Nutritional and lifestyle changes required for minimizing the recovery period in home quarantined COVID-19 patients of Punjab, Pakistan
et al., Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2458, Jul 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
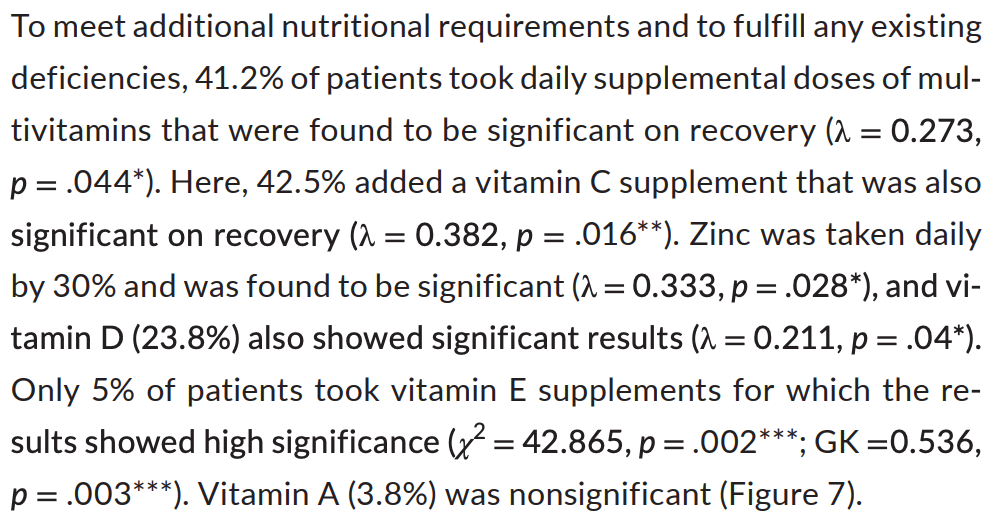
Survey of 80 recovered COVID-19 patients in Pakistan, showing faster recovery with vitamin C, vitamin D, and zinc supplementation.
Rabail et al., 9 Jul 2021, Pakistan, peer-reviewed, survey, 11 authors, study period November 2020 - February 2021.
Contact: emadkarrar26@uofg.edu.sd, raheemuaf@gmail.com, asimshabbir@live.com.
Nutritional and lifestyle changes required for minimizing the recovery period in home quarantined COVID‐19 patients of Punjab, Pakistan
Food Science & Nutrition, doi:10.1002/fsn3.2458
The COVID-19 pandemic has introduced a new battle in human history for a safe and fearless life. Therefore, this cross-sectional survey was conducted (Punjab, Pakistan) on healthy recovered, home quarantined COVID-19 patients to draw conclusive health support guidelines in the fight against this pandemic. COVID-19 recovered patients (n = 80) of age ≥14 years were randomly selected during the period November 2020 to February 2021. A nutrition and lifestyle changes questionnaire, containing ten sections and seventy questions, was completed through the telephone/WhatsApp. Data were transferred into an Excel spreadsheet and statistically analyzed by applying chi-square, correlation, and a t test of independent values using SPSS-16 software. The patients had an age range of 14 to 80 years, of which 52 (65%) were male and 28 (35%) were female, and 32 (40%) had a normal BMI. The patients had a peak COVID-19 recovery period of 2 weeks, and a mean recovery period of 2.8 ± 1.4 weeks. Certain variables, including gender (males), age (>40 years), sleep (≤5 hr), less/no physical activity, obesity, diabetes mellitus, and autoimmune diseases, were significantly associated with delayed recovery. Poor nutritional outcomes, including lower intakes of water, legumes, nuts, meat, and milk/yogurt; and
A PPEN D I X 1 N UTR ITI O N A N D LI FE S T Y LE M O D I FI C ATI O N Q U E S TI O N N A I R E FO R COV I D -19 PATI E NT S None/Half portions/1 portion/2 portions/> 2 portions How many portions of milk or yogurt do you consume per day? (1 serving =150 ml in a cup or 125 g a jar) None/Half portions/1 portion/2 portions/> 2 portions How many portions of cheese or dairy products do you consume per week? (1 portion of dairy product =100 g; 1 portion of matured cheese =50 g) None/Half portions/1 portion/2 portions/> 2 portions How many eggs do you consume per week? None/1 egg/2 eggs/4 eggs/> 4 eggs Did your lifestyle and eating habits changed during the COVID−19 pandemic period? No, they didn't/yes, it get worse/yes, it improved Did you change the number of daily meals, during this period? No, it did't/Yes, I skip 1 or more of the main meals (breakfast, lunch, dinner)/Yes, I skip 1 or more of snacks between meals/Yes I added 1 or more of the main meals/Yes, I added 1 or more of the snacks between meals/Yes, I eat out of the meals
References
Alagawany, Attia, Farag, Elnesr, Nagadi et al., The strategy of boosting the immune system under the COVID-19 pandemic, Frontiers in Veterinary Science
Aman, Masood, How nutrition can help to fight against COVID-19 pandemic, Pakistan Journal of Medical Sciences
Anker, Landmesser, Von Haehling, Butler, Coats et al., Weight loss, malnutrition, and cachexia in COVID-19: Facts and numbers, Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle
Antunes, Vinderola, Xavier-Santos, Sivieri, Potential contribution of bene fi cial microbes to face the COVID-19 pandemic, Food Research International
Ashwell, Gibson, Waist-to-height ratio as an indicator of early health risk: Simpler and more predictive than using a matrix based on BMI and waist circumference, British Medical Journal Open
Aspen, Nutrition and hydration : Key weapons in the fight against COVID-19
Barman, Rahman, Bora, Borgohain, COVID-19 pandemic and its recovery time of patients in India: A pilot study, Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews
Brahmaiah, Ankit, In silico screening of food bioactive compounds to predict potential inhibitors of COVID-19 main protease (Mpro) and RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)
Brugliera, Spina, Castellazzi, Cimino, Arcuri et al., Nutritional management of COVID-19 patients in a rehabilitation unit, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Bwire, Coronavirus: Why men are more vulnerable to Covid-19 than women?, SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine
Calder, Nutrition, immunity and COVID-19, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health
Cena, Chieppa, Coronavirus disease (COVID-19-SARS-CoV-2) and nutrition: Is infection in Italy suggesting a connection?, Frontiers in Immunology
