Nitric oxide versus epoprostenol for refractory hypoxemia in Covid-19
et al., PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0270646, Jun 2022
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
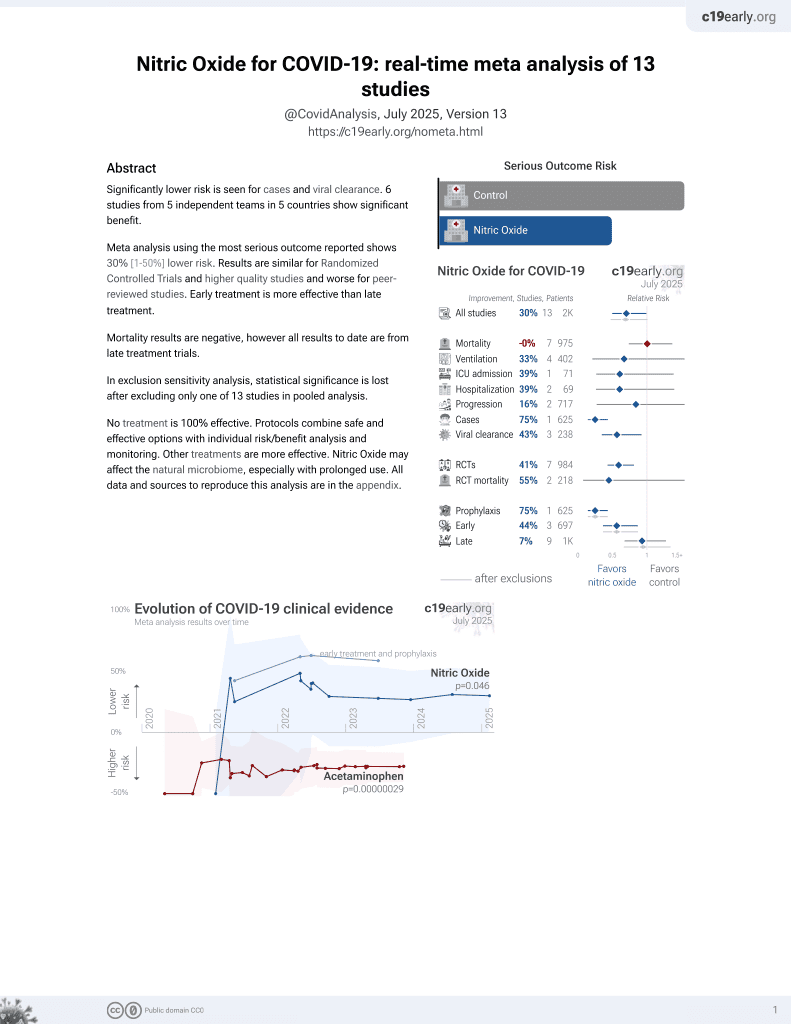
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
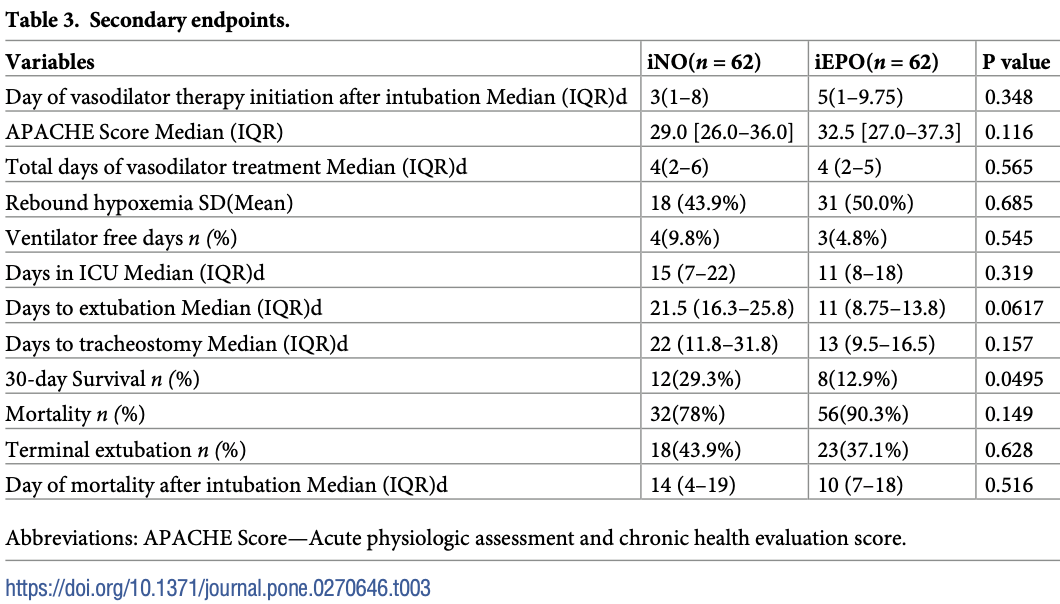
Retrospective 103 mechanically ventilated patients, 41 treated with inhaled nitric oxide, and 62 with inhaled epoprostenol, showing no significant difference in outcomes.
