Zinc use is associated with improved outcomes in COVID-19: results from the CRUSH-COVID registry
et al., Critical Care Medicine, doi:10.1097/01.ccm.0000807104.82650.d6, Dec 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000019 from 42 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
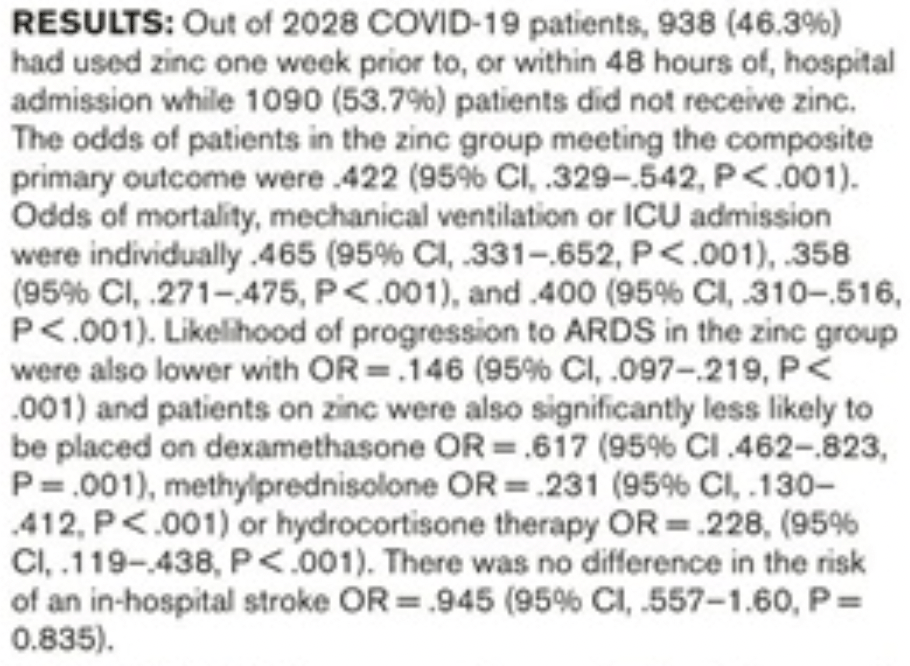
Retrospective 2,028 COVID patients in the USA, showing significantly lower mortality, ventilation, ICU admission, and progression to ARDS with zinc use, defined as at least one dose from one week prior to admission to 48 hours after admission.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of death, 53.5% lower, OR 0.47, p < 0.001, treatment 938, control 1,090, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 64.2% lower, OR 0.36, p < 0.001, treatment 938, control 1,090, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 60.0% lower, OR 0.40, p < 0.001, treatment 938, control 1,090, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
death/ventilation/ICU, 57.8% lower, OR 0.42, p < 0.001, treatment 938, control 1,090, adjusted per study, multivariable, primary outcome, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
progression to ARDS, 85.4% lower, OR 0.15, p < 0.001, treatment 938, control 1,090, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Mayberry et al., 16 Dec 2021, retrospective, USA, peer-reviewed, 14 authors, study period March 2020 - April 2021.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1097/01.ccm.0000807104.82650.d6",
"ISSN": [
"0090-3493"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/01.ccm.0000807104.82650.d6",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mayberry",
"given": "Miles",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Chow",
"given": "Jonathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Park",
"given": "Paul",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Harris",
"given": "Lynnette",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saha",
"given": "Amit",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Levine",
"given": "Andrea",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Smischney",
"given": "Nathan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wieruszewski",
"given": "Patrick",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Meena",
"given": "Nikhil",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yamane",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jackson",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kethireddy",
"given": "Shravan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Wiepking",
"given": "Matthew",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Khanna",
"given": "Ashish",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Critical Care Medicine"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-16T20:06:47Z",
"timestamp": 1639685207000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-21T12:16:45Z",
"timestamp": 1640089005000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-22T06:50:45Z",
"timestamp": 1640155845018
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0090-3493"
}
],
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://journals.lww.com/10.1097/01.ccm.0000807104.82650.d6",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "276",
"original-title": [],
"page": "81-81",
"prefix": "10.1097",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
16
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Ovid Technologies (Wolters Kluwer Health)",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Critical Care and Intensive Care Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"195: ZINC USE IS ASSOCIATED WITH IMPROVED OUTCOMES IN COVID-19: RESULTS FROM THE CRUSH-COVID REGISTRY"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "50"
}
