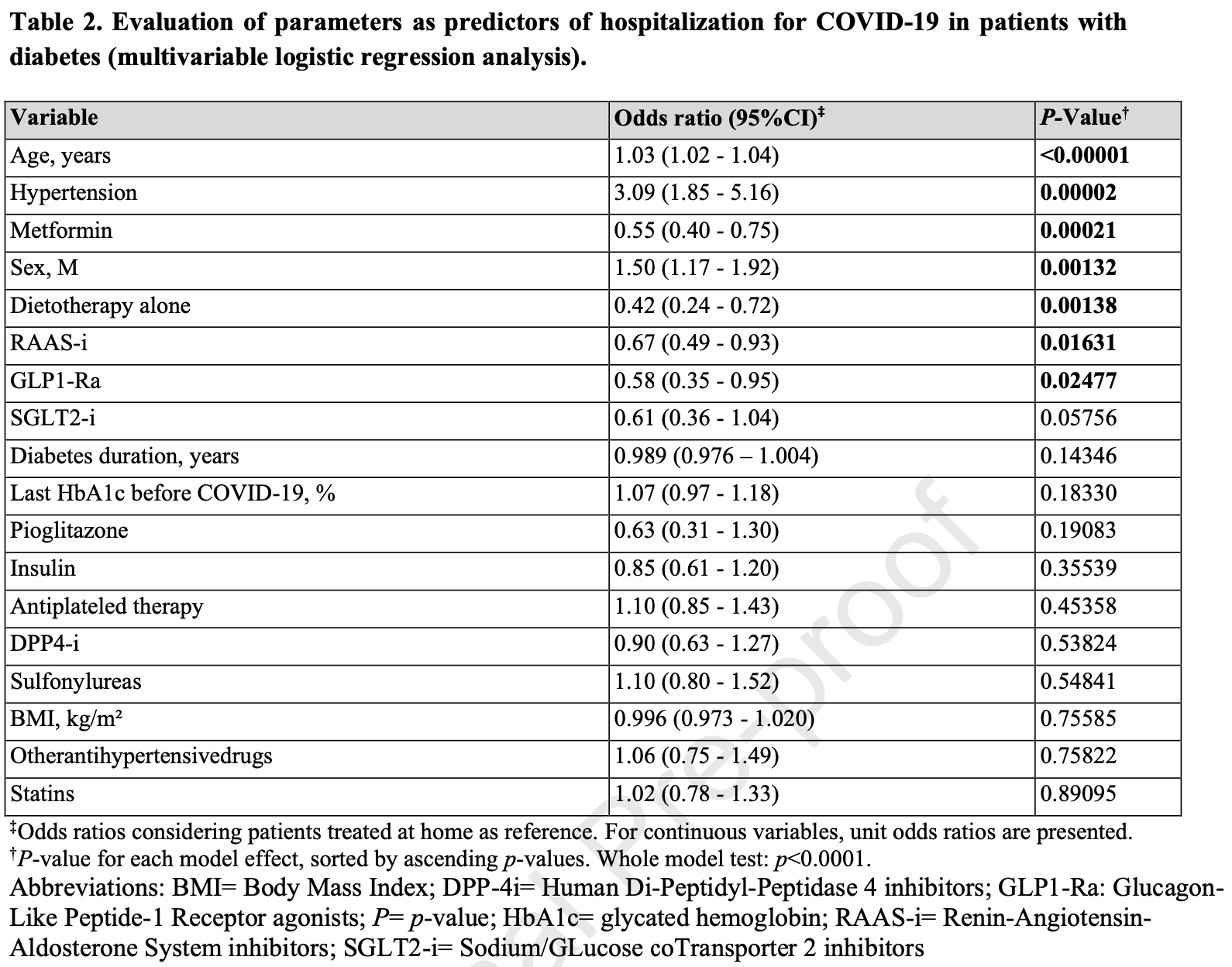
Association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors with best COVID-19 outcomes in a diabetic population of the Veneto Region (north-east Italy): a lesson for endemic phase?
et al., Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2023.06.016, Jun 2023
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective diabetic COVID-19 patients in Italy, showing lower risk of hospitalization with metformin use.
|
risk of death/ICU, 53.0% lower, OR 0.47, p = 0.08, treatment 1,444, control 1,009, adjusted per study, for all patients, combined odds of hospitalization and ICU/death for hospitalized patients, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of death/ICU, 15.0% lower, OR 0.85, p = 0.68, treatment 209, control 180, adjusted per study, among hospitalized patients, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 45.0% lower, OR 0.55, p < 0.001, treatment 1,444, control 1,009, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Piarulli et al., 24 Jun 2023, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 7 authors, study period February 2020 - February 2021.
Contact: francesco.piarulli@unipd.it, eugenio.ragazzi@unipd.it, drmassimocarollo@gmail.com, luca.benacchio@aulss6.veneto.it, fabio.piovanello@aulss6.veneto.it, ivana.simoncello@libero.it, annunziata.lapolla@unipd.it.
