Clinical Efficacy of Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Preventing the Progression of Moderate to Severe COVID-19 and Its Correlation to Viral Clearance: Results of a Pilot Study
et al., Infectious Microbes and Diseases, doi:10.1097/IM9.0000000000000079, ISRCTN16806663, Apr 2021 (preprint)
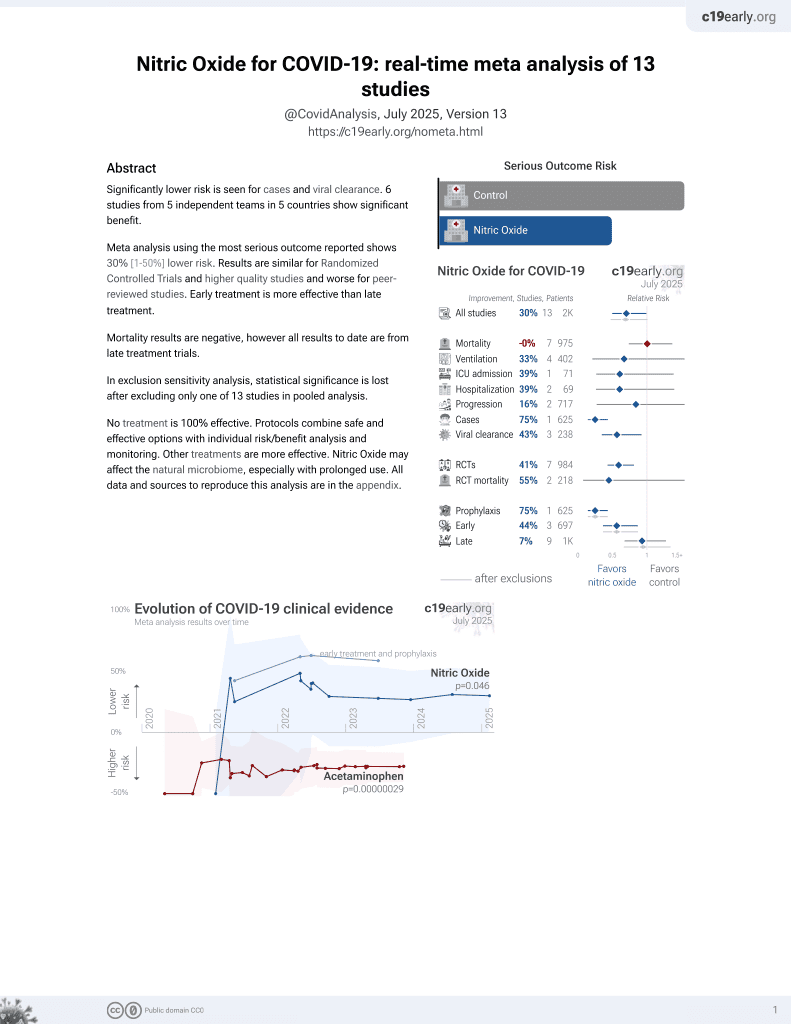
43rd treatment shown to reduce risk in
June 2022, now with p = 0.012 from 12 studies, recognized in 10 countries.
