Efficacy and Safety of Acetylcysteine for the Prevention of Liver Injury in Covid-19 Intensive Care Unit Patients Under Treatment with Remdesivir: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial: Prevention of liver injury in severe Covid-19 pneumonia
et al., Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Bed to Bench, doi:10.22037/ghfbb.v15i3.2565, IRCT20210726051995N1, Jun 2022
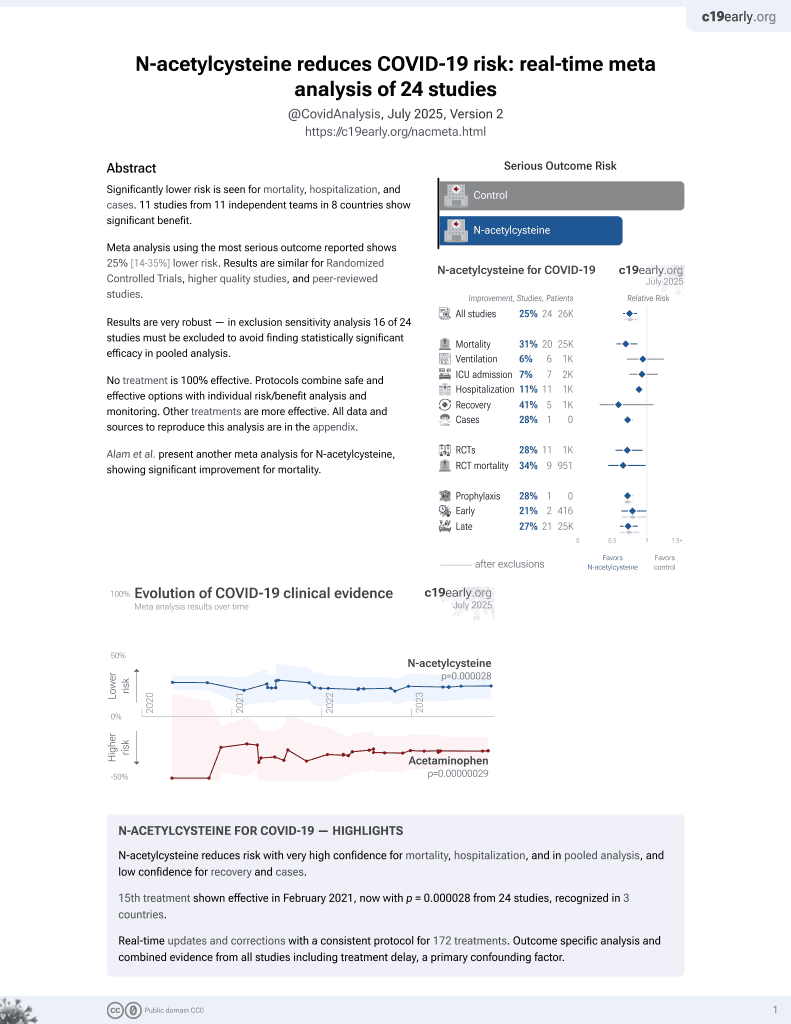
16th treatment shown to reduce risk in
February 2021, now with p = 0.0000032 from 25 studies, recognized in 3 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
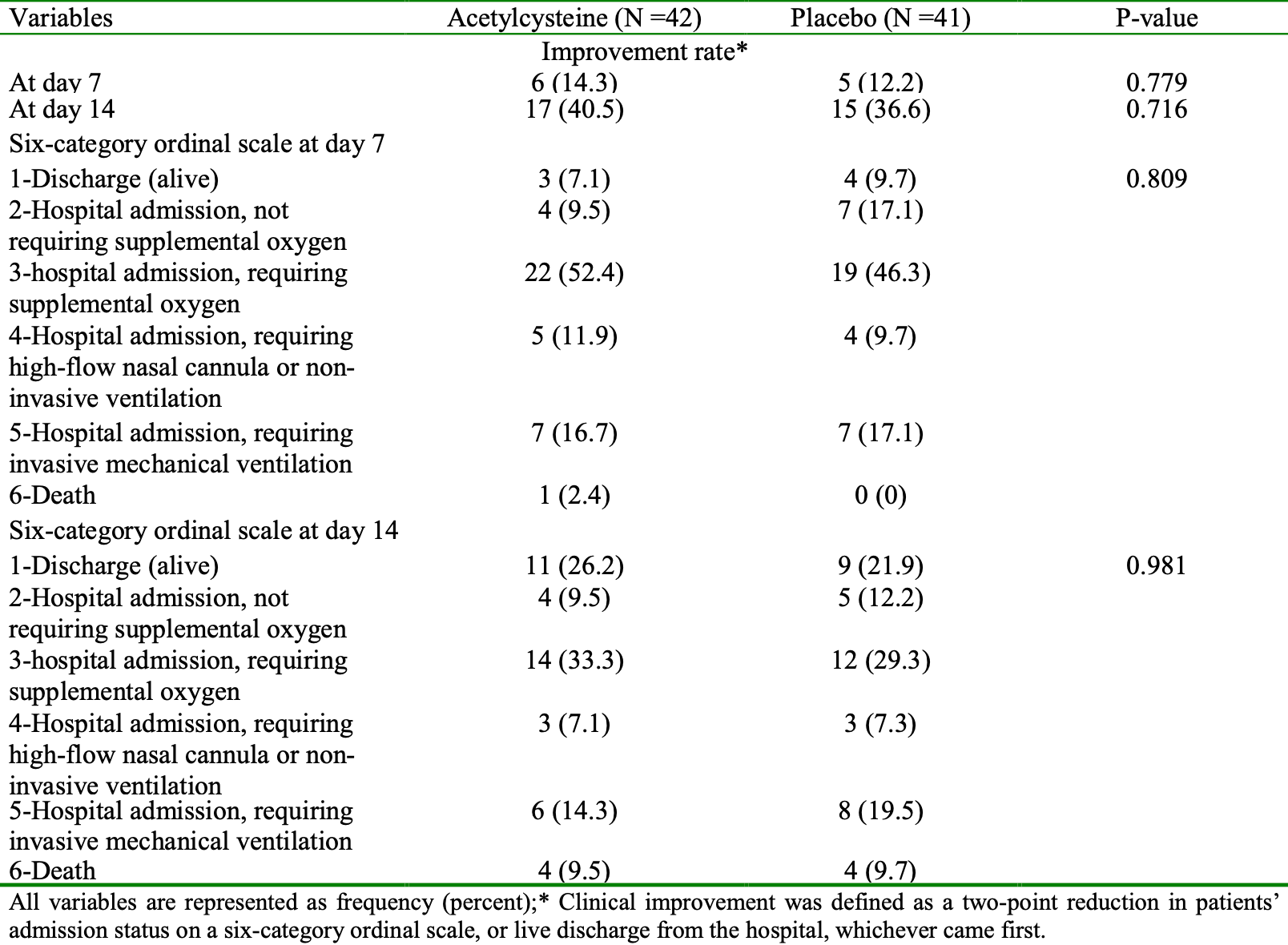
RCT 83 severe COVID-19 pnuemonia patients in Iran, 42 treated with acetylcysteine, showing no significant difference in clinical outcomes. All patients received remdesivir, famotidine, and vitamin C. More patients were at baseline category 4+ in the treatment group - 18 vs. 12. The trial focused on preventing liver injury in patients treated with remdesivir, showing improved AST/ALT levels with acetylcysteine.
|
risk of death, 2.4% lower, RR 0.98, p = 1.00, treatment 4 of 42 (9.5%), control 4 of 41 (9.8%), NNT 430, day 14.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 26.8% lower, RR 0.73, p = 0.57, treatment 6 of 42 (14.3%), control 8 of 41 (19.5%), NNT 19, day 14.
|
|
risk of no improvement, 6.1% lower, RR 0.94, p = 0.82, treatment 25 of 42 (59.5%), control 26 of 41 (63.4%), NNT 26, day 14.
|
|
risk of no hospital discharge, 5.4% lower, RR 0.95, p = 0.80, treatment 31 of 42 (73.8%), control 32 of 41 (78.0%), NNT 24, day 14.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mousapour et al., 20 Jun 2022, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 62.1, 5 authors, trial IRCT20210726051995N1.
Contact: dr.hazrati.e@ajaums.ac.ir.
