Symptom Alleviation/Resolution and Returns to Usual Health/Activities in Immunocompromised Adults with COVID-19 Treated with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Results from the EPIC-IC Trial
et al., Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w, EPIC-IC, NCT05438602, Oct 2025
RCT 156 immunocompromised COVID-19 patients comparing 5-day, 10-day, and 15-day paxlovid treatment showing no significant differences.
Mokgokong et al., 14 Oct 2025, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, median age 64.0, 5 authors, study period 3 August, 2022 - 13 November, 2023, trial NCT05438602 (history) (EPIC-IC).
Contact: ruth.mokgokong@pfizer.com.
Symptom Alleviation/Resolution and Returns to Usual Health/Activities in Immunocompromised Adults with COVID-19 Treated with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Results from the EPIC-IC Trial
Infectious Diseases and Therapy, doi:10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w
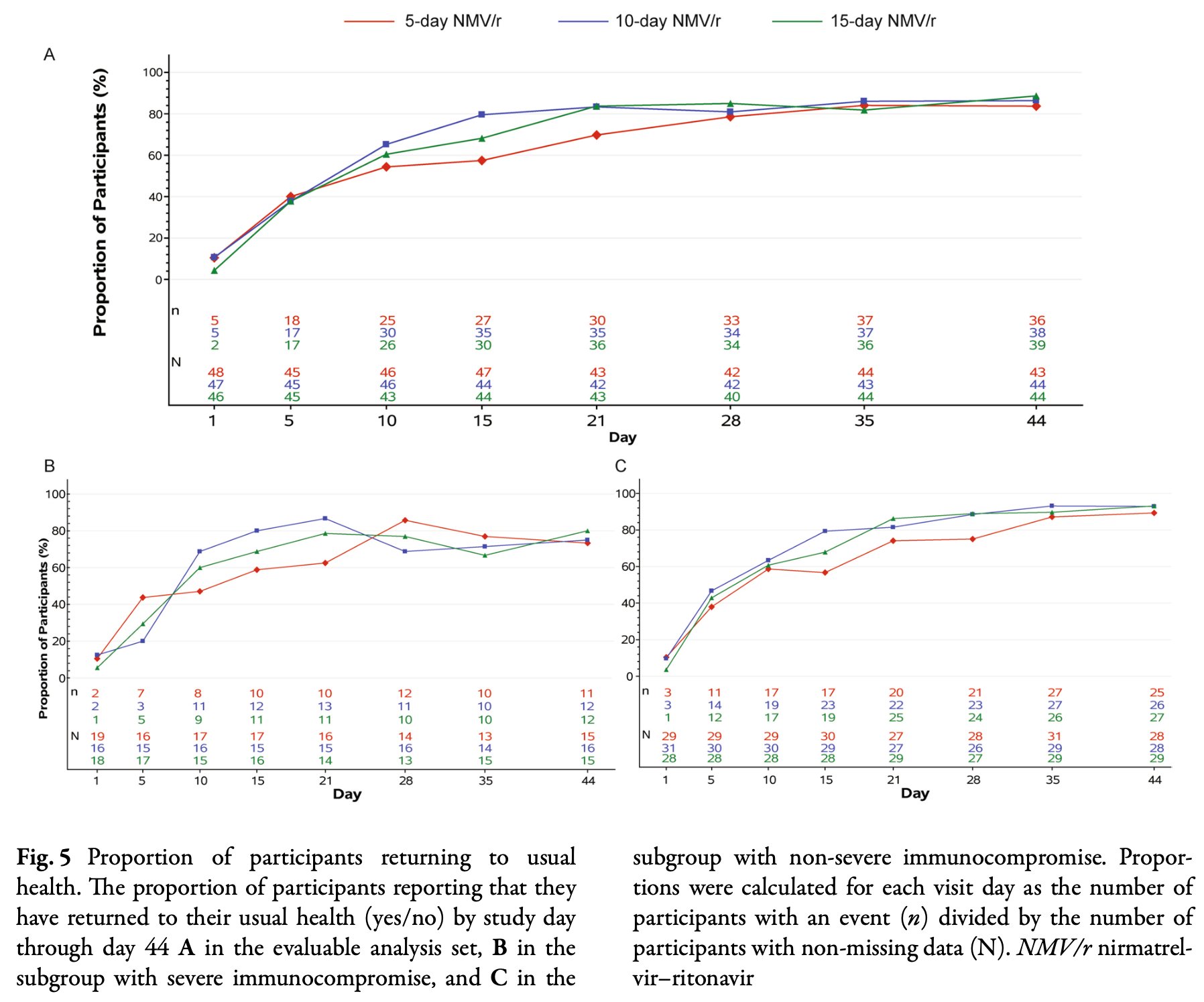
Introduction: EPIC-IC was a randomized, double-blind trial comparing the approved 5-day regimen of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir (NMV/r) vs. 10-day and 15-day NMV/r in immunocompromised individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19. We describe patient-reported global impressions of illness from EPIC-IC.