Association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors with best COVID-19 outcomes in a diabetic population of the Veneto Region (north-east Italy): a lesson for endemic phase?
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2023.06.016
This is a PDF file of an article that has undergone enhancements after acceptance, such as the addition of a cover page and metadata, and formatting for readability, but it is not yet the definitive version of record. This version will undergo additional copyediting, typesetting and review before it is published in its final form, but we are providing this version to give early visibility of the article. Please note that, during the production process, errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
J o u r n a l P r e -p r o o f
References
Al-Hashem, Al-Humayed, Amin, Metformin inhibits mTOR-HIF-1α axis and profibrogenic and inflammatory biomarkers in thioacetamide-induced hepatic tissue alterations, J Cell Physiol, doi:10.1002/jcp.27616
Apicella, Campopiano, Mantuano, Mazoni, Coppelli et al., COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Barron, Bakhai, Kar, Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30272-2
Bozkurt, Kovacs, Harrington, Joint HFSA/ACC/AHA Statement Addresses Concerns Re: Using RAAS Antagonists in COVID-19, J Card Fail, doi:10.1016/j.cardfail.2020.04.013
Ceriello, Monnier, Owens, Glycaemic variability in diabetes: clinical and therapeutic implications, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30136-0
Chao, Tseng, Wu, Shih, Yi et al., Higher glycemic variability within the first day of ICU admission is associated with increased 30-day mortality in ICU patients with sepsis, Ann Intensive Care, doi:10.1186/s13613-020-0635-3
Chen, Wu, Wang, Yu, Sun, The Impact of COVID-19 on Blood Glucose: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Endocrinol (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fendo.2020.574541
De, Vaccari, Dietrich, Keane, De et al., The Inflammasome in Times of COVID-19, Front Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.583373
Deng, Peng, Characteristics of and Public Health Responses to the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak in China, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9020575
Deng, Peng, Characteristics of and Public Health Responses to the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Outbreak in China, J Clin Med, doi:10.3390/jcm9020575
Fadini, Morieri, Longato, Avogaro, Prevalence and impact of diabetes among people infected with SARS-CoV-2, J Endocrinol Invest, doi:10.1007/s40618-020-01236-2
Fang, Karakiulakis, Roth, Are patients with hypertension and diabetes mellitus at increased risk for COVID-19 infection?, Lancet Respir Med, doi:10.1016/S2213-2600
Guo, Zhu, Hong, Decreased Mortality of COVID-19 With Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors Therapy in Patients With Hypertension: A Meta-Analysis, Hypertension, doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.120.15572
Han, Ma, Sun, Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Arch Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2021.08.002
Hickey, Grant, Dunning, Siepe, Statistical primer: sample size and power calculations-why, when and how?, Eur J Cardiothorac Surg, doi:10.1093/ejcts/ezy169
Hm, Gareeb, Alblihed, Cruz-Martins, Batiha, COVID-19 and Risk of Acute Ischemic Stroke and Acute Lung Injury in Patients With Type II Diabetes Mellitus: The Anti-inflammatory Role of Metformin, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.644295
Hm, Gareeb, Alblihed, Guerreiro, Cruz-Martins et al., COVID-19 in Relation to Hyperglycemia and Diabetes Mellitus, Front Cardiovasc Med, doi:10.3389/fcvm.2021.644095
Holman, Knighton, Kar, Risk factors for COVID-19-related mortality in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in England: a population-based cohort study, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30271-0
Hu, Guo, Zhou, Shi, Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19, Nat Rev Microbiol, doi:10.1038/s41579-020-00459-7
Iacobellis, COVID-19 and diabetes: Can DPP4 inhibition play a role?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108125
Iacobellis, Penaherrera, Bermudez, Mizrachi, Admission hyperglycemia and radiological findings of SARS-CoV2 in patients with and without diabetes, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108185
Li, Wang, Chen, Zhang, Deng, Association of Renin-Angiotensin System Inhibitors With Severity or Risk of Death in Patients With Hypertension Hospitalized for Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Infection in Wuhan, China, JAMA Cardiol, doi:10.1001/jamacardio.2020.1624
Lippi, Favaloro, D-dimer is Associated with Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Pooled Analysis, Thromb Haemost, doi:10.1055/s-0040-
Loader, Taylor, Lampa, Sundström, Renin-Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research, doi:10.1161/JAHA.122.025289
Longato, Camillo, Sparacino, Saccavini, Avogaro et al., Diabetes diagnosis from administrative claims and estimation of the true prevalence of diabetes among 4.2 million individuals of the Veneto region, Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis, doi:10.1016/j.numecd.2019.08.017
Luk, Yip, Zhang, Glucose-lowering drugs and outcome from COVID-19 among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a population-wide analysis in Hong Kong, BMJ Open, doi:10.1136/bmjopen-2021-052310
Mancia, Rea, Ludergnani, Apolone, Corrao, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Blockers and the Riskof Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2006923
Mirani, Favacchio, Carrone, Impact of Comorbidities and Glycemia at Admission and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Case Series From an Academic Hospitalin Lombardy, Italy. Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1340
Muniyappa, Gubbi, COVID-19 pandemic, coronaviruses, and diabetes mellitus, Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00124.2020
Nyland, Raja-Khan, Bettermann, Diabetes, Drug Treatment, and Mortality in COVID-19: A Multinational Retrospective Cohort Study, Diabetes, doi:10.2337/db21-0385
Petrilli, Jones, Yang, Factors associated with hospital admission and critical illness among 5279 people with coronavirus disease, BMJ, doi:10.1136/bmj.m1966
