Pathological Glucose Levels Enhance Entry Factor Expression and Hepatic SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection
et al., Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1111/jcmm.70581, May 2025
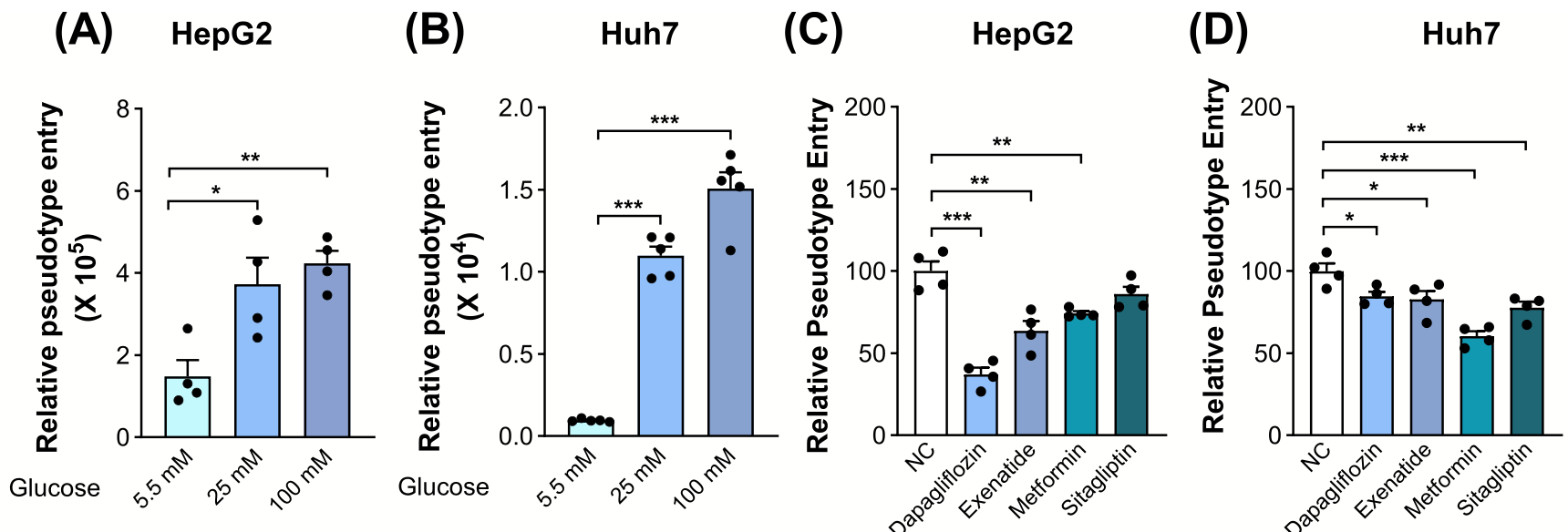
Analysis of high glucose levels on SARS-CoV-2 infection, showing that hyperglycemia significantly increases expression of viral entry factors (ACE2, TMPRSS2, TMPRSS4, FURIN, NRP1) in liver cells but not in lung and pancreatic cells, which enhances SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection in hepatocytes. Authors show that glucose-lowering drugs (metformin, dapagliflozin, sitagliptin, and exenatide) can reduce viral entry factor expression and SARS-CoV-2 infection under high glucose conditions.
Rao et al., 29 May 2025, China, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: tyfxh@163.com, xfu@scu.edu.cn.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Pathological Glucose Levels Enhance Entry Factor Expression and Hepatic SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, doi:10.1111/jcmm.70581
Accumulating clinical evidence suggests an intricate relationship between severe COVID-19 and preexisting metabolic complications, which share some metabolic dysregulations, including hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and hyperlipidaemia. However, the potential role of these metabolic risk factors in SARS-CoV-2 infection and entry factor expression remains unknown. Here we report the implication of hyperglycaemia in SARS-CoV-2 infection and therapy. Hyperglycaemia, instead of hyperinsulinaemia and hyperlipidaemia, can significantly induce the expression of SARS-CoV-2 entry factors (Ace2, Tmprss2, Tmprss4, Furin and Nrp1) in liver cells, but not in lung and pancreatic cells, which is attenuated by mTOR inhibition. Correspondingly, pathological glucose levels promote SARS-CoV-2 entry into cultured hepatocytes in pseudovirus cell systems. Conversely, representative glucose-lowering drugs (metformin, dapagliflozin, sitagliptin and exenatide) are able to diminish the enhancement of entry factor expression and SARS-CoV-2 infection in cultured hepatocytes under pathological glucose conditions. Intriguingly, SARS-CoV-2 entry factors are increased in the livers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes patients. These results define hyperglycaemia as a key susceptibility factor for hepatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, and provide insights into the clinical application of glucose-lowering therapies in COVID-19 patients under comorbid hyperglycaemia conditions.
