Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Intravenous Infusions of PF-07304814 (Lufotrelvir) in Participants Hospitalized With COVID-19
et al., Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad355, NCT04535167, Jul 2023
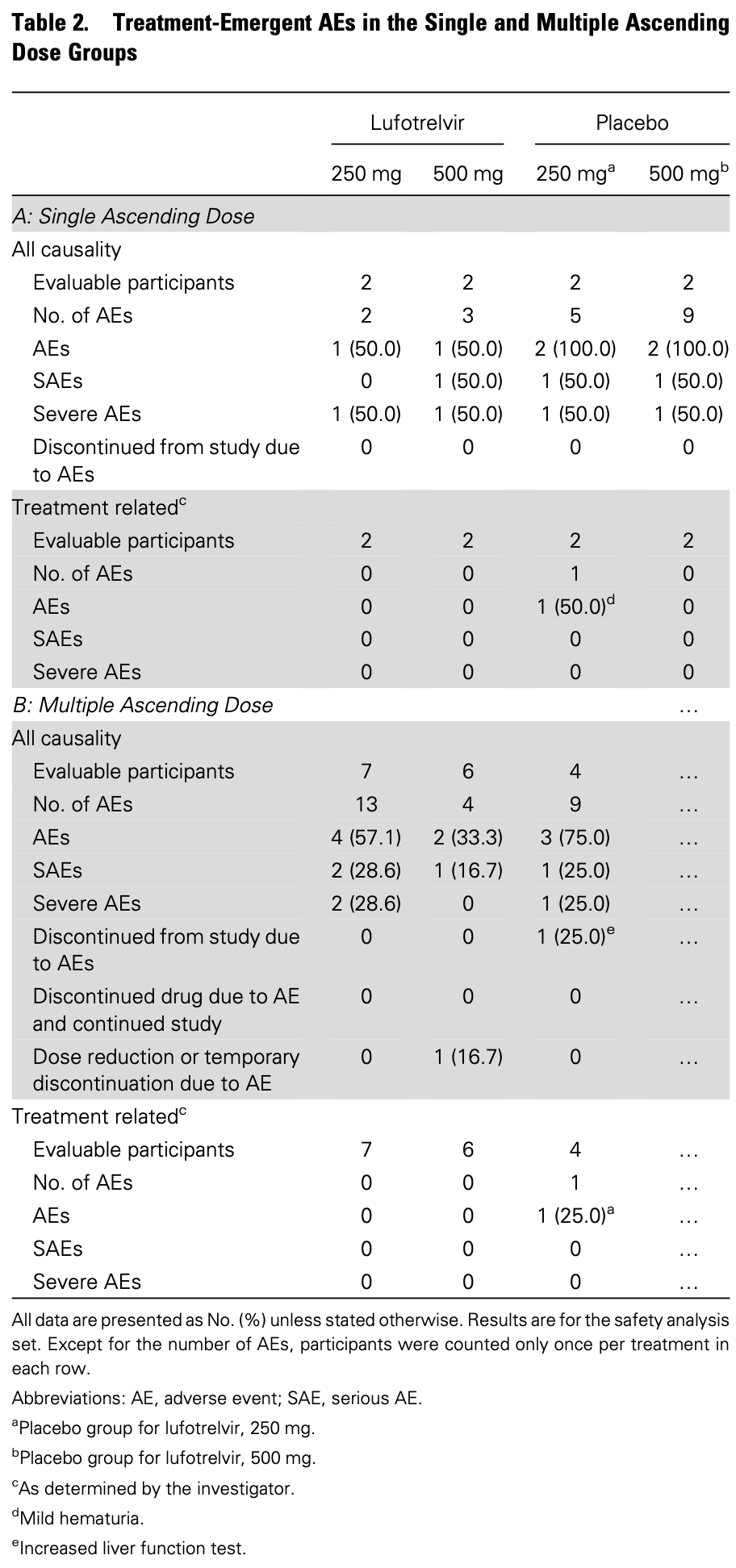
Phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetic study of lufotrelvir in 25 hospitalized COVID-19 patients. No adverse events or serious adverse events were considered related to lufotrelvir. Concentrations of lufotrelvir and its active moiety increased dose-proportionally, with mean steady-state concentrations of the active moiety above the EC90 for SARS-CoV-2.
Robinson et al., 10 Jul 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, 23 authors, study period September 2020 - May 2021, trial NCT04535167 (history).
