A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of a Nutritional Supplement (ImmuActive) for COVID-19 Patients
et al., Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2021/8447545, CTRI/2020/09/027841, Oct 2021
Zinc for COVID-19
2nd treatment shown to reduce risk in
July 2020, now with p = 0.00000028 from 47 studies, recognized in 23 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
RCT 100 patients in India, 50 treated with ImmuActive (curcumin, andrographolides, resveratrol, zinc, selenium, and piperine), showing improved recovery with treatment.
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 66.2% lower, RR 0.34, p = 1.00, treatment 0 of 45 (0.0%), control 1 of 47 (2.1%), NNT 47, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 79.7% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.49, treatment 0 of 45 (0.0%), control 2 of 47 (4.3%), NNT 24, relative risk is not 0 because of continuity correction due to zero events (with reciprocal of the contrasting arm).
|
|
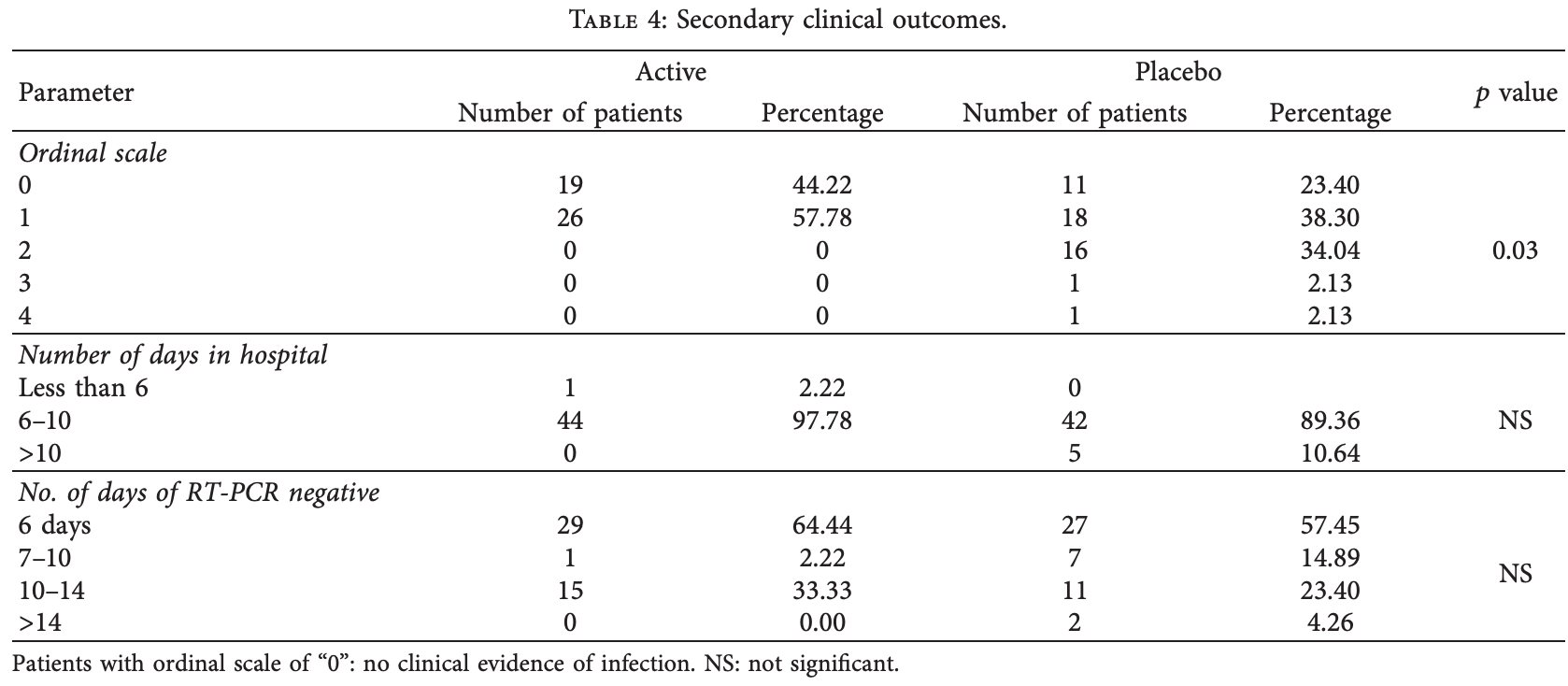
relative recovery - ordinal scale, 43.0% better, RR 0.57, p = 0.004, treatment 45, control 47, day 28.
