Intranasal trimeric sherpabody inhibits SARS-CoV-2 including recent immunoevasive Omicron subvariants
et al., Nature Communications, doi:10.1038/s41467-023-37290-6, Mar 2023
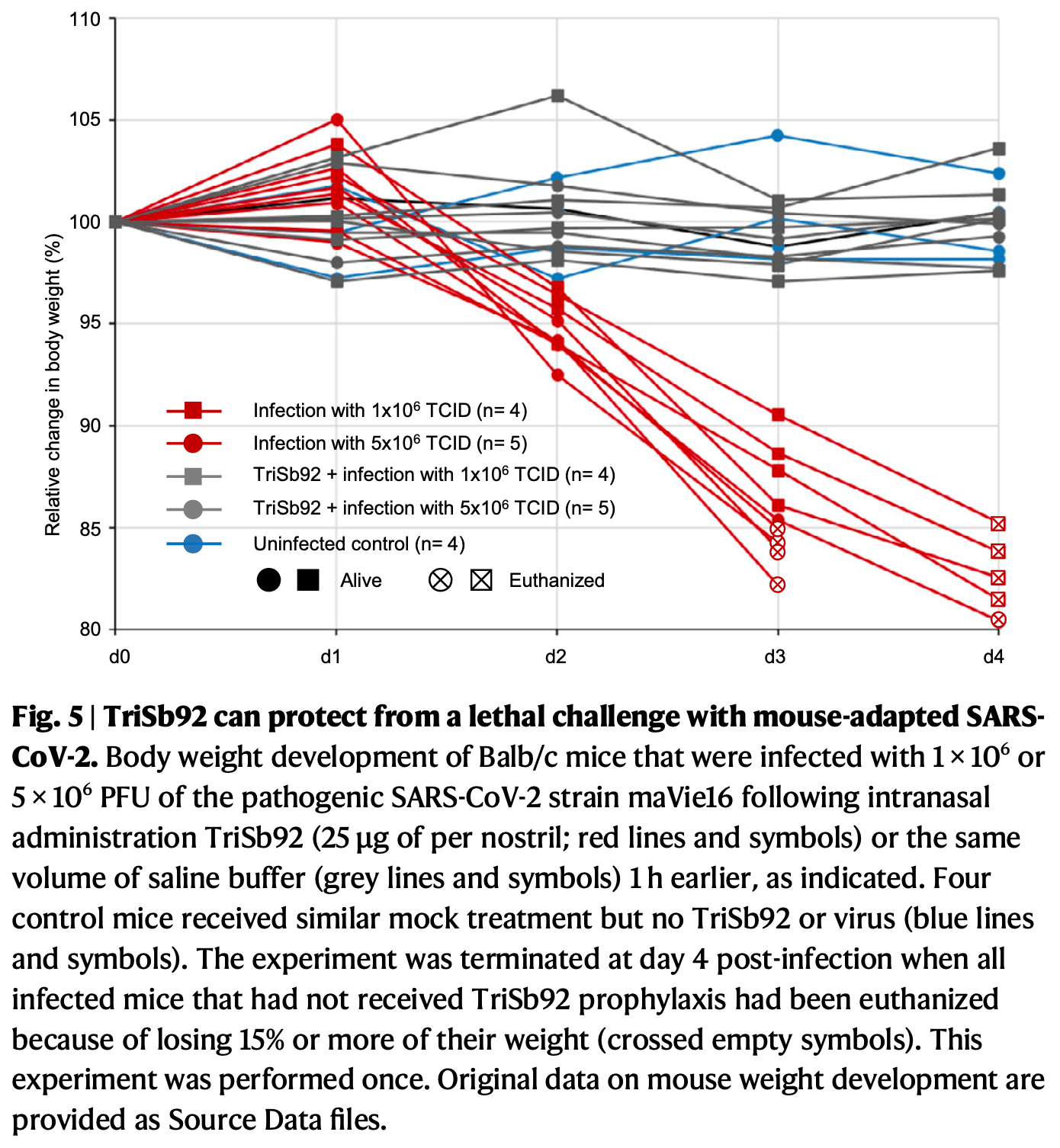
In vitro and mouse study showing that TriSb92, a trimeric antibody-mimetic sherpabody, potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 variants including recent Omicron subvariants. Authors found that TriSb92 targets a highly conserved region in the receptor binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein, inhibiting infection with IC50 values in the picomolar to low nanomolar range for all tested variants. Cryo-EM analysis revealed that TriSb92 binding induces conformational changes in the spike protein, preventing viral entry without interfering with ACE2 binding. In mice, intranasal administration of TriSb92 provided both prophylactic and early therapeutic protection against SARS-CoV-2 infection, significantly reducing viral loads and preventing weight loss even with a lethal challenge dose. The compound showed high stability and no toxicity in human nasal epithelial cells, suggesting potential for development as an intranasal spray for COVID-19 prevention. TriSb92 also neutralized SARS-CoV-1, indicating possible broad protection against sarbecoviruses.