Lower risk for cases and viral clearance.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
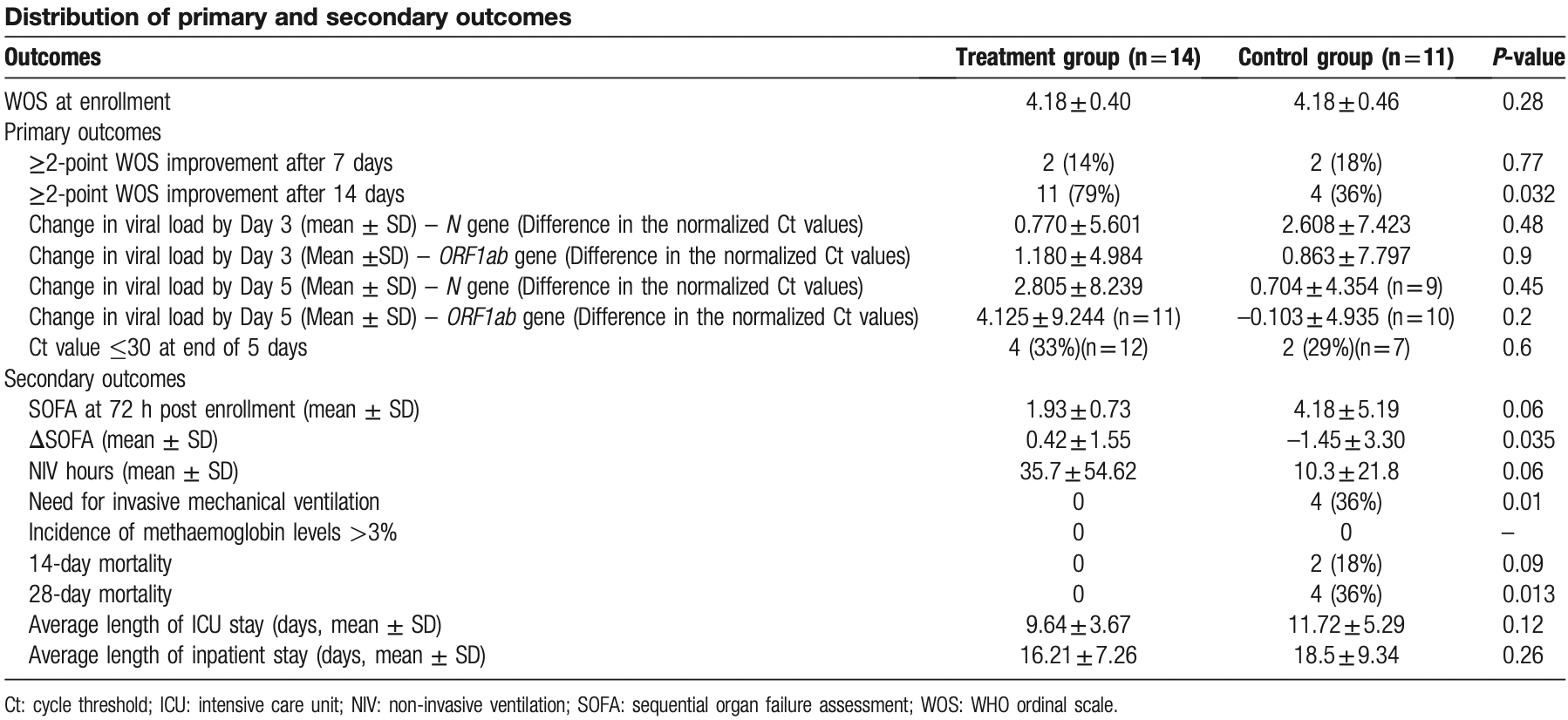
RCT 29 ICU patients in India, showing improved clinical outcomes and faster viral clearance with inhaled nitric oxide treatment. The treatment group was younger (mean 54 vs. 66) and had more patients on NIV at baseline (29% vs. 18%).
Targeted administration to the respiratory tract provides treatment directly
to the typical source of initial SARS-CoV-2 infection and replication, and
allows for rapid onset of action, higher local drug concentration, and reduced systemic side effects (early treatment may be more beneficial).
|
risk of death, 90.1% lower, RR 0.10, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 14 (0.0%), control 4 of 11 (36.4%), NNT 2.8, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 90.1% lower, RR 0.10, p = 0.03, treatment 0 of 14 (0.0%), control 4 of 11 (36.4%), NNT 2.8, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm), day 28.
|
|
risk of <2 point WOS improvement, 42.5% better, RR 0.58, p = 0.47, treatment 3 of 14 (21.4%), control 7 of 11 (63.6%), NNT 2.4, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, odds ratio converted to relative risk, day 14.
|
|
time to viral load reduction, 64.4% lower, RR 0.36, p = 0.005, treatment 14, control 11, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, N gene.
|
|
time to viral load reduction, 63.4% lower, RR 0.37, p = 0.005, treatment 14, control 11, adjusted per study, inverted to make RR<1 favor treatment, Orf1ab gene.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Moni et al., 20 Apr 2021, Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 16 authors, study period September 2020 - December 2020, average treatment delay 6.78 days, trial ISRCTN16806663.