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
This may explain in part the very high mortality seen in this study.
Results may differ in countries with improved SOC.
|
risk of death, 13.6% lower, RR 0.86, p = 0.10, treatment 32 of 41 (78.0%), control 56 of 62 (90.3%), NNT 8.1.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Poonam et al., 27 Jun 2022, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 5 authors, study period 1 March, 2020 - 30 June, 2020, this trial compares with another treatment - results may be better when compared to placebo.
Contact: poonampaibh@gmail.com.
Nitric oxide versus epoprostenol for refractory hypoxemia in Covid-19
PLOS ONE, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0270646
Objective To compare the efficacy and outcomes with inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) and inhaled epoprostenol (iEPO) in patients with refractory hypoxemia due to COVID-19.
Design Retrospective Cohort Study.
Setting Single health system multicenter academic teaching hospitals.
Patients OR subjects Age group of 18-80 years admitted to the medical ICU.
Interventions Mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 infection, who
Supporting information S1
References
Alhazzani, Møller, Arabi, Surviving Sepsis Campaign: guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06022-5
Ammar, Bauer, Bass, Noninferiority of Inhaled Epoprostenol to Inhaled Nitric Oxide for the Treatment of ARDS, Annals of Pharmacotherapy, doi:10.1177/1060028015595642
Boisrame, Helms, Kremer, Schini-Kerth, Endothelial dysfunction in sepsis, Curr Vasc Pharmacol
Fuller, Mohr, Skrupky, The use of inhaled prostaglandins in patients with ARDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Chest, doi:10.1378/chest.14-3161
Fumito, Jesse, Zapol Warren, Inhaled Nitric Oxide, Circulation, doi:10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62
Gattinoni, Chiumello, Caironi, COVID-19 pneumonia: different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes?, Intensive Care Med, doi:10.1007/s00134-020-06033-2
Gonzales, Lucas, Verin, The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mechanisms and Perspective Therapeutic Approaches, Austin J Vasc Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5
Jeremy, Szumita Paul, Schuler Brian, Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Inhaled Epoprostenol and Inhaled Nitric Oxide for Refractory Hypoxemia in Patients With Coronavirus Disease, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000259
Kaisers, Busch, Selective pulmonary vasodilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Crit Care Med, doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000057913.45273.1A
Kallet, Burns, Zhuo, Severity of hypoxemia and other factors that influence the response to aerosolized prostacyclin in ARDS, Respir Care, doi:10.4187/respcare.05268
Li, Fink, Augustynovich, Effects of Inhaled Epoprostenol and Prone Positioning in Intubated Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients With Refractory Hypoxemia, Crit Care Explor, doi:10.1097/CCE.0000000000000307
Lotz, Muellenbach, Meybohm, Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19-induced ARDS-Is it worthwhile?, Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, doi:10.1111/aas.13757
Potus, Mai, Lebret, Novel insights on the pulmonary vascular consequences of COVID-19, Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, doi:10.1152/ajplung.00195.2020
Price, Garfield, Bleakley, Rescue therapy with thrombolysis in patients with severe COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome, Pulm Circ, doi:10.1177/2045894020973906
Rocca, Coccia, Pompei, Hemodynamic and oxygenation changes of combined therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and inhaled prostacyclin, J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth, doi:10.1053/jcan.2001.21974
Sonti, Pike, Cobb, Responsiveness of Inhaled Epoprostenol in Respiratory Failure due to COVID-19, Journal of Intensive Care Medicine, doi:10.1177/0885066620976525
Torbic, Szumita, Anger, Inhaled epoprostenol vs inhaled nitric oxide for refractory hypoxemia in critically ill patients, J Crit Care, doi:10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.03.006
Walmrath, Schneider, Schermuly, Direct comparison of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized prostacyclin in acute respiratory distress syndrome, Am J Respir Crit Care Med, doi:10.1164/ajrccm.153.3.8630585
Wang, Hu, Hu, Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.1585
Wu, Chen, Cai, Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China, JAMA Intern Med, doi:10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0270646",
"ISSN": [
"1932-6203"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270646",
"abstract": "<jats:sec id=\"sec001\">\n<jats:title>Objective</jats:title>\n<jats:p>To compare the efficacy and outcomes with inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) and inhaled epoprostenol (iEPO) in patients with refractory hypoxemia due to COVID-19.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec002\">\n<jats:title>Design</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Retrospective Cohort Study.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec003\">\n<jats:title>Setting</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Single health system multicenter academic teaching hospitals.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec004\">\n<jats:title>Patients OR subjects</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Age group of 18–80 years admitted to the medical ICU.