46¢1], relative risk reduction 85%, p = 0¢07). In the pre-defined stratum with mild illness at baseline, nitazoxanide-treated participants experienced reductions in median TSR (3¢1 days, p = 0¢09) and usual health (5¢2 days, p < 0¢01) compared to placebo. Nitazoxanide was safe and well tolerated. Interpretation Further trials with larger numbers are warranted to evaluate efficacy of nitazoxanide therapy in preventing progression to severe illness in patients at high risk of severe illness and reducing TSR in patients with mild illness.
Contributors JFR supervised the design, conduct, analysis and reporting of the study; MB and DM had oversight of day-today clinical trial operations, laboratory oversight and safety monitoring; JF was responsible for data management, analysis and reporting; DM, MB and JF directly accessed and verified the underlying data reported. CB advised regarding the design and reporting of the study; JFR, CB, MB and JF participated in writing the manuscript; and JFR and CB made the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j. eclinm.2022.101310.
References
Blum, Cimerman, Hunter, Nitazoxanide superiority to placebo to treat moderate COVID-19 − a pilot prove of concept randomized double-blind clinical trial, doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100981
Bobrowski, Chen, Eastman, Synergistic and antagonistic drug combinations against SARS-CoV-2, Mol Ther
Cao, Forrest, Zhang, A screen of the NIH clinical collection small molecule library identifies potential anti-coronavirus drugs, Antivir Res
Chen, Nirula, Heller, SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Chen, Zhang, Case, Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies, Nat Med
Haffizulla, Hartman, Hoppers, A randomized, doubleblind, placebo controlled clinical trial of nitazoxanide in adults and adolescents with acute uncomplicated influenza, Lancet Infect Dis
Hong, Kim, Song, Choi, Lee et al., Nitazoxanide suppresses IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated mouse macrophages and TG-injected mice, Int Immunopharmacol
Kim, Read, Fauci, Therapy for early COVID-19, a critical need, JAMA
Korba, Elazar, Lui, Rossignol, Glenn, Potential for hepatitis C virus resistance to nitazoxanide or tizoxanide. Antimicrob, Agents Chemother
Lian, Mcalister, Ramirez, Triple combination nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and hydroxychloroquine results in the multiplicative reduction of in vitro SARS-CoV-2 viral replication, bioRxiv
Mccullough, Alexander, Armstrong, Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19), Rev Cardiovasc Med
Mostafa, Kandeil, Elshaier, FDA-approved drugs with potent in vitro antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2, Pharmaceuticals
Piacentini, Frazia, Riccio, Nitazoxanide inhibits paramyxovirus replication by targeting the fusion protein folding: role of glycoprotein-specific thiol oxidoreductase ERp57, Sci Rep
Powers, Bacci, Leidy, Performance of the inFLUenza patient-reported outcome (FLU-PRO) diary in patients with influenza-like illness (ILI), PLoS One
Riccio, Santopolo, Rossi, Piacentini, Rossignol et al., Impairment of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein maturation and fusion activity by the broad-spectrum anti-infective drug nitazoxanide, bioRxiv
Risner, Tieu, Wang, Maraviroc inhibits SARS-CoV-2 multiplication and s-protein mediated cell fusion in cell culture, bioRxiv
Rocco, Silva, Cruz, Early use of nitazoxanide in mild Covid-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial, Eur Respir J
Rossignol, Frazia, Chiappa, Ciucci, Santoro, Thiazolides, a new class of anti-influenza molecules targeting viral hemagglutinin at the post-translational level, J Biol Chem
Rossignol, Nitazoxanide, a new drug candidate for the treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J Infect Public Health
Rossignol, Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent, Antivir Res
Rossignol, Van Baalen, Broad-spectrum antiviral nitazoxanide inhibits ATP-dependent replication of respiratory viruses and proinflammatory cytokines
Silva, Espejo, Pereyra, Efficacy of nitazoxanide in reducing the viral load in COVID-19 patients. Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded, parallel group, pilot study
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310",
"ISSN": [
"2589-5370"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310",
"alternative-id": [
"S2589537022000402"
],
"article-number": "101310",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rossignol",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bardin",
"given": "Matthew C.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fulgencio",
"given": "Jessica",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mogelnicki",
"given": "Dena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Bréchot",
"given": "Christian",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"eClinicalMedicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T10:03:26Z",
"timestamp": 1646042606000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T10:03:45Z",
"timestamp": 1646042625000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-28T10:40:55Z",
"timestamp": 1646044855177
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "2589-5370"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1646092800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
4
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-04T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643932800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537022000402?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S2589537022000402?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "101310",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22813",
"article-title": "Therapy for early COVID-19, a critical need",
"author": "Kim",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2149",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0001",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31083/j.rcm.2020.04.264",
"article-title": "Multifaceted highly targeted sequential multidrug treatment of early ambulatory high-risk SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19)",
"author": "McCullough",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "517",
"journal-title": "Rev Cardiovasc Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0002",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0003",
"unstructured": "Bamlanivimab and Etesevimab Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers Emergency Use Authorization. Eli Lilly, Indianapolis, IN. Revised 03/2021. Available at: http://pi.lilly.com/eua/bam-and-ete-eua-factsheet-hcp.pdf. Accessed April 9, 2021."