| Introduction Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), caused by the SARS-CoV-2 virus, first emerged in December 2019. Despite the development of vaccines and improved therapies, global infections still spread at an alarming rate. Owing to its high contagiousness, the occurrence of asymptomatic carriers, and the rise of viral variants, SARS-CoV-2 remains a devastating threat to human lives, the
Author Contributions Guocheng Rao: investigation (lead), methodology (lead), writing -original draft (lead). Xiongbo Sang: conceptualization (equal), methodology (equal), writing -original draft (equal). Xinyue Zhu: investigation (equal), supervision (equal), writing -original draft (equal). Sailan Zou: formal analysis (equal), software (equal). Yanyan Zhang: formal analysis (equal), software (equal). Wei Cheng: data curation (equal). Yan Tian: methodology (equal), visualization (equal). Xianghui Fu: conceptualization (lead), project administration (lead), resources (lead), writing -review and editing (lead).
Ethics Statement The study was performed in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board and Biomedical Ethics Committee of West China Hospital of Sichuan University (WCH/SCU).
Consent Fully informed consent was obtained from all patients.
Conflicts of Interest The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Supporting Information Additional supporting information can be found online in the Supporting Information section.
References
Barreto, Cruz, Veras, COVID-19-Related Hyperglycemia Is Associated With Infection of Hepatocytes and Stimulation of Gluconeogenesis, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Battaglioni, Benjamin, Wälchli, Maier, Hall, mTOR Substrate Phosphorylation in Growth Control, Cell
Brevini, Maes, Webb, FXR Inhibition May Protect From SARS-CoV-2 Infection by Reducing ACE2, Nature
Cantuti-Castelvetri, Ojha, Pedro, Neuropilin-1 Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry and Infectivity, Science
Cao, Tian, Zhang, Signaling Pathways and Intervention for Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, MedComm
Chen, Fan, Chen, Nonmuscle Myosin Heavy Chain IIA Facilitates SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Human Pulmonary Cells, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America
Chen, Xu, Luo, NSUN2 Is a Glucose Sensor Suppressing cGAS/STING to Maintain Tumorigenesis and Immunotherapy Resistance, Cell Metabolism
Daly, Simonetti, Klein, Neuropilin-1 Is a Host Factor for SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Science
Delorey, Ziegler, Heimberg, COVID-19 Tissue Atlases Reveal SARS-CoV-2 Pathology and Cellular Targets, Nature
Drucker, Diabetes, Obesity, Metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: The End of the Beginning, Cell Metabolism
Du, Liu, Shi, A MicroRNA Checkpoint for Ca(2+) Signaling and Overload in Acute Pancreatitis, Molecular Therapy
Fan, Han, Zhao, The Effects of Obesity and Metabolic Abnormalities on Severe COVID-19-Related Outcomes After Vaccination: A Population-Based Study, Cell Metabolism
Frere, Tenoever, Cardiometabolic Syndrome: An Emergent Feature of Long COVID?, Nature Reviews Immunology
Fu, Dong, Tian, MicroRNA-26a Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolism of Glucose and Lipids, Journal of Clinical Investigation
Garreta, Prado, Stanifer, A Diabetic Milieu Increases ACE2 Expression and Cellular Susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 Infections in Human Kidney Organoids and Patient Cells, Cell Metabolism
Han, Yang, Lacko, Chen, Human Organoid Models to Study SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nature Methods
Handzlik, Gengatharan, Frizzi, Insulin-Regulated Serine and Lipid Metabolism Drive Peripheral Neuropathy, Nature
Hoffmann, Kleine-Weber, Schroeder, SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Jackson, Farzan, Chen, Choe, Mechanisms of SARS-CoV-2 Entry Into Cells, Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology
Khalatbari, Aghazadeh, Ji, Adverse Effects of Anti-Covid-19 Drug Candidates and Alcohol on Cellular Stress Responses of Hepatocytes, Hepatology Communications
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Prescription of Glucose-Lowering Therapies and Risk of COVID-19 Mortality in People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Observational Study in England, Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology
Liu, Du, Sang, RNA G-Quadruplex in TMPRSS2 Reduces SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nature Communications
Liu, Du, Xu, RNA G-Quadruplex Regulates MicroRNA-26a Biogenesis and Function, Journal of Hepatology
Liu, Zhang, Tian, Huang, Tong et al., Integrative Biology of Extracellular Vesicles in Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Complications, Theranostics
Ma, Zhang, Cao, UBE2O Promotes Lipid Metabolic Reprogramming and Liver Cancer Progression by Mediating HADHA Ubiquitination, Oncogene
Marjot, Webb, Barritt, COVID-19 and Liver Disease: Mechanistic and Clinical Perspectives, Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology
Muller, Gross, Conzelmann, SARS-CoV-2 Infects and Replicates in Cells of the Human Endocrine and Exocrine Pancreas, Nature Metabolism
Narayan, Staimez, Rising Diabetes Diagnosis in Long COVID, Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology
Norris, Razieh, Yates, Admission Blood Glucose Level and Its Association With Cardiovascular and Renal Complications in Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19, Diabetes Care