Methods: In EPIC-IC, 155 immunocompromised participants received 5-day, 10-day, or 15-day NMV/r (1:1:1). Participants completed the Global Impressions Questionnaire through week 24. Median times to first alleviation and resolution of symptoms and return to usual health and usual activities were estimated using Kaplan-Meier analyses for each treatment arm and post hoc subpopulations with severe vs. non-severe immunocompromise. Five-day arm times were compared vs. 10-day and 15-day arm times. Results: Symptoms were alleviated after a median 6.0 (95% CI 4.0-9.0) days with 5-day NMV/r, similar to 9.0 (5.0-9.0) days with 10-day NMV/r (p = 0.627) and 10.0 (6.0-11.0) days with 15-day NMV/r (p = 0.528). Symptoms resolved after a median 16.0 (10.0-22.0) days with 5-day NMV/r, similar to 13.0 (9.0-14.0) days with 10-day (p = 0.140) and 13.0 (11.0-21.0) days with 15-day NMV/r (p = 0.471). In the severely immunocompromised subpopulation, symptoms resolved later with 5-day vs. 10-day NMV/r (p = 0.026). Participants returned to usual health after a median 11.0 (6.0-16.0) days with 5-day NMV/r, similar to 9.0 (6.0-13.0) days with 10-day (p = 0.319) and 10.0 (6.0-13.0) days with 15-day NMV/r (p = 0.218), and to usual activities after 10.0 (9.0-15.0) days with 5-day NMV/r,
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Abbasi, Researchers tie severe immunosuppression to chronic COVID-19 and virus variants, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2021.7212
Ansari, Coetzer, Gebo, Patientreported outcomes of nirmatrelvir treatment for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with symptomatic COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf449
Antinori, Bausch-Jurken, The burden of COVID-19 in the immunocompromised patient: implications for vaccination and needs for the future, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiad181
Chatterjee, Bhattacharya, Nag, A detailed overview of SARS-CoV-2 omicron: its subvariants, mutations and pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, immunological landscape, immune escape, and therapies, Viruses, doi:10.3390/v15010167
Chew, Malani, Gandhi, COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients-updates and future directions, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2023.19542
Corey, Beyrer, Cohen, SARS-CoV-2 variants in patients with immunosuppression, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMsb2104756
Evans, Dube, Lu, Impact of COVID-19 on immunocompromised populations during the Omicron era: insights from the observational population-based INFORM study, The Lancet Regional Health, doi:10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100747
Gnanasakthy, Barrett, Norcross, Use of patient and investigator global impression scales: a review of Food and Drug Administrationapproved labeling, 2009 to 2019, Value Health, doi:10.1016/j.jval.2021.01.005
Götz, Mathé, Agarwal, Clinical phenotype and outcome of persistent SARS-CoV-2 replication in immunocompromised hosts: a retrospective observational study in the Omicron era, Infection, doi:10.1007/s15010-023-02138-0
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Of Coronavirus, Disease, Symptoms and reduction in healthcare utilization among highrisk patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NMV/R): a phase 3 randomized trial, Clin Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/cid/ciae551
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2118542
Huygens, Gharbharan, Serroukh, Hightiter convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients, J Antimicrob Chemother, doi:10.1093/jac/dkad144
Kaplan, Meier, Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations, J Am Stat Assoc, doi:10.2307/2281868
Li, Choudhary, Regan, SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and evolution varies by type and severity of immunodeficiency, Sci Transl Med
Lindahl, Ahava, Haukipää, Successful treatment of persisting SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient with repeated nirmatrelvir/ritonavir courses: a case report, Infect Dis (Lond), doi:10.1080/23744235.2023.2223274
Ma, Castro, Lambrou, Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: circulation of omicron XBB and JN.1 lineages-United States, May 2023-September 2024, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Meijer, Paran, Belkin, Persistent COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients-Israeli society of infectious diseases consensus statement on diagnosis and management, Clin Microbiol Infect, doi:10.1016/j.cmi.2024.04.009
Moser, Li, Eron, Predictors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from nasopharyngeal swabs and concordance with other compartments in nonhospitalized adults with mild to moderate COVID-19, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofac618
Pfizer, Paxlovid™, Receives FDA Approval for Adult Patients at High Risk of Progression to Severe COVID-19
Spinner, Bell, Einsele, Is COVID-19 still a threat? An expert opinion review on the continued healthcare burden in immunocompromised individuals, Adv Ther, doi:10.1007/s12325-024-03043-0
Vergouwe, Birnie, Van Veelen, A longitudinal description of the health-related quality of life among individuals at high risk after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a Dutch multicenter observational cohort study, Open Forum Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/ofid/ofaf055
