The role of N-acetylcysteine in decreasing neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19 patients: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial
et al., Narra J, doi:10.52225/narra.v3i2.121, NCT05658549, May 2023
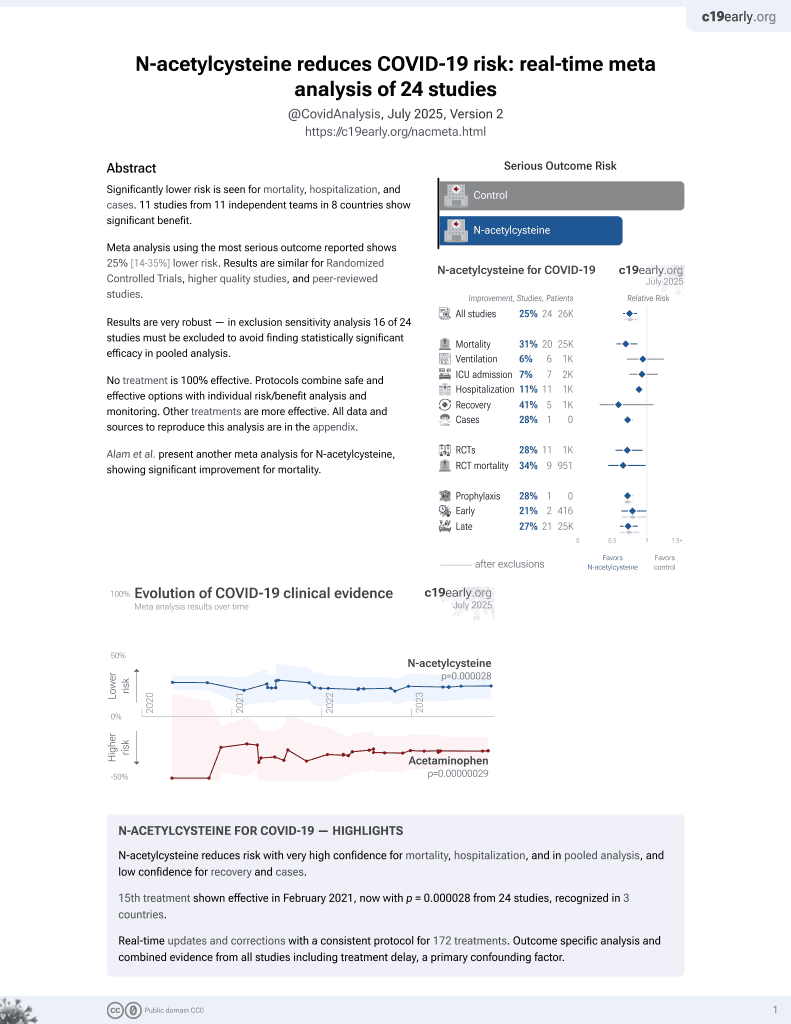
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
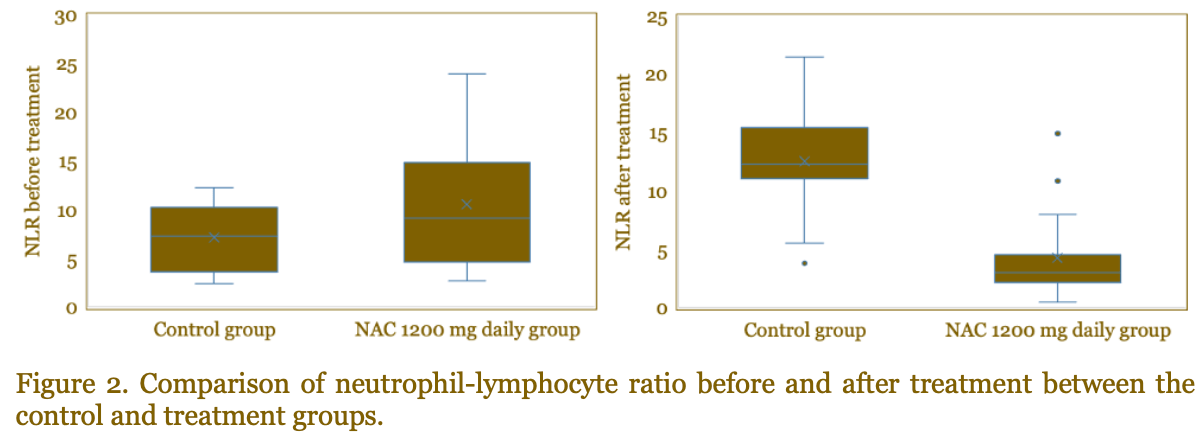
RCT 40 moderate/severe COVID-19 patients in Indonesia, showing significantly lower NLR with N-acetylcysteine treatment.
