Micronutrient status (vitamins A and D) and its effect on the severity of the course of COVID-19 in children
et al., Неонатологія, хірургія та перинатальна медицина, doi:10.24061/2413-4260.XIV.1.51.2024.6, Apr 2024
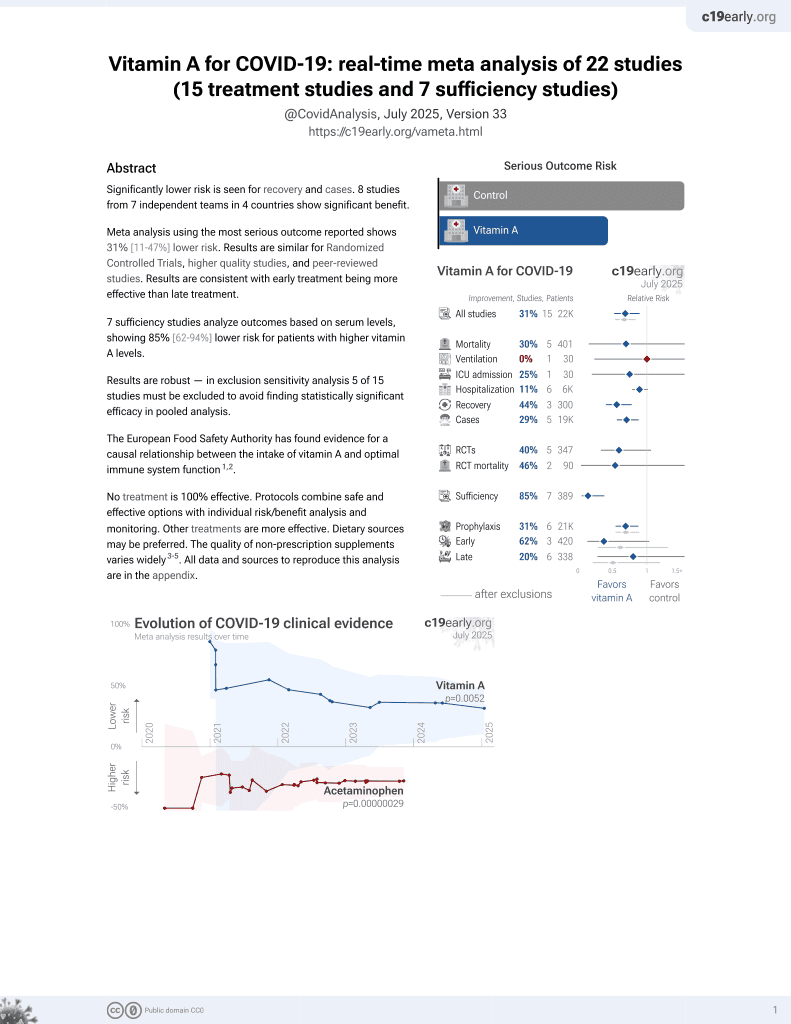
Vitamin A for COVID-19
49th treatment shown to reduce risk in
May 2023, now with p = 0.004 from 14 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
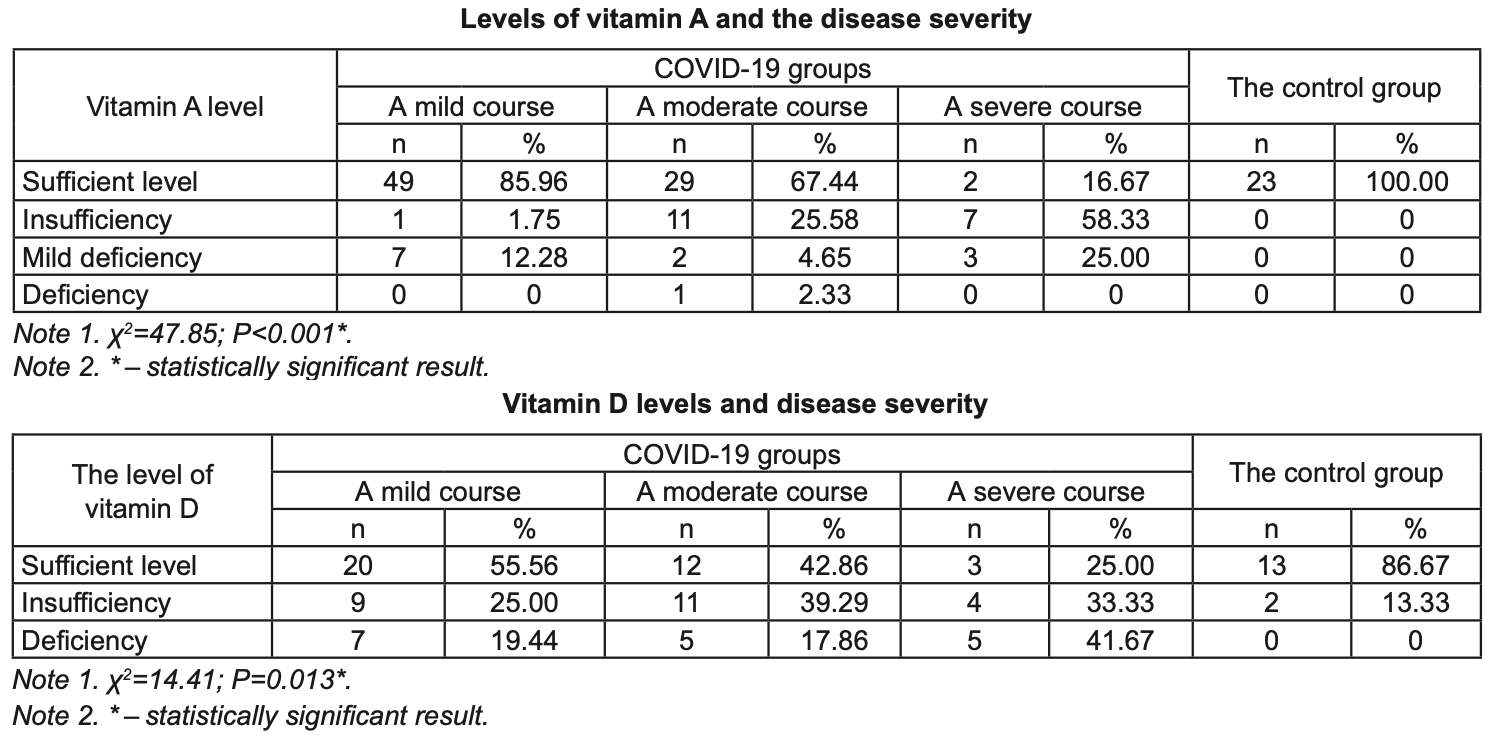
Retrospective 112 pediatric COVID-19 patients and 23 healthy controls showing lower levels of vitamins A and D associated with more severe disease. Patients with moderate and severe COVID-19 had significantly lower vitamin A, vitamin D, and retinol-binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels compared to those with mild disease and healthy controls. Lower vitamin A and D levels were associated with higher levels of inflammatory markers such as CRP, leukocytes, and ESR.
Study covers vitamin D and vitamin A.
|
risk of severe case, 60.6% lower, RR 0.39, p = 0.14, high vitamin A levels (≥200ng/ml) 9 of 99 (9.1%), low vitamin A levels (<200ng/ml) 3 of 13 (23.1%), NNT 7.1, (mild) deficiency vs. other.
|
|
risk of case, 84.3% lower, OR 0.16, p = 0.20, high vitamin A levels (≥200ng/ml) 99 of 112 (88.4%) cases,
23 of 23 (100.0%) controls, NNT 5.3, case control OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Pavlyshyn et al., 5 Apr 2024, retrospective, Ukraine, peer-reviewed, 3 authors.
