The difference in the dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake between COVID-19 patients and healthy persons
et al., Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, doi:10.3233/MNM-211521, Jan 2022
Vitamin C for COVID-19
6th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000068 from 74 studies, recognized in 22 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
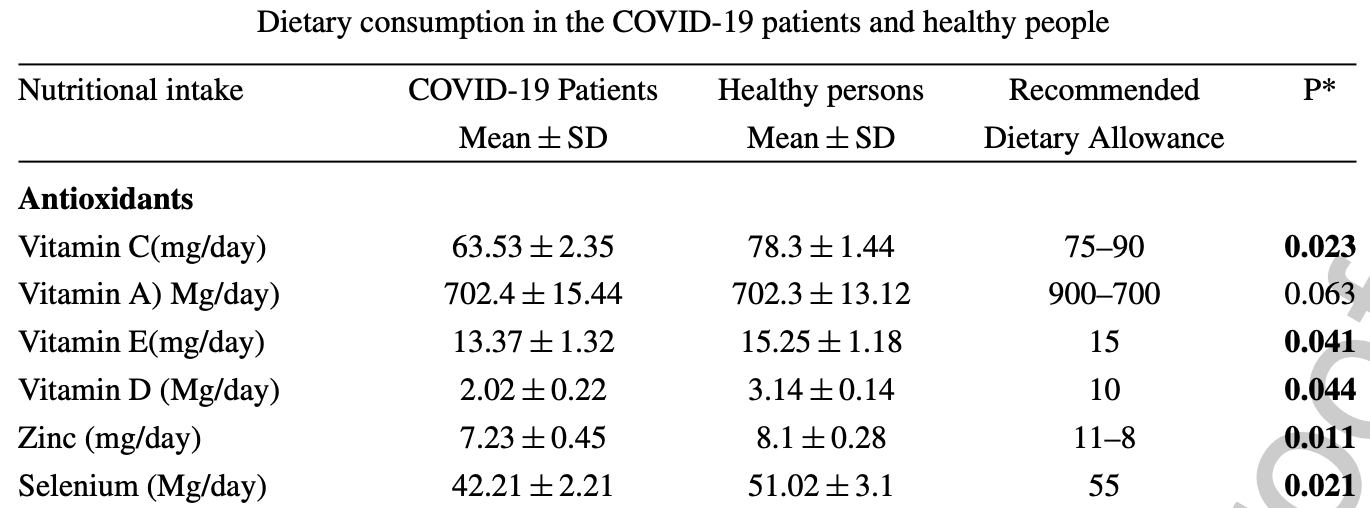
Retrospective dietary survey analysis of 500 COVID-19 patients and 500 healthy matched controls in Iran, showing that COVID-19 patients had lower daily consumption of vitamin C, vitamin D, vitamin E, zinc, and selenium. IR.ARUMS.REC.1400.008.
Mohajeri et al., 29 Jan 2022, retrospective, Iran, peer-reviewed, 4 authors.
The difference in the dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake between COVID -19 patients and healthy persons
Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism, doi:10.3233/mnm-211521
BACKGROUND: The healthy diet is important to maintain immunity against infection. This study aimed to assess and compare the consumption of functional foods, some antioxidants, and dietary inflammatory index between Iranian COVID-19 patients and healthy persons.
METHODS: This case-control study was conducted between 1000 (500 cases and 500 controls) adults aged 18-65years in Iran, that were sampling based on the snowball method and their information was collected electronically. The dietary intake was assessed using the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ).
RESULTS: There was a significant difference (p = 0.044) in vitamin D consumption between healthy people and COVID-19 patients. Vitamin E intake in healthy participants was significantly (p = 0.041) more than COVID-19 patients. There was a significant difference in Zinc (p = 0.011), selenium (p = 0.021), and vitamin C (p = 0.023) between healthy persons and COVID-19 patients. Healthy participants' consumption of onion (56.5 ± 7.82 g/day), garlic (4.32 ± 0.01 g/day) and oat (6.32 ± 0.71 g/day) was significantly (p ≤ 0.05) more than COVID-19 patients. With the increase of each unit in the score of the dietary inflammatory index, the risk of COVID-19 incidence increased 1.63 times (OR = 1.63 95%CI: 1.54-1.72). There was an inverse association between the consumption of antioxidants and functional foods with the risk of COVID-19 incidence in the study population (p ≤ 0.05).
