A graph neural network-based approach for predicting SARS-CoV-2–human protein interactions from multiview data
et al., PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0332794, Sep 2025
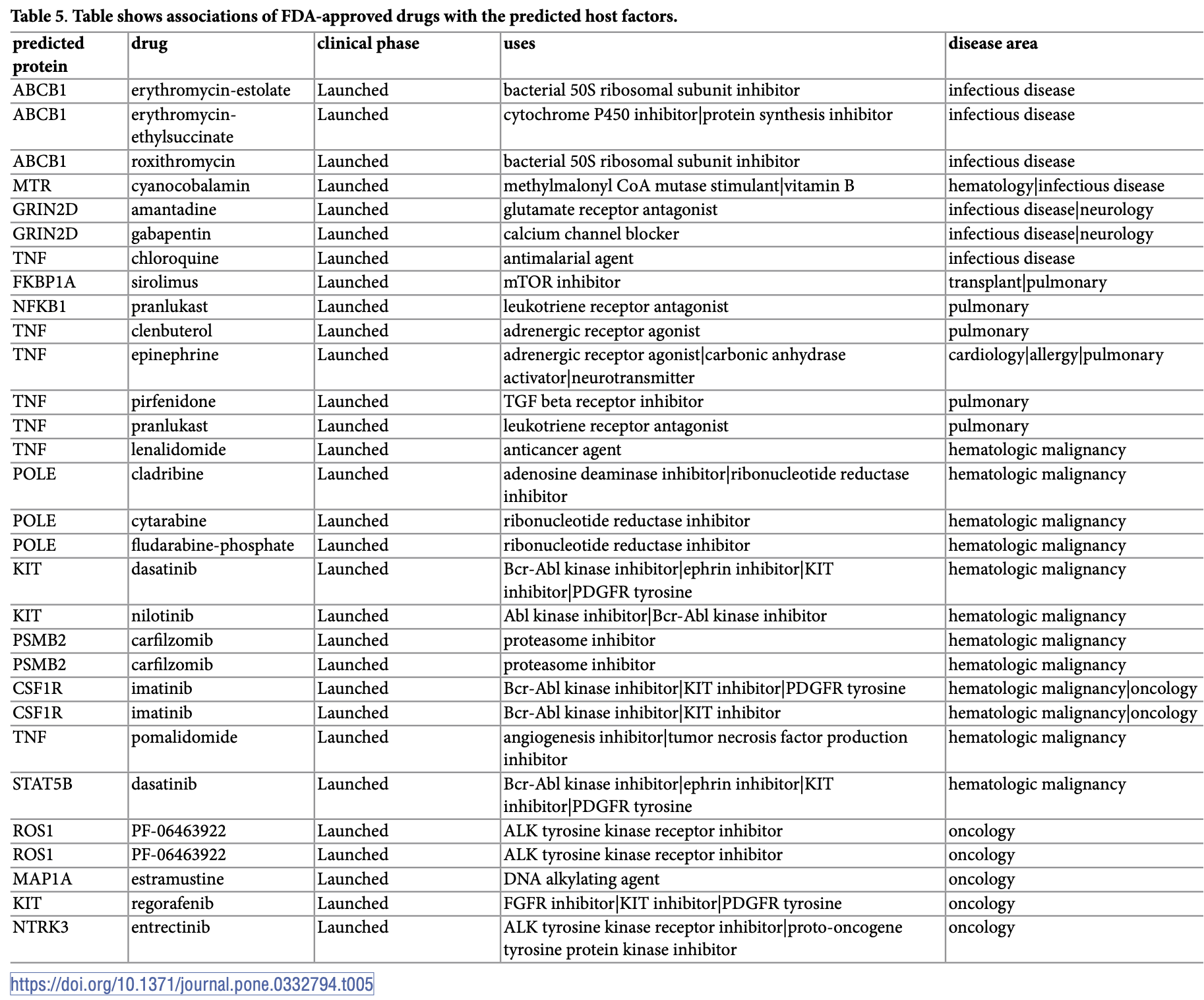
Computational study using a graph neural network-based approach to predict SARS-CoV-2-human protein interactions for drug repurposing. The study developed a multiview framework combining protein sequence data, gene ontology terms, and physical interaction information to identify 472 high-confidence predicted interactions between 280 host proteins and 27 SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The model achieved ROC-AUC scores of 85.9% (PPI network), 83.5% (GO similarity network), and 83.1% (sequence similarity network) on independent test sets, consistently outperforming single-view approaches. The researchers mapped predicted host factors to FDA-approved drugs and identified several candidates including lenalidomide and pirfenidone.