Contact: jayant.aveek@gmail.com.
Clinical Efficacy of Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Preventing the Progression of Moderate to Severe COVID-19 and Its Correlation to Viral Clearance: Results of a Pilot Study
Infectious Microbes and Diseases, doi:10.1097/im9.0000000000000079
Hypoxic patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are at high risk of adverse outcomes. Inhaled nitric oxide (iNO) has shown anti-viral and immunomodulatory effects in vitro. However, in vivo evidence of efficacy in hypoxic COVID-19 is sparse. This open label feasibility study was conducted at a single referral center in South India and evaluated the effectiveness of repurposed iNO in improving clinical outcomes in COVID-19 and its correlation with viral clearance. We recruited hypoxemic COVID-19 patients and allocated them into treatment (iNO) and control groups (1:1). Viral clearance on day 5 favored the treatment group (100% vs 72%, P < 0.01). The speed of viral clearance as adjudged by normalized longitudinal cycle threshold (Ct) values was positively impacted in the treatment group. The proportion of patients who attained clinical improvement, defined as a ≥2-point change on the World Health Organization ordinal scale, was higher in the iNO cohort (n = 11, 79%) as compared to the control group (n = 4, 36%) (odds ratio 6.42, 95% confidence interval 1.09-37.73, P = 0.032). The proportion of patients progressing to mechanical ventilation in the control group (4/11) was significantly higher than in the treatment group (0/14). The all-cause 28-day mortality was significantly different among the study arms, with 36% (4/11) of the patients dying in the control group while none died in the treatment group. The numbers needed to treat to prevent an additional poor outcome of death was estimated to be 2.8. Our study demonstrates the putative role of repurposed iNO in hypoxemic COVID-19 patients and calls for extended validation.
References
Abou-Arab, Huette, Debouvries, Dupont, Jounieaux et al., Inhaled nitric oxide for critically ill COVID-19 patients: a prospective study, Crit Care
Akaberi, Krambrich, Ling, Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro, Redox Biol
Bagate, Tuffet, Masi, Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Intensive Care
Bassenge, Stewart, Interdependence of pharmacologically-induced and endothelium-mediated coronary vasodilation in antianginal therapy, Cardiovasc Drugs Ther
Chen, Liu, Gao, Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing, Clin Infect Dis
De Groote, Fang, NO inhibitions: antimicrobial properties of nitric oxide, Clin Infect Dis
Etches, Finer, Barrington, Graham, Chan, Nitric oxide reverses acute hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in the newborn piglet, Pediatr Res
Fajnzylber, Regan, Coxen, SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality, Nat Commun
Fakhr, Wiegand, Pinciroli, High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), Obstet Gynecol
Fang, Jiang, Su, The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies, Free Radic Biol Med
Farooqui, Selvaraj, Mehta, Mathur, The impact of stringent prescription-only antimicrobial sale regulation (Schedule H1) in India: an interrupted time series analysis, 2008-18, JAC-Antimicrobial Resist
Ferrari, Santini, Protti, Inhaled nitric oxide in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19, J Crit Care
Frost, Jimenez-Solem, Ankarfeldt, Nyeland, Andreasen et al., The adaptive COVID-19 treatment trial-1 (ACTT-1) in a real-world population: a comparative observational study, Crit Care
Garfield, Mcfadyen, Briar, Potential for personalised application of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 pneumonia, Br J Anaesth
Gebistorf, Karam, Wetterslev, Afshari, Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults, Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Griffiths, Evans, Inhaled nitric oxide therapy in adults, N Engl J Med
Ignarro, Inhaled NO and COVID-19, Br J Pharmacol
Jen, Chang, Lin, Evaluating clinical efficacy of antiviral therapy for COVID-19: a surrogate endpoint approach, Infect Dis Ther
Kermarrec, Chollet-Martin, Beloucif, Faivre, Gougerot-Pocidalo et al., Alveolar neutrophil oxidative burst and beta2 integrin expression in experimental acute pulmonary inflammation are not modified by inhaled nitric oxide, Shock
Kobayashi, Murata, Nitric oxide inhalation as an interventional rescue therapy for COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Intensive Care
Moncada, Higgs, The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway, N Engl J Med
Moncada, Higgs, The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology, Br J Pharmacol
Qaseem, Yost, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta, Should remdesivir be used for the treatment of patients with COVID-19? Rapid, living practice points from the American College of Physicians (Version 2), Ann Intern Med
Scola, Bideau, Andreani, Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis
Tavazzi, Pozzi, Mongodi, Dammassa, Romito et al., Inhaled nitric oxide in patients admitted to intensive care unit with COVID-19 pneumonia, Crit Care
The, Group, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Åkerström, Gunalan, Keng, Tan, Mirazimi, Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected, Virology
Åkerström, Mousavi-Jazi, Klingström, Leijon, Lundkvist et al., Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, J Virol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/im9.0000000000000079",
"ISSN": [
"2641-5917"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/IM9.0000000000000079",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moni",
"given": "Merlin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Madathil",
"given": "Thushara",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sathyapalan",
"given": "Dipu T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Menon",