Mäkelä et al., 24 Mar 2023, peer-reviewed, 23 authors.
In vitro studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Abstract: Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37290-6
Intranasal trimeric sherpabody inhibits
SARS-CoV-2 including recent immunoevasive
Omicron subvariants
Received: 22 December 2022
Check for updates
1234567890():,;
1234567890():,;
Accepted: 10 March 2023
Anna R. Mäkelä1, Hasan Uğurlu 1, Liina Hannula2, Ravi Kant 1,3, Petja Salminen1,
Riku Fagerlund1, Sanna Mäki1, Anu Haveri 4, Tomas Strandin1, Lauri Kareinen1,3,
Jussi Hepojoki 1, Suvi Kuivanen1, Lev Levanov1, Arja Pasternack 5,
Rauno A. Naves5, Olli Ritvos5, Pamela Österlund 4, Tarja Sironen 1,3,
Olli Vapalahti 1,3,6, Anja Kipar 3,7, Juha T. Huiskonen 2, Ilona Rissanen 2 &
Kalle Saksela 1,6
The emergence of increasingly immunoevasive SARS-CoV-2 variants
emphasizes the need for prophylactic strategies to complement vaccination in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Intranasal administration of neutralizing antibodies has shown encouraging protective potential but there
remains a need for SARS-CoV-2 blocking agents that are less vulnerable to
mutational viral variation and more economical to produce in large scale.
Here we describe TriSb92, a highly manufacturable and stable trimeric
antibody-mimetic sherpabody targeted against a conserved region of the
viral spike glycoprotein. TriSb92 potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2, including the latest Omicron variants like BF.7, XBB, and BQ.1.1. In female Balb/c
mice intranasal administration of just 5 or 50 micrograms of TriSb92 as
early as 8 h before but also 4 h after SARS-CoV-2 challenge can protect from
infection. Cryo-EM and biochemical studies reveal triggering of a conformational shift in the spike trimer as the inhibitory mechanism of
TriSb92. The potency and robust biochemical properties of TriSb92 together with its resistance against viral sequence evolution suggest that
TriSb92 could be useful as a nasal spray for protecting susceptible individuals from SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The success of the current vaccines in the fight against the SARS-CoV-2
pandemic is challenged by the emergence of viral variants of concern
(VOCs) that show strong resistance to neutralizing antibodies induced
by vaccinations or prior infection. Moreover, immune disorders or
other health conditions can preclude appropriate vaccine responses in
many individuals. In addition to pharmaceuticals for treating COVID-19
disease, new approaches for preventing transmission and spreading of
SARS-CoV-2 are therefore urgently needed.
Since the nasal epithelium of the respiratory tract is the first
dominant replication site of SARS-CoV-2 preceding virus transport into
the lung1, intranasal administration of SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing agents
poses an attractive prophylactic concept. In animal models,
1
Department of Virology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. 2Institute of Biotechnology, Helsinki Institute of Life Science HiLIFE, University of Helsinki,
Helsinki, Finland. 3Department of Basic Veterinary Sciences, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. 4Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare, Helsinki, Finland.
