Metformin use is associated with a decrease in risk of hospitalization and mortality in COVID-19 diabetic patients: a population-based study in Lombardy
et al., Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, doi:10.1111/dom.14648, Jan 2022
Metformin for COVID-19
3rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 110 studies.
Lower risk for mortality, ventilation, ICU, hospitalization, progression, recovery, and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
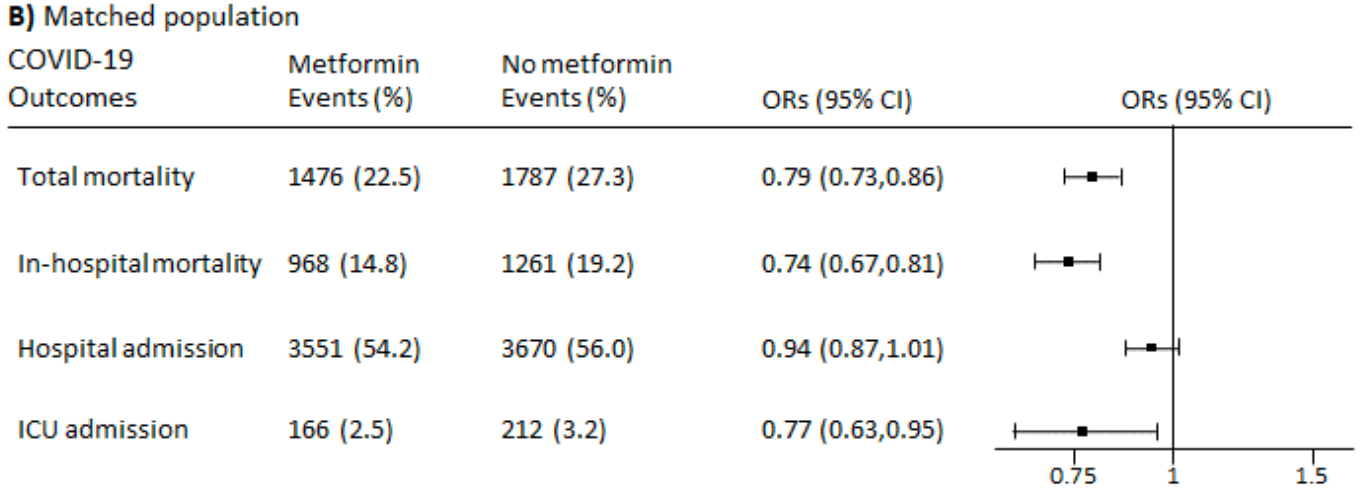
Retrospective 31,966 COVID+ patients using anti-hyperglycemic drugs in Italy, showing lower mortality and ICU admission with metformin use.
|
risk of death, 16.2% lower, RR 0.84, p < 0.001, treatment 1,476 of 6,556 (22.5%), control 1,787 of 6,556 (27.3%), NNT 21, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 22.1% lower, RR 0.78, p < 0.001, treatment 968 of 6,556 (14.8%), control 1,261 of 6,556 (19.2%), NNT 22, odds ratio converted to relative risk, in-hospital mortality, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 22.4% lower, RR 0.78, p = 0.01, treatment 166 of 6,556 (2.5%), control 212 of 6,556 (3.2%), NNT 143, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 2.7% lower, RR 0.97, p = 0.11, treatment 3,551 of 6,556 (54.2%), control 3,670 of 6,556 (56.0%), NNT 55, odds ratio converted to relative risk, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 8.3% lower, RR 0.92, p = 0.06, treatment 793 of 3,297 (24.1%), control 876 of 3,297 (26.6%), NNT 40, odds ratio converted to relative risk, excluding patients previously treated with insulin, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of death, 16.0% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.003, treatment 512 of 3,297 (15.5%), control 618 of 3,297 (18.7%), NNT 31, odds ratio converted to relative risk, excluding patients previously treated with insulin, in-hospital mortality, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 39.2% lower, RR 0.61, p = 0.002, treatment 64 of 3,297 (1.9%), control 102 of 3,297 (3.1%), NNT 87, odds ratio converted to relative risk, excluding patients previously treated with insulin, propensity score matching.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 2.2% higher, RR 1.02, p = 0.36, treatment 1,822 of 3,297 (55.3%), control 1,792 of 3,297 (54.4%), odds ratio converted to relative risk, excluding patients previously treated with insulin, propensity score matching.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Ojeda-Fernández et al., 10 Jan 2022, retrospective, Italy, peer-reviewed, 11 authors.