Ray et al., 25 Sep 2025, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Contact: sumantaray@nujs.edu.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
A graph neural network-based approach for predicting SARS-CoV-2–human protein interactions from multiview data
PLOS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0332794
The COVID-19 pandemic has demanded urgent and accelerated action toward developing effective therapeutic strategies. Drug repurposing models (in silico) are in high demand and require accurate and reliable molecular interaction data. While experimentally verified viral-host interaction data (SARS-CoV-2-human interactions published on April 30, 2020) provide an invaluable resource, these datasets include only a limited number of high-confidence interactions. Here, we extend these resources using a deep learning-based multiview graph neural network approach, coupled with optimal transport-based integration. Our comprehensive validation strategy confirms 472 high-confidence predicted interactions between 280 host proteins and 27 SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The proposed model demonstrates robust predictive performance, achieving ROC-AUC scores of 85.9% (PPI network), 83.5% (GO similarity network), and 83.1% (sequence similarity network), with corresponding average precision scores of 86.4%, 82.8%, and 82.3% on independent test sets. Comparative evaluation shows that our multiview approach consistently outperforms conventional single-view and baseline graph learning methods. The model combines features derived from protein sequences, gene ontology terms, and physical interaction information to improve interaction prediction. Furthermore, we systematically map the predicted host factors to FDA-approved drugs and identify several candidates, including lenalidomide and pirfenidone, which have established or emerging roles in COVID-19 therapy. Overall, our framework provides comprehensive and accurate predictions of SARS-CoV-2-host protein interactions and represents a valuable resource for drug repurposing efforts.
Supporting information S1 Table. A total of 472 interactions between SARS-CoV-2 proteins and human proteins
References
Ackerman, Kawakami, Katoh, Watanabe, Watanabe et al., Network-guided discovery of influenza virus replication host factors, mBio, doi:10.1128/mBio.02002-18
Agueh, Carlier, Barycenters in the Wasserstein space, SIAM J Math Anal, doi:10.7717/peerj.11117
Ako-Adjei, Fu, Wallin, Katz, Song et al., HIV-1, human interaction database: current status and new features, Nucleic Acids Res, doi:10.1093/nar/gku1126
Cuturi, Doucet, Fast computation of Wasserstein barycenters, doi:10.48550/arXiv.1310.4375
Derakhshan, Ansarian, Ghomshei, Possible effect of epinephrine in minimizing COVID-19 severity: a review, J Int Med Res, doi:10.1177/0300060520958594
Dessimoz, Škunca, Semantic similarity in the gene ontology, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-3743-1
Dey, Chakraborty, Mukhopadhyay, Machine learning techniques for sequence-based prediction of viral-host interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and human proteins, Biomed J, doi:10.1016/j.bj.2020.08.003
Dey, Mukhopadhyay, DenvInt: a database of protein-protein interactions between dengue virus and its hosts, PLoS Negl Trop Dis
Dick, Biggar, Green, Comprehensive prediction of the SARS-CoV-2 vs. human interactome using PIPE4, SPRINT, and PIPE-Sites, doi:10.5683/SP2/JZ77XA
Dick, Chopra, Biggar, Green, Multi-schema computational prediction of the comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 vs. human interactome, PeerJ, doi:10.7717/peerj.11117
Duvenaud, Maclaurin, Iparraguirre, Bombarell, Hirzel et al., Convolutional networks on graphs for learning molecular fingerprints, Advances in neural information processing systems, doi:10.48550/arXiv.1509.09292
Elzupir, Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease 3CLpro by means of 𝛼-ketoamide and pyridone-containing pharmaceuticals using in silico molecular docking, J Mol Struct, doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128878
Ghosh, Sil, Roy, Fajriyah, Mondal, Finding prediction of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and human protein: a data-driven approach, J Inst Eng India Ser B, doi:10.1007/s40031-021-00569-7
Gordon, Jang, Bouhaddou, Xu, Obernier et al., A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9
Gurumayum, Brahma, Naorem, Muthaiyan, Gopal et al., ZikaBase: an integrated ZIKV-human interactome map database, Virology, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.007
Gysi, Valle, Zitnik, Ameli, Gan et al., Network medicine framework for identifying drug-repurposing opportunities for COVID-19, Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, doi:10.1073/pnas.2025581118
Holcomb, Alexaki, Hernandez, Kames, Hamasaki-Katagiri, Potential impact on coagulopathy of gene variants of coagulation related proteins that interact with SARS-CoV-2, bioRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.09.08.272328
Hosur, Peng, Vinayagam, Stelzl, Xu et al., A computational framework for boosting confidence in high-throughput protein-protein interaction datasets, Genome Biol, doi:10.1186/gb-2012-13-8-r76
Ichida, Kamatani, Nishino, Saji, Okabe et al., Mutations in xanthine dehydrogenase gene in subjects with hereditary xanthinuria, Adv Exp Med Biol, doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-5381-6_65
Jeronimo, Forget, Bouchard, Li, Chua et al., Systematic analysis of the protein interaction network for the human transcription machinery reveals the identity of the 7SK capping enzyme, Mol Cell, doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.027
Kaufmann, Dorhoi, Hotchkiss, Bartenschlager, Host-directed therapies for bacterial and viral infections, Nat Rev Drug Discov, doi:10.1038/nrd.2017.162