Efficacy and safety of acetylcysteine for the prevention of liver injury in COVID-19 intensive care unit patients under treatment with remdesivir
Aim: The present double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial evaluated prophylactic use of acetylcysteine for the prevention of liver injury in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia under treatment with remdesivir. Background: Liver injury is reportedly common in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia and can occur not only as a result of disease progression, but as an iatrogenic reaction to remdesivir. Methods: A total of 83 adult patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia were randomly assigned in parallel groups to receive either acetylcysteine or placebo. All the patients received standard care according to institutional protocols, including remdesivir for a total of five days. One gram acetylcysteine was administered intravenously every 12 hours for 42 patients, and 41 patients received the same volume of 0.9% sodium chloride as placebo (Trial Registration: www.irct.ir identifier, IRCT20210726051995N1). Results: After 5 days, median aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels were significantly lower in the acetylcysteine than in the placebo group. Of those who received the placebo, 30 (73.2%), 4 (9.7%), and 3 (7.3%) patients had serum AST levels elevated between 1-2.5, 2.5-5, and over 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), respectively; while in the acetylcysteine group, 33 (78.6%) and 0 patients had AST levels between 1-2.5 and over 2.5 times ULN, respectively (p-value=0.037). In the acetylcysteine group, 23 (54.8%), 1 (2.4%), and 1 (2.4%) patient had serum ALT levels elevated between 1-2.5, 2.5-5, and over 5 times ULN, respectively; in the placebo group, however, 24 (58.5%), 7 (17.1%), and 1 (2.4%) patient had serum ALT levels between 1-2.5, 2.5-5, and over 5 times ULN,. Conclusion: Intravenous administration of acetylcysteine significantly prevents liver transaminases elevation and liver injury in seriously ill COVID-19 patients treated with remdesivir.
Conflict of interests The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
References
Avdeev, Gaynitdinova, Merzhoeva, Berikkhanov, N-acetylcysteine for the treatment of COVID-19 among hospitalized patients, J Infect
Bloom, Meyerowitz, Reinus, Daidone, Gustafson et al., Liver biochemistries in hospitalized patients with COVID 19, Hepatology
Carothers, Birrer, Vo, Acetylcysteine for the treatment of suspected remdesivir associated acute liver failure in COVID 19: A case series, Pharmacotherapy
De Alencar, Cdl, Müller, Chaves, Fukuhara et al., Double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial with Nacetylcysteine for treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome caused by Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19), Clin Infect Dis
Farooqi, Morgan, Dhawan, Dinh, Yatzkan et al., Airway hygiene in COVID-19 pneumonia: treatment responses of 3 critically ill cruise ship employees, Am J Case Rep
Grein, Ohmagari, Shin, Diaz, Asperges et al., Compassionate use of remdesivir for patients with severe Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Guan, Ni, -Y, Hu, Liang et al., Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Gurala, Moussawi, Philipose, Abergel, Acute liver failure in a COVID-19 patient without any preexisting liver disease, Cureus
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Lee, Hynan, Rossaro, Fontana, Stravitz et al., Intravenous Nacetylcysteine improves transplant-free survival in early stage non-acetaminophen acute liver failure, Gastroenterology
Leegwater, Strik, Wilms, Bosma, Burger et al., Drug-induced liver injury in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019: Potential interaction of remdesivir with P-Glycoprotein inhibitors, Clin Infect Dis
Lescure, Bouadma, Nguyen, Parisey, Wicky et al., Clinical and virological data of the first cases of COVID-19 in Europe: A case series, Lancet Infect Dis
Liu, Wang, Luo, Qian, Wu et al., Experience of N-acetylcysteine airway management in the successful treatment of one case of critical condition with COVID-19: A case report, Medicine
Madsen, Remdesivir for the Treatment of Covid-19-Final Report, N Engl J Med
Makarem, Naghibi, Beigmohammadi, Foroumandi, Mehrpooya, A case report of progressive liver failure inappropriate to decompensated heart failure following infection with COVID-19, Cureus
Metawea, Yousif, Moheb, COVID 19 and liver: An A-Z literature review, Dig Liver Dis
Montastruc, Thuriot, Durrieu, Hepatic disorders with the use of remdesivir for coronavirus 2019, Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol
Poe, Corn, N-Acetylcysteine: A potential therapeutic agent for SARS-CoV-2, Med Hypotheses
