Evaluation of the Clinical Effects of an Antiviral, Immunostimulant and Antioxidant Phytotherapy in Patients Suffering from COVID-19 Infection: An Observational Pilot Study
et al., International Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.3390/ijtm2020022, Jun 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Retrospective case series of 240 patients in Italy in 2020, up to 96 years old, showing no mortality and 1.6% hospitalization with early treatment including vitamin C, quercetin, and green tea and red wine polyphenols.
The formulation was based on SARS-CoV-2 molecular docking studies. Low bioavailability is a known issue for polyphenols. Authors note that bioavailability may be improved with combinations of polyphenols which may have a synergistic effect, and via consumption with dietary fat.
Study covers quercetin and vitamin C.
Ortore et al., 16 Jun 2022, Italy, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period September 2020 - December 2021.
Contact: eliana.tranchita@gmail.com (corresponding author), ortore.massimiliano@libero.it, alessiamanteca@yahoo.it, sinerfitonlus@gmail.com, iginofabi@libero.it, antonella.foti2010@libero.it, giovanna.borriello@gmail.com, paoloriondino@gmail.com, elisa.grazioli@uniroma4.it, carlo.minganti@uniroma4.it, claudia.cerulli@uniroma4.it, attilio.parisi@uniroma4.it.
Evaluation of the Clinical Effects of an Antiviral, Immunostimulant and Antioxidant Phytotherapy in Patients Suffering from COVID-19 Infection: An Observational Pilot Study
International Journal of Translational Medicine, doi:10.3390/ijtm2020022
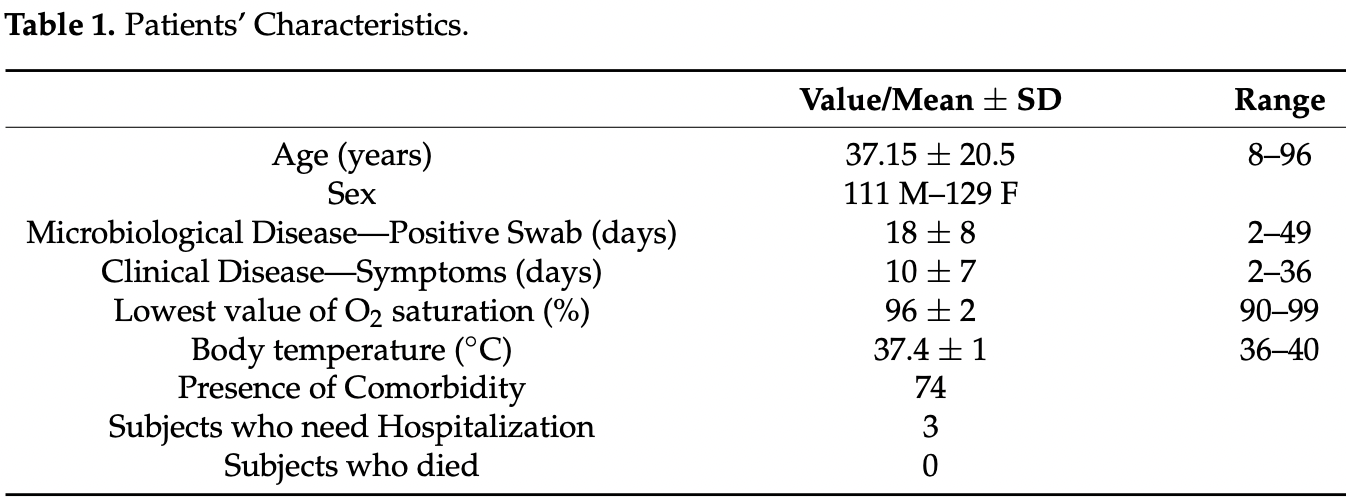
Background: In the last two years, the COVID-19 pandemic has spread all over the world, affecting millions of people. The same infection can manifest in different clinical conditions, ranging from mild situations to severe patient impairment, up to their death. The COVID-19 infection can activate innate and adaptive immune systems and cause massive inflammatory responses that is important to treat as soon as possible. Methods: In the initial phase of the pandemic, a group of 240 unvaccinated subjects with COVID-19 disease was administered phytotherapy with immunostimulant and antioxidant property to evaluate the role of this phytotherapeutic preparation in counteracting the progression of the COVID-19 disease both in duration and complexity. Results: 161 patients were treated with phytotherapy alone and the prevailing symptoms in the acute phase were rhinitis, fever, cough, osteo-muscular pains; the other 79 patients were given a therapy with NSAIDs, symptomatic drugs, monoclonal antibodies, corticosteroids, antibiotics, and/or heparin. The coexistence of comorbidity (such as diabetes, hypertension, gastro-intestinal disease) was recorded in 74 out of 240 subjects, more frequently in the older subjects; there was no statistically significant correlation between the presence of comorbidity and the duration of disease. Hospitalization rate in this population was 1.6% and lethality rate was 0%. Conclusion: The use of phytotherapy can represent a valid weapon against COVID-19, since it showed no side effects and can also be used in association with other pharmacological therapies to reduce the massive inflammatory responses of this infection.
