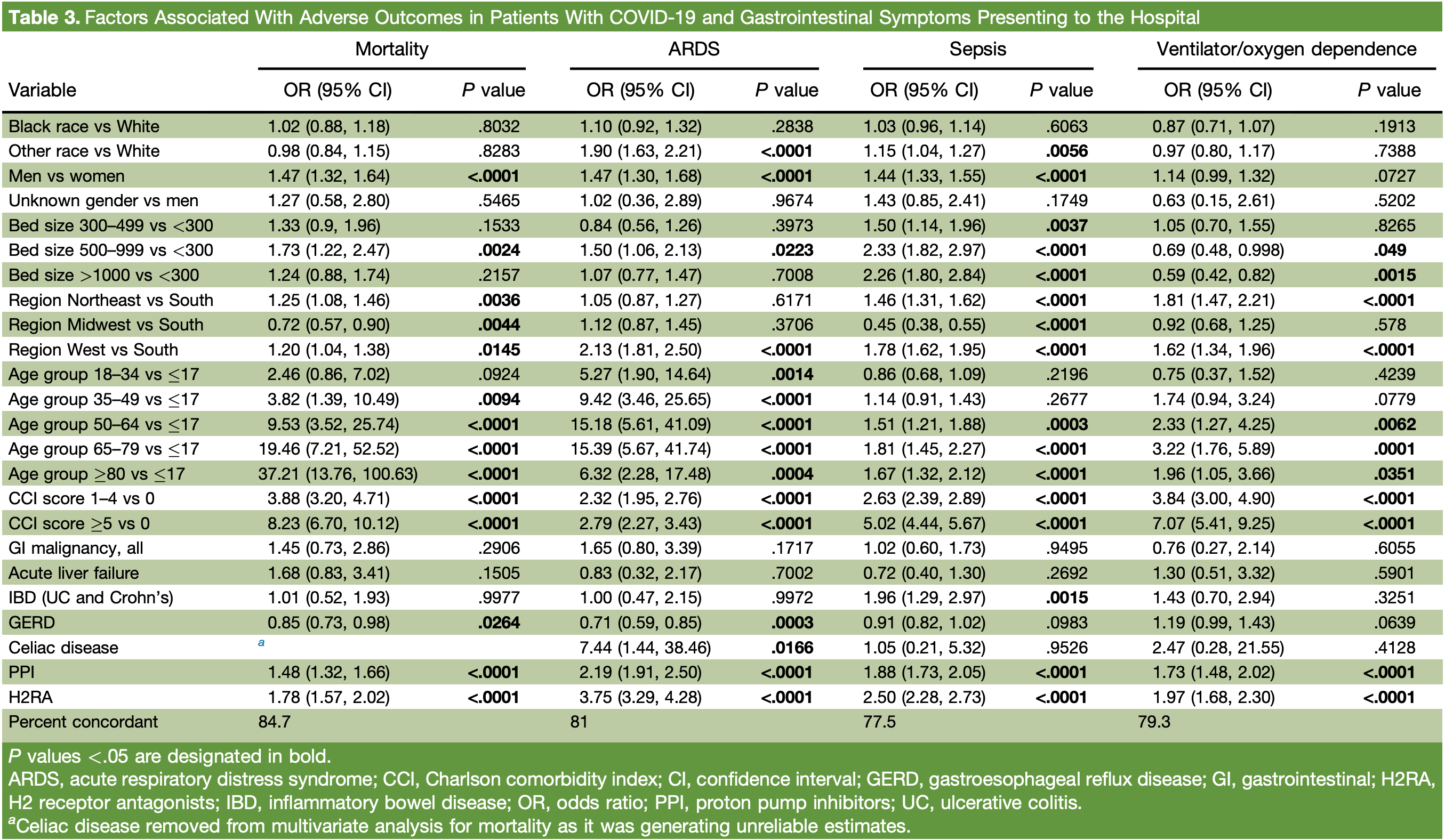
Factors Associated With Poor Outcomes Among Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Infection and Gastrointestinal Symptoms
et al., Gastro Hep Advances, doi:10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004, Dec 2023
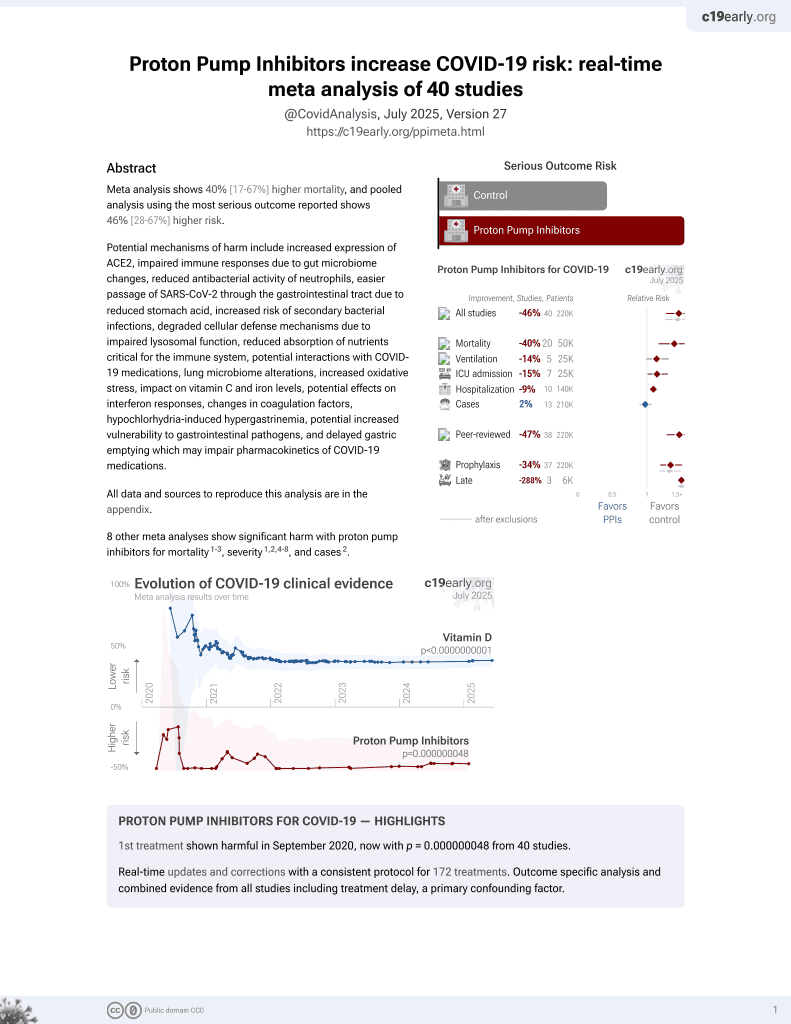
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective 19,915 hospitalized COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms, showing that use of proton pump inhibitors or H2 receptor antagonists was associated with higher mortality, ARDS, sepsis, and ventilator or oxygen requirement among patients
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 48.0% higher, OR 1.48, p < 0.001, treatment 4,566, control 15,349, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ARDS, 119.0% higher, OR 2.19, p < 0.001, treatment 4,566, control 15,349, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
sepsis, 88.0% higher, OR 1.88, p < 0.001, treatment 4,566, control 15,349, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of oxygen therapy, 73.0% higher, OR 1.73, p < 0.001, treatment 4,566, control 15,349, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Patil et al., 31 Dec 2023, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, mean age 52.0, 7 authors.
