Evaluation and comparison of the effect of vitamin A supplementation with standard therapies in the treatment of patients with COVID-19
et al., Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, doi:10.26719/emhj.22.064, IRCT46974, Aug 2022
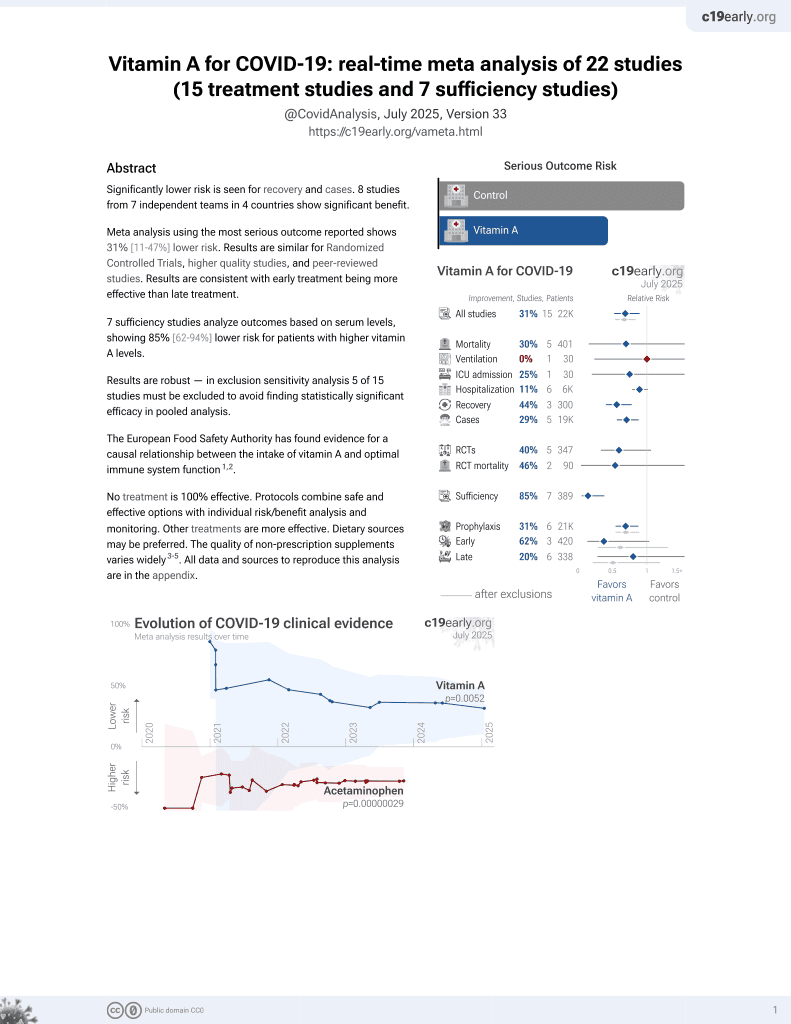
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
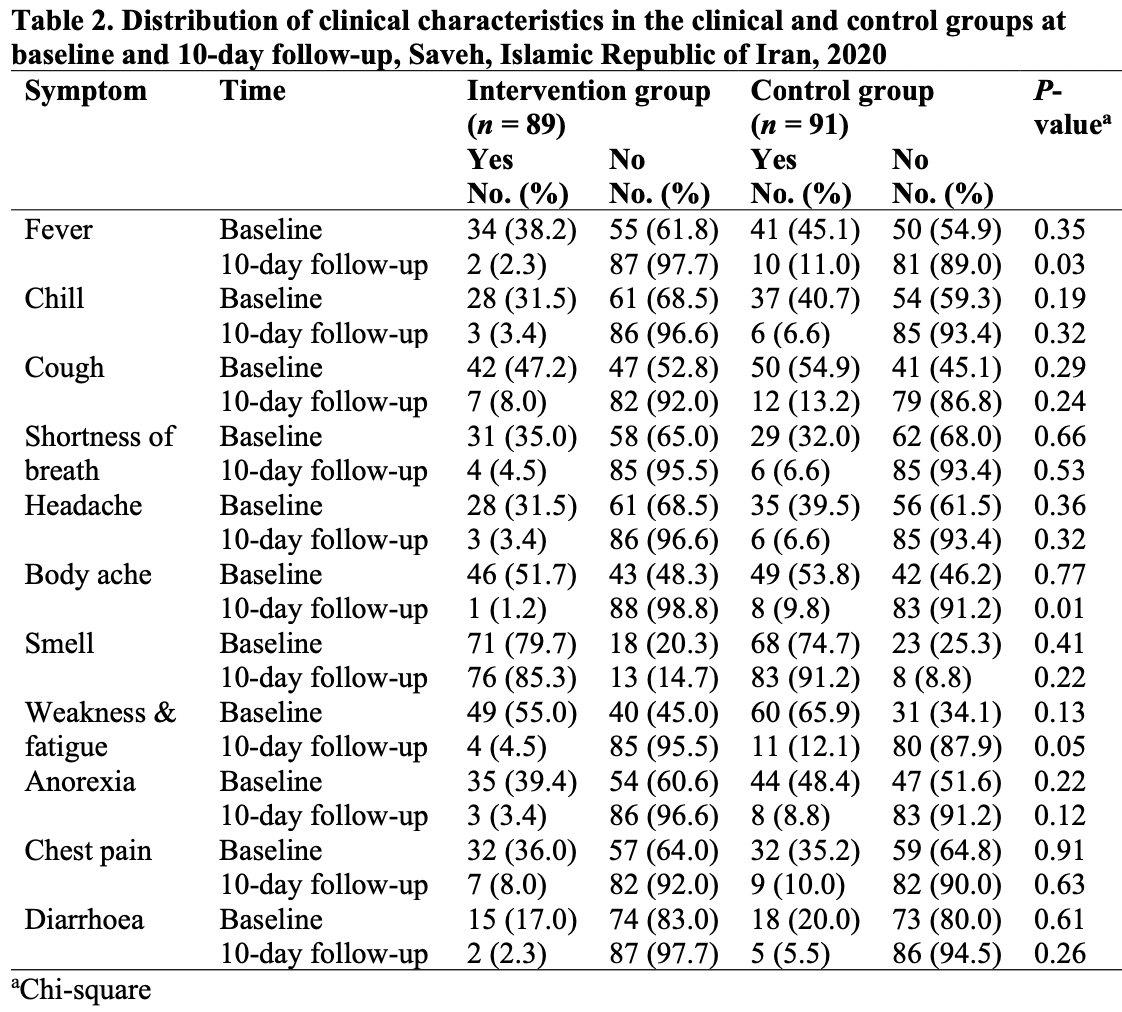
RCT 91 vitamin A and 91 control patients in Iran, showing improved recovery with treatment. All patients received HCQ. 25,000IU/day oral vitamin A for 10 days.
|
risk of hospitalization, 25.6% lower, RR 0.74, p = 0.63, treatment 8 of 89 (9.0%), control 11 of 91 (12.1%), NNT 32.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 31.8% lower, RR 0.68, p = 0.53, treatment 4 of 89 (4.5%), control 6 of 91 (6.6%), NNT 48, dyspnea.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 79.6% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.03, treatment 2 of 89 (2.2%), control 10 of 91 (11.0%), NNT 11, fever.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 87.2% lower, RR 0.13, p = 0.01, treatment 1 of 89 (1.1%), control 8 of 91 (8.8%), NNT 13, body ache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 48.9% lower, RR 0.51, p = 0.32, treatment 3 of 89 (3.4%), control 6 of 91 (6.6%), NNT 31, headache.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 62.8% lower, RR 0.37, p = 0.05, treatment 4 of 89 (4.5%), control 11 of 91 (12.1%), NNT 13, weakness and fatigue.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 20.5% lower, RR 0.80, p = 0.63, treatment 7 of 89 (7.9%), control 9 of 91 (9.9%), NNT 49, chest pain.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 40.4% lower, RR 0.60, p = 0.24, treatment 7 of 89 (7.9%), control 12 of 91 (13.2%), NNT 19, cough.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Rohani et al., 18 Aug 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 39.4, 6 authors, study period 1 May, 2020 - 1 September, 2020, trial IRCT46974.
Contact: karimymahmood@yahoo.com.
Evaluation and comparison of vitamin A supplementation with standard therapies in the treatment of patients with COVID-19
Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal, doi:10.26719/emhj.22.064
Background: Incomplete data are presented to determine the role of vitamin A supplement therapy to improve outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).
Aims: We compared treatment effects between a groups that received vitamin A added to the standard COVID-19 treatment and a group that received the standard drug treatment alone. Methods: In this triple-blind controlled trial, the participants comprised 182 COVID-19 outpatients in Saveh city, Markazi Province, Islamic Republic of Iran, in 2020. Patients were randomly divided into experimental (n = 91) and control (n = 91) groups. Patients in the control group received the national standard treatment for COVID-19 (hydroxychloroquine), and those in the intervention group received 25 000 IU/d oral vitamin A for 10 days in addition to the standard treatment recommended by the national protocol. We evaluated the clinical symptoms, paraclinical criteria and hospitalization status before and 10 days after both interventions .