Conflict of interest The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
Bahrami, Bahrami-Taghanaki, Khorasanchi, Tayefi, Ferns et al., the association between neuropsychological function with serum vitamins A, D, and E and hs-CRP concentrations, Journal of Molecular Neuroscience
Bayir, An, ¸yi Gi T A, The importance of polyphenols as functional food in health, Bezmialem Science
Beltrán-García, Osca-Verdegal, Pallardó, Ferreres, Rodríguez et al., Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: the potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression, Antioxidants
Calder, Carr, Gombart, Eggersdorfer, Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections, Nutrients
Darenskaya, Kolesnikova, Kolesnikov, The Association of Respiratory Viruses with Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants. Implications for the COVID-19 Pandemic, Current Pharmaceutical Design
Das, Jahan, Uddin, Hossain, Chowdhury et al., Serum CRP, MDA, vitamin C, and trace elements in Bangladeshi patients with rheumatoid arthritis, Biological Trace Element Research
De Flora, Balansky, Maestra S, Antioxidants and COVID-19, Journal of Preventive Medicine and Hygiene
Díaz, Fernández-Ruiz, Cámara, An international regulatory review of food health-related claims in functional food products labeling, Journal of Functional Foods
Ebadi, Montano-Loza, Perspective: improving vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Farag, Abdelwareth, Sallam, Shorbagi, Jehmlich et al., Metabolomics reveals impact of seven functional foods on metabolic pathways in a gut microbiota model, Journal of Advanced Research
Iddir, Brito, Dingeo, Del Campo, Samouda et al., Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis, Nutrients
Jakubczyk, Kochman, Kwiatkowska, Kal -Duńska, Dec et al., Antioxidant properties and nutritional composition of matcha green tea, Foods
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, Nallathambi, Ramachandran et al., COVID-19: Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Lenssen, Bast, De Boer, Clarifying the health claim assessment procedure of EFSA will benefit functional food innovation, Journal of Functional Foods
Li, Rahman, Huang, Zhang, Zhu, Green tea polyphenols decrease weight gain, ameliorate alteration of gut microbiota, and mitigate intestinal inflammation in canines with high-fat-diet-induced obesity, The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry
Liu, Li, Zhou, Guan, Xiang, Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)?, Journal of Autoimmunity
Maqsood, Adiamo, Ahmad, Mudgil, Bioactive compounds from date fruit and seed as potential nutraceutical and functional food ingredients, Food Chemistry
Masek, Chrzescijanska, Latos, Zaborski, Podsedek, Antioxidant and antiradical properties of green tea extract compounds, Int J Electrochem Sci
Mohajeri, Ghannadiasl, Narimani, Nemati, The food choice determinants and adherence to Mediterranean diet in Iranian adults before and during COVID-19 lockdown: population-based study, Nutrition & Food Science
Mohajeri, Horriatkhah, Mohajery, The effect of glutamine supplementation on serum levels of some inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and appetite in COVID-19 patients: a case-control study, Inflammopharmacology
Mohajeri, Houjeghani, Ghahremanzadeh, Borghei, Moradi et al., Some behavioral risk factors of obesity in Ardabil-Iran adults, Obesity Medicine
Mohajeri, The dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake in COVID -19 patients 9
Mohammadifard, Sajjadi, Maghroun, Alikhasi, Nilforoushzadeh et al., Validation of a simplified food frequency questionnaire for the assessment of dietary habits in Iranian adults: Isfahan Healthy Heart Program, Iran, ARYA Atherosclerosis
Naja, Hamadeh, Nutrition amid the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-level framework for action, European Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Rad, Maleki, Kafil, Zavoshti, Abbasi, Postbiotics as novel health-promoting ingredients in functional foods, Health Promotion Perspectives
Rouf, Uddin, Sarker, Islam, Ali et al., Antiviral potential of garlic (Allium sativum) and its organosulfur compounds: A systematic update of pre-clinical and clinical data, Trends Food Sci Technol
Selvan, Mahendiran, Kumar, Rahiman, Garlic, green tea and turmeric extracts-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Phytochemical, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxicity studies, Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology
Shehzad, Zahid, Mahmood, Suleria, Functional Foods: Concepts and Their Health Perspectives
Shivappa, Hébert, Rietzschel, Buyzere, Langlois et al., Associations between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the Asklepios Study, British Journal of Nutrition
Szulińska, Stępień, Kręgielska-Narożna, Suliburska, Skrypnik et al., Effects of green tea supplementation on inflammation markers, antioxidant status and blood pressure in NaCl-induced hypertensive rat model, Food & Nutrition Research
Taborelli, Polesel, Parpinel, Stocco, Birri et al., Fruit and vegetables consumption is directly associated to survival after prostate cancer, Molecular Nutrition & Food Research