Rao, Peng, Zhang, Fu, Tian et al., MicroR-NAs in Diabetic Macroangiopathy, Cardiovascular Diabetology
Russell, Lone, Baillie, Comorbidities, Multimorbidity and COVID-19, Nature Medicine
Smet, Verhulst, Van Grunsven, Single Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis Did Not Predict Hepatocyte Infection by SARS-CoV-2, Journal of Hepatology
Steenblock, Schwarz, Ludwig, COVID-19 and Metabolic Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Management, Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology
Stefan, Metabolic Disorders, COVID-19 and Vaccine-Breakthrough Infections, Nature Reviews. Endocrinology
Sun, Li, Ju, In Vivo Structural Characterization of the SARS-CoV-2 RNA Genome Identifies Host Proteins Vulnerable to Repurposed Drugs, Cell
Tang, Uhl, Zhang, SARS-CoV-2 Infection Induces Beta Cell Transdifferentiation, Cell Metabolism
Tian, Xu, Du, Fu, The Interplay Between Noncoding RNAs and Insulin in Diabetes, Cancer Letters
Tong, Liu, Sang, Targeting RNA G-Quadruplex With Repurposed Drugs Blocks SARS-CoV-2 Entry, PLoS Pathogens
Van Cleemput, Van Snippenberg, Lambrechts, Organ-Specific Genome Diversity of Replication-Competent SARS-CoV-2, Nature Communications
Van Der Klaauw, Horner, Pereyra-Gerber, Accelerated Waning of the Humoral Response to COVID-19 Vaccines in Obesity, Nature Medicine
Wander, Lowy, Beste, Prior Glucose-Lowering Medication Use and 30-Day Outcomes Among 64,892 Veterans With Diabetes and COVID-19, Diabetes Care
Wang, De Carvalho Ribeiro, Iracheta-Vellve, Macrophage-Specific Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1α Contributes to Impaired Autophagic Flux in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis, Hepatology
Wanner, Andrieux, Badia, Molecular Consequences of SARS-CoV-2 Liver Tropism, Nature Metabolism
Willyard, Are Repeat COVID Infections Dangerous? What the Science Says, Nature
Wise, Covid-19: Infection Raises Risk of Diabetes and Heart Disease Diagnoses in Following Weeks, Study Finds, British Medical Journal
Wu, Lidsky, Xiao, SARS-CoV-2 Infects Human Pancreatic β Cells and Elicits β Cell Impairment, Cell Metabolism
Xie, Xu, Bowe, Al-Aly, Long-Term Cardiovascular Outcomes of COVID-19, Nature Medicine
Xu, Du, Liu, The Pseudokinase MLKL Regulates Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity Independently of Inflammation, Molecular Metabolism
Xu, Du, Xu, Pancreatic β Cell MicroRNA-26a Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes by Improving Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity and Preserving β Cell Function, PLoS Biology
Xu, Jiang, Wu, PLSCR1 Is a Cell-Autonomous Defence Factor Against SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Nature
Xu, Tian, Tang, An Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-MicroRNA-26a Feedback Circuit in NAFLD, Hepatology
Yu, Li, Sun, Wang, Insulin Treatment Is Associated With Increased Mortality in Patients With COVID-19 and Type 2 Diabetes, Cell Metabolism
Zadoorian, Du, Yang, Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Functions in Health and Disease, Nature Reviews. Endocrinology
Zhang, Chen, Tian, Fu, Host Factors of SARS-CoV-2 in Infection, Pathogenesis, and Long-Term Effects, Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology
Zhang, Jin, Wu, High Glucose Intake Exacerbates Autoimmunity Through Reactive-Oxygen-Species-Mediated TGF-β Cytokine Activation, Immunity
Zhou, Liu, Gupta, A Comprehensive SARS-CoV-2-Human Protein-Protein Interactome Reveals COVID-19 Pathobiology and Potential Host Therapeutic Targets, Nature Biotechnology
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jcmm.70581",
"ISSN": [
"1582-1838",
"1582-4934"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.70581",
"abstract": "<jats:title>ABSTRACT</jats:title><jats:p>Accumulating clinical evidence suggests an intricate relationship between severe COVID‐19 and preexisting metabolic complications, which share some metabolic dysregulations, including hyperglycaemia, hyperinsulinaemia and hyperlipidaemia. However, the potential role of these metabolic risk factors in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and entry factor expression remains unknown. Here we report the implication of hyperglycaemia in SARS‐CoV‐2 infection and therapy. Hyperglycaemia, instead of hyperinsulinaemia and hyperlipidaemia, can significantly induce the expression of SARS‐CoV‐2 entry factors (<jats:italic>Ace2</jats:italic>, <jats:italic>Tmprss2</jats:italic>, <jats:italic>Tmprss4</jats:italic>, <jats:italic>Furin</jats:italic> and <jats:italic>Nrp1</jats:italic>) in liver cells, but not in lung and pancreatic cells, which is attenuated by mTOR inhibition. Correspondingly, pathological glucose levels promote SARS‐CoV‐2 entry into cultured hepatocytes in pseudovirus cell systems. Conversely, representative glucose‐lowering drugs (metformin, dapagliflozin, sitagliptin and exenatide) are able to diminish the enhancement of entry factor expression and SARS‐CoV‐2 infection in cultured hepatocytes under pathological glucose conditions. Intriguingly, SARS‐CoV‐2 entry factors are increased in the livers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes patients. These results define hyperglycaemia as a key susceptibility factor for hepatic SARS‐CoV‐2 infection, and provide insights into the clinical application of glucose‐lowering therapies in COVID‐19 patients under comorbid hyperglycaemia conditions.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/jcmm.70581"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2024-10-16"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "2025-04-23"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 3,