"given": "Veena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gutjahr",
"given": "Georg",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Edathadathil",
"given": "Fabia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sureshkumar",
"given": "Deepthi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Prasanna",
"given": "Preetha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jose",
"given": "Soumya",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jerome",
"given": "Roshni",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Krishnan",
"given": "Ajai",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Pillai",
"given": "Indulekha C.L.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kumar",
"given": "Geetha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nair",
"given": "Bipin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nizet",
"given": "Victor",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jayant",
"given": "Aveek",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Microbes and Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-30T09:13:25Z",
"timestamp": 1640855605000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-03-31T21:01:06Z",
"timestamp": 1648760466000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
4,
3
]
],
"date-time": "2022-04-03T21:21:02Z",
"timestamp": 1649020862040
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/IM9.0000000000000079",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "26-33",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
3
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference": [
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.",
"first-page": "693",
"issue": "(8)",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R1-5-20220331",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "The L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway.",
"author": "Moncada",
"first-page": "2002",
"issue": "(27)",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R2-5-20220331",
"volume": "329",
"year": "1993"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/sj.bjp.0706458",
"article-title": "The discovery of nitric oxide and its role in vascular biology.",
"author": "Moncada",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S193",
"issue": "(S1)",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "R3-5-20220331",
"volume": "147",
"year": "2006"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/BF00054249",
"article-title": "Interdependence of pharmacologically-induced and endothelium-mediated coronary vasodilation in antianginal therapy.",
"author": "Bassenge",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "27",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Cardiovasc Drugs Ther",
"key": "R4-5-20220331",
"volume": "2",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1203/00006450-199401000-00004",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide reverses acute hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in the newborn piglet.",
"author": "Etches",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "15",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Res",
"key": "R5-5-20220331",
"volume": "35",
"year": "1994"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.12.008",
"article-title": "The role of NO in COVID-19 and potential therapeutic strategies.",
"author": "Fang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "153",
"journal-title": "Free Radic Biol Med",
"key": "R6-5-20220331",
"volume": "163",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/clinids/21.Supplement_2.S162",
"article-title": "NO inhibitions: antimicrobial properties of nitric oxide.",
"author": "De Groote",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "S162",
"issue": "(Supplement_2)",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R7-5-20220331",
"volume": "21",
"year": "1995"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.79.3.1966-1969.2005",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide inhibits the replication cycle of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus.",
"author": "Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1966",
"issue": "(3)",
"journal-title": "J Virol",
"key": "R8-5-20220331",
"volume": "79",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.redox.2020.101734",
"article-title": "Mitigation of the replication of SARS-CoV-2 by nitric oxide in vitro.",
"author": "Akaberi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "101734",
"journal-title": "Redox Biol",
"key": "R9-5-20220331",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1086/425357",
"article-title": "Inhalation of nitric oxide in the treatment of severe acute respiratory syndrome: a rescue trial in Beijing.",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1531",
"issue": "(10)",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "R10-5-20220331",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19057-5",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral load is associated with increased disease severity and mortality.",
"author": "Fajnzylber",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5493",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "R11-5-20220331",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M20-5831",
"article-title": "Should remdesivir be used for the treatment of patients with COVID-19? Rapid, living practice points from the American College of Physicians (Version 2).",
"author": "Qaseem",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"issue": "(2)",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "R12-5-20220331",
"volume": "174",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03406-3",
"article-title": "The adaptive COVID-19 treatment trial-1 (ACTT-1) in a real-world population: a comparative observational study.",