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0004",
"unstructured": "REGEN-COV Fact Sheet for Health Care Providers Emergency Use Authorization. Regeneron pharmaceuticals, Inc., Tarrytown, NY. Revised 03/2021. Available at: https://www.fda.gov/media/145611/download. Accessed April 9, 2021."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01294-w",
"article-title": "Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0005",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.07.014",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide: a first-in-class broad-spectrum antiviral agent",
"author": "Rossignol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "94",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0006",
"volume": "110",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.antiviral.2014.11.010",
"article-title": "A screen of the NIH clinical collection small molecule library identifies potential anti-coronavirus drugs",
"author": "Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Antivir Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0007",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2016.04.001",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide, a new drug candidate for the treatment of Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus",
"author": "Rossignol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "227",
"journal-title": "J Infect Public Health",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0008",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"article-title": "Broad-spectrum antiviral nitazoxanide inhibits ATP-dependent replication of respiratory viruses and proinflammatory cytokines",
"author": "Rossignol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0009",
"series-title": "Proceedings of the 2nd International Meeting on Respiratory Pathogens",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.intimp.2012.03.002",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide suppresses IL-6 production in LPS-stimulated mouse macrophages and TG-injected mice",
"author": "Hong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "23",
"journal-title": "Int Immunopharmacol",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0010",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir and chloroquine effectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "269",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0011",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.04.12.439201",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0012",
"unstructured": "Riccio A, Santopolo S, Rossi A, Piacentini S., Rossignol J.F., Santoro M.G. Impairment of SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein maturation and fusion activity by the broad-spectrum anti-infective drug nitazoxanide [Preprint]. bioRxiv 2021 Apr 12: 04.12.439201."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ymthe.2020.12.016",
"article-title": "Synergistic and antagonistic drug combinations against SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "Bobrowski",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "873",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mol Ther",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0013",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ph13120443",
"article-title": "FDA-approved drugs with potent in vitro antiviral activity against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2",
"author": "Mostafa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "443",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Pharmaceuticals",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0014",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.11.25.399055",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0015",
"unstructured": "Lian E, McAlister C, Ramirez G. et al. Triple combination nitazoxanide, ribavirin, and hydroxychloroquine results in the multiplicative reduction of in vitro SARS-CoV-2 viral replication [Preprint]. bioRxiv 2020 Nov 26: 11.25.399055."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1074/jbc.M109.029470",
"article-title": "Thiazolides, a new class of anti-influenza molecules targeting viral hemagglutinin at the post-translational level",
"author": "Rossignol",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29798",
"journal-title": "J Biol Chem",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0016",
"volume": "284",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-018-28172-9",
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide inhibits paramyxovirus replication by targeting the fusion protein folding: role of glycoprotein-specific thiol oxidoreductase ERp57",
"author": "Piacentini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "10425",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0017",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/AAC.00078-08",
"article-title": "Potential for hepatitis C virus resistance to nitazoxanide or tizoxanide",
"author": "Korba",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4069",
"journal-title": "Antimicrob Agents Chemother",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0018",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.08.12.246389",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0019",
"unstructured": "Risner KH, Tieu KV, Wang Y. et al. Maraviroc inhibits SARS-CoV-2 multiplication and s-protein mediated cell fusion in cell culture [Preprint]. bioRxiv 2020 Aug 13: 2020.08.12.246389."
},
{
"article-title": "Nitazoxanide superiority to placebo to treat moderate COVID-19 – a pilot prove of concept randomized double-blind clinical trial",
"author": "Blum",
"journal-title": "EClinicalMedicine",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0020",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0194180",
"article-title": "Performance of the inFLUenza patient-reported outcome (FLU-PRO) diary in patients with influenza-like illness (ILI)",
"author": "Powers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0021",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(14)70717-0",
"article-title": "A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled clinical trial of nitazoxanide in adults and adolescents with acute uncomplicated influenza",
"author": "Haffizulla",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "609",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0022",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0023",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with Covid-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0024",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Early use of nitazoxanide in mild Covid-19 disease: randomised, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Rocco",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0025",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.03.03.21252509",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101310_bib0026",
"unstructured": "Silva M, Espejo AL, Pereyra M. et al. Efficacy of nitazoxanide in reducing the viral load in COVID-19 patients. Randomized, placebo-controlled, single-blinded, parallel group, pilot study [Preprint]. medRxiv 2021 Mar 5: 03.03.21252509."
}
],
"reference-count": 26,
"references-count": 26,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"eClinicalMedicine"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"A randomized double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial of nitazoxanide for treatment of mild or moderate COVID-19"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "45"
}