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec005\">\n<jats:title>Interventions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>Mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19 infection, who received either iNO or iEPO between March 1<jats:sup>st</jats:sup>, 2020, and June 30<jats:sup>th</jats:sup>, 2020.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec006\">\n<jats:title>Measurements and main results</jats:title>\n<jats:p>The primary outcome was the change in the PaO2/FiO2 (P/F) ratio 1 hour after initiation of pulmonary vasodilator therapy. Secondary outcomes include P/F ratios on days 1–3 after initiation, positive response in P/F ratio (increase of at least 20% in PaO2), total days of treatment, rebound hypoxemia (if there was a drop in oxygen saturation after treatment was stopped), ventilator free days (if any patient was extubated), days in ICU, days to extubation, days to tracheostomy, mortality days after intubation, 30-day survival and mortality. 183 patients were excluded, as they received both iNO and iEPO. Of the remaining 103 patients, 62 received iEPO and 41 received iNO. The severity of ARDS was similar in both groups. Change in P/F ratio at one hour was 116 (70.3) with iNO and 107 (57.6) with iEPO (Mean/SD). Twenty-two (53.7%) patients in the iNO group and 25 (40.3%) in the iEPO group were responders to pulmonary vasodilators <jats:italic>n(%)(</jats:italic>p = 0.152) (more than 20% increase in partial pressure of oxygen, Pao2), and 18 (43.9%) and 31 (50%) patients in the iNO and iEPO group (p = 0.685), respectively, had rebound hypoxemia. Only 7 patients in the cohort achieved ventilator free days (3 in the iEPO group and 4 in iNO group).</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>\n<jats:sec id=\"sec007\">\n<jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n<jats:p>We found no significant difference between iNO and iEPO in terms of change in P/F ratio, duration of mechanical ventilation, ICU, in-hospital mortality in this cohort of mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19. Larger, prospective studies are necessary to validate these results.</jats:p>\n</jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7089-8715",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Poonam",
"given": "Pai B. H.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koscik",
"given": "Rebecca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nguyen",
"given": "Trong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Rikhi",
"given": "Shefali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lin",
"given": "Hung-Mo",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "PLOS ONE",
"container-title-short": "PLoS ONE",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"www.plosone.org"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-27T17:24:46Z",
"timestamp": 1656350686000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-27T17:25:05Z",
"timestamp": 1656350705000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Torrens",
"given": "Christopher",
"sequence": "first"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-27T17:42:28Z",
"timestamp": 1656351748037
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-27T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1656288000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270646",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "340",
"original-title": [],
"page": "e0270646",
"prefix": "10.1371",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
27
]
]
},
"publisher": "Public Library of Science (PLoS)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "D Wang",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref001",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "C Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"issue": "10223",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref002",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994",
"article-title": "Risk Factors Associated With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome and Death in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pneumonia in Wuhan, China",
"author": "C Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "934",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref003",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06033-2",
"article-title": "COVID-19 pneumonia: different respiratory treatments for different phenotypes?",
"author": "L Gattinoni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1099",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref004",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm.153.3.8630585",
"article-title": "Direct comparison of inhaled nitric oxide and aerosolized prostacyclin in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "D Walmrath",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "991",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Am J Respir Crit Care Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref005",
"volume": "153",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/jcan.2001.21974",
"article-title": "Hemodynamic and oxygenation changes of combined therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and inhaled prostacyclin",
"author": "GD Rocca",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "224",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref006",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2001"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1378/chest.14-3161",