"value": "2025-05-29"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Rao",
"given": "Guocheng",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Sang",
"given": "Xiongbo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Xinyue",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Zou",
"given": "Sailan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
},
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism Gansu Provincial Hospital Lanzhou China"
}
],
"family": "Zhang",
"given": "Yanyan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Cheng",
"given": "Wei",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"family": "Tian",
"given": "Yan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9808-3892",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Biotherapy, Center for Diabetes and Metabolism Research, State Key Laboratory of Biotherapy and Cancer Center, West China Hospital Sichuan University Chengdu Sichuan China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Fu",
"given": "Xianghui",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine",
"container-title-short": "J Cellular Molecular Medi",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-30T04:54:18Z",
"timestamp": 1748580858000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-30T04:54:27Z",
"timestamp": 1748580867000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100018537",
"award": [
"2023ZD0507500"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100018537",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Science and Technology Major Project"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100001809",
"award": [
"81970561",
"82172986",
"92157205"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/501100001809",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "National Natural Science Foundation of China"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-31T04:05:23Z",
"timestamp": 1748664323563,
"version": "3.41.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "11",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
29
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "11",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
29
]
],
"date-time": "2025-05-29T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1748476800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/jcmm.70581",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
29
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
5,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-023-01371-9",
"article-title": "Are Repeat COVID Infections Dangerous? What the Science Says",
"author": "Willyard C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "650",
"issue": "7958",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_13_2_1",
"volume": "616",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41580-021-00418-x",
"article-title": "Mechanisms of SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry Into Cells",
"author": "Jackson C. B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_3_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41587-022-01474-0",
"article-title": "A Comprehensive SARS‐CoV‐2‐Human Protein‐Protein Interactome Reveals COVID‐19 Pathobiology and Potential Host Therapeutic Targets",
"author": "Zhou Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "128",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature Biotechnology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_4_1",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-022-29135-5",
"article-title": "RNA G‐Quadruplex in TMPRSS2 Reduces SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection",
"author": "Liu G.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1444",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature Communications",
"key": "e_1_2_13_5_1",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd2985",
"article-title": "Neuropilin‐1 Facilitates SARS‐CoV‐2 Cell Entry and Infectivity",
"author": "Cantuti‐Castelvetri L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"issue": "6518",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "e_1_2_13_6_1",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd3072",
"article-title": "Neuropilin‐1 Is a Host Factor for SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection",
"author": "Daly J. L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"issue": "6518",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "e_1_2_13_7_1",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1011131",
"article-title": "Targeting RNA G‐Quadruplex With Repurposed Drugs Blocks SARS‐CoV‐2 Entry",
"author": "Tong Q.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "PLoS Pathogens",
"key": "e_1_2_13_8_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-023-02343-2",
"article-title": "Accelerated Waning of the Humoral Response to COVID‐19 Vaccines in Obesity",
"author": "Klaauw A. A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1146",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_13_9_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01689-3",
"article-title": "Long‐Term Cardiovascular Outcomes of COVID‐19",