Neonatology, surgery and perinatal medicine
doi:10.24061/2413-4260
A strong immune response is important during recovery from COVID-19, and its status is infl uenced by several micronutrients. Vitamin D is important in regulating the immune response and protecting against respiratory infections. Vitamin A also has immunomodulatory eff ects, inhibiting viral replication and enhancing immune responses, thereby reducing morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. The aim of research was to study the levels of vitamins A, D, and retinol-binding protein 4 in children with COVID-19, and their associations with the severity of the disease. Material and Methods. 112 children aged 1 month to 18 years with COVID-19 confi rmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) in nasal swabs or by a positive serologic test (IgM and IgG or IgM). In all children, vitamin D levels were determined by the colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the Monobind test system. Vitamin A and retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels were determined by the colorimetric enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the Elabscience test system. Statistical analysis was performed using Stat Plus (its 95 % confi dence interval (95 % CI) was calculated for the mean values, and the Kruskal-Wallis test (H-test) was used as the reliability criterion for checking the equality of the medians of several samples). The level of statistical signifi cance was set at P<0.05). The study was conducted in accordance with the rules of patient safety and ethical principles of scientifi c medical research involving human subjects (2000). The permission to conduct this study was granted by the Bioethics Commission (Protocol No. 73, dated April 3, 2023). The parents (legal representatives) of the patients gave their written consent to the conduct of this study. No. 0123U100064, 2023No. 0123U100064, -2025)).
This study is a fragment of research work «Optimizing the diagnosis of clinical and pathogenetic characteristics of the COVID-19 coronavirus infection in children with comorbid pathology and treatment features» (state registration Results. The mean age of the children was (7.04±5.75) years . According to the severity of the disease, 57 children ( 50 .89 %) had a mild course, 43 children (38.39 %) had a moderate course, and 12 children (10.72 %) had a severe course. The concentration of vitamin D in children with mild course of COVID-19 was 30.91 ng/ml, in children with moderate course -29.10 ng/ml, in children with severe course -22.42 ng/ml (Р<0.05). The level of vitamin A also varied in children with diff erent severity of the disease: in mild COVID-19 it was 456.10 ng/ml, in moderate -347.30 ng/ml, and in severe -242.90 ng/ ml (Р <0.001). At the same time, the level of retinol binding protein 4 was 30.66 ng/ml in mild disease, 33.07 ng/ml in moderate disease and 23.28 ng/ml in severe disease. Conclusions. Children with moderate and severe COVID-19 have signifi cantly lower levels of vitamins A, D, and RBP4 compared to uninfected..
References
Balla, Merugu, Konala, Sangani, Kondakindi et al., Back to basics: review on vitamin D and respiratory viral infections including COVID-19, Journal of community hospital internal medicine perspectives, doi:10.1080/20009666.2020.1811074
Blanchard-Rohner, Didierlaurent, Tilmanne, Smeesters, Marchant, Pediatric COVID-19: immunopathogenesis, transmission and prevention, Vaccines, doi:10.3390/vaccines9091002
Brodin, Why is COVID-19 so mild in children?, Acta Paediatrica, doi:10.1111/apa.15271
Esposito, Lelii, Vitamin D and respiratory tract infections in childhood, BMC infectious diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-015-1196-1
Fabbri, Infante, Ricordi, Editorial-Vitamin D status: a key modulator of innate immunity and natural defense from acute viral respiratory infections, Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci, doi:10.26355/eurrev_202004_20876
Felsenstein, Herbert, Mcnamara, Hedrich, COVID-19: Immunology and treatment options, Clinical immunology, doi:10.1016/j.clim.2020.108448
Hurwitz, Jones, Penkert, Gansebom, Sun et al., Low retinolbinding protein and vitamin D levels are associated with severe outcomes in children hospitalized with lower respiratory tract infection and respiratory syncytial virus or human metapneumovirus detection, doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2017
Kozak -Cadidate Of, Павлишин Галина Андріївнадоктор медичних наук, завідувач кафедри педіатрії № 2 Тернопільського національного медичного університету
Kunisawa, Kiyono, Vitamin-mediated regulation of intestinal immunity, Frontiers in immunology, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00189
Lee, Ko, New perspectives regarding the antiviral eff ect of vitamin A on norovirus using modulation of gut microbiota, Gut Microbes, doi:10.1080/19490976.2017.1353842