Weinstein, Paredes, Gardner, Extended nirmatrelvir-ritonavir treatment durations for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19 (EPIC-IC): a placebo-controlled, randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial, Lancet Infect Dis, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00221-X
Weir, BMI Classification Percentile And Cut Off Points
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w",
"ISSN": [
"2193-8229",
"2193-6382"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w",
"alternative-id": [
"1228"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "3 July 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "27 August 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "14 October 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Conflict of Interest",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "Ruth Mokgokong is an employee and a minority shareholder of Pfizer, which funded this study. Paul Cislo is an employee and a minority shareholder of Pfizer, which funded this study. Elena Tudone is an employee and a minority shareholder of Pfizer, which funded this study. Edward Weinstein is an employee and a minority shareholder of Pfizer, which funded this study. Joseph C. Cappelleri is an employee and a minority shareholder of Pfizer, which funded this study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethical Approval",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Ethics approval for the EPIC-IC protocol, amendments, and other relevant documents was granted by the appropriate institutional review boards and ethics committees (Supplementary Materials), as documented in Weinstein et al., 2025 []. The study did not have a ‘master’ ethics committee or a main center; the principal investigator who signed the clinical study report was Dr. Roger Paredes, Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol, Spain. Participants provided written informed consent before enrolling in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with consensus ethical principles, including those in the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and the Council for International Organizations of Medical Sciences (CIOMS) International Ethical Guidelines; with applicable International Council for Harmonisation of Technical Requirements of Pharmaceuticals for Human Use (ICH) guidelines for Good Clinical Practice; and with applicable laws and regulations, including applicable privacy laws."
}
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6278-4969",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Mokgokong",
"given": "Ruth",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0009-0004-3130-2818",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cislo",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tudone",
"given": "Elena",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Weinstein",
"given": "Edward",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9586-0748",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Cappelleri",
"given": "Joseph C.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"clinical-trial-number": [
{
"clinical-trial-number": "nct05438602",
"registry": "10.18810/clinical-trials-gov"
}
],
"container-title": "Infectious Diseases and Therapy",
"container-title-short": "Infect Dis Ther",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-14T11:17:14Z",
"timestamp": 1760440634000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-14T11:17:17Z",
"timestamp": 1760440637000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100004319",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100004319",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Pfizer"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-14T11:40:43Z",
"timestamp": 1760442043044,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1760400000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-14T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1760400000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1007",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
14
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.7212",
"author": "J Abbasi",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2033",
"issue": "20",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1228_CR1",
"unstructured": "Abbasi J. Researchers tie severe immunosuppression to chronic COVID-19 and virus variants. JAMA. 2021;325(20):2033–5. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.7212.",
"volume": "325",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMsb2104756",
"author": "L Corey",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "562",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1228_CR2",
"unstructured": "Corey L, Beyrer C, Cohen MS, et al. SARS-CoV-2 variants in patients with immunosuppression. N Engl J Med. 2021;385(6):562–6. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMsb2104756.",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100747",
"author": "RA Evans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "The Lancet Regional Health",
"key": "1228_CR3",
"unstructured": "Evans RA, Dube S, Lu Y, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on immunocompromised populations during the Omicron era: insights from the observational population-based INFORM study. The Lancet Regional Health. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lanepe.2023.100747.",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiad181",
"author": "A Antinori",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S4",
"issue": "Supplement_1",