Khalid, Ahmad, Sarfraz, Iqbal, Nishan et al., Screening Asian medicinal plants for SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors: a computational approach, Chem Biodivers, doi:10.1002/cbdv.202402548
Khorsand, Savadi, Naghibzadeh, Comprehensive host-pathogen protein-protein interaction network analysis, BMC Bioinformatics, doi:10.1186/s12859-020-03706-z
Khorsand, Savadi, Naghibzadeh, SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction network, Inform Med Unlocked, doi:10.1016/j.imu.2020.100413
Kipf, Welling, Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks, doi:10.48550/arXiv.1609.02907
Kwofie, Schaefer, Sundararajan, Bajic, Christoffels, HCVpro: hepatitis C virus protein interaction database, Infect Genet Evol, doi:10.1016/j.meegid.2011.09.001
Li, Zhao, Su, Yang, Hu et al., Discovering consensus regions for interpretable identification of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification sites via graph contrastive clustering, IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, doi:10.1109/JBHI.2024.3357979
Liu-Wei, Kafkas, Chen, Dimonaco, Tegnér et al., DeepViral: infectious disease phenotypes improve prediction of novel virus-host interactions, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, doi:10.1101/2020.04.22.055095
Luck, Kim, Lambourne, Spirohn, Begg et al., A reference map of the human binary protein interactome, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2188-x
Nielsen, Hierarchical Clustering, doi:10.1007/978-3-319-21903-5_8
Pele, Werman, Fast and robust Earth Mover's Distances, doi:10.1109/iccv.2009.5459199
Peri, Navarro, Amanchy, Kristiansen, Jonnalagadda et al., Development of human protein reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems biology in humans, Genome Res, doi:10.1101/gr.1680803
Peyré, Cuturi, Computational optimal transport: with applications to data science, Found Trend Mach Learn, doi:10.1561/2200000073
Ray, Alberuni, Maulik, Computational prediction of HCV-human protein-protein interaction via topological analysis of HCV infected PPI modules, IEEE Trans Nanobioscience, doi:10.1109/TNB.2018.2797696
Ray, Lall, Bandyopadhyay, A deep integrated framework for predicting SARS-CoV2-human protein-protein interaction, IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput Intell, doi:10.1109/tetci.2022.3182354
Ray, Lall, Mukhopadhyay, Bandyopadhyay, Schönhuth, Deep variational graph autoencoders for novel host-directed therapy options against COVID-19, Artif Intell Med, doi:10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102418
Rolland, Taşan, Charloteaux, Pevzner, Zhong et al., A proteome-scale map of the human interactome network, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.050
Rual, Venkatesan, Hao, Hirozane-Kishikawa, Dricot et al., Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network, Nature, doi:10.1038/nature04209
Rubner, Guibas, Tomasi, The earth mover's distance, multi-dimensional scaling, and color-based image retrieval
Sadegh, Matschinske, Blumenthal, Galindez, Kacprowski et al., Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 virus-host-drug interactome for drug repurposing, Nat Commun, doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17189-2
Seifirad, Pirfenidone: a novel hypothetical treatment for COVID-19, Med Hypotheses, doi:10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110005
Shah, Yamin, Ahmad, Wu, Jahangir et al., In-silico evaluation of natural alkaloids against the main protease and spike glycoprotein as potential therapeutic agents for SARS-CoV-2, PLoS One, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0294769
Shang, Ye, Shi, Wan, Luo et al., Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y
Shapira, Gat-Viks, Shum, Dricot, De Grace et al., A physical and regulatory map of host-influenza interactions reveals pathways in H1N1 infection, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.018
Subramanian, Narayan, Corsello, Peck, Natoli et al., A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the first 1,000,000 profiles, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.049
Villani, Optimal Transport: old and new, doi:10.1007/978-3-540-71050-9
Wang, Du, Payattakool, Yu, Chen, A new method to measure the semantic similarity of GO terms, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btm087
Wang, Liang, Hancock, Khoshgoftaar, Feature selection strategies: a comparative analysis of SHAP-value and importance-based methods, J Big Data, doi:10.1186/s40537-024-00905-w
Weisberg, Parent, Yang, Sattler, Liu et al., Repurposing of kinase inhibitors for treatment of COVID-19, Pharm Res, doi:10.1007/s11095-020-02851-7
Wu, Zhao, Yu, Chen, Song, Author Correction: a new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2202-3
Yamin, Ahmad, Khalid, Perveen, Abbasi et al., Identifying plant-derived antiviral alkaloids as dual inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease and spike glycoprotein through computational screening, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2024.1369659
Yang, Su, Zhao, Li, Hu et al., Fuzzy-based deep attributed graph clustering, IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst, doi:10.1109/tfuzz.2023.3338565
Ye, Li, Zhang, Li, Liu et al., Predicting drug-target interactions by measuring confidence with consistent causal neighborhood interventions, Methods, doi:10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.08.009
Yu, Li, Qin, Bo, Wu et al., GOSemSim: an R package for measuring semantic similarity among GO terms and gene products, Bioinformatics, doi:10.1093/bioinformatics/btq064
Yu, Tardivo, Tam, Weiner, Gebreab et al., Next-generation sequencing to generate interactome datasets, Nat Methods, doi:10.1038/nmeth.1597