Contact: sima.toussi@pfizer.com, sudeepta.aggarwal@pfizer.com, sions@oup.com.
Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Intravenous Infusions of PF-07304814 (Lufotrelvir) in Participants Hospitalized With COVID-19
Open Forum Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofad355
Background. An urgent need remains for antiviral therapies to treat patients hospitalized with COVID-19. PF-07304814-the prodrug (lufotrelvir) and its active moiety (PF-00835231)-is a potent inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease. Method. Eligible participants were 18 to 79 years old and hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19. This first-in-human phase 1b study was designed with 2 groups: single ascending dose (SAD) and multiple ascending dose (MAD). Participants could receive local standard-of-care therapy. In SAD, participants were randomized to receive a 24-hour infusion of lufotrelvir/placebo. In MAD, participants were randomized to receive a 120-hour infusion of lufotrelvir/placebo. The primary endpoint was to assess the safety and tolerability of lufotrelvir. The secondary endpoint was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of lufotrelvir and PF-00835231. Results. In SAD, participants were randomized to receive 250 mg lufotrelvir (n = 2), 500 mg lufotrelvir (n = 2), or placebo (n = 4) by continuous 24-hour infusion. In MAD, participants were randomized to receive 250 mg lufotrelvir (n = 7), 500 mg lufotrelvir (n = 6), or placebo (n = 4) by continuous 120-hour infusion. No adverse events or serious adverse events were considered related to lufotrelvir. At doses of 250 and 500 mg, concentrations for the prodrug lufotrelvir and active moiety PF-00835231 increased in a dose-related manner. Unbound concentrations of the lufotrelvir active metabolite reached steady state approximately 2-and 4-fold that of in vitro EC 90 following 250-and 500-mg doses, respectively. Conclusions. These safety and pharmacokinetic findings support the continued evaluation of lufotrelvir in clinical studies.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Open Forum Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the Phase 1 Safety and Pharmacokinetics of PF-07304814 • OFID • 7
Notes Acknowledgments. Medical writing support was provided by Sheena Hunt, PhD, and Allison R. Gillies, PhD, of ICON and was funded by Pfizer. We thank William Reagan, Norimitsu Shirai, Daniel Lettiere, Frank Geoly, and Jeremy Dugas for expert input into the nonclinical studies. We also thank all the participants who volunteered for this study and all the study investigators and site personnel for their contributions to this study. Data sharing. Upon request and subject to review, Pfizer will provide the data that support the findings of this study. Subject to certain criteria, conditions, and exceptions, Pfizer may also provide access to the related individual deidentified participant data. See https://www.pfizer.com/science/ clinical-trials/trial-data-and-results for more information. Financial support.
References
Ader, Bouscambert-Duchamp, Hites, Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): a phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial, Lancet Infect Dis
Anand, Ziebuhr, Wadhwani, Mesters, Hilgenfeld, Coronavirus main proteinase (3CL pro ) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs, Science
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Bernal, Da Silva, Musungaie, Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients, N Engl J Med
Boras, Jones, Anson, Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19, Nat Commun
Chi, Lee, Jamil, Venous thromboembolism among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 undergoing thromboprophylaxis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Med
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Harder, Külper-Schiek, Reda, Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25, Euro Surveill
Hilgenfeld, From SARS to MERS: crystallographic studies on coronaviral proteases enable antiviral drug design, FEBS J
Lilbert, Burnett, Main vascular changes seen in the saline controls of continuous infusion studies in the cynomolgus monkey over an eight-year period, Toxicol Pathol
Lilbert, Mowat, Common vascular changes in the jugular vein of saline controls in continuous infusion in the beagle dog, Toxicol Pathol
Ning, Liu, Li, Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection in a renal transplant recipient: case report, Am J Transplant
Nopp, Moik, Jilma, Pabinger, Ay, Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Res Pract Thromb Haemost
Owen, Allerton, Anderson, An oral SARS-CoV-2 M pro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19, Science
Pan, Peto, Henao-Restrepo, Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19-interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med
Resendez, Rehagen, Infusion toxicology and techniques
Weber, Mowat, Hartmann, Pathology in continuous infusion studies in rodents and non-rodents and ITO (infusion technology organisation)-recommended protocol for tissue sampling and terminology for procedure-related lesions, J Toxicol Pathol
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Yang, Xie, Xue, Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases, PLoS Biol
Zheng, Shao, Chen, Zhang, Wang et al., Real-world effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines: a literature review and meta-analysis, Int J Infect Dis
Zhu, Pawlak, Toussi, Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of intravenous doses of PF-07304814, a phosphate prodrug protease inhibitor for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2, in healthy adult participants, Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofad355",
"ISSN": [
