Safety and efficacy of inhaled IBIO123 for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, dose-ascending, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial
et al., The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6, NCT05298813, Jan 2024
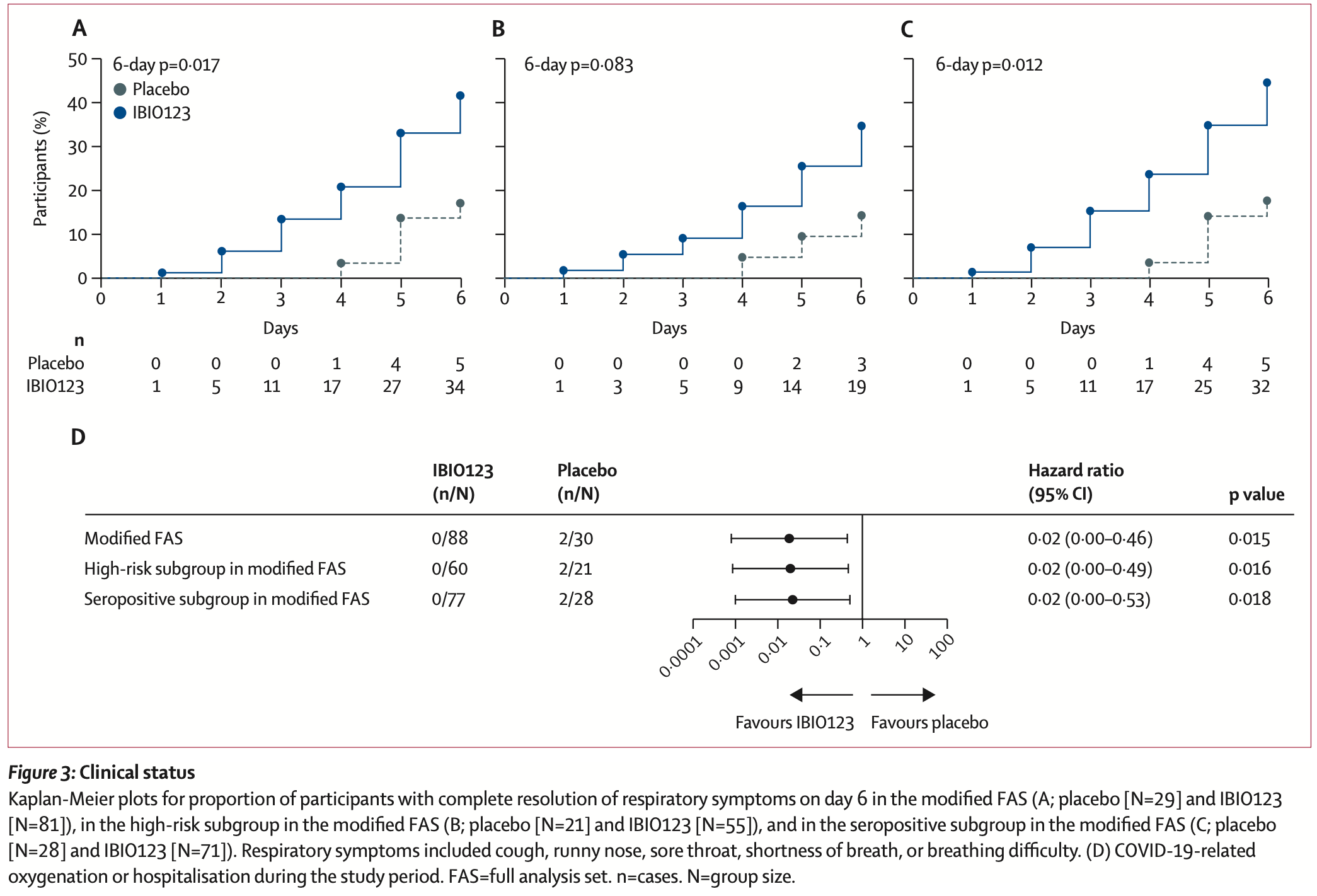
RCT 162 mild-to-moderate COVID-19 outpatients showing improved respiratory symptom resolution with inhaled IBIO123 monoclonal antibody cocktail. 42% of participants receiving IBIO123 had complete resolution of respiratory symptoms by day 6 versus 17% in the placebo group. The primary endpoint of viral load reduction was not significantly different. There were no hospitalizations or deaths in the IBIO123 group compared to two hospitalizations and one death in the placebo group. The treatment was well-tolerated with no safety concerns. The study was stopped early due to declining COVID-19 incidence.