Prabowo et al., 19 May 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Indonesia, peer-reviewed, mean age 44.7, 3 authors, trial NCT05658549 (history).
Contact: dr.nurhasan21@staff.uns.ac.id.
c cerebellum
doi:10.52225/narraj.v3i2.121
N-acetylcysteine has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities that could potentially improve the clinical outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. Nacetylcysteine potentially inhibits NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR-and pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and results in control oxidative stress and cytokine release in COVID-19 patients. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of N-acetylcysteine in reducing the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in COVID-19 patients. A randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted among severe and moderate COVID-19 patients. The treatment group received oral 1200 mg daily of N-acetylcysteine (three times a day) and the standard care for COVID-19, while the control group received standard care for COVID-19 and a placebo. The NLR was determined on the first day of admission and after the seventh day of treatment. A paired Student t-test was used to compare the NLR before and after treatment while independent Student t-test was used to compare the NLR between treatment and control groups. A total of 40 severe and moderate COVID-19 were enrolled, 20 people in each group, with a mean age was 44.68±13.24 years old. The mean NLR on the first day was 9.44 in the treatment group and 8.84 in the control group. After the seventh day, the mean NLR was 4.27 and 11.54 in the treatment group and control group, respectively. The mean changes of NLR (the pre-treatment compared to posttreatment) in the treatment and control group were reduced 4.05 and increased 3.34, respectively. The NLR in treatment group significantly decreased compared to the control group (p<0.001). In conclusion, N-acetylcysteine 1200 mg daily could reduce the NLR in severe and moderate COVID-19 patients.
Ethics approval The Health Research Ethics Committee of Dr. Moewardi Hospital Surakarta has approved this research by approval Number: 149/II/HREC/2021. All participants provided informed consent before the study started.
Conflict of interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Underlying data Derived data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author on request.
References
Arulselvan, Fard, Tan, Role of Antioxidants and Natural Products in Inflammation, Oxid Med Cell Longev
Buonacera, Stancanelli, Colaci, Malatino, Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio: An emerging marker of the relationships between the immune system and diseases, Int J Mol Sci
Channappanavar, Fehr, Vijay, Dysregulated type I interferon and inflammatory monocyte-macrophage responses cause lethal pneumonia in SARS-CoV-infected mice, Cell Host Microbe
Ciccullo, Borghetti, Dal Verme, Neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio and clinical outcome in COVID-19: a report from the Italian front line, Int J Antimicrob Agents
Dahlan, Sample Size & sampling method in medicine and health research (Besar sampel dan cara pengambilan sampel dalam penelitian kedokteran dan kesehatan)
Fahriani, Ilmawan, Fajar, Persistence of long COVID symptoms in COVID-19 survivors worldwide and its potential pathogenesis -A systematic review and meta-analysis, Narra J
Ferrero-Miliani, Nielsen, Andersen, Girardin, Chronic inflammation: importance of NOD2 and NALP3 in interleukin-1β generation, Clinical and Experimental Immunology
Hecke, N-Acetylcysteine, A rapid review of the evidence for effectiveness in treating COVID-19. The Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine
Jomah, Asdaq, Mj, Clinical efficacy of antivirals against novel coronavirus (COVID-19): A review, J Infect Public Health
Kelley, Jeltema, Duan, He, The NLRP3 inflammasome: An overview of mechanisms of activation and regulation, Int J Mol Sci
Kotani, Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio and the oxidative stress burden, Can J Cardiol
Kovacic, Somanathan, Inflammation and anti-inflammatory agents -reactive oxygen species and toxicity
Li, Guan, Wu, Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia, N Engl J Med
Mccreary, Pogue, Coronavirus disease 2019 treatment: A review of early and emerging options, Open Forum Infect Dis
Milara, Martínez-Expósito, Montero, N-acetylcysteine reduces inflammasome activation induced by SARS-CoV-2 proteins in vitro, Int J Mol Sci
Prabowo, Apriningsih, Colchicine reduces the degree of inflammation in COVID-19 patients, IOP Conf Ser: Earth Environ Sci
Prabowo, Myrtha, Apriningsih, Lupus flares in COVID-19 patients: A case report, Malays J Med Health Sci
Prabowo, Setyaningrum, Apriningsih, Interleukin 6 associated with adrenal insufficiency in COVID-19 patient, Malays J Med Health Sci
Qin, Zhou, Hu, Dysregulation of immune response in patients with coronavirus 2019 (COVID-19) in Wuhan, Clin Infect Dis