Results: The treatment groups did not differ significantly in terms of clinical and paraclinical symptoms before the intervention, but clinical symptoms such as fever, body ache, weakness and fatigue, paraclinical symptoms, white blood cell count and C-reactive protein showed a significantly greater decrease in the experimental group 10 days post-intervention compared with the standard treatment alone (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: Vitamin A supplement demonstrated efficacy in improving some clinical and paraclinical symptoms in patients with COVID-19. Future studies should evaluate vitamin A supplementation with a larger sample size and compare different dosages, especially in hospitalized patients.
References
Ahmad, Kushwaha, Kant, Natu, Singh et al., Role of vitamin A and zinc supplementation on sputum smear conversion time in pulmonary tuberculosis patients, J Recent Adv Appl Sci
Aluisio, Perera, Yam, Garbern, Peters et al., Vitamin A supplementation was associated with reduced mortality in patients with Ebola virus disease during the West African outbreak, J Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/nxz142
Araban, Karimy, Koohestani, Montazeri, Delaney, Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of patients with COVID-19 in Islamic Republic of Iran, East Mediterr Health J, doi:10.26719/emhj.22.008
Brinckerhoff, Mcmillan, Dayer, Jr, Inhibition by retinoic acid of collagenase production in rheumatoid synovial cells, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJM198008213030805
Clos, Pentraxins: structure, function, and role in inflammation, ISRN Inflamm, doi:10.1155/2013/379040
Hanekom, Yogev, Heald, Edwards, Hussey et al., Effect of vitamin A therapy on serologic responses and viral load changes after influenza vaccination in children infected with the human immunodeficiency virus, J Pediatr, doi:10.1016/s0022-3476(00)90024-6
Iluz-Freundlich, Zhang, Uhanova, Minuk, The relative expression of hepatocellular and cholestatic liver enzymes in adult patients with liver disease, Ann Hepatol, doi:10.1016/j.aohep.2019.08.004Baseline31
Kahbazi, Sharafkhah, Yousefichaijan, Taherahmadi, Rafiei et al., Vitamin A supplementation is effective for improving the clinical symptoms of urinary tract infections and reducing renal scarring in girls with acute pyelonephritis: a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled, clinical trial study, Complement Ther Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2018.12.007
Kasem, Almansour, COVID-19 during the crisis in the Syrian Arab Republic, East Mediterr Health J, doi:10.26719/2021.27.1.5
Kazeminia, Jalali, Vaisi-Raygani, Khaledi-Paveh, Salari et al., Fever and cough are two important factors in identifying patients with the Covid-19: a meta-analysis, J Military Med, doi:10.30491/JMM.22.2.193
Keflie, Samuel, Woldegiorgis, Mihret, Abebe et al., Vitamin A and zinc deficiencies among tuberculosis patients in Ethiopia, J Clin Tuberc Other Mycobact Dis, doi:10.1016/j.jctube.2018.05.002
Kennedy, Stoll, Ehrenkranz, Oh, Wright et al., Vitamin A to prevent bronchopulmonary dysplasia in very-low-birth-weight infants: has the dose been too low? Early, Hum Dev, doi:10.1016/s0378-3782(97)01869-0
Leal, Castejón, Romero, Ortega, Gómez et al., alores séricos de citocinas en niños con desórdenes por deficiencia de vitamina A [Serum values of cytokines in children with vitamin A deficiency disorders, Invest Clin
Lehr, Sixteen S-squared over D-squared: A relation for crude sample size estimates, Stat Med, doi:10.1002/sim.4780110811
Mesri, Saber, Godazi, Shirdel, Montazer et al., The effects of combination of Zingiber officinale and Echinacea on alleviation of clinical symptoms and hospitalization rate of suspected COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized controlled trial, J Complement Integr Med, doi:10.1515/jcim-2020-0283
Patrick, Nutrients and HIV: part two--vitamins A and E, zinc, B-vitamins, and magnesium, Altern Med Rev
Semba, Vitamin A and immunity to viral, bacterial and protozoan infections, Proc Nutr Soc, doi:10.1017/s0029665199000944
Shaker, Fathy, Abdelall, Said, The effect of zinc and Vitamin A supplements in treating and reducing the incidence of upper respiratory tract infections in children, Nat J Physiol Pharmacy Pharmacol, doi:10.5455/njppp.2018.8.0104206032018
Shenai, Chytil, Parker, Stahlman, Vitamin A status and airway infection in mechanically ventilated very-low-birth-weight neonates, Pediatr Pulmonol, doi:10.1002/ppul.1950190503
Shirazi, Nikniaz, Shirazi, Rohani, Vitamin A supplementation decreases disease activity index in patients with ulcerative colitis: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Complementary therapies in medicine, Complement Ther Med, doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2018.09.026