Maranda et al., 31 Jan 2024, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, mean age 48.5, 12 authors, study period 4 December, 2021 - 23 May, 2022, trial NCT05298813 (history).
Contact: bmaranda@ibiosolutions.com.
Safety and efficacy of inhaled IBIO123 for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, dose-ascending, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial
The Lancet Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1016/s1473-3099(23)00393-6
Background COVID-19 severity is associated with its respiratory manifestations. Neutralising antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 administered systemically have shown clinical efficacy. However, immediate and direct delivery of neutralising antibodies via inhalation might provide additional respiratory clinical benefits. IBIO123 is a cocktail of three, fully human, neutralising monoclonal antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. We aimed to assess the safety and efficacy of inhaled IBIO123 in individuals with mild-to-moderate COVID-19.
Methods This double-blind, dose-ascending, placebo-controlled, first-in-human, phase 1/2 trial recruited symptomatic and non-hospitalised participants with COVID-19 in South Africa and Brazil across 11 centres. Eligible participants were adult outpatients (aged ≥18 years; men and non-pregnant women) infected with COVID-19 (first PCR-confirmed within 72 h) and with mild-to-moderate symptoms, the onset of which had to be within 10 days of randomisation. Using permuted blocks of four, stratified by site, we randomly assigned participants (1:3) to receive single-dose placebo or IBIO123 (1 mg, 5 mg, or 10 mg) in phase 1, and single-dose placebo or IBIO123 (10 mg) in phase 2, in addition to local standard of care. Participants underwent serological testing to identify antibodies against SARS-CoV-2. Participants, investigators, and the study team were masked to treatment assignment. In phase 1, the primary outcome was the safety assessment in the safety population (ie, all participants who received an intervention). In phase 2, the primary outcome was the mean absolute change from baseline to day 5 in SARS-CoV-2 viral load measured by nasopharyngeal swabs analysed using a mixed model for repeated measures in the full analysis set (FAS; ie, participants with one analysable viral load value at baseline and at least one analysable viral load value at day 3 or day 5). Secondary clinical outcomes included safety from baseline to day 29, assessed by evaluating adverse events; the effect of IBIO123 on baseline COVID-19 symptoms resolution until day 6, with symptoms systemically evaluated by the investigators; and disease progression as measured by the COVID-19 WHO Clinical Progression Scale. For clinical endpoints in phase 2, we used a modified FAS (ie, participants who had at least one analysable viral load value over the course of the study, confirming that they were infected with SARS-CoV-2). This trial is now completed and is registered with ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT05298813. Findings Between Dec 4, 2021, and May 23, 2022, 24 participants were enrolled in phase 1. Between July 20, 2022, and Jan 4, 2023, 138 participants were enrolled in phase 2 and five were excluded because they did not meet the inclusion criteria. Participants were randomly assigned to receive IBIO123 (n=18) or placebo (n=6) in phase 1, and randomly assigned to receive IBIO123 (n=104) or placebo (n=34) in phase 2. In phase 2, the study was stopped before reaching the..
References
Abebe, Dejenie, Protective roles and protective mechanisms of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 infection and their potential clinical implications, Front Immunol
Behr, Maddox, Epstein, Orav, Barnett, Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody distribution to high-risk medicare beneficiaries, 2020-2021, JAMA
Butler, Hobbs, Gbinigie, Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial, Lancet
Chatterjee, Jensen, Harris, Admission respiratory status predicts mortality in COVID-19, Influenza Other Respir Viruses
Chen, Bobrovitz, Premji, Koopmans, Fisman et al., SARS-CoV-2 shedding dynamics across the respiratory tract, sex, and disease severity for adult and pediatric COVID-19, eLife
Chen, Nirula, Heller, SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Chow, Pan, Seow, Lam, Inhalable neutralizing antibodies-promising approach to combating respiratory viral infections, Trends Pharmacol Sci
Guan, Ni, Hu, Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China, N Engl J Med
Guilleminault, Azzopardi, Arnoult, Fate of inhaled monoclonal antibodies after the deposition of aerosolized particles in the respiratory system, J Control Release
Gungor, Nematollahi, Effectiveness of casirivimab-imdevimab monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 B.1.617.2 (delta variant) infection, Open Forum Infect Dis
Hammond, Leister-Tebbe, Gardner, Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Huang, Wang, Li, Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China, Lancet
Hui, Ho, Cheung, SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo, Nature
Hurlburt, Homad, Sinha, Structural definition of a pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing epitope on the spike S2 subunit, Commun Biol
Kip, Mccreary, Collins, Evolving real-world effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19: a cohort study, Ann Intern Med
Levin, Ustianowski, Wit, Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Li, Chen, Prévost, Structural basis and mode of action for two broadly neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants of concern, Cell Rep
Matthews, A cocktail of antibodies for COVID-19 therapy, Nat Rev Immunol
Matthews, Ee, Ge, Developing inhaled protein therapeutics for lung diseases, Mol Biomed
Murugapandian, Gungor, Al-Obaidi, Effectiveness of casirivimab-imdevimab and sotrovimab monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a real-world experience, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2022.12.23.22283921(preprint
Nichols, Deveau, Upadhyaya, Bebtelovimab: considerations for global access to treatments during a rapidly evolving pandemic, Lancet Infect Dis
Parray, Shukla, Perween, Inhalation monoclonal antibody therapy: a new way to treat and manage respiratory infections, Appl Microbiol Biotechnol
Prévost, Ullah, Molecular basis for antiviral activity of two pediatric neutralizing antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD, iScience
Tomasicchio, Jaumdally, Pooran, SARS-CoV-2 viral replication persists in the human lung for several weeks after onset of symptomatic severe COVID-19 and is associated with attenuated pulmonary immunity and variant-specific clinical sequalae, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2023.03.06.23286834