Zhao, Su, Hu, Ma, Zhou et al., A geometric deep learning framework for drug repositioning over heterogeneous information networks, Brief Bioinform, doi:10.1093/bib/bbac384
Zhou, Park, Choi, Han, A generalized approach to predicting protein-protein interactions between virus and host, BMC Genomics, doi:10.1186/s12864-018-4924-2
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0332794",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0332794",
"abstract": "<jats:p>The COVID-19 pandemic has demanded urgent and accelerated action toward developing effective therapeutic strategies. Drug repurposing models (in silico) are in high demand and require accurate and reliable molecular interaction data. While experimentally verified viral–host interaction data (SARS-CoV-2–human interactions published on April 30, 2020) provide an invaluable resource, these datasets include only a limited number of high-confidence interactions. Here, we extend these resources using a deep learning–based multiview graph neural network approach, coupled with optimal transport–based integration.</jats:p>\n<jats:p>Our comprehensive validation strategy confirms 472 high-confidence predicted interactions between 280 host proteins and 27 SARS-CoV-2 proteins. The proposed model demonstrates robust predictive performance, achieving ROC-AUC scores of 85.9% (PPI network), 83.5% (GO similarity network), and 83.1% (sequence similarity network), with corresponding average precision scores of 86.4%, 82.8%, and 82.3% on independent test sets. Comparative evaluation shows that our multiview approach consistently outperforms conventional single-view and baseline graph learning methods.</jats:p>\n<jats:p>The model combines features derived from protein sequences, gene ontology terms, and physical interaction information to improve interaction prediction. Furthermore, we systematically map the predicted host factors to FDA-approved drugs and identify several candidates, including lenalidomide and pirfenidone, which have established or emerging roles in COVID-19 therapy. Overall, our framework provides comprehensive and accurate predictions of SARS-CoV-2–host protein interactions and represents a valuable resource for drug repurposing efforts.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3371-8516",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Ray",
"given": "Sumanta",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Alberuni",
"given": "Syed",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Schönhuth",
"given": "Alexander",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS One",
"container-title-short": "PLoS One",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-25T17:52:34Z",
"timestamp": 1758822754000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-25T17:52:43Z",
"timestamp": 1758822763000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Selvaraj",
"given": "Chandrabose",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-26T00:22:15Z",
"timestamp": 1758846135291,
"version": "3.44.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2025-09-25T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1758758400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0332794",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0332794",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
9,
25
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Author Correction: a new coronavirus associated with human respiratory disease in China",
"author": "F Wu",
"issue": "7803",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref001",
"volume": "580",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nrd.2017.162",
"article-title": "Host-directed therapies for bacterial and viral infections",
"author": "SHE Kaufmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "35",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Drug Discov.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref002",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.02002-18",
"article-title": "Network-guided discovery of influenza virus replication host factors",
"author": "EE Ackerman",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "mBio.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref003",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2024.1369659",
"article-title": "Identifying plant-derived antiviral alkaloids as dual inhibitors of SARS-CoV-2 main protease and spike glycoprotein through computational screening",
"author": "R Yamin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1369659",
"journal-title": "Front Pharmacol.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref004",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/cbdv.202402548",
"article-title": "Screening Asian medicinal plants for SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors: a computational approach",
"author": "H Khalid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Chem Biodivers.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref005",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0294769",
"article-title": "In-silico evaluation of natural alkaloids against the main protease and spike glycoprotein as potential therapeutic agents for SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "M Shah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS One.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref006",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "Comprehensive prediction of the SARS-CoV-2 vs. human interactome using PIPE4, SPRINT, and PIPE-Sites",
"author": "K Dick",
"journal-title": "Scholars Portal Dataverse.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref007",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2286-9",
"article-title": "A SARS-CoV-2 protein interaction map reveals targets for drug repurposing",
