The effect of Nutrition Bio-shield superfood (NBS) on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial
et al., Microbial Pathogenesis, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792, IRCT20200426047206N1, Sep 2022
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 70 hospitalized severe COVID-19 patients in Iran, showing lower mortality and improved clinical markers with treatment combining vitamins A, B1-B3, B5, B6, B9, C, D, K, and magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, manganese, calcium, iron, boron, copper, zinc, omega-3, omega-6, and omega-9. The median age was lower in the treatment group 49 (29-77) vs. 55 (29-81).
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
combination of several treatments showing efficacy in other trials.
|
risk of death, 60.9% lower, RR 0.39, p = 0.002, treatment 9 of 35 (25.7%), control 23 of 35 (65.7%), NNT 2.5.
|
|
hospitalization time, 28.2% lower, relative time 0.72, p = 0.001, treatment 35, control 35.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mosadegh et al., 19 Sep 2022, Single Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, median age 48.7, 4 authors, study period 9 May, 2020 - 10 July, 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with vitamins A, B1–B3, B5, B6, B9, C, D, K, and magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, sulfur, manganese, calcium, iron, boron, copper, zinc, omega-3, omega-6, omega-9) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial IRCT20200426047206N1.
Contact: m-mosadegh@razi.tums.ac.ir.
The effect of Nutrition Bio-shield superfood (NBS) on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial
Microbial Pathogenesis, doi:10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792
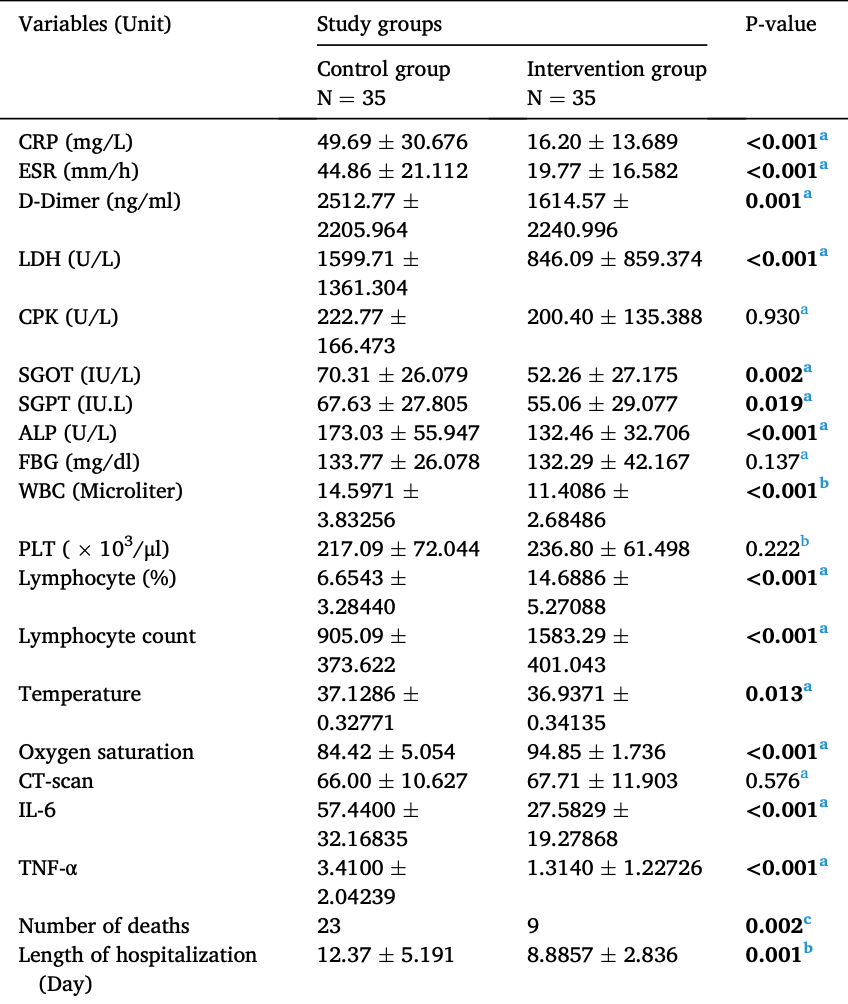
Background: Nutrition Bio-shield Superfood (NBS) is an organic and viable herbal supplement that could improve the function of the immune system. The present study aims to determine the effect of NBS on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19. Methods: This current study was a randomized, comparative, parallel two-arm and single-blind clinical trial study performed in Tehran, Iran. In total, 70 patients with COVID-19 were included in the present study and assigned to two groups including 1) intervention group (n = 35) and 2) control group (n = 35). All patients included in the intervention group received 4.5 gr daily rate of NBS superfood, three times the daily rate of 1.5 gr for 14 days. In contrast, patients included in the control group received a placebo three times a day for 14 days. The measurement of laboratory parameters including CRP, ESR, D-Dimer, LDH, CPK, SGOT, SGPT, ALP, FBG, WBC count, PLT, and lymphocyte count was performed using standard kits and methods. Moreover, all serum samples were tested to determine the levels of IL-6 and TNF-ɑ using specific commercially available ELISA kits according to the instructions of the manufacturer. Results: A significant decrease in the mean serum level of several variables including CRP (p < 0.001), ESR (p < 0.001), D-Dimer (p = 0.001), LDH (p < 0.001), SGOT (p = 0.002), SGPT (p = 0.019), ALP (p < 0.001), WBC count (p < 0.001), body temperature (p = 0.013), IL-6 (p < 0.001), and TNF-α (p < 0.001) was seen 14 days after intervention from baseline in the intervention group than control group. In contrast, in the intervention group, the significant increase from baseline of lymphocyte percentage (p < 0.001) and oxygen saturation (p < 0.001) was seen 14 days after receiving NBS superfood than the control group. Conclusion: Results showed that the use of NBS superfood had various beneficial effects on COVID-19 disease severity. These results suggest that NBS superfood can be used as an effective natural supplement in the treatment process of COVID-19 disease.