Sijtsma, Rombout, West, Van Der Zijpp, Vitamin A deficiency impairs cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity in Newcastle disease virus-infected chickens, Vet Immunol Immunopathol, doi:10.1016/0165-2427(90)90067-3
Stephensen, Vitamin A, infection, and immune function, Annu Rev Nutr, doi:10.1146/annurev.nutr.21.1.167
Thompson, Pandemic potential of 2019-nCoV, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30068-2
Thornton, Mora-Plazas, Marín, Villamor, Vitamin A deficiency is associated with gastrointestinal and respiratory morbidity in school-age children, J Nutr, doi:10.3945/jn.113.185876
Wan, Shang, Sun, Tai, Chen et al., Molecular mechanism for antibody-dependent enhancement of coronavirus entry, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.02015-19
Wang, Cao, Zhang, Yang, Liu et al., Remdesivir and chloroquine ceffectively inhibit the recently emerged novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) in vitro, Cell Res, doi:10.1038/s41422-020-0282-0
Wang, Hu, Hu, Zhu, Liu et al., Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wang, Wang, Ye, Liu, Review of the 2019 novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) based on current evidence, Int J Antimicrob Agents, doi:10.1016/j.ijantimicag.2020.105948
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.26719/emhj.22.064",
"ISSN": [
"1020-3397",
"1687-1634"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.26719/emhj.22.064",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: Incomplete data are presented to determine the role of vitamin A supplement therapy to improve outcomes in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Aims: We compared treatment effects between a groups that received vitamin A added to the standard COVID-19 treatment and a group that received the standard drug treatment alone. Methods: In this triple-blind controlled trial, the participants comprised 182 COVID-19 outpatients in Saveh city, Markazi Province, Islamic Republic of Iran, in 2020. Patients were randomly divided into experimental (n = 91) and control (n = 91) groups. Patients in the control group received the national standard treatment for COVID-19 (hydroxychloroquine), and those in the intervention group received 25 000 IU/d oral vitamin A for 10 days in addition to the standard treatment recommended by the national protocol. We evaluated the clinical symptoms, paraclinical criteria and hospitalization status before and 10 days after both interventions. Results: The treatment groups did not differ significantly in terms of clinical and paraclinical symptoms before the intervention, but clinical symptoms such as fever, body ache, weakness and fatigue, paraclinical symptoms, white blood cell count and C-reactive protein showed a significantly greater decrease in the experimental group 10 days post-intervention compared with the standard treatment alone (P < 0.05). Conclusion: Vitamin A supplement demonstrated efficacy in improving some clinical and paraclinical symptoms in patients with COVID-19. Future studies should evaluate vitamin A supplementation with a larger sample size and compare different dosages, especially in hospitalized patients.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rohani",
"given": "Mohamad R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mozaffar",
"given": "Hasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mesri",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shokri",
"given": "Mehdi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Delaney",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karimy",
"given": "Mahmood",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Eastern Mediterranean Health Journal",
"container-title-short": "East Mediterr Health J.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-18T11:51:40Z",
"timestamp": 1660823500000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-18T11:51:40Z",
"timestamp": 1660823500000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-18T12:14:50Z",
"timestamp": 1660824890338
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://www.emro.who.int/in-press/research/evaluation-and-comparison-of-the-effect-of-vitamin-a-supplementation-with-standard-therapies-in-the-treatment-of-patients-with-covid-19.html",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "11263",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.26719",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
18
]
]
},
"publisher": "World Health Organization Regional Office for the Eastern Mediterranean (WHO/EMRO)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://www.emro.who.int/in-press/research/evaluation-and-comparison-of-the-effect-of-vitamin-a-supplementation-with-standard-therapies-in-the-treatment-of-patients-with-covid-19.html"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation and comparison of the effect of vitamin A supplementation with standard therapies in the treatment of patients with COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article"
}