"author": "DE Gordon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "459",
"issue": "7816",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref008",
"volume": "583",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.artmed.2022.102418",
"article-title": "Deep variational graph autoencoders for novel host-directed therapy options against COVID-19",
"author": "S Ray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "102418",
"journal-title": "Artif Intell Med.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref009",
"volume": "134",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2025581118",
"article-title": "Network medicine framework for identifying drug-repurposing opportunities for COVID-19",
"author": "D Morselli Gysi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref010",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-17189-2",
"article-title": "Exploring the SARS-CoV-2 virus-host-drug interactome for drug repurposing",
"author": "S Sadegh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3518",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref011",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.imu.2020.100413",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2-human protein-protein interaction network",
"author": "B Khorsand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100413",
"journal-title": "Inform Med Unlocked.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref012",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7717/peerj.11117",
"article-title": "Multi-schema computational prediction of the comprehensive SARS-CoV-2 vs. human interactome",
"author": "K Dick",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PeerJ.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref013",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/TETCI.2022.3182354",
"article-title": "A deep integrated framework for predicting SARS-CoV2–human protein-protein interaction",
"author": "S Ray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1463",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput Intell.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref014",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bj.2020.08.003",
"article-title": "Machine learning techniques for sequence-based prediction of viral-host interactions between SARS-CoV-2 and human proteins",
"author": "L Dey",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "438",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Biomed J.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref015",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40031-021-00569-7",
"article-title": "Finding prediction of interaction between SARS-CoV-2 and human protein: a data-driven approach",
"author": "M Ghosh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1293",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "J Inst Eng India Ser B.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref016",
"volume": "102",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12859-020-03706-z",
"article-title": "Comprehensive host-pathogen protein-protein interaction network analysis",
"author": "B Khorsand",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "400",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinformatics.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref017",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/TNB.2018.2797696",
"article-title": "Computational prediction of HCV-human protein-protein interaction via topological analysis of HCV infected PPI modules",
"author": "S Ray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "55",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "IEEE Trans Nanobioscience.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref018",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2020.04.22.055095",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref019",
"unstructured": "Liu-Wei W, Kafkas Ş, Chen J, Dimonaco N, Tegnér J, Hoehndorf R. <refbooktitle>DeepViral: infectious disease phenotypes improve prediction of novel virus–host interactions</refbooktitle>. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory; 2020. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.04.22.055095"
},
{
"article-title": "Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks",
"author": "TN Kipf",
"journal-title": "arXiv preprint.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref020",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1561/2200000073",
"article-title": "Computational optimal transport: with applications to data science",
"author": "G Peyré",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "355",
"journal-title": "Found Trend Mach Learn.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref021",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-319-21903-5_8",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref022",
"unstructured": "Nielsen F. Hierarchical Clustering. <refbooktitle>Undergraduate Topics in Computer Science</refbooktitle>. Springer International Publishing; 2016. p. 195–211. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21903-5_8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s40537-024-00905-w",
"article-title": "Feature selection strategies: a comparative analysis of SHAP-value and importance-based methods",
"author": "H Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "J Big Data.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref023",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"article-title": "Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "J Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "221",
"issue": "7807",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref024",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4615-5381-6_65",