"author": "Xie Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "583",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_13_10_1",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00739-8",
"article-title": "Cardiometabolic Syndrome: An Emergent Feature of Long COVID?",
"author": "Frere J. J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "399",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Immunology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_11_1",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-02156-9",
"article-title": "Comorbidities, Multimorbidity and COVID‐19",
"author": "Russell C. D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "334",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nature Medicine",
"key": "e_1_2_13_12_1",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.canlet.2018.01.038",
"article-title": "The Interplay Between Noncoding RNAs and Insulin in Diabetes",
"author": "Tian Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "53",
"journal-title": "Cancer Letters",
"key": "e_1_2_13_13_1",
"volume": "419",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/JCI75438",
"article-title": "MicroRNA‐26a Regulates Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolism of Glucose and Lipids",
"author": "Fu X.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2497",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Journal of Clinical Investigation",
"key": "e_1_2_13_14_1",
"volume": "125",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05637-6",
"article-title": "Insulin‐Regulated Serine and Lipid Metabolism Drive Peripheral Neuropathy",
"author": "Handzlik M. K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "118",
"issue": "7946",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_13_15_1",
"volume": "614",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-023-00845-0",
"article-title": "Lipid Droplet Biogenesis and Functions in Health and Disease",
"author": "Zadoorian A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "443",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews. Endocrinology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_16_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2022.04.009",
"article-title": "A Diabetic Milieu Increases ACE2 Expression and Cellular Susceptibility to SARS‐CoV‐2 Infections in Human Kidney Organoids and Patient Cells",
"author": "Garreta E.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "857",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_17_1",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.033",
"article-title": "A MicroRNA Checkpoint for Ca(2+) Signaling and Overload in Acute Pancreatitis",
"author": "Du W.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1754",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Molecular Therapy",
"key": "e_1_2_13_18_1",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pbio.3000603",
"article-title": "Pancreatic β Cell MicroRNA‐26a Alleviates Type 2 Diabetes by Improving Peripheral Insulin Sensitivity and Preserving β Cell Function",
"author": "Xu H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "PLoS Biology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_19_1",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2111011118",
"article-title": "Nonmuscle Myosin Heavy Chain IIA Facilitates SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection in Human Pulmonary Cells",
"author": "Chen J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "50",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "e_1_2_13_20_1",
"volume": "118",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep4.1887",
"article-title": "Adverse Effects of Anti‐Covid‐19 Drug Candidates and Alcohol on Cellular Stress Responses of Hepatocytes",
"author": "Khalatbari A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1262",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Hepatology Communications",
"key": "e_1_2_13_21_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2019.08.001",
"article-title": "High Glucose Intake Exacerbates Autoimmunity Through Reactive‐Oxygen‐Species‐Mediated TGF‐β Cytokine Activation",
"author": "Zhang D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "671",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "e_1_2_13_22_1",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41388-022-02509-1",
"article-title": "UBE2O Promotes Lipid Metabolic Reprogramming and Liver Cancer Progression by Mediating HADHA Ubiquitination",
"author": "Ma M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5199",
"issue": "48",
"journal-title": "Oncogene",
"key": "e_1_2_13_23_1",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.31428",
"article-title": "An Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress‐MicroRNA‐26a Feedback Circuit in NAFLD",
"author": "Xu H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_24_1",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.02.032",
"article-title": "RNA G‐Quadruplex Regulates MicroRNA‐26a Biogenesis and Function",
"author": "Liu G.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "371",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Hepatology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_25_1",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00244-8",
"article-title": "COVID‐19 and Metabolic Disease: Mechanisms and Clinical Management",