"2328-8957"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofad355",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>An urgent need remains for antiviral therapies to treat patients hospitalized with COVID-19. PF-07304814—the prodrug (lufotrelvir) and its active moiety (PF-00835231)—is a potent inhibitor of the SARS-CoV-2 3CL protease.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Method</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Eligible participants were 18 to 79 years old and hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19. This first-in-human phase 1b study was designed with 2 groups: single ascending dose (SAD) and multiple ascending dose (MAD). Participants could receive local standard-of-care therapy. In SAD, participants were randomized to receive a 24-hour infusion of lufotrelvir/placebo. In MAD, participants were randomized to receive a 120-hour infusion of lufotrelvir/placebo. The primary endpoint was to assess the safety and tolerability of lufotrelvir. The secondary endpoint was to evaluate the pharmacokinetics of lufotrelvir and PF-00835231.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In SAD, participants were randomized to receive 250 mg lufotrelvir (n = 2), 500 mg lufotrelvir (n = 2), or placebo (n = 4) by continuous 24-hour infusion. In MAD, participants were randomized to receive 250 mg lufotrelvir (n = 7), 500 mg lufotrelvir (n = 6), or placebo (n = 4) by continuous 120-hour infusion. No adverse events or serious adverse events were considered related to lufotrelvir. At doses of 250 and 500 mg, concentrations for the prodrug lufotrelvir and active moiety PF-00835231 increased in a dose-related manner. Unbound concentrations of the lufotrelvir active metabolite reached steady state approximately 2- and 4-fold that of in vitro EC90 following 250- and 500-mg doses, respectively.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>These safety and pharmacokinetic findings support the continued evaluation of lufotrelvir in clinical studies.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Clinical Trials Registration. ClinicalTrials.gov NCT04535167.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Infectious Disease, Hoag Memorial Hospital Presbyterian , Newport Beach, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Robinson",
"given": "Philip",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Inc, Pearl River, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Toussi",
"given": "Sima S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Early Clinical Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Aggarwal",
"given": "Sudeepta",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Inc, Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bergman",
"given": "Arthur",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Inc, Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Tong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Ltd, Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Hackman",
"given": "Frances",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Drug Safety Unit, Pfizer Inc , Pearl River, New York , USA"
}
],
"family": "Sathish",
"given": "Jean G",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Drug Safety Unit, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Updyke",
"given": "Lawrence",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Tenpoint Therapeutics , Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Loudon",
"given": "Peter",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "El Camino Health , Mountain View, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Krishna",
"given": "Ganesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "University Hospital Brugmann , Brussels , Belgium"
}
],
"family": "Clevenbergh",
"given": "Philippe",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Universitario Fundación Jiménez Díaz, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid , Madrid , Spain"
}
],
"family": "Hernandez-Mora",
"given": "Miguel Gorgolas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Hospital Universitario Virgen Del Rocio , Sevilla , Spain"
}
],
"family": "Cisneros Herreros",
"given": "Jose Miguel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "UC Davis Medical Center , Sacramento, California , USA"
}
],
"family": "Albertson",
"given": "Timothy E",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Massachusetts General Hospital , Boston, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Dougan",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Regional One Health , Memphis, Tennessee , USA"
}
],
"family": "Thacker",
"given": "Amber",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Early Clinical Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Baniecki",
"given": "Mary Lynn",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Early Clinical Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge, Massachusetts , USA"
}
],
"family": "Soares",
"given": "Holly",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Early Clinical Development, Pfizer Inc , Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Whitlock",
"given": "Mark",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Ltd, Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Nucci",
"given": "Gianluca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Ltd, Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "Sandeep",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Ltd, Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Anderson",
"given": "Annaliesa S",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pfizer Worldwide Research, Development and Medical , Pfizer Ltd, Cambridge , UK"
}
],
"family": "Binks",
"given": "Michael",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Open Forum Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-07T13:22:14Z",
"timestamp": 1688736134000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-08T06:09:55Z",
"timestamp": 1691474995000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Pfizer"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
3,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2024-03-02T05:25:01Z",
"timestamp": 1709357101009
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "8",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "8",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2023-07-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1688947200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofad355/50850400/ofad355.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/10/8/ofad355/51050930/ofad355.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article-pdf/10/8/ofad355/51050930/ofad355.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
10
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Estimated COVID-19 burden",
"author": "Centers for Disease Control and Prevention",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B1"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 infection with the Delta (B.1.617.2) variant: second interim results of a living systematic review and meta-analysis, 1 January to 25 August 2021",
"author": "Harder",
"journal-title": "Euro Surveill",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B2",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2021.11.009",
"article-title": "Real-world effectiveness of COVID-19 vaccines: a literature review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "252",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Dis",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B3",
"volume": "114",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treatment guidelines",