Factors Associated With Poor Outcomes Among Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Infection and Gastrointestinal Symptoms
Gastro Hep Advances, doi:10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004
BACKGROUND AND AIMS: Gastrointestinal (GI) symptoms are present in 20% of patients with SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus infection (COVID-19). We studied the association of GI symptoms (in patients with COVID-19) with adverse outcomes and factors associated with poor outcomes in these patients. METHODS: The study cohort included 100,902 patients from the Cerner Real-World Data COVID-19 Database of hospital encounters and emergency department visits with COVID-19 infection from December 1, 2019, to November 30, 2020. Multivariate analysis was used to study the effect of GI symptoms on adverse outcomes and the factors associated with mortality, acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), sepsis, and ventilator requirement or oxygen dependence in patients with COVID-19 and GI symptoms. RESULTS: Patients with COVID-19 and GI symptoms were significantly more likely to have ARDS (odds ratio [OR] 1.20, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.11, 1.29), sepsis (OR 1.19, 95% CI 1.14, 1.24), acute kidney injury (OR 1.30, 95% CI 1.24, 1.36), venous thromboembolism (OR 1.36, 95% CI 1.22, 1.52), or GI bleed (OR 1.62, 95% CI 1.47, 1.79) and less likely to experience cardiomyopathy (OR 0.87, 95% CI 0.77, 0.99) or death (OR 0.71, 95% CI 0.67, 0.75). Among those with GI symptoms, older age, higher Charlson comorbidity index scores, and use of proton pump inhibitors/H2 receptor antagonists were associated with higher mortality, ARDS, sepsis, and ventilator or oxygen requirement. CONCLUSION: Patients with COVID-19 who have GI symptoms have overall worse in-hospital complications but less cardiomyopathy and mortality. Older age, higher comorbidity scores, and the use of proton pump inhibitors and H2 receptor antagonists are associated with poor outcomes in these patients.
Supplementary Materials Material associated with this article can be found in the online version at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08. 004. Authors' Contributions: Nikita Patil contributed to conceptualization, methodology, and writing, reviewing, and editing the article. Pankush Kalgotra contributed to data curation, formal analysis, software, and reviewing and editing the article. Suneha Sundaram contributed to conceptualization, methodology, and reviewing and editing the article. Stephanie Melquist contributed to methodology and writing, reviewing, and editing the article. Sravanthi Parasa contributed to conceptualization, methodology, supervision, and reviewing and editing the article. Madhav Desai contributed to conceptualization, methodology, and reviewing and editing the article. Prateek Sharma contributed to conceptualization, methodology, supervision, and reviewing and editing the article.
Conflicts of Interest: These authors disclose the following: P.S. is a consultant for Medtronic, Olympus, Boston Scientific, Fujifilm, and Lumendi; and received grant support from Ironwood, Erbe, Docbot, Cosmo pharmaceuticals, and CDx labs. S.P. is a member of Medical Advisory Board, Fujifilm. M.D. contributed to grant support from Intercept Pharma. The remaining authors disclose no conflicts.
Ethical Statement: The corresponding author, on behalf of all authors, jointly and severally, certifies that their institution has approved the protocol for any investigation..
References
Almario, Chey, Spiegel, Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors, Am J Gastroenterol
Bishehsari, Deshmukh, Gastrointestinal symptoms predict the outcomes from COVID-19 infection, J Clin Gastroenterol
De-Madaria, Capurso, COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: examining the causality, Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol
Dibner, Direct COVID-19 infection of enterocytes: the role of hypochlorhydria, Am J Infect Control
Dong, Xiang, Jiang, The prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms, abnormal liver function, digestive system disease and liver disease in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis, J Clin Gastroenterol
Elshazli, Kline, Elgaml, Gastroenterology manifestations and COVID-19 outcomes: a metaanalysis of 25,252 cohorts among the first and second waves, J Med Virol
Freedberg, Conigliaro, Wang, Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study, Gastroenterology
Fried, Crawford, Mospan, Patient characteristics and outcomes of 11,721 patients with COVID19 hospitalized across the United States, Clin Infect Dis
Ghimire, Sharma, Patel, Diarrhea is associated with increased severity of disease in COVID-19: systemic review and metaanalysis, SN Compr Clin Med
Gu, Mack, Salvatore, Characteristics associated with racial/ethnic disparities in COVID-19 outcomes in an academic health care system, JAMA Netw Open
Gul, Lo, Peterson, Meta-analysis of outcomes of patients with COVID-19 infection with versus without gastrointestinal symptoms, Baylor Univ Med Cent Proc
Imam, Odish, Gill, Older age and comorbidity are independent mortality predictors in a large cohort of 1305 COVID-19 patients in Michigan, United States, J Intern Med
Ioannou, Locke, Green, Risk factors for hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, or death among 10 131 US veterans with SARS-CoV-2 infection, JAMA Netw Open
Israelsen, Ernst, Lundh, Proton pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Kuswardhani, Henrina, Pranata, Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Laszkowska, Faye, Kim, Disease course and outcomes of COVID-19 among hospitalized patients with gastrointestinal manifestations, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Lee, Ha, Yeniova, Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching, Gut
Marasco, Cremon, Barbaro, Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: results of the prospective controlled multinational GI-COVID-19 study, Am J Gastroenterol
Nardo, Schneeweiss-Gleixner, Bakail, Pathophysiological mechanisms of liver injury in COVID-19, Liver Int
Qeadan, Vansant-Webb, Tingey, Racial disparities in COVID-19 outcomes exist despite comparable Elixhauser comorbidity indices between Blacks, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Whites, Sci Rep
Quan, Sundararajan, Halfon, Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data, Med Care
Ramachandran, Onukogu, Ghanta, Gastrointestinal symptoms and outcomes in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients, Dig Dis