Ullah, Prévost, Ladinsky, Live imaging of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice reveals that neutralizing antibodies require Fc function for optimal efficacy, Immunity
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Weinreich, Sivapalasingam, Norton, REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Yang, Li, Song, Ying, Wu, Inhalable antibodies for the treatment of COVID-19, Innovation (Camb)
Zhang, Stacey, Agostino, Tugg, Marzok et al., Beyond neutralization: Fc-dependent antibody effector functions in SARS-CoV-2 infection, Nat Rev Immunol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(23)00393-6",
"ISSN": [
"1473-3099"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6",
"alternative-id": [
"S1473309923003936"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Safety and efficacy of inhaled IBIO123 for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, dose-ascending, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to the associated document",
"name": "associatedlink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00454-1"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2023 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maranda",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Labbé",
"given": "Sébastien M",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lurquin",
"given": "Magali",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brabant",
"given": "Pascal",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fugère",
"given": "Alexandre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Larrivée",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Grbic",
"given": "Djordje",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leroux",
"given": "Annie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Leduc",
"given": "Frédéric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Finzi",
"given": "Andrés",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gaudreau",
"given": "Simon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Swart",
"given": "Yolandi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "The Lancet Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"em-consulte.com",
"thelancet.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
8,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2023-08-21T22:28:25Z",
"timestamp": 1692656905000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-09T23:32:17Z",
"timestamp": 1704843137000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100015403",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100015403",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Strategic Innovation Fund"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
3,
27
]
],
"date-time": "2025-03-27T20:22:28Z",
"timestamp": 1743106948159,
"version": "3.37.3"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 6,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-017",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-037",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-012",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-029",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://doi.org/10.15223/policy-004",
"content-version": "stm-asf",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2024-01-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1704067200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309923003936?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1473309923003936?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "25-35",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30183-5",
"article-title": "Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China",
"author": "Huang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "497",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib1",
"volume": "395",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04479-6",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant replication in human bronchus and lung ex vivo",
"author": "Hui",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "715",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib2",
"volume": "603",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2108163",
"article-title": "REGEN-COV antibody combination and outcomes in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e81",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib3",
"volume": "385",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Effectiveness of casirivimab-imdevimab and sotrovimab monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a real-world experience",
"author": "Murugapandian",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib4",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00592-8",
"article-title": "Bebtelovimab: considerations for global access to treatments during a rapidly evolving pandemic",
"author": "Nichols",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Lancet Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib5",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/ofid/ofac186",
"article-title": "Effectiveness of casirivimab-imdevimab monoclonal antibody treatment among high-risk patients with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 B.1.617.2 (delta variant) infection",
"author": "Al-Obaidi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Open Forum Infect Dis",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib6",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s43556-020-00014-z",
"article-title": "Developing inhaled protein therapeutics for lung diseases",
"author": "Matthews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "11",
"journal-title": "Mol Biomed",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib7",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.10.003",
"article-title": "Fate of inhaled monoclonal antibodies after the deposition of aerosolized particles in the respiratory system",
"author": "Guilleminault",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "344",
"journal-title": "J Control Release",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib8",
"volume": "196",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.tips.2022.11.006",
"article-title": "Inhalable neutralizing antibodies—promising approach to combating respiratory viral infections",
"author": "Chow",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "85",
"journal-title": "Trends Pharmacol Sci",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib9",
"volume": "44",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s00253-021-11488-4",
"article-title": "Inhalation monoclonal antibody therapy: a new way to treat and manage respiratory infections",
"author": "Parray",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6315",
"journal-title": "Appl Microbiol Biotechnol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib10",