"author": "COVID-19 Treatment Guidelines Panel, National Institutes of Health",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B5",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Fact sheet for healthcare providers: emergency use authorization for PAXLOVID",
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116044",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir for oral treatment of COVID-19 in nonhospitalized patients",
"author": "Jayk Bernal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "509",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B7",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Emergency use authorization 091 (casirivimab and imdevimab)",
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B8"
},
{
"article-title": "Emergency use authorization 094 (bamlanivimab and etesevimab)",
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B9"
},
{
"article-title": "Emergency use authorization 100 (sotrovimab)",
"author": "US Food and Drug Administration",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"article-title": "Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19—final report",
"author": "Beigel",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1813",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B11",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2023184",
"article-title": "Repurposed antiviral drugs for COVID-19—interim WHO solidarity trial results",
"author": "Pan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B12",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(21)00485-0",
"article-title": "Remdesivir plus standard of care versus standard of care alone for the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (DisCoVeRy): a phase 3, randomised, controlled, open-label trial",
"author": "Ader",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "209",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B13",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26239-2",
"article-title": "Preclinical characterization of an intravenous coronavirus 3CL protease inhibitor for the potential treatment of COVID19",
"author": "Boras",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6055",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B14",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/febs.12936",
"article-title": "From SARS to MERS: crystallographic studies on coronaviral proteases enable antiviral drug design",
"author": "Hilgenfeld",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4085",
"journal-title": "FEBS J",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B15",
"volume": "281",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.0030324",
"article-title": "Design of wide-spectrum inhibitors targeting coronavirus main proteases",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e324",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biol",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B16",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ajt.15897",
"article-title": "Novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) infection in a renal transplant recipient: case report",
"author": "Ning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1864",
"journal-title": "Am J Transplant",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B17",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1085658",
"article-title": "Coronavirus main proteinase (3CLpro) structure: basis for design of anti-SARS drugs",
"author": "Anand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1763",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B18",
"volume": "300",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abl4784",
"article-title": "An oral SARS-CoV-2 Mpro inhibitor clinical candidate for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Owen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1586",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B19",
"volume": "374",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B20",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cpdd.1174",
"article-title": "Safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of intravenous doses of PF-07304814, a phosphate prodrug protease inhibitor for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2, in healthy adult participants",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1382",
"journal-title": "Clin Pharmacol Drug Dev",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B21",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01926230390204306",
"article-title": "Main vascular changes seen in the saline controls of continuous infusion studies in the cynomolgus monkey over an eight-year period",
"author": "Lilbert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Pathol",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B22",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/01926230490524274",
"article-title": "Common vascular changes in the jugular vein of saline controls in continuous infusion in the beagle dog",
"author": "Lilbert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "694",
"journal-title": "Toxicol Pathol",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B23",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"author": "Resendez",
"first-page": "555",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B24",
"volume-title": "Infusion toxicology and techniques",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1293/tox.24.113",
"article-title": "Pathology in continuous infusion studies in rodents and non-rodents and ITO (infusion technology organisation)—recommended protocol for tissue sampling and terminology for procedure-related lesions",
"author": "Weber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "113",
"journal-title": "J Toxicol Pathol",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B25",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9082489",
"article-title": "Venous thromboembolism among hospitalized patients with COVID-19 undergoing thromboprophylaxis: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Chi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2489",
"journal-title": "J Clin Med",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B26",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rth2.12439",
"article-title": "Risk of venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Nopp",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1178",
"journal-title": "Res Pract Thromb Haemost",
"key": "2023080806092124000_ofad355-B27",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/ofid/article/doi/10.1093/ofid/ofad355/7222288"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of Single and Multiple Ascending Intravenous Infusions of PF-07304814 (Lufotrelvir) in Participants Hospitalized With COVID-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "10"
}