Chowdhury, Hossain, Kashem, Shahid, Alam, Immune response in COVID-19: A review, Journal of Infection and Public Health
De Faria Coelho-Ravagnani, Corgosinho, Sanches, Prado, Laviano et al., Dietary recommendations during the COVID-19 pandemic, Nutrition Reviews
Dhar, Mohanty, Gut microbiota and Covid-19-possible link and implications, Virus Research
Di Renzo, Gualtieri, Pivari, Soldati, Attinà et al., Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey, Journal of Translational Medicine
Dietz, Santos-Burgoa, Obesity and its implications for COVID-19 mortality, Obesity
Do, Tran, Phan, Nguyen, Nguyen et al., Health literacy, ehealth literacy, adherence to infection prevention and control procedures, lifestyle changes, and suspected COVID-19 symptoms among health care workers during lockdown: Online survey, Journal of Medical Internet Research
Ettman, Abdalla, Cohen, Sampson, Vivier et al., Prevalence of depression symptoms in US adults before and during the COVID-19 pandemic
Filippo, Lorenzo, D'amico, Sofia, Roveri et al., COVID-19 is associated with clinically significant weight loss and risk of malnutrition, independent of hospitalisation: A post-hoc analysis of a prospective cohort study, Clinical Nutritionon
Griffith, Sharma, Holliday, Enyia, Valliere et al., Men and COVID-19: A biopsychosocial approach to understanding sex differences in mortality and recommendations for practice and policy interventions, Preventing Chronic Disease
Hariri, Narin, Deep neural networks for COVID-19 detection and diagnosis using images and acoustic-based techniques: A recent review
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Fernandez Del Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: Considerations during the covid-19 crisis, Nutrients
Im, Je, Baek, Chung, Kwon et al., Nutritional status of patients with COVID-19, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Jaggers, Watkins, Rodriguez, COVID-19: Repositioning nutrition research for the next pandemic, Nutrition Research
Jayawardena, Sooriyaarachchi, Chourdakis, Jeewandara, Ranasinghe, Enhancing immunity in viral infections, with special emphasis on COVID-19: A review, Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research and Reviews
Kamyari, Soltanian, Mahjub, Moghimbeigi, Diet, nutrition, obesity, and their implications for COVID-19 mortality: Development of a marginalized two-part model for semicontinuous data, JMIR Public Health and Surveillance
Khoramipour, Basereh, Hekmatikar, Castell, Ruhee et al., Physical activity and nutrition guidelines to help with the fight against COVID-19, Journal of Sports Sciences
Kieliszek, Lipinski, Selenium supplementation in the prevention of coronavirus infections, Medical Hypotheses
Kohlmeier, Avoidance of vitamin D deficiency to slow the COVID-19 pandemic, BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health
La Marca, Barp, Frenos, Mugelli, Galli et al., Thermal inactivation of SARS COVID-2 virus: Are steam inhalations a potential treatment?, Life Sciences
Lange, Nakamura, Movement and nutrition in COVID-19, Movement and Nutrition in Health and Disease
Liu, Chen, Wu, Lin, Wang et al., Effects of progressive muscle relaxation on anxiety and sleep quality in patients with COVID-19, Complementary Therapies in Clinical Practice
Liu, Liu, The management of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Journal of Medical Virology
Manzoor, Ahmad, Ahmed, Siddique, Zeng et al., Novel extraction techniques and pharmaceutical activities of luteolin and its derivatives, Journal of Food Biochemistry
Manzoor, Ahmad, Manzoor, Kalsoom, Food based phytochemical luteolin their derivatives, sources and medicinal benefits, International Journal of Agriculture Life Science
Messina, Polito, Monda, Cipolloni, Di Nunno et al., Functional role of dietary intervention to improve the outcome of COVID-19: A hypothesis of work, International Journal of Molecular Sciences
Morais, Passos, Vale, Maia, Maciel, Obesity and the increased risk for COVID-19: Mechanisms and nutritional management, Nutrition Research Reviews
Morrow-Howell, Galucia, Swinford, Recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic: A focus on older adults, Journal of Aging and Social Policy
Muhammad, None
Naja, Hamadeh, Nutrition amid the COVID-19 pandemic: A multi-level framework for action, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Nizami, Uddin, Strong immunity-A major weapon to fight against Covid-19 period with/without, IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences
Peckham, De Gruijter, Raine, Radziszewska, Ciurtin et al., Male sex identified by global COVID-19 meta-analysis as a risk factor for death and ITU admission, Nature Communications
Pi-Sunyer, Obesity: Criteria and classification, Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
Polverino, Cigarette smoking and COVID-19: A complex interaction, American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine
Popkin, Du, Green, Beck, Algaith et al., Individuals with obesity and COVID-19: A global perspective on the epidemiology and biological relationships, Obesity Reviews
Pradhan, Olsson, Sex differences in severity and mortality from COVID-19: Are males more vulnerable?, Biology of Sex Differences
Reddy, Charles, Sklavounos, Dutt, Seed et al., The effect of smoking on COVID-19 severity: A systematic review and meta-analysis, Journal of Medical Virology
Rossato, Russo, Mazzocut, Vincenzo, Fioretto et al., Current smoking is not associated with COVID-19
Shahid, Kalayanamitra, Mcclafferty, Kepko, Ramgobin et al., COVID-19 and older adults: What we know, Journal of the American Geriatrics Society
Silva, Ono, Souza, Sleep and immunity in times of COVID-19, Revista Da Associacao Medica Brasileira
Silverio, Gonçalves, Andrade, Seelaender, Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and nutritional status: The missing link?, Advances in Nutrition
Sr, No, Questions Answers 63 What activity you followed at quarantine? No/walk/weightless workout/weight training at home/tapis roulant/functional training/yoga/postural gymnastics/other 64 Did you inhale steam regularly during infection. Yes/No 65 Did you regularly check your BP, Glucose, and Oxygen level? Yes/No IX Recovery period 66 For how many days did you isolate yourself? Yes/No 67 What was your average recovery time
Swain, Sahu, Steam inhalation as an adjuvant treatment in COVID-19 positive health care professionals: Our experiences at tertiary care teaching hospital, International Journal of Current Research and Review
Thibault, Coëffier, Joly, Bohé, Schneider et al., How the Covid-19 epidemic is challenging our practice in clinical nutrition-feedback from the field, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Winskill, Whittaker et al., Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: A model-based analysis, The Lancet Infectious Diseases
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, Rabail et al., Nutritional and lifestyle changes required for minimizing the recovery period in home quarantined COVID-19 patients of Punjab, Pakistan, Food Science & Nutrition
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1002/fsn3.2458",
"ISSN": [
"2048-7177",
"2048-7177"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/fsn3.2458",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1002/fsn3.2458"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-06-07"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2021-06-23"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2021-07-09"
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1600-5191",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Food Science and TechnologyUniversity of Agriculture Faisalabad Pakistan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rabail",
"given": "Roshina",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Public Health, Institute of Social and Cultural Studies University of the Punjab Lahore Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Saleem",
"given": "Javeria",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Molecular Biology and Biotechnology (IMBB) University of Lahore Lahore Pakistan"
},
{
"name": "Department of Physiology Bolan University of Medical and Health Sciences (BUMHS) Quetta Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Tanveer",
"given": "Zunera",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Biomedical Sciences and Astbury Centre for Structural Molecular Biology University of Leeds Leeds UK"
}
],
"family": "Patching",
"given": "Simon G.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Livestock and Poultry Production Faculty of Veterinary Sciences Bahauddin Zakariya University Multan Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Khalid",
"given": "Abdur Rauf",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Institute of Food Science and Nutrition Bahauddin Zakariya University Multan Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Sultan",
"given": "Muhammad Tauseef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3705-0277",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Food and Biological Engineering Jiangsu University Zhenjiang China"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Manzoor",
"given": "Muhammad Faisal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5430-4083",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Food Engineering and Technology Faculty of Engineering and Technology University Gezira Wad Medani Sudan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Karrar",
"given": "Emad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Food Science and TechnologyUniversity of Agriculture Faisalabad Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Inam‐Ur‐Raheem",
"given": "Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Food Science and TechnologyUniversity of Agriculture Faisalabad Pakistan"
}
],
"family": "Shabbir",