References
Albassam, Markowitz, An Appraisal of Drug-Drug Interactions with Green Tea (Camellia sinensis), Planta Medica, doi:10.1055/s-0043-100934
Amr, Abo-Ghalia, Moustafa, Al-Omar, Nossier et al., Design, synthesis and docking studies of novel macrocyclic pentapeptides as anticancer multi-targeted kinase inhibitors, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules23102416
Andres, Pevny, Ziegenhagen, Bakhiya, Schäfer et al., Safety Aspects of the Use of Quercetin as a Dietary Supplement, Mol. Nutr. Food Res, doi:10.1002/mnfr.201700447
Anka, Tahir, Abubakar, Alsabbagh, Zian et al., Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): An overview of the immunopathology, serological diagnosis and management, Scand. J. Immunol
Attia, Alagawany, Farag, Alkhatib, Khafaga et al., Phytogenic Products and Phytochemicals as a Candidate Strategy to Improve Tolerance to Coronavirus, Front. Veter. Sci, doi:10.3389/fvets.2020.573159
Brglez Mojzer, Knez Hrnčič, Škerget, Knez, Bren, Polyphenols: Extraction Methods, Antioxidative Action, Bioavailability and Anticarcinogenic Effects, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules21070901
Brodin, Immune determinants of COVID-19 disease presentation and severity, Nat. Med, doi:10.1038/s41591-020-01202-8
Chen, Zhang, Zhu, Liu, Chen et al., Quercetin inhibits TNF-α induced HUVECs apoptosis and inflammation via downregulating NF-kB and AP-1 signaling pathway in vitro, Medicine, doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000022241
Chilamakuri, Agarwal, COVID-19: Characteristics and Therapeutics, Cells, doi:10.3390/cells10020206
Chourasia, Koppula, Battu, Ouseph, Singh et al., a Green Tea Catechin, as a Potential Therapeutic Agent for Symptomatic and Asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 Infection, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules26051200
Chowdhury, Barooah, Tea Bioactive Modulate Innate Immunity: In Perception to COVID-19 Pandemic, Front. Immunol, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.590716
Da, Silva, Fighting coronaviruses with natural polyphenols, Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol, doi:10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102179
Dabeek, Marra, Dietary Quercetin and Kaempferol: Bioavailability and Potential Cardiovascular-Related Bioactivity in Humans, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu11102288
Derosa, Maffioli, D'angelo, Di Pierro, A role for quercetin in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.6887
Diniz, Souza, Duarte, De Sousa, Mechanistic Aspects and Therapeutic Potential of Quercetin against COVID-19-Associated Acute Kidney Injury, Molecules, doi:10.3390/molecules25235772
Eisvand, Tajbakhsh, Seidel, Zirak, Tabeshpour et al., Quercetin and its role in modulating endoplasmic reticulum stress: A review, Phytother. Res, doi:10.1002/ptr.7283
Filardo, Di Pietro, Mastromarino, Sessa, Therapeutic potential of resveratrol against emerging respiratory viral infections, Pharmacol. Ther, doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107613
Gao, Ding, Dong, Zhang, Azkur et al., Risk factors for severe and critically ill COVID-19 patients: A review, Allergy, doi:10.1111/all.14657
Gerotziafas, Catalano, Colgan, Pecsvarady, Wautrecht et al., Guidance for the Management of Patients with Vascular Disease or Cardiovascular Risk Factors and COVID-19: Position Paper from VAS-European Independent Foundation in Angiology/Vascular Medicine, Thromb. Haemost, doi:10.1055/s-0040-1715798
Gu, Zhang, Cen, Wu, Lu et al., Quercetin as a potential treatment for COVID-19-induced acute kidney injury: Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking study, PLoS ONE
Hu, Webster, Cao, Shao, The safety of green tea and green tea extract consumption in adults -Results of a systematic review, Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.03.019
Hussain, Mahawar, Xia, Yang, El-Hasani et al., Obesity and mortality of COVID-19. Meta-analysis, Obes. Res. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1016/j.orcp.2020.07.002
Ita, Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19): Current Status and Prospects for Drug and Vaccine Development, Arch. Med Res, doi:10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.09.010
Kandeil, Mostafa, Kutkat, Moatasim, Al-Karmalawy et al., Bioactive Polyphenolic Compounds Showing Strong Antiviral Activities against Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2, Pathogens, doi:10.3390/pathogens10060758
Lesser, Cermak, Wolffram, Bioavailability of Quercetin in Pigs Is Influenced by the Dietary Fat Content, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/134.6.1508
Lim, Min, Park, Kim, Flavonoids interfere with NLRP3 inflammasome activation, Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.022
Luca, Macovei, Bujor, Miron, Skalicka-Woźniak et al., Bioactivity of dietary polyphenols: The role of metabolites, Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr, doi:10.1080/10408398.2018.1546669
Marin, Aghagoli, Lavine, Yang, Siff et al., Predictors of COVID -19 severity: A literature review, Rev. Med. Virol, doi:10.1002/rmv.2146
Marinella, Indomethacin and resveratrol as potential treatment adjuncts for SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19, Int. J. Clin. Pract, doi:10.1111/ijcp.13535
Matta, Chopra, Arora, Morbidity and mortality trends of COVID 19 in top 10 countries, Indian J. Tuberc, doi:10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.09.031
Mhatre, Srivastava, Naik, Patravale, Antiviral activity of green tea and black tea polyphenols in prophylaxis and treatment of COVID-19: A review, Phytomedicine, doi:10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153286
O'driscoll, Dos Santos, Wang, Cummings, Azman et al., Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0
Okamoto, Safety of quercetin for clinical application, Int. J. Mol. Med
Paces, Strizova, Smrz, Cerny, COVID-19 and the Immune System, Physiol. Res, doi:10.33549/physiolres.934492