References
Alagawany, Attia, Farag, Elnesr, Nagadi et al., The strategy of boosting the immune system under the COVID-19 pandemic, Front. Vet. Sci
Aujla, Patel, Creatine Phosphokinase
Azimi, Hamidi-Farahani, Asgari, Rajabi, Ahmadi et al., Molecular detection and clinical characteristics of bacterial and viral main etiological agents causing respiratory tract infections in Tehran, Iran, Gene Reports
Bayat, Khalkhali, Mahjoub, Nutrition bio-shield superfood: healthy and live herbal supplement for immune system enhancement, International Journal of Nutrition and Food Engineering
Beigmohammadi, Bitarafan, Hoseindokht, Abdollahi, Amoozadeh et al., The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, Trials
Brigden, Clinical utility of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate, Am. Fam. Physician
Cattelan, Di Meco, Trevenzoli, Frater, Ferrari et al., Clinical characteristics and laboratory biomarkers changes in COVID-19 patients requiring or not intensive or sub-intensive care: a comparative study, BMC Infect. Dis
Farhana, Lappin, None, Biochemistry, Lactate Dehydrogenase
Farid, Sridharan, Alsegai, Khawaja, Mansoor et al., Utility of inflammatory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19 infections: Bahrain experience, Biomarkers Med
Giannini, Testa, Savarino, Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians, CMAJ (Can. Med. Assoc. J.)
Gönen, Alaylıoglu, Durcan, Özdemir, ¸ahin et al., Rapid and effective vitamin D supplementation may present better clinical outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) patients by altering serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1, Nutrients
Huang, Wang, Li, Ren, Zhao et al., Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Khan, Shah, Mushtaq, Jehanzeb, Profiling laboratory biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression: a single-center experience, International Journal of Microbiology
Leulseged, Hassen, Ayele, Tsegay, Abebe et al., Laboratory biomarkers of COVID-19 disease severity and outcome: findings from a developing country, PLoS One
Mancini, Defant, Guella, Recent synthesis of marine natural products with antibacterial activities, Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem
Mortaz, Tabarsi, Jamaati, Roofchayee, Dezfuli et al., Increased serum levels of soluble TNF-α receptor is associated with ICU mortality in COVID-19 patients, Front. Immunol
Samprathi, Jayashree, Biomarkers in COVID-19: an up-to-date review, Frontiers in pediatrics
She, Jiang, Ye, Hu, Bai et al., Novel coronavirus of pneumonia in Wuhan, China: emerging attack and management strategies, Clin. Transl. Med
Sproston, Ashworth, Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection, Front. Immunol
Terpos, Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, Elalamy, Kastritis, Sergentanis et al., Hematological findings and complications of COVID-19, Am. J. Hematol
Tourkochristou, Triantos, Mouzaki, The influence of nutritional factors on immunological outcomes, Front. Immunol
Vatansever, Becer, Relationship between IL-6 and COVID-19: to be considered during treatment, Future Virol
Velazquez-Salinas, Verdugo-Rodriguez, Rodriguez, Borca, The role of interleukin 6 during viral infections, Front. Microbiol
Yamamoto, Wada, Ichikawa, Mizuno, Tomida et al., Evaluation of biomarkers of severity in patients with COVID-19 infection, J. Clin. Med
Zheng, Xu, Yang, Zeng, Chen et al., Epidemiological characteristics and clinical features of 32 critical and 67 noncritical cases of COVID-19 in Chengdu, J. Clin. Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792",
"ISSN": [
"0882-4010"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792",
"alternative-id": [
"S0882401022004053"
],
"article-number": "105792",
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "The effect of Nutrition Bio-shield superfood (NBS) on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Microbial Pathogenesis"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mosadegh",
"given": "Mehrdad",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khalkhali",
"given": "Aref",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erfani",
"given": "Yousef",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nezamdoost",
"given": "Manije",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Microbial Pathogenesis",
"container-title-short": "Microbial Pathogenesis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-19T05:36:11Z",
"timestamp": 1663565771000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-28T00:45:52Z",
"timestamp": 1664325952000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
9,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2022-09-28T05:27:16Z",
"timestamp": 1664342836311
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1667260800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0882401022004053?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S0882401022004053?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "105792",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/jcm10173775",
"article-title": "Evaluation of biomarkers of severity in patients with COVID-19 infection",
"author": "Yamamoto",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3775",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib1",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu13114047",
"article-title": "Rapid and effective vitamin D supplementation may present better clinical outcomes in COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2) patients by altering serum INOS1, IL1B, IFNg, cathelicidin-LL37, and ICAM1",
"author": "Gönen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "4047",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib2",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-020-05647-7",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics and laboratory biomarkers changes in COVID-19 patients requiring or not intensive or sub-intensive care: a comparative study",
"author": "Cattelan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "BMC Infect. Dis.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib3",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Profiling laboratory biomarkers associated with COVID-19 disease progression: a single-center experience",
"author": "Khan",
"first-page": "2021",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Microbiology",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib4",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.genrep.2021.101267",