Qu, Ling, Zhang, Platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio is associated with prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease-19, J Med Virol
Sanders, Monogue, Jodlowski, Cutrell, Pharmacologic Treatments for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): A Review, JAMA
Shah, Novel coronavirus-induced NLRP3 Inflammasome activation: A potential drug target in the treatment of COVID-19, Front Immunol
Sharun, Tiwari, Yatoo, A comprehensive review on pharmacologic agents, immunotherapies and supportive therapeutics for COVID-19, Narra J
Shi, Puyo, N-Acetylcysteine to combat COVID-19: An evidence review, Ther Clin Risk Manag
Toori, Qureshi, Chaudhry, Safdar, Neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in COVID-19: A cheap prognostic marker in a resource constraint setting, Pak J Med Sci
Turkmen, Tonbul, Toker, The Relationship between oxidative stress, inflammation, and atherosclerosis in renal transplant and end-stage renal disease patients, Renal Failure
Washington, Bashur, Delivery of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory agents for tissue engineered vascular grafts, Front Pharmacol
Yang, Liu, Tao, Li, The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients, Int Immunopharmacol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.52225/narra.v3i2.121",
"ISSN": [
"2807-2618"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.52225/narra.v3i2.121",
"abstract": "<jats:p>\n\nN-acetylcysteine has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities that could potentially improve the clinical outcomes of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients. N-acetylcysteine potentially inhibits NLRP3 (NOD-, LRR- and pyrin domain-containing protein 3) inflammasome and results in control oxidative stress and cytokine release in COVID-19 patients. The aim of this study was to assess the effect of N-acetylcysteine in reducing the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) in COVID-19 patients. A randomized controlled clinical trial was conducted among severe and moderate COVID-19 patients. The treatment group received oral 1200 mg daily of N-acetylcysteine (three times a day) and the standard care for COVID-19, while the control group received standard care for COVID-19 and a placebo. The NLR was determined on the first day of admission and after the seventh day of treatment. A paired Student t-test was used to compare the NLR before and after treatment while independent Student t-test was used to compare the NLR between treatment and control groups. A total of 40 severe and moderate COVID-19 were enrolled, 20 people in each group, with a mean age was 44.68±13.24 years old. The mean NLR on the first day was 9.44 in the treatment group and 8.84 in the control group. After the seventh day, the mean NLR was 4.27 and 11.54 in the treatment group and control group, respectively. The mean changes of NLR (the pre-treatment compared to post-treatment) in the treatment and control group were reduced 4.05 and increased 3.34, respectively. The NLR in treatment group significantly decreased compared to the control group (p<0.001). In conclusion, N-acetylcysteine 1200 mg daily could reduce the NLR in severe and moderate COVID-19 patients.\n\n</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2016-5649",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Prabowo",
"given": "Nurhasan A.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Megantara",
"given": "Marcellino A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3811-2633",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Apriningsih",
"given": "Hendrastutik",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Narra J",
"container-title-short": "Narra J",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
20
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-20T09:58:13Z",
"timestamp": 1684576693000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-23T09:58:38Z",
"timestamp": 1684835918000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-24T04:40:09Z",
"timestamp": 1684903209330
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2023-05-19T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1684454400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://narraj.org/main/article/download/121/109",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://narraj.org/main/article/download/121/109",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "29794",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e121",
"prefix": "10.52225",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
5,
19
]
]
},
"publisher": "Narra T",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://narraj.org/main/article/view/121"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The role of N-acetylcysteine in decreasing neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio in COVID-19 patients: A double-blind, randomized controlled trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "3"
}