Tay, Poh, Rénia, Macary, Ng, The trinity of COVID-19: immunity, inflammation and intervention, Nature Reviews Immunology
Temesi, Bacsó, Grunert, Lakner, Perceived correspondence of health effects as a new determinant influencing purchase intention for functional food, Nutrients
Vimaleswaran, Forouhi, Khunti, Vitamin D and covid-19
Wang, Yang, Celi, Yan, Ding et al., Alteration of the antioxidant capacity and gut microbiota under high levels of molybdenum and green tea polyphenols in laying hens, Antioxidants
Yang, Zhang, Tariq, Jiang, Ahmed et al., Food as medicine: A possible preventive measure against coronavirus disease (COVID-19), Phytotherapy Research
Zabetakis, Lordan, Norton, Tsoupras, COVID-19: the inflammation link and the role of nutrition in potential mitigation, Nutrients
Zeng, Huang, Guo, Yin, Chen et al., Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID-19: a meta-analysis, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Zeng, Yu, Chen, Qi, Chen et al., Longitudinal changes of inflammatory parameters and their correlation with disease severity and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 from Wuhan, China, Critical Care
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3233/mnm-211521",
"ISSN": [
"1973-798X",
"1973-7998"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3233/mnm-211521",
"abstract": "<jats:p>BACKGROUND: The healthy diet is important to maintain immunity against infection. This study aimed to assess and compare the consumption of functional foods, some antioxidants, and dietary inflammatory index between Iranian COVID-19 patients and healthy persons. METHODS: This case-control study was conducted between 1000 (500 cases and 500 controls) adults aged 18–65years in Iran, that were sampling based on the snowball method and their information was collected electronically. The dietary intake was assessed using the Food Frequency Questionnaire (FFQ). RESULTS: There was a significant difference (p = 0.044) in vitamin D consumption between healthy people and COVID-19 patients. Vitamin E intake in healthy participants was significantly (p = 0.041) more than COVID-19 patients. There was a significant difference in Zinc (p = 0.011), selenium (p = 0.021), and vitamin C (p = 0.023) between healthy persons and COVID-19 patients. Healthy participants’ consumption of onion (56.5±7.82 g/day), garlic (4.32±0.01 g/day) and oat (6.32±0.71 g/day) was significantly (p≤0.05) more than COVID-19 patients. With the increase of each unit in the score of the dietary inflammatory index, the risk of COVID-19 incidence increased 1.63 times (OR = 1.63 95% CI: 1.54–1.72). There was an inverse association between the consumption of antioxidants and functional foods with the risk of COVID-19 incidence in the study population (p≤0.05). CONCLUSION: Healthy people consumption of antioxidants and functional foods was more than COVID-19 patients and there was a significant inverse association between the risk of COVID- 19 incidence with the consumption of functional foods and antioxidants. Increasing the dietary inflammatory index score increased the risk of COVID- 19 incidence. There is a need for further clinical trials to confirm the effect of consuming functional foods and antioxidants on the prevention or treatment of COVID-19.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Digestive Disease Research Center, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research, Ardabil, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mohajeri",
"given": "Mahsa",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Academic Center for Education, Culture and Research, Ardabil, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Energy Management Research Center, University of Mohaghegh Ardabili, Ardabil, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Mohajery",
"given": "Reza",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Digestive Disease Research Center, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran"
},
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Biochemistry, School of Medicine, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Nemati",
"given": "Ali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Digestive Disease Research Center, Ardabil University of Medical Sciences, Ardabil, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Pourfarzi",
"given": "Farhad",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T18:54:42Z",
"timestamp": 1643741682000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-01T18:55:18Z",
"timestamp": 1643741718000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-02T15:41:59Z",
"timestamp": 1643816519383
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "1973-798X"
},
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1973-7998"
}
],
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
29
]
]
},
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://content.iospress.com/download?id=10.3233/MNM-211521",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "7437",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-9",
"prefix": "10.3233",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
29
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
29
]
]
},