"author": "Frost",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "677",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R13-5-20220331",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-021-00431-9",
"article-title": "Evaluating clinical efficacy of antiviral therapy for COVID-19: a surrogate endpoint approach.",
"author": "Jen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "815",
"issue": "(2)",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis Ther",
"key": "R14-5-20220331",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/bph.15085",
"article-title": "Inhaled NO and COVID-19.",
"author": "Ignarro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3848",
"issue": "(16)",
"journal-title": "Br J Pharmacol",
"key": "R15-5-20220331",
"volume": "177",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00681-9",
"article-title": "Nitric oxide inhalation as an interventional rescue therapy for COVID-19-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Kobayashi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "61",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "R16-5-20220331",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03222-9",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide in patients admitted to intensive care unit with COVID-19 pneumonia.",
"author": "Tavazzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "508",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R17-5-20220331",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcrc.2020.08.007",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide in mechanically ventilated patients with COVID-19.",
"author": "Ferrari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "159",
"journal-title": "J Crit Care",
"key": "R18-5-20220331",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03371-x",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide for critically ill COVID-19 patients: a prospective study.",
"author": "Abou-Arab",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "645",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Crit Care",
"key": "R19-5-20220331",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13613-020-00769-2",
"article-title": "Rescue therapy with inhaled nitric oxide and almitrine in COVID-19 patients with severe acute respiratory distress syndrome.",
"author": "Bagate",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "151",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Ann Intensive Care",
"key": "R20-5-20220331",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bja.2020.11.006",
"article-title": "Potential for personalised application of inhaled nitric oxide in COVID-19 pneumonia.",
"author": "Garfield",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e72",
"issue": "(2)",
"journal-title": "Br J Anaesth",
"key": "R21-5-20220331",
"volume": "126",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/AOG.0000000000004128",
"article-title": "High concentrations of nitric oxide inhalation therapy in pregnant patients with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).",
"author": "Safaee Fakhr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1109",
"issue": "(6)",
"journal-title": "Obstet Gynecol",
"key": "R22-5-20220331",
"volume": "136",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2009.09.007",
"article-title": "Dual effect of nitric oxide on SARS-CoV replication: viral RNA production and palmitoylation of the S protein are affected.",
"author": "Åkerström",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "(1)",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "R23-5-20220331",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jacamr/dlaa076",
"article-title": "The impact of stringent prescription-only antimicrobial sale regulation (Schedule H1) in India: an interrupted time series analysis, 2008-18.",
"author": "Farooqui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "dlaa076",
"issue": "(3)",
"journal-title": "JAC-Antimicrobial Resist",
"key": "R24-5-20220331",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra051884",
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide therapy in adults.",
"author": "Griffiths",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2683",
"issue": "(25)",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "R25-5-20220331",
"volume": "353",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1097/00024382-199808000-00008",
"article-title": "Alveolar neutrophil oxidative burst and beta2 integrin expression in experimental acute pulmonary inflammation are not modified by inhaled nitric oxide.",
"author": "Kermarrec",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "129",
"issue": "(2)",
"journal-title": "Shock",
"key": "R26-5-20220331",
"volume": "10",
"year": "1998"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhaled nitric oxide for acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in children and adults.",
"author": "Gebistorf",
"first-page": "CD002787",
"issue": "(6)",
"journal-title": "Cochrane Database Syst Rev",
"key": "R27-5-20220331",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10096-020-03913-9",
"article-title": "Viral RNA load as determined by cell culture as a management tool for discharge of SARS-CoV-2 patients from infectious disease wards.",
"author": "La Scola",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1059",
"issue": "(6)",
"journal-title": "Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis",
"key": "R31-5-20220331",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 28,
"references-count": 28,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/IM9.0000000000000079"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Clinical Efficacy of Inhaled Nitric Oxide in Preventing the Progression of Moderate to Severe COVID-19 and Its Correlation to Viral Clearance: Results of a Pilot Study",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "4"
}