"journal-title": "J Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR4",
"unstructured": "Antinori A, Bausch-Jurken M. The burden of COVID-19 in the immunocompromised patient: implications for vaccination and needs for the future. J Infect Dis. 2023;228(Supplement_1):S4–12. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jiad181.",
"volume": "228",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1397",
"issue": "15",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "1228_CR5",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, et al. Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with Covid-19. N Engl J Med. 2022;386(15):1397–408. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa2118542.",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"key": "1228_CR6",
"unstructured": "U.S. Food and Drug Administration. HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: PAXLOVID™ (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets), co-packaged for oral use. 2025. Updated 12-Feb-2025. Available from: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/label/2025/217188s010lbl.pdf. Accessed 19 Feb 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00221-X",
"author": "E Weinstein",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR7",
"unstructured": "Weinstein E, Paredes R, Gardner A, et al. Extended nirmatrelvir–ritonavir treatment durations for immunocompromised patients with COVID-19 (EPIC-IC): a placebo-controlled, randomised, double-blind, phase 2 trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2025. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(25)00221-X.",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2023.19542",
"author": "KW Chew",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1519",
"issue": "16",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "1228_CR8",
"unstructured": "Chew KW, Malani PN, Gandhi RT. COVID-19 therapeutics for nonhospitalized patients—updates and future directions. JAMA. 2023;330(16):1519–20. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2023.19542.",
"volume": "330",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"key": "1228_CR9",
"unstructured": "Infectious Diseases Society of America. IDSA Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. 2023. Updated 04-Jun-2025. Available from: https://www.idsociety.org/COVID19guidelines. Accessed 13 Jun 2025."
},
{
"key": "1228_CR10",
"unstructured": "US Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Underlying Conditions and the Higher Risk for Severe COVID-19. 2025. Updated 06-Feb-2025. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/covid/hcp/clinical-care/underlying-conditions.html. Accessed 12 Jun 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciae551",
"author": "J Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR11",
"unstructured": "Hammond J, Leister-Tebbe H, Gardner A, Alleviation of Coronavirus Disease, et al. Symptoms and reduction in healthcare utilization among high-risk patients treated with nirmatrelvir/ritonavir (NMV/R): a phase 3 randomized trial. Clin Infect Dis. 2019. https://doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciae551.",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"key": "1228_CR12",
"unstructured": "Pfizer’s PAXLOVID™ Receives FDA Approval for Adult Patients at High Risk of Progression to Severe COVID-19 [press release]. 25-May-2023. Available from: https://www.pfizer.com/news/press-release/press-release-detail/pfizers-paxlovidtm-receives-fda-approval-adult-patients. Accessed 21 Feb 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaf449",
"author": "W Ansari",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR13",
"unstructured": "Ansari W, Coetzer H, Gebo KA, et al. Patient-reported outcomes of nirmatrelvir treatment for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with symptomatic COVID-19. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaf449.",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.adk1599",
"author": "Y Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "731",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "1228_CR14",
"unstructured": "Li Y, Choudhary MC, Regan J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 viral clearance and evolution varies by type and severity of immunodeficiency. Sci Transl Med. 2024;16(731):eadk1599.",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s15010-023-02138-0",
"author": "V Götz",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "923",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Infection",
"key": "1228_CR15",
"unstructured": "Götz V, Mathé P, Agarwal P, et al. Clinical phenotype and outcome of persistent SARS-CoV-2 replication in immunocompromised hosts: a retrospective observational study in the Omicron era. Infection. 2024;52(3):923–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-023-02138-0.",
"volume": "52",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/jac/dkad144",
"author": "S Huygens",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1644",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "J Antimicrob Chemother",
"key": "1228_CR16",
"unstructured": "Huygens S, Gharbharan A, Serroukh Y, et al. High-titer convalescent plasma plus nirmatrelvir/ritonavir treatment for non-resolving COVID-19 in six immunocompromised patients. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2023;78(7):1644–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkad144.",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/23744235.2023.2223274",