Pandey, Rane, Chatterjee, Kumar, Khan et al., Targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein of COVID-19 with naturally occurring phytochemicals: An in silico study for drug development, J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn
Prasansuklab, Theerasri, Rangsinth, Sillapachaiyaporn, Chuchawankul et al., Anti-COVID-19 drug candidates: A review on potential biological activities of natural products in the management of new coronavirus infection, J. Tradit. Complement. Med, doi:10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.12.001
Salian, Wright, Vedell, Nair, Li et al., COVID-19 Transmission, Current Treatment, and Future Therapeutic Strategies, Mol. Pharm, doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00608
Sapra, Bhardwaj, Azam, Madhry, Verma et al., Phytotherapy for treatment of cytokine storm in COVID-19, Front. Biosci, doi:10.52586/4924
Scalbert, Williamson, Dietary Intake and Bioavailability of Polyphenols, J. Nutr, doi:10.1093/jn/130.8.2073S
Schultze, Aschenbrenner, COVID-19 and the human innate immune system, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.029
Shohan, Nashibi, Mahmoudian-Sani, -R.; Abolnezhadian, Ghafourian et al., The therapeutic efficacy of quercetin in combination with antiviral drugs in hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized controlled trial, Eur. J. Pharmacol, doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174615
Stravalaci, Pagani, Paraboschi, Pedotti, Doni et al., Recognition and inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 by humoral innate immunity pattern recognition molecules, Nat. Immunol, doi:10.1038/s41590-021-01114-w
To, Sridhar, Chiu, Hung, Li et al., Lessons learned 1 year after SARS-CoV-2 emergence leading to COVID-19 pandemic, Emerg. Microbes Infect, doi:10.1080/22221751.2021.1898291
Türsen, Türsen, Lotti, Cutaneous sıde-effects of the potential COVID-19 drugs, Dermatol. Ther, doi:10.1111/dth.13476
Walle, Absorption and metabolism of flavonoids, Free. Radic. Biol. Med, doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.002
Wang, Heber, Henning, Quercetin increased bioavailability and decreased methylation of green tea polyphenols in vitro and in vivo, Food Funct, doi:10.1039/c2fo10254d
Yin, Wang, Yu, Chen, Zhu et al., Pharmacological Effects of Polyphenol Phytochemicals on the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway, Front. Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.716672
Younes, Aggett, Aguilar, Crebelli, Dusemund et al., Scientific opinion on the safety of green tea catechins, EFSA J, doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5239
Yu, Rohli, Yang, Jia, Impact of obesity on COVID-19 patients, J. Diabetes Complicat, doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107817
Zhang, Zhang, Bi, He, Yan et al., Potential protective mechanisms of green tea polyphenol EGCG against COVID-19, Trends Food Sci. Technol, doi:10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.023
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijtm2020022",
"ISSN": [
"2673-8937"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3390/ijtm2020022",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background: In the last two years, the COVID-19 pandemic has spread all over the world, affecting millions of people. The same infection can manifest in different clinical conditions, ranging from mild situations to severe patient impairment, up to their death. The COVID-19 infection can activate innate and adaptive immune systems and cause massive inflammatory responses that is important to treat as soon as possible. Methods: In the initial phase of the pandemic, a group of 240 unvaccinated subjects with COVID-19 disease was administered phytotherapy with immunostimulant and antioxidant property to evaluate the role of this phytotherapeutic preparation in counteracting the progression of the COVID-19 disease both in duration and complexity. Results: 161 patients were treated with phytotherapy alone and the prevailing symptoms in the acute phase were rhinitis, fever, cough, osteo-muscular pains; the other 79 patients were given a therapy with NSAIDs, symptomatic drugs, monoclonal antibodies, corticosteroids, antibiotics, and/or heparin. The coexistence of comorbidity (such as diabetes, hypertension, gastro-intestinal disease) was recorded in 74 out of 240 subjects, more frequently in the older subjects; there was no statistically significant correlation between the presence of comorbidity and the duration of disease. Hospitalization rate in this population was 1.6% and lethality rate was 0%. Conclusion: The use of phytotherapy can represent a valid weapon against COVID-19, since it showed no side effects and can also be used in association with other pharmacological therapies to reduce the massive inflammatory responses of this infection.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"ijtm2020022"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ortore",
"given": "Massimiliano",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4245-1320",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Grazioli",
"given": "Elisa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tranchita",
"given": "Eliana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Minganti",
"given": "Carlo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Manteca",
"given": "Alessia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tinto",
"given": "Ludovico",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2637-7968",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cerulli",
"given": "Claudia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fabi",
"given": "Igino",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Foti",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Borriello",
"given": "Giovanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-8901-0501",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Riondino",