Ramachandran, Perisetti, Gajendran, Prehospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19, Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol
Reynolds, Kashyap, Wallace, Older adult patients are at lower risk of ARDS compared to younger patients at risk: secondary analysis of a multicenter cohort study, J Intensive Care Med
Shoaibi, Fortin, Weinstein, Comparative effectiveness of famotidine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Am J Gastroenterol
Singh, Zaheer, Kumar, Covid19, beyond just the lungs: a review of multisystemic involvement by Covid19, Pathol Res Pract
Tariq, Saha, Furqan, Prevalence and mortality of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Mayo Clin Proc
Tian, Ye, Hepatic complications of COVID-19 and its treatment, J Med Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004",
"ISSN": [
"2772-5723"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004",
"alternative-id": [
"S277257232200142X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Factors Associated With Poor Outcomes Among Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Infection and Gastrointestinal Symptoms"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Gastro Hep Advances"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. on behalf of the AGA Institute."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Patil",
"given": "Nikita",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kalgotra",
"given": "Pankush",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sundaram",
"given": "Suneha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Melquist",
"given": "Stephanie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Parasa",
"given": "Sravanthi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "Madhav",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sharma",
"given": "Prateek",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Gastro Hep Advances",
"container-title-short": "Gastro Hep Advances",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"ghadvances.org",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
26
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-26T09:04:57Z",
"timestamp": 1661504697000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
10,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-10-21T22:57:59Z",
"timestamp": 1697929079000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100008497",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Boston Scientific Corporation"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100018262",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Intercept Pharmaceuticals"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-30T10:42:34Z",
"timestamp": 1706611354696
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 2,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1672531200000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
8,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-08-12T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1660262400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S277257232200142X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S277257232200142X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "37-45",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.prp.2021.153384",
"article-title": "Covid19, beyond just the lungs: a review of multisystemic involvement by Covid19",
"author": "Singh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153384",
"journal-title": "Pathol Res Pract",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib2",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mayocp.2020.06.003",
"article-title": "Prevalence and mortality of COVID-19 patients with gastrointestinal symptoms: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tariq",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1632",
"journal-title": "Mayo Clin Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib3",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001541",
"article-title": "Prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms in severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection: results of the prospective controlled multinational GI-COVID-19 study",
"author": "Marasco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "147",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib4",
"volume": "117",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"article-title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"author": "Lee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib5",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000000798",
"article-title": "Increased risk of COVID-19 among users of proton pump inhibitors",
"author": "Almario",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1707",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib6",
"volume": "115",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2021.05.011",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitor use is not strongly associated with SARS-CoV-2 related outcomes: a nationwide study and meta-analysis",
"author": "Israelsen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1845",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib7",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCG.0000000000001513",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms predict the outcomes from COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Bishehsari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e145",
"journal-title": "J Clin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib8",
"volume": "56",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000509774",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms and outcomes in hospitalized coronavirus disease 2019 patients",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "373",
"journal-title": "Dig Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib9",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00662-w",
"article-title": "Diarrhea is associated with increased severity of disease in COVID-19: systemic review and metaanalysis",
"author": "Ghimire",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "SN Compr Clin Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib10",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.mlr.0000182534.19832.83",
"article-title": "Coding algorithms for defining comorbidities in ICD-9-CM and ICD-10 administrative data",
"author": "Quan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1130",
"journal-title": "Med Care",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib11",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cgh.2020.09.037",