"article-title": "Mutations in xanthine dehydrogenase gene in subjects with hereditary xanthinuria",
"author": "K Ichida",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"journal-title": "Adv Exp Med Biol.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref025",
"volume": "431",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "Potential impact on coagulopathy of gene variants of coagulation related proteins that interact with SARS-CoV-2",
"author": "D Holcomb",
"journal-title": "bioRxiv.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref026",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "DenvInt: a database of protein–protein interactions between dengue virus and its hosts",
"author": "L Dey",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "PLoS Negl Trop Dis.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref027",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gku1126",
"article-title": "HIV-1, human interaction database: current status and new features",
"author": "D Ako-Adjei",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref028",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.meegid.2011.09.001",
"article-title": "HCVpro: hepatitis C virus protein interaction database",
"author": "SK Kwofie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1971",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Infect Genet Evol.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref029",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12864-018-4924-2",
"article-title": "A generalized approach to predicting protein-protein interactions between virus and host",
"author": "X Zhou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "568",
"journal-title": "BMC Genomics.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref030",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2017.11.007",
"article-title": "ZikaBase: an integrated ZIKV- human interactome map database",
"author": "S Gurumayum",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "203",
"journal-title": "Virology.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref031",
"volume": "514",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2009.12.018",
"article-title": "A physical and regulatory map of host-influenza interactions reveals pathways in H1N1 infection",
"author": "SD Shapira",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1255",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref032",
"volume": "139",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2017.10.049",
"article-title": "A next generation connectivity map: L1000 platform and the first 1,000,000 profiles",
"author": "A Subramanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1437",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref033",
"volume": "171",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molstruc.2020.128878",
"article-title": "Inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 main protease 3CLpro by means of α-ketoamide and pyridone-containing pharmaceuticals using in silico molecular docking",
"author": "AO Elzupir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128878",
"journal-title": "J Mol Struct.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref034",
"volume": "1222",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.110005",
"article-title": "Pirfenidone: a novel hypothetical treatment for COVID-19",
"author": "S Seifirad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "110005",
"journal-title": "Med Hypotheses.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref035",
"volume": "144",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0300060520958594",
"article-title": "Possible effect of epinephrine in minimizing COVID-19 severity: a review",
"author": "M Derakhshan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "J Int Med Res.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref036",
"volume": "48",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11095-020-02851-7",
"article-title": "Repurposing of kinase inhibitors for treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "E Weisberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "167",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Pharm Res.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref037",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nature04209",
"article-title": "Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein-protein interaction network",
"author": "J-F Rual",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1173",
"issue": "7062",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref038",
"volume": "437",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2014.10.050",
"article-title": "A proteome-scale map of the human interactome network",
"author": "T Rolland",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1212",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Cell.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref039",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2188-x",
"article-title": "A reference map of the human binary protein interactome",
"author": "K Luck",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "402",
"issue": "7803",
"journal-title": "Nature.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref040",
"volume": "580",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.1680803",
"article-title": "Development of human protein reference database as an initial platform for approaching systems biology in humans",
"author": "S Peri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2363",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Genome Res.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref041",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molcel.2007.06.027",