"author": "AL Lindahl",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "585",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Infect Dis (Lond)",
"key": "1228_CR17",
"unstructured": "Lindahl AL, Ahava MJ, Haukipää M, et al. Successful treatment of persisting SARS-CoV-2 infection in an immunocompromised patient with repeated nirmatrelvir/ritonavir courses: a case report. Infect Dis (Lond). 2023;55(8):585–9. https://doi.org/10.1080/23744235.2023.2223274.",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2024.04.009",
"author": "SE Meijer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1012",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "1228_CR18",
"unstructured": "Meijer SE, Paran Y, Belkin A, et al. Persistent COVID-19 in immunocompromised patients-Israeli society of infectious diseases consensus statement on diagnosis and management. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2024;30(8):1012–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmi.2024.04.009.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12325-024-03043-0",
"author": "CD Spinner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "666",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Adv Ther",
"key": "1228_CR19",
"unstructured": "Spinner CD, Bell S, Einsele H, et al. Is COVID-19 still a threat? An expert opinion review on the continued healthcare burden in immunocompromised individuals. Adv Ther. 2025;42(2):666–719. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12325-024-03043-0.",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jval.2021.01.005",
"author": "A Gnanasakthy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1016",
"issue": "7",
"journal-title": "Value Health",
"key": "1228_CR20",
"unstructured": "Gnanasakthy A, Barrett A, Norcross L, et al. Use of patient and investigator global impression scales: a review of Food and Drug Administration–approved labeling, 2009 to 2019. Value Health. 2021;24(7):1016–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jval.2021.01.005.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"key": "1228_CR21",
"unstructured": "US Food and Drug Administration. Assessing COVID-19-Related Symptoms in Outpatient Adult and Adolescent Subjects in Clinical Trials of Drugs and Biological Products for COVID-19 Prevention or Treatment: Guidance for Industry. 2024. Available from: https://www.fda.gov/media/167275/download. Accessed 10 Feb 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.2307/2281868",
"author": "EL Kaplan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "457",
"issue": "282",
"journal-title": "J Am Stat Assoc",
"key": "1228_CR22",
"unstructured": "Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53(282):457–81. https://doi.org/10.2307/2281868.",
"volume": "53",
"year": "1958"
},
{
"key": "1228_CR23",
"unstructured": "Weir CJ, A. BMI Classification Percentile And Cut Off Points. StatPearls [Internet]. 2025. Updated 26-Jun-2023. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK541070/. Accessed 28 Jan 2025."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v15010167",
"author": "S Chatterjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "1228_CR24",
"unstructured": "Chatterjee S, Bhattacharya M, Nag S, et al. A detailed overview of SARS-CoV-2 omicron: its sub-variants, mutations and pathophysiology, clinical characteristics, immunological landscape, immune escape, and therapies. Viruses. 2023;15(1):167. https://doi.org/10.3390/v15010167.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15585/mmwr.mm7342a1",
"author": "KC Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "938",
"journal-title": "MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep",
"key": "1228_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ma KC, Castro J, Lambrou AS, et al. Genomic surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants: circulation of omicron XBB and JN.1 lineages—United States, May 2023–September 2024. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2024;73:938–45.",
"volume": "73",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofaf055",
"author": "M Vergouwe",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR26",
"unstructured": "Vergouwe M, Birnie E, van Veelen S, et al. A longitudinal description of the health-related quality of life among individuals at high risk after SARS-CoV-2 infection: a Dutch multicenter observational cohort study. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2025;12(2):ofaf055. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofaf055.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2025"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac618",
"author": "C Moser",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"issue": "11",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "1228_CR27",
"unstructured": "Moser C, Li JZ, Eron JJ, et al. Predictors of SARS-CoV-2 RNA from nasopharyngeal swabs and concordance with other compartments in nonhospitalized adults with mild to moderate COVID-19. Open Forum Infect Dis. 2022;9(11):ofac618. https://doi.org/10.1093/ofid/ofac618.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 27,
"references-count": 27,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/10.1007/s40121-025-01228-w"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Symptom Alleviation/Resolution and Returns to Usual Health/Activities in Immunocompromised Adults with COVID-19 Treated with Nirmatrelvir-Ritonavir: Results from the EPIC-IC Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}