"publisher": "IOS Press",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.05.055",
"article-title": "Association of inflammatory markers with the severity of COVID- a meta-analysis",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "467",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref1",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Can we use interleukin-6 (IL-6) blockade for coronavirus disease (COVID-19)-induced cytokine release syndrome (CRS)?",
"author": "Liu",
"first-page": "102452",
"journal-title": "Journal of Autoimmunity",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref2",
"volume": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12041181",
"article-title": "Optimal nutritional status for a well-functioning immune system is an important factor to protect against viral infections",
"author": "Calder",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1181",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref3",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0634-3",
"article-title": "Nutrition amid the COVID-19 pandemic: a multi-level framework for action",
"author": "Naja",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1117",
"issue": "8",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref4",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jare.2020.01.001",
"article-title": "Metabolomics reveals impact of seven functional foods on metabolic pathways in a gut microbiota model",
"author": "Farag",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "47",
"journal-title": "Journal of Advanced Research",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref5",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10787-021-00881-0",
"article-title": "The effect of glutamine supplementation on serum levels of some inflammatory factors, oxidative stress, and appetite in COVID-19 patients: a case–control study",
"author": "Mohajeri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1769",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Inflammopharmacology",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref6",
"volume": "29",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.obmed.2019.100167",
"article-title": "Some behavioral risk factors of obesity in Ardabil–Iran adults",
"author": "Mohajeri",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "100167",
"journal-title": "Obesity Medicine",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref7",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12061562",
"article-title": "Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis",
"author": "Iddir",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1562",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref9",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6770",
"article-title": "Food as medicine: A possible preventive measure against coronavirus disease (COVID-19)",
"author": "Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3124",
"issue": "12",
"journal-title": "Phytotherapy Research",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref10",
"volume": "34",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2020.103896",
"article-title": "An international regulatory review of food health-related claims in functional food products labeling",
"author": "Díaz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "103896",
"journal-title": "Journal of Functional Foods",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref11",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-0311-8",
"article-title": "The trinity of COVID- immunity, inflammation and intervention",
"author": "Tay",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "363",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "Nature Reviews Immunology",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref12",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Validation of a simplified food frequency questionnaire for the assessment of dietary habits in Iranian adults: Isfahan Healthy Heart Program, Iran",
"author": "Mohammadifard",
"first-page": "139",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "ARYA Atherosclerosis",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref13",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/S000711451400395X",
"article-title": "Associations between dietary inflammatory index and inflammatory markers in the Asklepios Study",
"author": "Shivappa",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "665",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "British Journal of Nutrition",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref14",
"volume": "113",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41430-020-0661-0",
"article-title": "Perspective: improving vitamin D status in the management of COVID-19",
"author": "Ebadi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "856",
"issue": "6",
"journal-title": "European Journal of Clinical Nutrition",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref15",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.n544",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref16",
"unstructured": "Vimaleswaran KS , Forouhi NG , Khunti K . Vitamin D and covid-19. British Medical Journal Publishing Group; 2021."