5
Department of Physiology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland. 6HUS Diagnostic Centre, HUSLAB, Clinical Microbiology, Helsinki University Hospital,
Helsinki, Finland. 7Laboratory for Animal Model Pathology, Institute of Veterinary Pathology, Vetsuisse Faculty, University of Zurich, Zurich, Switzerland.
e-mail: kalle.saksela@helsinki.fi
Nature Communications | (2023)14:1637
1
Article
https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37290-6
monoclonal antibodies..
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-37290-6",
"ISSN": [
"2041-1723"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-37290-6",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title><jats:p>The emergence of increasingly immunoevasive SARS-CoV-2 variants emphasizes the need for prophylactic strategies to complement vaccination in fighting the COVID-19 pandemic. Intranasal administration of neutralizing antibodies has shown encouraging protective potential but there remains a need for SARS-CoV-2 blocking agents that are less vulnerable to mutational viral variation and more economical to produce in large scale. Here we describe TriSb92, a highly manufacturable and stable trimeric antibody-mimetic sherpabody targeted against a conserved region of the viral spike glycoprotein. TriSb92 potently neutralizes SARS-CoV-2, including the latest Omicron variants like BF.7, XBB, and BQ.1.1. In female Balb/c mice intranasal administration of just 5 or 50 micrograms of TriSb92 as early as 8 h before but also 4 h after SARS-CoV-2 challenge can protect from infection. Cryo-EM and biochemical studies reveal triggering of a conformational shift in the spike trimer as the inhibitory mechanism of TriSb92. The potency and robust biochemical properties of TriSb92 together with its resistance against viral sequence evolution suggest that TriSb92 could be useful as a nasal spray for protecting susceptible individuals from SARS-CoV-2 infection.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"37290"
],
"article-number": "1637",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "22 December 2022"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "10 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "24 March 2023"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "K.S. is a founder and shareholder of Next Biomed Therapies Oy that develops SH3 scaffold targeting technologies. ARM is a founder and shareholder of the start-up Pandemblock Oy that has acquired commercial rights for TriSb92. The authors are inventors of the related patents/applications WO2017009533 (K.S.) and PCT/FI2022/050764 (K.S. and A.R.M.). The other authors have no competing interests to declare."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mäkelä",
"given": "Anna R.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3849-7847",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Uğurlu",
"given": "Hasan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hannula",
"given": "Liina",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-3878-9775",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kant",
"given": "Ravi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Salminen",
"given": "Petja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Fagerlund",
"given": "Riku",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mäki",
"given": "Sanna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4620-7536",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Haveri",
"given": "Anu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strandin",
"given": "Tomas",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kareinen",
"given": "Lauri",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5699-214X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Hepojoki",
"given": "Jussi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kuivanen",
"given": "Suvi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Levanov",
"given": "Lev",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-6088-4245",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Pasternack",
"given": "Arja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Naves",
"given": "Rauno A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ritvos",
"given": "Olli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2229-6661",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Österlund",
"given": "Pamela",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2344-2755",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Sironen",
"given": "Tarja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2270-6824",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Vapalahti",
"given": "Olli",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-7289-3459",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Kipar",
"given": "Anja",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-0348-7323",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Huiskonen",
"given": "Juha T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-4937-1825",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Rissanen",
"given": "Ilona",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-0827-122X",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Saksela",
"given": "Kalle",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Nature Communications",
"container-title-short": "Nat Commun",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T10:03:44Z",
"timestamp": 1679652224000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T11:05:58Z",
"timestamp": 1679655958000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100002341",
"award": [
"331787"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Academy of Finland"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
25
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-25T04:54:38Z",
"timestamp": 1679720078150
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1679616000000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-24T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1679616000000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37290-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37290-6",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37290-6.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