"given": "Paolo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2648-8406",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Parisi",
"given": "Attilio",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "International Journal of Translational Medicine",
"container-title-short": "IJTM",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T05:48:12Z",
"timestamp": 1655444892000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T07:08:20Z",
"timestamp": 1655449700000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-17T07:41:39Z",
"timestamp": 1655451699885
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2022-06-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1655337600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8937/2/2/22/pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "1968",
"original-title": [],
"page": "242-251",
"prefix": "10.3390",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "MDPI AG",
"reference": [
{
"key": "ref1",
"unstructured": "Latest Data OMS Source Health Emergency Dashboard\nhttps://covid19.who.int"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00608",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/22221751.2021.1898291",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.33549/physiolres.934492",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/sji.12998",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref5"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.orcp.2020.07.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref6"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2020.107817",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref7"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/rmv.2146",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-020-01202-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/all.14657",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/pathogens10060758",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1796811",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref12"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fvets.2020.573159",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref13"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bcab.2021.102179",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref14"
},
{
"key": "ref15"
},
{
"key": "ref16"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells10020206",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.52586/4924",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2021.02.029",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref19"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.arcmed.2020.09.010",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6887",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules25235772",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tifs.2021.05.023",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules23102416",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref25"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/ijcp.13535",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref26"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.phymed.2020.153286",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref27"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/MD.0000000000022241",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.7283",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref29"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0245209",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref30"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/130.8.2073S",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.01.002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11102288",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/10408398.2018.1546669",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jn/134.6.1508",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules21070901",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1039/c2fo10254d",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2918-0",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijtb.2020.09.031",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0040-1715798",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dth.13476",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref41"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201700447",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref42"
},
{
"article-title": "Safety of quercetin for clinical application",
"author": "Okamoto",
"first-page": "275",
"journal-title": "Int. J. Mol. Med.",
"key": "ref43",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yrtph.2018.03.019",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2903/j.efsa.2018.5239",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jtcme.2020.12.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1055/s-0043-100934",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174615",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-021-01114-w",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref49"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2021.716672",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref50"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.taap.2018.06.022",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref51"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.590716",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref52"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/molecules26051200",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "ref53"
}
],
"reference-count": 53,
"references-count": 53,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.mdpi.com/2673-8937/2/2/22"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of the Clinical Effects of an Antiviral, Immunostimulant and Antioxidant Phytotherapy in Patients Suffering from COVID-19 Infection: An Observational Pilot Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2"
}
ortore