},
{
"article-title": "Antioxidants and COVID-19",
"author": "DE FLORA",
"first-page": "E34",
"issue": "1 Suppl 3",
"journal-title": "Journal of Preventive Medicine and Hygiene",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref17",
"volume": "62",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2174/1381612827666210222113351",
"article-title": "The Association of Respiratory Viruses with Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants",
"author": "Darenskaya",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1618",
"issue": "13",
"journal-title": "Implications for the COVID-19 Pandemic. Current Pharmaceutical Design",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref18",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox9100936",
"article-title": "Oxidative stress and inflammation in COVID-19-associated sepsis: the potential role of anti-oxidant therapy in avoiding disease progression",
"author": "Beltrán-García",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "936",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref19",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu12051466",
"article-title": "COVID- the inflammation link and the role of nutrition in potential mitigation",
"author": "Zabetakis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1466",
"issue": "5",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref20",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"article-title": "COVID- Poor outcomes in patients with zinc deficiency",
"author": "Jothimani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "343",
"journal-title": "International Journal of Infectious Diseases",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref21",
"volume": "100",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.20964/2017.07.06",
"article-title": "Antioxidant and antiradical properties of green tea extract compounds",
"author": "Masek",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6600",
"journal-title": "Int J Electrochem Sci",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jnutbio.2019.108324",
"article-title": "Green tea polyphenols decrease weight gain, ameliorate alteration of gut microbiota, and mitigate intestinal inflammation in canines with high-fat-diet-induced obesity",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "108324",
"journal-title": "The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref23",
"volume": "78",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/16546628.2017.1295525",
"article-title": "Effects of green tea supplementation on inflammation markers, antioxidant status and blood pressure in NaCl-induced hypertensive rat model",
"author": "Szulińska",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1295525",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Food & Nutrition Research",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref24",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2018.02.014",
"article-title": "Garlic, green tea and turmeric extracts-mediated green synthesis of silver nanoparticles: Phytochemical, antioxidant and in vitro cytotoxicity studies",
"author": "Selvan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"journal-title": "Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref25",
"volume": "180",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/foods9040483",
"article-title": "Antioxidant properties and nutritional composition of matcha green tea",
"author": "Jakubczyk",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "483",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Foods",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref26",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/antiox8100503",
"article-title": "Alteration of the antioxidant capacity and gut microbiota under high levels of molybdenum and green tea polyphenols in laying hens",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "503",
"issue": "10",
"journal-title": "Antioxidants",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref27",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tifs.2020.08.006",
"article-title": "Antiviral potential of garlic (Allium sativum) and its organosulfur compounds: A systematic update of pre-clinical and clinical data",
"author": "Rouf",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "219",
"journal-title": "Trends Food Sci Technol",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref28",
"volume": "104",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref29",
"unstructured": "Shehzad A , Zahid A , Mahmood S , Suleria HAR . Functional Foods: Concepts and Their Health Perspectives. Human Health Benefits of Plant Bioactive Compounds: Apple Academic Press; 2019. pp. 3–20."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125522",
"article-title": "Bioactive compounds from date fruit and seed as potential nutraceutical and functional food ingredients",
"author": "Maqsood",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125522",
"journal-title": "Food Chemistry",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref30",
"volume": "308",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15171/hpp.2020.02",
"article-title": "Postbiotics as novel health-promoting ingredients in functional foods",
"author": "Rad",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Health Promotion Perspectives",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref31",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14235/bas.galenos.2018.2486",
"article-title": "The importance of polyphenols as functional food in health",
"author": "BAYIR",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "157",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Bezmialem Science",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref32",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11040740",
"article-title": "Perceived correspondence of health effects as a new determinant influencing purchase intention for functional food",
"author": "Temesi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "740",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Nutrients",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref33",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jff.2018.05.047",
"article-title": "Clarifying the health claim assessment procedure of EFSA will benefit functional food innovation",
"author": "Lenssen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "386",
"journal-title": "Journal of Functional Foods",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref34",
"volume": "47",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13054-020-03255-0",
"article-title": "Longitudinal changes of inflammatory parameters and their correlation with disease severity and outcomes in patients with COVID-19 from Wuhan, China",
"author": "Zeng",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Critical Care",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref35",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/mnfr.201600816",
"article-title": "Fruit and vegetables consumption is directly associated to survival after prostate cancer",
"author": "Taborelli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1600816",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Molecular Nutrition & Food Research",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref36",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12011-020-02142-7",
"article-title": "Serum CRP, MDA, vitamin C, and trace elements in Bangladeshi patients with rheumatoid arthritis",
"author": "Das",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "76",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Biological Trace Element Research",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref37",
"volume": "199",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s12031-019-01288-x",
"article-title": "the association between neuropsychological function with serum vitamins A, D, and E and hs-CRP concentrations",
"author": "Bahrami",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "243",
"issue": "2",
"journal-title": "Journal of Molecular Neuroscience",
"key": "10.3233/MNM-211521_ref38",
"volume": "68",
"year": "2019"
}
],
"reference-count": 37,
"references-count": 37,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"MNM"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Nutrition and Dietetics",
"Food Science",
"Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"The difference in the dietary inflammatory index, functional food, and antioxidants intake between COVID -19 patients and healthy persons"
],
"type": "journal-article"
}
mohajeri