"author": "Steenblock C.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "786",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_26_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mco2.283",
"article-title": "Signaling Pathways and Intervention for Therapy of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus",
"author": "Cao R.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "MedComm",
"key": "e_1_2_13_27_1",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2024.1407261",
"article-title": "Host Factors of SARS‐CoV‐2 in Infection, Pathogenesis, and Long‐Term Effects",
"author": "Zhang Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_28_1",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-022-00552-6",
"article-title": "Molecular Consequences of SARS‐CoV‐2 Liver Tropism",
"author": "Wanner N.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "310",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Nature Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_29_1",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42255-021-00347-1",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 Infects and Replicates in Cells of the Human Endocrine and Exocrine Pancreas",
"author": "Muller J. A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "149",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nature Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_30_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.015",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection Induces Beta Cell Transdifferentiation",
"author": "Tang X.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1577",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_31_1",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.05.013",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 Infects Human Pancreatic β Cells and Elicits β Cell Impairment",
"author": "Wu C. T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1565",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_32_1",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-021-00426-4",
"article-title": "COVID‐19 and Liver Disease: Mechanistic and Clinical Perspectives",
"author": "Marjot T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "348",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_33_1",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05594-0",
"article-title": "FXR Inhibition May Protect From SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection by Reducing ACE2",
"author": "Brevini T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"issue": "7950",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_13_34_1",
"volume": "615",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1073/pnas.2217119120",
"article-title": "COVID‐19‐Related Hyperglycemia Is Associated With Infection of Hepatocytes and Stimulation of Gluconeogenesis",
"author": "Barreto E. A.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "21",
"journal-title": "Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America",
"key": "e_1_2_13_35_1",
"volume": "120",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molmet.2019.02.003",
"article-title": "The Pseudokinase MLKL Regulates Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity Independently of Inflammation",
"author": "Xu H.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "14",
"journal-title": "Molecular Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_36_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/hep.30215",
"article-title": "Macrophage‐Specific Hypoxia‐Inducible Factor‐1α Contributes to Impaired Autophagic Flux in Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis",
"author": "Wang X.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "545",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Hepatology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_37_1",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2023.07.009",
"article-title": "NSUN2 Is a Glucose Sensor Suppressing cGAS/STING to Maintain Tumorigenesis and Immunotherapy Resistance",
"author": "Chen T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1782",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_38_1",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.04.013",
"article-title": "mTOR Substrate Phosphorylation in Growth Control",
"author": "Battaglioni S.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1814",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "e_1_2_13_39_1",
"volume": "185",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS‐CoV‐2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "e_1_2_13_40_1",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(21)00050-4",
"article-title": "Prescription of Glucose‐Lowering Therapies and Risk of COVID‐19 Mortality in People With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Observational Study in England",
"author": "Khunti K.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "293",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_41_1",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7150/thno.65778",
"article-title": "Integrative Biology of Extracellular Vesicles in Diabetes Mellitus and Diabetic Complications",
"author": "Liu J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1342",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Theranostics",
"key": "e_1_2_13_42_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12933-024-02405-w",