Contact: luisa.ojeda@marionegri.it.
Metformin use is associated with a decrease in the risk of hospitalization and mortality in COVID ‐19 patients with diabetes: A population‐based study in Lombardy
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism, doi:10.1111/dom.14648
Aims. We compared the association of metformin use and COVID-19 outcomes in a cohort of 31,966 patients with diabetes in Lombardy. Methods. We used a COVID-19 linkable administrative regional database to select diabetic patients over 40 years old. They had at least two prescriptions of antidiabetic drugs in 2019 and a positive test for SARS-CoV-2 between 15 February 2020 and 15 March 2021. The association of metformin use and clinical outcomes was assessed by multivariable logistic regression analyses and after propensity score matching. Clinical outcomes were all-cause mortality, in-hospital mortality, hospitalization for COVID-19 and admission to an intensive care unit (ICU). Results. In multivariable models metformin use was associated with a significantly lower risk of total mortality (OR 0.70; 95% CI 0.66-0.75), in-hospital mortality (OR 0.68; 95% CI 0.63-0.73), hospitalization for COVID-19 (OR 0.86; 95% CI 0.81-0.91) and ICU admission (OR 0.81; 95% CI 0.69-0.94) compared with metformin non-users. Results were similar in propensity score analysis; metformin was associated with significantly lower risk of total mortality (OR 0.79; 95% CI, 0.73-0.86), in-hospital mortality (OR 0.74; 95% CI, 0.67-0.81) and ICU admission (OR 0.77; 95% CI, 0.63-0.95).
Conclusions. In this large cohort, metformin use was associated with a protective effect in COVID-19 clinical outcomes, suggesting that it might be a potentially useful drug to prevent severe COVID-19 disease, although randomized clinical trials (RCT) are needed to confirm this. While awaiting the results of RCT, we suggest continuing prescribing metformin to diabetic patients with COVID-19.
part by confounding by indication, because metformin is used early in the trajectory of T2DM whereas insulin is typically started later. 28, 29 To minimize the effect of bias by indication, in a sensitivity analysis we excluded patients treated with insulin before and after PSM, substantially confirming result of the main analysis.
Conclusions 1. Our results show that metformin use is associated with a lower risk of total and in-hospital mortality and with a good prognosis in patients with diabetes and COVID-19 compared to metformin non-users. 2. Since metformin is an inexpensive and well-tolerated drug, it is suitable for investigating the effectiveness in COVID-19 patients in randomized clinical trials (RCT) to overcome the limits of observational studies. 3. While awaiting results from RCT, we suggest continuing prescribing this drug.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST All authors declare no conflict of interest
References
Akash, Rehman, Liaqat, Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha: Role in Development of Insulin Resistance and Pathogenesis of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, J Cell Biochem
Blüher, Fasshauer, Tönjes, Kratzsch, Schön et al., Association of interleukin-6, C-reactive protein, interleukin-10 and adiponectin plasma concentrations with measures of obesity, insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes
Bramante, Ingraham, Murray, Marmor, Hovertsen et al., This article is protected by copyright
Cameron, Morrison, Levin, Mohan, Forteath et al., Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Metformin Irrespective of Diabetes Status, Circulation research
Carter, Bennett, Bostock, Grant, Metformin reduces C-reactive protein but not complement factor C3 in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, Diabetic Med
Chen, Qian, Shi, Franklin, Comparing performance between log-binomial and robust Poisson regression models for estimating risk ratios under model misspecification, BMC Med Res Methodol
Christiansen, Johansen, Christensen, 'brien, Tønnesen et al., Preadmission metformin use and mortality among intensive care patients with diabetes: a cohort study, Crit Care
Connors, Levy, COVID-19 and its implications for thrombosis and anticoagulation, Blood
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill
Flory, Lipska, Metformin in 2019, JAMA
Gupta-Ganguli, Cox, Means, Gerling, Solomon, Does Therapy With Anti-TNFα Improve Glucose Tolerance and Control in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes?, Diabetes care
Han, Ma, Sun, Zhang, Qu et al., The Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Arch Med Res
Hayek, Ben-Shlomo, Balicer, Byrne, Katz et al., Preinfection glycaemic control and disease severity among patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A retrospective, cohort study, Diabetes Obes Metab
Huang, Lim, Pranata, Diabetes mellitus is associated with increased mortality and severity of disease in COVID-19 pneumonia -A systematic review, meta-analysis, and metaregression, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Kan, Zhang, Han, Xu, Ye et al., Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis, Front Endocrinol
Karbalaee-Hasani, Khadive, Eskandari, Shahidi, Mosavi et al., Effect of Metformin on Circulating Levels of Inflammatory Markers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials, Ann Pharmacother
Khunti, Knighton, Zaccardi, Bakhai, Barron et al., Prescription of glucoselowering therapies and risk of COVID-19 mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide observational study in England, Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol
Lalau, Al-Salameh, Hadjadj, Goronflot, Wiernsperger et al., Metformin use is associated with a reduced risk of mortality in patients with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19, Diabetes Metab
Lukito, Pranata, Henrina, Lim, Lawrensia et al., The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and metaanalysis, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Mcfadyen, Stevens, Peter, The Emerging Threat of (Micro)Thrombosis in COVID-19 and Its Therapeutic Implications, Circ Res
Mirzaei, Khodadadi, Vafaei, Abbasi-Oshaghi, Tayebinia et al., Prim Importance of hyperglycemia in COVID-19 intensive-care patients: Mechanism and treatment strategy, Care Diabetes
Robusto, Lepore, 'ettorre, Lucisano, Berardis et al., The Drug Derived Complexity Index (DDCI) Predicts Mortality, Unplanned Hospitalization and Hospital Readmissions at the Population Level, PLoS One
Schlesinger, Neuenschwander, Lang, Pafili, Kuss et al., Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: a living systematic review and meta-analysis, Diabetologia
Singh, Singh, Saboo, Misra, Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A Critical Appraisal of Literature, Diabetes Metab Syndr
Smati, Tramunt, Wargny, Caussy, Gaborit et al., Relationship between obesity and severe COVID-19 outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: Results from the CORONADO study, Diabetes Obes Metab
Vojta, Tignanelli, Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis, Lancet Healthy Longev
Yang, Sun, Zhang, Zhang, The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus, Diabetes Res Clin Pract
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1111/dom.14648",
"ISSN": [
"1462-8902",
"1463-1326"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/dom.14648",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1111/dom.14648"
],
"archive": [
"Portico"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 0,
"value": "2021-10-27"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 1,
"value": "2022-01-06"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Publication History",
"name": "publication_history"
},
"label": "Published",
"name": "published",
"order": 2,
"value": "2022-01-10"
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Ojeda‐Fernández",
"given": "Luisa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Foresta",
"given": "Andreana",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Macaluso",
"given": "Giulia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Colacioppo",
"given": "Pierluca",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Geriatric Neuropsychiatry Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Tettamanti",
"given": "Mauro",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Statistics and Quantitative Methods University of Milano Bicocca Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Zambon",
"given": "Antonella",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Centro Cardiologico Monzino IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Genovese",
"given": "Stefano",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unità Organizzativa Osservatorio Epidemiologico Regionale, Lombardy Region Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Fortino",
"given": "Ida",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Unità Organizzativa Osservatorio Epidemiologico Regionale, Lombardy Region Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Leoni",
"given": "Olivia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"family": "Roncaglioni",
"given": "Maria Carla",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0264-151X",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Laboratory of Cardiovascular Prevention Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS Milan Italy"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baviera",
"given": "Marta",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"onlinelibrary.wiley.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-11T06:44:55Z",
"timestamp": 1641883495000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-11T06:44:55Z",
"timestamp": 1641883495000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
12
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-12T06:54:45Z",
"timestamp": 1641970485883
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1462-8902"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1463-1326"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/termsAndConditions#vor",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1641772800000
}
},
{
"URL": "http://doi.wiley.com/10.1002/tdm_license_1.1",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1641772800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/dom.14648",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1111/dom.14648",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "311",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1111",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Wiley",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Diabetes Obesity Metabolism"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Endocrinology",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism",
"Internal Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Metformin use is associated with a decrease in risk of hospitalization and mortality in\n COVID\n ‐19 diabetic patients: a population‐based study in Lombardy"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/crossmark_policy"
}