Piarulli, Lapolla, COVID 19 and low-glucose levels: Is there a link?, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108283
Piarulli, Sartore, Sechi, Low Glucose Concentrations Induce a Similar Inflammatory Response in Monocytes from Type 2 Diabetic Patients and Healthy Subjects, Oxid Med Cell Longev, doi:10.1155/2017/9185272
Rameshrad, Razavi, Ferns, Hosseinzadeh, Pharmacology of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and its use in the management of metabolic syndrome: a comprehensive review on drug repositioning, Daru, doi:10.1007/s40199-019-00238-7
Rawshani, Kjölhede, Rawshani, Severe COVID-19 in people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Sweden: A nationwide retrospective cohort study, Lancet Reg Health Eur, doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2021.100105
Rayman, Lumb, Kennon, Guidance on the management of Diabetic Ketoacidosis in the exceptional circumstances of the COVID-19 pandemic, Diabet Med, doi:10.1111/dme.14328
Reynolds, Adhikari, Pulgarin, Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Risk of Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2008975
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area [published correction appears in JAMA, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.6775
Scheen, Marre, Thivolet, Prognostic factors in patients with diabetes hospitalized for COVID-19: Findings from the CORONADO study and other recent reports, Diabetes Metab, doi:10.1016/j.diabet.2020.05.008
Singh, Rathore, Khan, Mortality and Severity in COVID-19 Patients on ACEIs and ARBs-A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression Analysis, Front Med (Lausanne), doi:10.3389/fmed.2021.703661
Singh, Singh, Hyperglycemia without diabetes and new-onset diabetes are both associated with poorer outcomes in COVID-19, Diabetes Res Clin Pract, doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2020.108382
Solerte, 'addio, Trevisan, Sitagliptin Treatment at the Time of Hospitalization Was Associated With Reduced Mortality in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19: A Multicenter, Case-Control, Retrospective, Observational Study, Diabetes Care, doi:10.2337/dc20-1521
Superiore, Sanità, Iss), Characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 patients dying in Italy
Toniolo, Mantoan, Maresso, Veneto Region, Italy. Health system review, Health Syst Transit
Vaduganathan, Vardeny, Michel, Mcmurray, Pfeffer et al., Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsr2005760
Valencia, Peiró, Lorenzo, Sánchez-Ferrer, Eckel et al., DPP4 and ACE2 in Diabetes and COVID-19: Therapeutic Targets for Cardiovascular Complications?, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.01161
Vankadari, Wilce, Emerging WuHan (COVID-19) coronavirus: glycan shield and structure prediction of spike glycoprotein and its interaction with human CD26, Emerg Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2020.1739565
Wargny, Potier, Gourdy, Predictors of hospital discharge and mortality in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: updated results from the nationwide CORONADO study, Diabetologia, doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05351-w
Zhang, Dong, Cao, Clinical characteristics of 140 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 in Wuhan, China, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14238
Zhang, Zhu, Cai, Association of Inpatient Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers With Mortality Among Patients With Hypertension Hospitalized With COVID-19 [published correction appears in Circ Res, Circ Res, doi:10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317134
Zhou, Chi, Lv, Wang, Obesity and diabetes as high-risk factors for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19), Diabetes Metab Res Rev, doi:10.1002/dmrr.3377
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.numecd.2023.06.016",
"ISSN": [
"0939-4753"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2023.06.016",
"alternative-id": [
"S0939475323002491"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors with best COVID-19 outcomes in a diabetic population of the Veneto Region (north-east Italy): a lesson for endemic phase?"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2023.06.016"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 The Italian Diabetes Society, the Italian Society for the Study of Atherosclerosis, the Italian Society of Human Nutrition and the Department of Clinical Medicine and Surgery, Federico II University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1193-4410",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Piarulli",
"given": "Francesco",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0390-6823",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Ragazzi",
"given": "Eugenio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6523-6036",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Carollo",
"given": "Massimo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Benacchio",
"given": "Luca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Piovanello",
"given": "Fabio",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Simoncello",
"given": "Ivana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lapolla",
"given": "Annunziata",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases",
"container-title-short": "Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"nmcd-journal.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-25T08:20:12Z",
"timestamp": 1687681212000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-25T08:20:12Z",
"timestamp": 1687681212000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-26T04:34:56Z",
"timestamp": 1687754096806
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1685577600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0939475323002491?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0939475323002491?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0939475323002491"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Cardiology and Cardiovascular Medicine",
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Medicine (miscellaneous)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors with best COVID-19 outcomes in a diabetic population of the Veneto Region (north-east Italy): a lesson for endemic phase?",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy"
}