"article-title": "Molecular detection and clinical characteristics of bacterial and viral main etiological agents causing respiratory tract infections in Tehran, Iran",
"author": "Azimi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Gene Reports",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib5",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2020.104366",
"article-title": "Epidemiological characteristics and clinical features of 32 critical and 67 noncritical cases of COVID-19 in Chengdu",
"author": "Zheng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J. Clin. Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib6",
"volume": "127",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/bmm-2020-0422",
"article-title": "Utility of inflammatory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19 infections: Bahrain experience",
"author": "Farid",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "541",
"journal-title": "Biomarkers Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib7",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Novel coronavirus of pneumonia in Wuhan, China: emerging attack and management strategies",
"author": "She",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin. Transl. Med.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib8",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib9",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-021-05795-4",
"article-title": "The effect of supplementation with vitamins A, B, C, D, and E on disease severity and inflammatory responses in patients with COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Beigmohammadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib10",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fvets.2020.570748",
"article-title": "The strategy of boosting the immune system under the COVID-19 pandemic",
"author": "Alagawany",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "712",
"journal-title": "Front. Vet. Sci.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib11",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.665968",
"article-title": "The influence of nutritional factors on immunological outcomes",
"author": "Tourkochristou",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1913",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib12",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib13",
"unstructured": "Bayat A, Khalkhali A, Mahjoub AR. Nutrition bio-shield superfood: healthy and live herbal supplement for immune system enhancement. International Journal of Nutrition and Food Engineering.15:6-9."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/187152107779314151",
"article-title": "Recent synthesis of marine natural products with antibacterial activities",
"author": "Mancini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "17",
"journal-title": "Anti-Infect. Agents Med. Chem.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib14",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2018.00754",
"article-title": "Role of C-reactive protein at sites of inflammation and infection",
"author": "Sproston",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "754",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib15",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"article-title": "Clinical utility of the erythrocyte sedimentation rate",
"author": "Brigden",
"first-page": "1443",
"journal-title": "Am. Fam. Physician",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib16",
"volume": "60",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"author": "Farhana",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib17",
"series-title": "Biochemistry, Lactate Dehydrogenase",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ajh.25829",
"article-title": "Hematological findings and complications of COVID‐19",
"author": "Terpos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "834",
"journal-title": "Am. J. Hematol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib18",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Biomarkers in COVID-19: an up-to-date review",
"author": "Samprathi",
"first-page": "972",
"journal-title": "Frontiers in pediatrics",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib19",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "Aujla",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib20",
"series-title": "Creatine Phosphokinase",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1503/cmaj.1040752",
"article-title": "Liver enzyme alteration: a guide for clinicians",
"author": "Giannini",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "367",
"journal-title": "CMAJ (Can. Med. Assoc. J.)",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib21",
"volume": "172",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0246087",
"article-title": "Laboratory biomarkers of COVID-19 disease severity and outcome: findings from a developing country",
"author": "Leulseged",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib22",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.592727",
"article-title": "Increased serum levels of soluble TNF-α receptor is associated with ICU mortality in COVID-19 patients",
"author": "Mortaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front. Immunol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib23",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0168",
"article-title": "Relationship between IL-6 and COVID-19: to be considered during treatment",
"author": "Vatansever",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "817",
"journal-title": "Future Virol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib24",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2019.01057",
"article-title": "The role of interleukin 6 during viral infections",
"author": "Velazquez-Salinas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1057",
"journal-title": "Front. Microbiol.",
"key": "10.1016/j.micpath.2022.105792_bib25",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 25,
"references-count": 25,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S0882401022004053"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The effect of Nutrition Bio-shield superfood (NBS) on disease severity and laboratory biomarkers in patients with COVID-19: A randomized clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "172"
}
mosadegh