Rezagholizadeh, Khiali, Sarbakhsh, Entezari-Maleki, Remdesivir for treatment of COVID-19
Richardson, Hirsch, Narasimhan, Crawford, Mcginn et al., Presenting characteristics, comorbidities, and outcomes among 5700 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in the New York City area, JAMA
Ridruejo, Soza, The liver in times of COVID-19: What hepatologists should know, Ann Hepatol
Shi, Han, Jiang, Cao, Alwalid et al., Radiological findings from 81 patients with COVID-19 pneumonia in Wuhan, China: A descriptive study, Lancet Infec Dis
Spinner, Gottlieb, Criner, López, Cattelan et al., Effect of remdesivir vs standard care on clinical status at 11 days in patients with moderate COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Wang, Zhang, Du, Du, Zhao et al., Remdesivir in adults with severe COVID-19: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet
Will, Snyder, Westerfield, N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) for the prevention of liver failure in heat injury-mediated ischemic hepatitis, Mil Med
Wu, Mcgoogan, Characteristics of and important lessons from the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak in China: summary of a report of 72 314 cases from the Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, JAMA
Xu, Tao, Bai, Deng, Chen, Effectiveness of N acetylcysteine for the prevention of contrast induced nephropathy: a systematic review and meta analysis of randomized controlled trials, J Am Heart Assoc
Zampino, Mele, Florio, Bertolino, Andini et al., Liver injury in remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patients, Hepatol Int
Zhou, Yu, Du, Fan, Liu et al., Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study, Lancet
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.22037/ghfbb.v15i3.2565",
"ISSN": "20084234, 20082258",
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.22037/ghfbb.v15i3.2565",
"abstract": "Aim: The objective of this double-blinded placebo-controlled randomized clinical trial was to evaluate prophylactic use of acetylcysteine for prevention of liver injury in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia under treatment with remdesivir. Background: Liver injury is reportedly common in patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia, and can occur not only as a result of disease progression but as an iatrogenic reaction to remdesivir. Methods: A total of 83 adult patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia were randomly assigned in parallel groups to receive either acetylcysteine or placebo. All the patients received standard care according to institutional protocols including remdesivir for a total of five days. One gram acetylcysteine was administered intravenously every 12 hours for 42 patients, and 41 patients received the same volume of 0.9% sodium chloride as placebo. Results: After 5 days, median aspartate transaminase (AST) and alanine transaminase (ALT) levels were significantly lower in the acetylcysteine than in the placebo group. Of those who received placebo, 30 (73.2%), 4 (9.7%) and 3 (7.3%) patients had serum AST levels elevated between 1-2.5, 2.5-5 and over 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), respectively; while in the acetylcysteine group, 33 (78.6%) and 0 patients had AST levels between 1-2.5 and over 2.5 times ULN, respectively (p-value=0.037). In the acetylcysteine group, 23 (54.8%), 1 (2.4%) and 1 (2.4%) patients had serum ALT levels elevated between 1-2.5, 2.5-5 and over 5 times ULN, respectively; while in the placebo group, 24 (58.5%), 7 (17.1%) and 1 (2.4%) patients had serum ALT levels between 1-2.5, 2.5-5 and over 5 times ULN, respectively (p-value=0.073). Conclusion: Intravenous administration of acetylcysteine significantly prevents liver transaminases elevation and liver injury in seriously ill COVID-19 patients treated with remdesivir. (Trial Registration: www.irct.ir identifier, IRCT20210726051995N1)",
"author": [
{
"family": "Mousapour",
"given": "Pouria"
},
{
"family": "Hamidi Farahani",
"given": "Ramin"
},
{
"family": "Mosaed",
"given": "Reza"
},
{
"family": "Asgari",
"given": "Ali"
},
{
"family": "Hazrati",
"given": "Ebrahim"
}
],
"container-title": "Gastroenterology and Hepatology from Bed to Bench",
"issue": "Vol 15, No 3 (2022): Summer",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
6,
20
]
]
},
"language": "eng",
"medium": "JB",
"publisher": "Publisher: Research Institute for Gastroenterology and Liver Diseases (RIGLD)",
"publisher-place": "IR",
"title": "Efficacy and Safety of Acetylcysteine for the Prevention of Liver Injury in Covid-19 Intensive Care Unit Patients Under Treatment with Remdesivir: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial: Prevention of liver injury in severe Covid-19 pneumonia",
"type": "article-journal"
}