"article-title": "MicroRNAs in Diabetic Macroangiopathy",
"author": "Rao G.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cardiovascular Diabetology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_43_1",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2021.01.016",
"article-title": "Diabetes, Obesity, Metabolism, and SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection: The End of the Beginning",
"author": "Drucker D. J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "479",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_44_1",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2023.02.016",
"article-title": "The Effects of Obesity and Metabolic Abnormalities on Severe COVID‐19‐Related Outcomes After Vaccination: A Population‐Based Study",
"author": "Fan X.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "585",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_45_1",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03570-8",
"article-title": "COVID‐19 Tissue Atlases Reveal SARS‐CoV‐2 Pathology and Cellular Targets",
"author": "Delorey T. M.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"issue": "7865",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_13_46_1",
"volume": "595",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.008",
"article-title": "In Vivo Structural Characterization of the SARS‐CoV‐2 RNA Genome Identifies Host Proteins Vulnerable to Repurposed Drugs",
"author": "Sun L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1865",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "e_1_2_13_47_1",
"volume": "184",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-26884-7",
"article-title": "Organ‐Specific Genome Diversity of Replication‐Competent SARS‐CoV‐2",
"author": "Van Cleemput J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6612",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Nature Communications",
"key": "e_1_2_13_48_1",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jhep.2020.05.030",
"article-title": "Single Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis Did Not Predict Hepatocyte Infection by SARS‐CoV‐2",
"author": "De Smet V.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "993",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Journal of Hepatology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_49_1",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-022-01453-y",
"article-title": "Human Organoid Models to Study SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection",
"author": "Han Y.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "418",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nature Methods",
"key": "e_1_2_13_50_1",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06322-y",
"article-title": "PLSCR1 Is a Cell‐Autonomous Defence Factor Against SARS‐CoV‐2 Infection",
"author": "Xu D.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "819",
"issue": "7971",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "e_1_2_13_51_1",
"volume": "619",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1709",
"article-title": "Admission Blood Glucose Level and Its Association With Cardiovascular and Renal Complications in Patients Hospitalized With COVID‐19",
"author": "Norris T.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1132",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "e_1_2_13_52_1",
"volume": "45",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41574-021-00608-9",
"article-title": "Metabolic Disorders, COVID‐19 and Vaccine‐Breakthrough Infections",
"author": "Stefan N.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "75",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews. Endocrinology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_53_1",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.o1838",
"article-title": "Covid‐19: Infection Raises Risk of Diabetes and Heart Disease Diagnoses in Following Weeks, Study Finds",
"author": "Wise J.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "British Medical Journal",
"key": "e_1_2_13_54_1",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-8587(22)00078-X",
"article-title": "Rising Diabetes Diagnosis in Long COVID",
"author": "Narayan K. M. V.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "298",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology",
"key": "e_1_2_13_55_1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2337/dc21-1351",
"article-title": "Prior Glucose‐Lowering Medication Use and 30‐Day Outcomes Among 64,892 Veterans With Diabetes and COVID‐19",
"author": "Wander P. L.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2708",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Care",
"key": "e_1_2_13_56_1",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.014",
"article-title": "Insulin Treatment Is Associated With Increased Mortality in Patients With COVID‐19 and Type 2 Diabetes",
"author": "Yu B.",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "65",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Cell Metabolism",
"key": "e_1_2_13_57_1",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 56,
"references-count": 56,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/jcmm.70581"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Pathological Glucose Levels Enhance Entry Factor Expression and Hepatic <scp>SARS</scp>‐<scp>CoV</scp>‐2 Infection",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "29"
}
rao3