"given": "Muhammad Asim",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0185-0096",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "National Institute of Food Science and TechnologyUniversity of Agriculture Faisalabad Pakistan"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Aadil",
"given": "Rana Muhammad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Food Science & Nutrition",
"container-title-short": "Food Sci Nutr",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-09T09:52:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625824320000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9,
15
]
],
"date-time": "2021-09-15T07:30:49Z",
"timestamp": 1631691049000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-01T09:10:33Z",
"timestamp": 1648804233037
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "9",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "9",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625788800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-07-09T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1625788800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/fsn3.2458",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full-xml/10.1002/fsn3.2458",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/fsn3.2458",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"page": "5036-5059",
"prefix": "10.1002",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
7,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
9
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fvets.2020.570748",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_2_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.12669/pjms.36.COVID19-S4.2776",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_3_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcsm.12674",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_4_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109577",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_5_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Waist‐to‐height ratio as an indicator of early health risk: Simpler and more predictive than using a matrix based on BMI and waist circumference",
"author": "Ashwell M.",
"first-page": "e010159",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "British Medical Journal Open",
"key": "e_1_2_9_6_1",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"author": "ASPEN",
"key": "e_1_2_9_7_1",
"volume-title": "Nutrition and hydration : Key weapons in the fight against COVID‐19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.07.004",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_8_1"
},
{
"author": "Brahmaiah P.",
"key": "e_1_2_9_9_1",
"volume-title": "In silico screening of food bioactive compounds to predict potential inhibitors of COVID‐19 main protease (Mpro) and RNA‐dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp)",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0664-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_10_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00341-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_11_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000085",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_12_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.00944",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_13_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_14_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nutrit/nuaa067",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_15_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_16_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02399-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_17_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/oby.22818",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_18_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/22894",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_19_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.19686",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_20_1"
},
{
"author": "FAO",
"key": "e_1_2_9_21_1",
"volume-title": "Maintaining a healthy diet during the COVID‐19 pandemic",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm9082589",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_22_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clnu.2020.10.043",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_23_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5888/pcd17.200247",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_24_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Deep neural networks for COVID‐19 detection and diagnosis using images and acoustic‐based techniques: A recent review",
"author": "Hariri W.",
"journal-title": "ArXiv",