24
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.05.042",
"author": "YJ Hou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "429",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "37290_CR1",
"unstructured": "Hou, Y. J. et al. SARS-CoV-2 reverse genetics reveals a variable infection gradient in the respiratory tract. Cell 182, 429–446.e414 (2020).",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe2402",
"author": "A Baum",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1110",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "37290_CR2",
"unstructured": "Baum, A. et al. REGN-COV2 antibodies prevent and treat SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques and hamsters. Science 370, 1110–1115 (2020).",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25480-z",
"author": "J Huo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "37290_CR3",
"unstructured": "Huo, J. et al. A potent SARS-CoV-2 neutralising nanobody shows therapeutic efficacy in the Syrian golden hamster model of COVID-19. Nat. Commun. 12, 5469 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03673-2",
"author": "Z Ku",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "718",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR4",
"unstructured": "Ku, Z. et al. Nasal delivery of an IgM offers broad protection from SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature 595, 718–723 (2021).",
"volume": "595",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.abh0319",
"author": "S Nambulli",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eabh0319",
"journal-title": "Sci. Adv.",
"key": "37290_CR5",
"unstructured": "Nambulli, S. et al. Inhalable Nanobody (PiN-21) prevents and treats SARS-CoV-2 infections in Syrian hamsters at ultra-low doses. Sci. Adv. 7, eabh0319 (2021).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109869",
"author": "X Wu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "109869",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "37290_CR6",
"unstructured": "Wu, X. et al. A potent bispecific nanobody protects hACE2 mice against SARS-CoV-2 infection via intranasal administration. Cell Rep. 37, 109869 (2021).",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-021-00752-2",
"author": "L Du",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2293",
"journal-title": "Cell Mol. Immunol.",
"key": "37290_CR7",
"unstructured": "Du, L., Yang, Y. & Zhang, X. Neutralizing antibodies for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19. Cell Mol. Immunol. 18, 2293–2306 (2021).",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.031",
"author": "D Wrapp",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1004",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "37290_CR8",
"unstructured": "Wrapp, D. et al. Structural basis for potent neutralization of betacoronaviruses by single-domain camelid antibodies. Cell 181, 1004–1015.e1015 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe3255",
"author": "M Schoof",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1473",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "37290_CR9",
"unstructured": "Schoof, M. et al. An ultrapotent synthetic nanobody neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 by stabilizing inactive Spike. Science 370, 1473–1479 (2020).",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abe4747",
"author": "Y Xiang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1479",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "37290_CR10",
"unstructured": "Xiang, Y. et al. Versatile and multivalent nanobodies efficiently neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Science 370, 1479–1484 (2020).",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03676-z",
"author": "J Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "278",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR11",
"unstructured": "Xu, J. et al. Nanobodies from camelid mice and llamas neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants. Nature 595, 278–282 (2021).",
"volume": "595",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13238-017-0386-6",
"author": "R Simeon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "3",
"journal-title": "Protein Cell",
"key": "37290_CR12",
"unstructured": "Simeon, R. & Chen, Z. In vitro-engineered non-antibody protein therapeutics. Protein Cell 9, 3–14 (2018).",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prot.20344",
"author": "A le Maire",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "347",
"journal-title": "Proteins",
"key": "37290_CR13",
"unstructured": "le Maire, A. et al. Solution NMR structure of the SH3 domain of human nephrocystin and analysis of a mutation-causing juvenile nephronophthisis. Proteins 59, 347–355 (2005).",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12050513",
"author": "KHD Crawford",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "37290_CR14",
"unstructured": "Crawford, K. H. D. et al. Protocol and reagents for pseudotyping lentiviral particles with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for neutralization assays. Viruses 12, 513 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04980-y",
"author": "Y Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "593",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR15",
"unstructured": "Cao, Y. et al. BA.2.12.1, BA.4 and BA.5 escape antibodies elicited by Omicron infection. Nature 608, 593–602 (2022).",
"volume": "608",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v13112263",
"author": "R Kant",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2263",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "37290_CR16",
"unstructured": "Kant, R. et al. Common laboratory mice are susceptible to infection with the SARS-CoV-2 beta variant. Viruses 13, 2263 (2021).",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.74623",