Lev, Gottesman, Levin, Lederfein, Berkov et al., Observational cohort study of IP-10's potential as a biomarker to aid in infl ammation regulation within a clinical decision support protocol for patients with severe COVID-19, Plos one, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0245296
Mawson, Role of fat-soluble vitamins A and D in the pathogenesis of infl uenza: a new perspective, ISRN infectious diseases, doi:10.5402/2013/246737
Michienzi, Badowski, Can vitamins and/or supplements provide hope against coronavirus?, Drugs in context, doi:10.7573/dic.2020-5-7
Mikroelementy, vitaminy ta probiotyky u pidtrymtsi imunnoho zakhystu orhanizmu, Tematychnyi nomer «Pediatriia
Osuna-Padilla, Briceno, Aguilar-Vargas, Rodríguez-Moguel, Rosa et al., Zinc and selenium indicators and their relation to immunologic and metabolic parameters in male patients with human immunodefi ciency virus, Nutrition, doi:10.1016/j.nut.2019.110585
Pavlyshyn, Labivka, Klinichni osoblyvosti COVID-19 u ditei. Aktualni pytannia pediatrii, akusherstva ta hinekolohii, doi:10.11603/24116-4944.2021.2.12889
Pavlyshyn, Sliiva, The role of selenium and zinc in allergic hypersensitization in children, Biomedical Reviews, doi:10.14748/bmr.v30.6387
Pereira, Damascena, Azevedo, De Almeida Oliveira, Da et al., Vitamin D defi ciency aggravates COVID-19: systematic review and meta-analysis, Critical reviews in food science and nutrition, doi:i:10.1080/10408398.2020.1841090
Pham, Waterhouse, Baxter, Romero, Mcleod et al., The eff ect of vitamin D supplementation on acute respiratory tract infection in older Australian adults: an analysis of data from the D-Health Trial, The lancet Diabetes & endocrinology, doi:10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30380-6
Pletz, Terkamp, Schumacher, Rohde, Schütte et al., Vitamin D deficiency in communityacquired pneumonia: low levels of 1, 25 (OH) 2 D are associated with disease severity, Respiratory research, doi:10.1186/1465-9921-15-53
Ponti, Maccaferri, Ruini, Tomasi, Ozben, Biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression, Critical reviews in clinical laboratory sciences, doi:10.1080/10408363.2020.1770685
Shakoor, Feehan, Dhaheri, Ali, Platat et al., Immune-boosting role of vitamins D, C, E, zinc, selenium and omega-3 fatty acids: Could they help against COVID-19?, Maturitas, doi:10.1016/j.maturitas.2020.08.003
Tagarro, Epalza, Santos, Sanz-Santaeufemia, Otheo et al., Screening and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children in Madrid, Spain, JAMA Pediatr, doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1346
Tagarro, Epalza, Santos, Sanz-Santaeufemia, Otheo et al., Screening and severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in children in Madrid, Spain, JAMA pediatrics, doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.1346
Taha, Abureesh, Alghamdi, Hassan, Cheikh et al., The relationship between vitamin D and infections including COVID-19: any hopes?, International journal of general medicine, doi:10.2147/IJGM.S317421
Wang, Chen, Du, Guo, Zhao et al., Nutrition assessment of vitamin A and vitamin D in northeast Chinese population based-on SPE/UPLC/PDA, BMC nutrition, doi:10.1186/s40795-018-0219-x
Zhang, Zhou, Yan, Liu, Zhou et al., A review of the extraction and determination methods of thirteen essential vitamins to the human body: An update from 2010, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules23061484
Дане Дослідження, фрагментом науково-дослідної роботи «Оптимізація діагностики клініко-патогенетичних характеристик коронавірусної інфекції COVID-19 у дітей з коморбідною патологією та особливості лікування, державна реєстрація
Метою, Матеріал і методи дослідження: обстежено 112 дітей віком від 1 місяця до 18 років із COVID-19, підтвердженим методом полімеразної ланцюгової реакції (ПЛР) у мазках з носа або позитивним серологічним тестом (IgM та IgG або IgM). У всіх дітей визначали рівень вітаміну D колориметричним методом імуноферментного аналізу (ІФА) з використанням тест-системи Monobind. Рівні вітаміну А та ретинолзв'язуючого білка 4 (RBP4) визначали колориметричним методом імуноферментного аналізу (ELISA) з використанням тест-системи Elabscience. Комісія з біоетики Тернопільського національного медичного університету імені І, значущості прийнято
Нижчий, Пов, язаний з більш високим рівнем прозапальних маркерів
Результати Дослідження, вік дітей становив (7,04 ± 5,75) років (95 % ДІ 5,96-8,12). За ступенем тяжкості у 57 дітей (50,89 %) перебіг захворювання був легким, у 43 дітей (38,39 %)середньої тяжкості, у
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.24061/2413-4260.xiv.1.51.2024.6",
"ISSN": [
"2413-4260",
"2226-1230"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.24061/2413-4260.XIV.1.51.2024.6",