"key": "e_1_2_9_25_1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_26_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.08.018",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_27_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nutres.2020.07.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_28_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.015",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_29_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2196/22717",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_30_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/02640414.2020.1807089",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_31_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109878",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_32_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmjnph-2020-000096",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_33_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2020.118801",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_34_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Movement and nutrition in COVID‐19",
"author": "Lange K. W.",
"first-page": "89",
"journal-title": "Movement and Nutrition in Health and Disease",
"key": "e_1_2_9_35_1",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.25965",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_36_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctcp.2020.101132",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_37_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jfbc.12974",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_38_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Food based phytochemical luteolin their derivatives, sources and medicinal benefits",
"author": "Manzoor M. F.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Agriculture Life Science",
"key": "e_1_2_9_39_1",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms21093104",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_40_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S095442242000027X",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_41_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08959420.2020.1759758",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_42_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0634-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_43_1"
},
{
"key": "e_1_2_9_44_1",
"unstructured": "NIH(2020).Laboratory‐testing‐recommendations‐for‐COVID‐19.pdf. In laboratory testing recommendation for COVID‐19 ‐ NIH. Retrieved fromhttps://www.nih.org.pk/wp‐content/uploads/2020/04/Laboratory‐Testing‐Recommendations‐for‐COVID‐19.pdf"
},
{
"article-title": "Strong immunity‐ A major weapon to fight against Covid‐19 period with/without",
"author": "Nizami N. S.",
"first-page": "22",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "IOSR Journal of Pharmacy and Biological Sciences",
"key": "e_1_2_9_45_1",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19741-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_46_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S0029665100000732",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_47_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/rccm.202005-1646LE",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_48_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/obr.13128",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_49_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13293-020-00330-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_50_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26389",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_51_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.01290-2020",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_52_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/jgs.16472",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_53_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1590/1806-9282.66.s2.143",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_54_1"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID‐19) and nutritional status: The missing link?",
"author": "Silverio R.",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Advances in Nutrition",
"key": "e_1_2_9_55_1",
"volume": "2019",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31782/IJCRR.2021.13525",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_56_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-00757-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_57_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_58_1"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051466",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "e_1_2_9_59_1"
}
],
"reference-count": 58,
"references-count": 58,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/fsn3.2458"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Food Science"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nutritional and lifestyle changes required for minimizing the recovery period in home quarantined COVID‐19 patients of Punjab, Pakistan",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy",
"volume": "9"
}