"author": "R Gawish",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e74623",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "37290_CR17",
"unstructured": "Gawish, R. et al. ACE2 is the critical in vivo receptor for SARS-CoV-2 in a novel COVID-19 mouse model with TNF- and IFNgamma-driven immunopathology. Elife 11, e74623 (2022).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2179-y",
"author": "J Shang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "221",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR18",
"unstructured": "Shang, J. et al. Structural basis of receptor recognition by SARS-CoV-2. Nature 581, 221–224 (2020).",
"volume": "581",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"author": "AC Walls",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "37290_CR19",
"unstructured": "Walls, A. C. et al. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181, 281–292.e286 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ncomms15092",
"author": "Y Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "37290_CR20",
"unstructured": "Yuan, Y. et al. Cryo-EM structures of MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV spike glycoproteins reveal the dynamic receptor binding domains. Nat. Commun. 8, 15092 (2017).",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkv342",
"author": "J Yang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "W174",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "37290_CR21",
"unstructured": "Yang, J. & Zhang, Y. I-TASSER server: new development for protein structure and function predictions. Nucleic Acids Res 43, W174–W181 (2015).",
"volume": "43",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abb7269",
"author": "M Yuan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "630",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "37290_CR22",
"unstructured": "Yuan, M. et al. A highly conserved cryptic epitope in the receptor binding domains of SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV. Science 368, 630–633 (2020).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03777-9",
"author": "D Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "276",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR23",
"unstructured": "Planas, D. et al. Reduced sensitivity of SARS-CoV-2 variant Delta to antibody neutralization. Nature 596, 276–280 (2021).",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01318-5",
"author": "D Planas",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "917",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med",
"key": "37290_CR24",
"unstructured": "Planas, D. et al. Sensitivity of infectious SARS-CoV-2 B.1.1.7 and B.1.351 variants to neutralizing antibodies. Nat. Med 27, 917–924 (2021).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-03720-y",
"author": "RE Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR25",
"unstructured": "Chen, R. E. et al. In vivo monoclonal antibody efficacy against SARS-CoV-2 variant strains. Nature 596, 103–108 (2021).",
"volume": "596",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41392-021-00796-w",
"author": "Y Dong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "387",
"journal-title": "Signal Transduct. Target Ther.",
"key": "37290_CR26",
"unstructured": "Dong, Y. et al. The way of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine development: success and challenges. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 6, 387 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/2021.12.12.21267646",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "37290_CR27",
"unstructured": "Schmidt, F. et al. Plasma neutralization properties of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant. medRxiv. (2021)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.isci.2021.103341",
"author": "T Tada",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "103341",
"journal-title": "iScience",
"key": "37290_CR28",
"unstructured": "Tada, T. et al. Partial resistance of SARS-CoV-2 Delta variants to vaccine-elicited antibodies and convalescent sera. iScience 24, 103341 (2021).",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.025",
"author": "CO Barnes",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "828",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "37290_CR29",
"unstructured": "Barnes, C. O. et al. Structures of human antibodies bound to SARS-CoV-2 spike reveal common epitopes and recurrent features of antibodies. Cell 182, 828–842.e816 (2020).",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2665-2",
"author": "Z Ke",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "498",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "37290_CR30",
"unstructured": "Ke, Z. et al. Structures and distributions of SARS-CoV-2 spike proteins on intact virions. Nature 588, 498–502 (2020).",
"volume": "588",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-021-00490-0",
"author": "R Yan",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "717",
"journal-title": "Cell Res",
"key": "37290_CR31",
"unstructured": "Yan, R. et al. Structural basis for the different states of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2 in complex with ACE2. Cell Res. 31, 717–719 (2021).",
"volume": "31",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.11.001",
"author": "M Lu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "880",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "37290_CR32",
"unstructured": "Lu, M. et al. Real-Time Conformational Dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 Spikes on Virus Particles. Cell Host Microbe 28, 880–891.e888 (2020).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-25997-3",
"author": "T Li",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "37290_CR33",
"unstructured": "Li, T. et al. Cross-neutralizing antibodies bind a SARS-CoV-2 cryptic site and resist circulating variants. Nat. Commun. 12, 5652 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.chom.2020.06.010",
"author": "J Huo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "445",
"journal-title": "Cell Host Microbe",
"key": "37290_CR34",