"article-title": "Disease course and outcomes of COVID-19 among hospitalized patients with gastrointestinal manifestations",
"author": "Laszkowska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1402",
"journal-title": "Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib12",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/08998280.2020.1771164",
"article-title": "Meta-analysis of outcomes of patients with COVID-19 infection with versus without gastrointestinal symptoms",
"author": "Gul",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "366",
"journal-title": "Baylor Univ Med Cent Proc",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib13",
"volume": "33",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26836",
"article-title": "Gastroenterology manifestations and COVID-19 outcomes: a meta-analysis of 25,252 cohorts among the first and second waves",
"author": "Elshazli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2740",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib14",
"volume": "93",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41575-020-00389-y",
"article-title": "COVID-19 and acute pancreatitis: examining the causality",
"author": "de-Madaria",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib15",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.26036",
"article-title": "Hepatic complications of COVID-19 and its treatment",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1818",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib16",
"volume": "92",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/liv.14730",
"article-title": "Pathophysiological mechanisms of liver injury in COVID-19",
"author": "Nardo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Liver Int",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib17",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa1268",
"article-title": "Patient characteristics and outcomes of 11,721 patients with COVID19 hospitalized across the United States",
"author": "Fried",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e558",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib18",
"volume": "72",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.22310",
"article-title": "Risk factors for hospitalization, mechanical ventilation, or death among 10 131 US veterans with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Ioannou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2022310",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib19",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1177/0885066619848357",
"article-title": "Older adult patients are at lower risk of ARDS compared to younger patients at risk: secondary analysis of a multicenter cohort study",
"author": "Reynolds",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "J Intensive Care Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib20",
"volume": "35",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.25197",
"article-title": "Characteristics associated with racial/ethnic disparities in COVID-19 outcomes in an academic health care system",
"author": "Gu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e2025197",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib21",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-021-88308-2",
"article-title": "Racial disparities in COVID-19 outcomes exist despite comparable Elixhauser comorbidity indices between Blacks, Hispanics, Native Americans, and Whites",
"author": "Qeadan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "8738",
"journal-title": "Sci Rep",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib22",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.dsx.2020.10.022",
"article-title": "Charlson comorbidity index and a composite of poor outcomes in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Tuty Kuswardhani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2103",
"journal-title": "Diabetes Metab Syndr",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib23",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/joim.13119",
"article-title": "Older age and comorbidity are independent mortality predictors in a large cohort of 1305 COVID-19 patients in Michigan, United States",
"author": "Imam",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "469",
"journal-title": "J Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib24",
"volume": "288",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MCG.0000000000001424",
"article-title": "The prevalence of gastrointestinal symptoms, abnormal liver function, digestive system disease and liver disease in COVID-19 infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "67",
"journal-title": "J Clin Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib25",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ajic.2020.08.002",
"article-title": "Direct COVID-19 infection of enterocytes: the role of hypochlorhydria",
"author": "Dibner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "385",
"journal-title": "Am J Infect Control",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib26",
"volume": "49",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14309/ajg.0000000000001153",
"article-title": "Comparative effectiveness of famotidine in hospitalized COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Shoaibi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "692",
"journal-title": "Am J Gastroenterol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib27",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.053",
"article-title": "Famotidine use is associated with improved clinical outcomes in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a propensity score matched retrospective cohort study",
"author": "Freedberg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1129",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib28",
"volume": "159",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MEG.0000000000002013",
"article-title": "Pre-hospitalization proton pump inhibitor use and clinical outcomes in COVID-19",
"author": "Ramachandran",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "137",
"journal-title": "Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol",
"key": "10.1016/j.gastha.2022.08.004_bib29",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S277257232200142X"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Factors Associated With Poor Outcomes Among Patients With SARS-CoV-2 Coronavirus Infection and Gastrointestinal Symptoms",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "2"
}