"article-title": "The use of inhaled prostaglandins in patients with ARDS: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "BM Fuller",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1510",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Chest",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref007",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1161/01.CIR.0000134595.80170.62",
"article-title": "Inhaled Nitric Oxide",
"author": "Fumito Ichinose",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3106",
"journal-title": "Circulation",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref008",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2013.03.006",
"article-title": "Inhaled epoprostenol vs inhaled nitric oxide for refractory hypoxemia in critically ill patients",
"author": "H Torbic",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "844",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref009",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/2045894020973906",
"article-title": "Rescue therapy with thrombolysis in patients with severe COVID-19-associated acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "LC Price",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Pulm Circ",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref010",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "The Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Mechanisms and Perspective Therapeutic Approaches",
"author": "JN Gonzales",
"first-page": "1009",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Austin J Vasc Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref011",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.CCM.0000057913.45273.1A",
"article-title": "Selective pulmonary vasodilation in acute respiratory distress syndrome",
"author": "U Kaisers",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S337",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref012",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/1060028015595642",
"article-title": "Noninferiority of Inhaled Epoprostenol to Inhaled Nitric Oxide for the Treatment of ARDS",
"author": "MA Ammar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1105",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Annals of Pharmacotherapy",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref013",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000259",
"article-title": "Evaluation of the Efficacy and Safety of Inhaled Epoprostenol and Inhaled Nitric Oxide for Refractory Hypoxemia in Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019",
"author": "Jeremy R. DeGrado",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0259",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Critical Care Explorations",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref014",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00134-020-06022-5",
"article-title": "Surviving Sepsis Campaign: guidelines on the management of critically ill adults with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19)",
"author": "W Alhazzani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "854",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Intensive Care Med",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref015",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/aas.13757",
"article-title": "Effects of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19–induced ARDS–Is it worthwhile?",
"author": "C Lotz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "629",
"journal-title": "Acta Anaesthesiol Scand",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref016",
"volume": "65",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/CCE.0000000000000307",
"article-title": "Effects of Inhaled Epoprostenol and Prone Positioning in Intubated Coronavirus Disease 2019 Patients With Refractory Hypoxemia",
"author": "J Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e0307",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Crit Care Explor",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref017",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0885066620976525",
"article-title": "Responsiveness of Inhaled Epoprostenol in Respiratory Failure due to COVID-19",
"author": "R Sonti",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "327",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Journal of Intensive Care Medicine",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref018",
"volume": "36",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4187/respcare.05268",
"article-title": "Severity of hypoxemia and other factors that influence the response to aerosolized prostacyclin in ARDS",
"author": "RH Kallet",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1014",
"journal-title": "Respir Care",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref019",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Endothelial dysfunction in sepsis",
"author": "J Boisrame'-Helms",
"first-page": "150",
"journal-title": "Curr Vasc Pharmacol",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref020",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1152/ajplung.00195.2020",
"article-title": "Novel insights on the pulmonary vascular consequences of COVID-19",
"author": "F Potus",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "L277",
"journal-title": "Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol",
"key": "pone.0270646.ref021",
"volume": "319",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0270646"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Nitric oxide versus epoprostenol for refractory hypoxemia in Covid-19",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.corrections_policy",
"volume": "17"
}