"unstructured": "Huo, J. et al. Neutralization of SARS-CoV-2 by Destruction of the Prefusion Spike. Cell Host Microbe 28, 445–454.e446 (2020).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/infdis/jiab222",
"author": "P Jalkanen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "218",
"journal-title": "J. Infect. Dis.",
"key": "37290_CR35",
"unstructured": "Jalkanen, P. et al. A Combination of N and S Antigens With IgA and IgG Measurement Strengthens the Accuracy of SARS-CoV-2 Serodiagnostics. J. Infect. Dis. 224, 218–228 (2021).",
"volume": "224",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/mBio.00902-21",
"author": "J Rusanen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e00902",
"journal-title": "mBio",
"key": "37290_CR36",
"unstructured": "Rusanen, J. et al. A generic, scalable, and rapid time-resolved forster resonance energy transfer-based assay for antigen detection-SARS-CoV-2 as a proof of concept. mBio 12, e00902–e00921 (2021).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JVI.02370-20",
"author": "G Dagotto",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e02370",
"journal-title": "J. Virol.",
"key": "37290_CR37",
"unstructured": "Dagotto, G. et al. Comparison of subgenomic and total RNA in SARS-CoV-2 challenged rhesus macaques. J. Virol. 95, e02370–20 (2021).",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jim.2011.02.004",
"author": "M Zivcec",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "J. Immunol. Methods",
"key": "37290_CR38",
"unstructured": "Zivcec, M., Safronetz, D., Haddock, E., Feldmann, H. & Ebihara, H. Validation of assays to monitor immune responses in the Syrian golden hamster (Mesocricetus auratus). J. Immunol. Methods 368, 24–35 (2011).",
"volume": "368",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nprot.2008.73",
"author": "TD Schmittgen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1101",
"journal-title": "Nat. Protoc.",
"key": "37290_CR39",
"unstructured": "Schmittgen, T. D. & Livak, K. J. Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nat. Protoc. 3, 1101–1108 (2008).",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4169",
"author": "A Punjani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "37290_CR40",
"unstructured": "Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2015.08.008",
"author": "A Rohou",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "216",
"journal-title": "J. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "37290_CR41",
"unstructured": "Rohou, A. & Grigorieff, N. CTFFIND4: Fast and accurate defocus estimation from electron micrographs. J. Struct. Biol. 192, 216–221 (2015).",
"volume": "192",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-019-0575-8",
"author": "T Bepler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "37290_CR42",
"unstructured": "Bepler, T. et al. Positive-unlabeled convolutional neural networks for particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs. Nat. Methods 16, 1153–1160 (2019).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2021.107702",
"author": "A Punjani",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "107702",
"journal-title": "J. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "37290_CR43",
"unstructured": "Punjani, A. & Fleet, D. J. 3D variability analysis: Resolving continuous flexibility and discrete heterogeneity from single particle cryo-EM. J. Struct. Biol. 213, 107702 (2021).",
"volume": "213",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-020-19204-y",
"author": "TF Custodio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nat. Commun.",
"key": "37290_CR44",
"unstructured": "Custodio, T. F. et al. Selection, biophysical and structural analysis of synthetic nanobodies that effectively neutralize SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Commun. 11, 5588 (2020).",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/pro.3943",
"author": "EF Pettersen",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "70",
"journal-title": "Protein Sci.",
"key": "37290_CR45",
"unstructured": "Pettersen, E. F. et al. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Sci. 30, 70–82 (2021).",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444904019158",
"author": "P Emsley",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2126",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "37290_CR46",
"unstructured": "Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: Model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 60, 2126–2132 (2004).",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S2059798319011471",
"author": "D Liebschner",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "37290_CR47",
"unstructured": "Liebschner, D. et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: Recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol. 75, 861–877 (2019).",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S2059798318002425",
"author": "TI Croll",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "519",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "37290_CR48",
"unstructured": "Croll, T. I. ISOLDE: A physically realistic environment for model building into low-resolution electron-density maps. Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol. 74, 519–530 (2018).",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41594-020-0478-5",
"author": "X Xiong",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "934",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "37290_CR49",
"unstructured": "Xiong, X. et al. A thermostable, closed SARS-CoV-2 spike protein trimer. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 27, 934–941 (2020).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2020"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-023-37290-6"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Physics and Astronomy",
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Chemistry",
"Multidisciplinary"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Intranasal trimeric sherpabody inhibits SARS-CoV-2 including recent immunoevasive Omicron subvariants",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "14"
}