"volume": "105",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "Inhalable antibodies for the treatment of COVID-19",
"author": "Yang",
"journal-title": "Innovation (Camb)",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib11",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"article-title": "Molecular basis for antiviral activity of two pediatric neutralizing antibodies targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike RBD",
"author": "Chen",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib12",
"volume": "26",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.110210",
"article-title": "Structural basis and mode of action for two broadly neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 emerging variants of concern",
"author": "Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib13",
"volume": "38",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-022-03262-7",
"article-title": "Structural definition of a pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing epitope on the spike S2 subunit",
"author": "Hurlburt",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "342",
"journal-title": "Commun Biol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib14",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.immuni.2021.08.015",
"article-title": "Live imaging of SARS-CoV-2 infection in mice reveals that neutralizing antibodies require Fc function for optimal efficacy",
"author": "Ullah",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2143",
"journal-title": "Immunity",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib15",
"volume": "54",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-020-00431-9",
"article-title": "A cocktail of antibodies for COVID-19 therapy",
"author": "Matthews",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "591",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib16",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2035002",
"article-title": "REGN-COV2, a neutralizing antibody cocktail, in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Weinreich",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "238",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib17",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2116620",
"article-title": "Intramuscular AZD7442 (tixagevimab-cilgavimab) for prevention of COVID-19",
"author": "Levin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2188",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib18",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2022.1243",
"article-title": "Anti-SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody distribution to high-risk medicare beneficiaries, 2020–2021",
"author": "Behr",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "980",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib20",
"volume": "327",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2118542",
"article-title": "Oral nirmatrelvir for high-risk, nonhospitalized adults with COVID-19",
"author": "Hammond",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1397",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib21",
"volume": "386",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2029849",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibody LY-CoV555 in outpatients with COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "229",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib22",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.70458",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 shedding dynamics across the respiratory tract, sex, and disease severity for adult and pediatric COVID-19",
"author": "Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "eLife",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib23",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 viral replication persists in the human lung for several weeks after onset of symptomatic severe COVID-19 and is associated with attenuated pulmonary immunity and variant-specific clinical sequalae",
"author": "Tomasicchio",
"journal-title": "medRxiv",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib24",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2023.1055457",
"article-title": "Protective roles and protective mechanisms of neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 infection and their potential clinical implications",
"author": "Abebe",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib25",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41577-022-00813-1",
"article-title": "Beyond neutralization: Fc-dependent antibody effector functions in SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "381",
"journal-title": "Nat Rev Immunol",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib26",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2002032",
"article-title": "Clinical characteristics of coronavirus disease 2019 in China",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1708",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib27",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/irv.12869",
"article-title": "Admission respiratory status predicts mortality in COVID-19",
"author": "Chatterjee",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "569",
"journal-title": "Influenza Other Respir Viruses",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib28",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(22)02597-1",
"article-title": "Molnupiravir plus usual care versus usual care alone as early treatment for adults with COVID-19 at increased risk of adverse outcomes (PANORAMIC): an open-label, platform-adaptive randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Butler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib29",
"volume": "401",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-1286",
"article-title": "Evolving real-world effectiveness of monoclonal antibodies for treatment of COVID-19: a cohort study",
"author": "Kip",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "496",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "10.1016/S1473-3099(23)00393-6_bib30",
"volume": "176",
"year": "2023"
}
],
"reference-count": 29,
"references-count": 29,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1473309923003936"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Safety and efficacy of inhaled IBIO123 for mild-to-moderate COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, dose-ascending, placebo-controlled, phase 1/2 trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"updated-by": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(23)00628-x",
"label": "Erratum",
"source": "publisher",
"type": "erratum",
"updated": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
11,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2023-11-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1698796800000
}
}
],
"volume": "24"
}