"article-title": "Systematic analysis of the protein interaction network for the human transcription machinery reveals the identity of the 7SK capping enzyme",
"author": "C Jeronimo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "262",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Mol Cell.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref042",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/gb-2012-13-8-r76",
"article-title": "A computational framework for boosting confidence in high-throughput protein-protein interaction datasets",
"author": "R Hosur",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Genome Biol.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref043",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ymeth.2024.08.009",
"article-title": "Predicting drug-target interactions by measuring confidence with consistent causal neighborhood interventions",
"author": "W Ye",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"journal-title": "Methods.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref044",
"volume": "231",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.1597",
"article-title": "Next-generation sequencing to generate interactome datasets",
"author": "H Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "478",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nat Methods.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref045",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"key": "pone.0332794.ref046",
"unstructured": "Duvenaud D, Maclaurin D, Iparraguirre J, Bombarell R, Hirzel T, Aspuru-Guzik A, et al. Convolutional networks on graphs for learning molecular fingerprints. In: Advances in neural information processing systems. 2015. p. 2224–32. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1509.09292"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-3-540-71050-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref047",
"unstructured": "Villani C. <refbooktitle>Optimal Transport: old and new</refbooktitle>. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. 2009. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-71050-9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/ICCV.2009.5459199",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref048",
"unstructured": "Pele O, Werman M. Fast and robust Earth Mover’s Distances. In: 2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. 2009. p. 460–7. https://doi.org/10.1109/iccv.2009.5459199"
},
{
"key": "pone.0332794.ref049",
"unstructured": "Rubner Y, Guibas L, Tomasi C. The earth mover’s distance, multi-dimensional scaling, and color-based image retrieval. In: Proceedings of the ARPA image understanding workshop. 1997. p. 668."
},
{
"author": "M Cuturi",
"first-page": "685",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref050",
"volume-title": "International conference on machine learning",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1137/100805741",
"article-title": "Barycenters in the Wasserstein space",
"author": "M Agueh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "904",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "SIAM J Math Anal.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref051",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/978-1-4939-3743-1",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref052",
"unstructured": "Dessimoz C, Škunca N. Semantic similarity in the gene ontology. <refbooktitle>The Gene Ontology Handbook</refbooktitle>. Springer New York; 2017. p. 161–73. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-3743-1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btm087",
"article-title": "A new method to measure the semantic similarity of GO terms",
"author": "JZ Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1274",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref053",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/bioinformatics/btq064",
"article-title": "GOSemSim: an R package for measuring semantic similarity among GO terms and gene products",
"author": "G Yu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "976",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Bioinformatics.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref054",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/TFUZZ.2023.3338565",
"article-title": "Fuzzy-based deep attributed graph clustering",
"author": "Y Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1951",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "IEEE Trans Fuzzy Syst.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref055",
"volume": "32",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1109/JBHI.2024.3357979",
"article-title": "Discovering consensus regions for interpretable identification of RNA N6-methyladenosine modification sites via graph contrastive clustering",
"author": "G Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2362",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "IEEE J Biomed Health Inform.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref056",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"article-title": "A geometric deep learning framework for drug repositioning over heterogeneous information networks",
"author": "B-W Zhao",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Brief Bioinform.",
"key": "pone.0332794.ref057",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 57,
"references-count": 57,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0332794"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A graph neural network-based approach for predicting SARS-CoV-2–human protein interactions from multiview data",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "20"
}