"abstract": "<jats:p>A strong immune response is important during recovery from COVID-19, and its status is infl uenced by several micronutrients. Vitamin D is important in regulating the immune response and protecting against respiratory infections. Vitamin A also has immunomodulatory eff ects, inhibiting viral replication and enhancing immune responses, thereby reducing morbidity and mortality from COVID-19. The aim of research was to study the levels of vitamins A, D, and retinol- binding protein 4 in children with COVID-19, and their associations with the severity of the disease.Material and Methods. 112 children aged 1 month to 18 years with COVID-19 confi rmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR)in nasal swabs or by a positive serologic test (IgM and IgG or IgM). In all children, vitamin D levels were determined by thecolorimetric enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the Monobind test system. Vitamin A and retinol binding protein 4 (RBP4) levels were determined by the colorimetric enzyme- linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) using the Elabscience test system. Statistical analysis was performed using Stat Plus (its 95 % confi dence interval (95 % CI) was calculated for the mean values, and the Kruskal- Wallis test (H-test) was used as the reliability criterion for checking the equality of the medians of several samples). The level of statistical signifi cance was set at P<0.05). The study was conducted in accordance with the rules of patient safety and ethical principles of scientifi c medical research involving human subjects (2000). The permission to conduct this study was granted by the Bioethics Commission (Protocol No. 73, dated April 3, 2023). The parents (legal representatives) of the patients gave their written consent to the conduct of this study. This study is a fragment of research work «Optimizing the diagnosis of clinical and pathogenetic characteristics of the COVID-19 coronavirus infection in children with comorbid pathology and treatment features» (state registration No. 0123U100064, 2023-2025).Results. The mean age of the children was (7.04±5.75) years (95 % CI 5.96-8.12). According to the severity of the disease,57 children (50.89 %) had a mild course, 43 children (38.39 %) had a moderate course, and 12 children (10.72 %) had a severe course. The concentration of vitamin D in children with mild course of COVID-19 was 30.91 ng/ml, in children with moderate course – 29.10 ng/ml, in children with severe course – 22.42 ng/ml (Р<0.05). The level of vitamin A also varied in children with diff erent severity of the disease: in mild COVID-19 it was 456.10 ng/ml, in moderate – 347.30 ng/ml, and in severe – 242.90 ng/ ml (Р <0.001). At the same time, the level of retinol binding protein 4 was 30.66 ng/ml in mild disease, 33.07 ng/ml in moderate disease and 23.28 ng/ml in severe disease.Conclusions. Children with moderate and severe COVID-19 have signifi cantly lower levels of vitamins A, D, and RBP4compared to uninfected individuals. Vitamin A and RBP4 levels were age-dependent, and vitamin D levels did not show agerelated patterns. Lower levels of vitamins A and D are associated with higher levels of pro-infl ammatory markers – CRP,leukocytes and ESR.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pavlyshyn",
"given": "H.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Labivka",
"given": "O.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kozak",
"given": "K.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Neonatology, Surgery and Perinatal Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Neonatol. hìr. perinat. med.",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T14:48:14Z",
"timestamp": 1712587694000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T14:48:52Z",
"timestamp": 1712587732000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-09T00:34:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712622840392
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1(51)",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1(51)",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-05T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1712275200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://neonatology.bsmu.edu.ua/article/download/301276/293438",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://neonatology.bsmu.edu.ua/article/download/301276/293587",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://neonatology.bsmu.edu.ua/article/download/301276/293438",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "10153",
"original-title": [],
"page": "41-47",
"prefix": "10.24061",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
5
]
]
},
"publisher": "Higher State Educational Establishment of Ukraine Bukovinian State Medical University",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://neonatology.bsmu.edu.ua/article/view/301276"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Surgery",
"Pediatrics, Perinatology and Child Health",
"Obstetrics and Gynecology",
"Genetics (clinical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "MICRONUTRIENT STATUS (VITAMINS A AND D) AND ITS EFFECT ON THE SEVERITY OF THE COURSE OF COVID-19 IN CHILDREN",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "14"
}
pavlyshyn