|
|
relative time to improve one unit on ordinal scale, 30.1% lower, relative time 0.70, treatment 45, control 47.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 24.6% lower, RR 0.75, p = 0.08, treatment 26 of 45 (57.8%), control 36 of 47 (76.6%), NNT 5.3, day 28.
|
|
time to viral-, 5.8% lower, relative time 0.94, p = 0.47, treatment 45, control 47.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Majeed et al., 11 Oct 2021, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, India, peer-reviewed, 4 authors, study period September 2020 - November 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with curcumin, andrographolides, resveratrol, selenium, and piperine) - results of individual treatments may vary, trial CTRI/2020/09/027841.
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of a Nutritional Supplement (ImmuActiveTM) for COVID-19 Patients
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, doi:10.1155/2021/8447545
Background. SARS-CoV-2 has emerged as a global threat due to its infectivity and rapid transmission. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of herbal and mineral formulation (ImmuActive) as an adjunct therapy in COVID-19 patients. Methods. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 100 COVID-19 patients in three centers in Southern India, and 92 subjects completed the study. Subjects were followed up until they were discharged from the hospital or for a maximum of 28 days, whichever was earlier. e primary outcome parameters were the mean change and time required to change the ordinal scale of disease severity by one unit. e secondary outcomes were the time required to turn RT-PCR negative or get discharged from the hospital, change in modified Jackson's Symptom Severity score, and COVID-19 quality of life questionnaire. Results. e ordinal scale at the end of the study was significantly lower in COVID-19 patients supplemented with ImmuActive (0.57) than placebo (1.0), with a p value of 0.0043. e ordinal scale decreased by one unit within 2.35 days in ImmuActive-supplemented patients, while it took 3.36 days in placebo-supplemented patients. Days of hospitalization and time required to turn RT-PCR negative were comparatively lower in the ImmuActive arm than the placebo arm. Change in modified Jackson's Symptom Severity Score and COVID-19 QOL were significant from screening to the end of the study in both ImmuActive and placebo arms. ere were no adverse events observed during the study period. Conclusion. e study results suggest that ImmuActive could be a beneficial and safe adjunct treatment for effectively managing COVID-19 infection symptoms.
Conflicts of Interest All the authors are affiliated to Sami-Sabinsa Group Limited or Sabinsa Corporation.
References
Akbar, Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects, Alternative Medicine Review: A Journal of Clinical erapeutic
Ali, COVID-19: are we ready for the second wave?, Disaster Medicine and Public Health Preparedness
Askari, Ravansalar, Naghizadeh, e efficacy of topical sesame oil in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized double-blinded active-controlled noninferiority clinical trial, Complementary erapies in Medicine
Barnes, Bloom, Nahin, Complementary and alternative medicine use among adults and children: United States, 2007, Natural Health State Report
Basak, Cooper, Roberge, Banik, Chrétien et al., Inhibition of proprotein convertases-1, -7 and furin by diterpines of Andrographis paniculata and their succinoyl esters, Biochemical Journal
Benarba, Pandiella, Medicinal plants as sources of active molecules against COVID-19, Frontiers in Pharmacology
Chakraborty, Sharma, Sharma, Bhattacharya, Lee, SARS-CoV-2 causing pneumonia-associated respiratory disorder (COVID-19): diagnostic and proposed therapeutic options, European Review for Medical and Pharmacological Sciences
Chang, Wallis, Tiralongo, Use of complementary and alternative medicine among People with type 2 diabetes in Taiwan: a cross-sectional survey, Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM
Chowdhury, Hossain, Kashem, Shahid, Alam, Immune response in COVID-19: a review, Journal of Infection and Public Health
Coon, Ernst, Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of safety and efficacy, Planta Medica
Du, Shi, Cao, Zuo, Zhou, Add-on effect of Chinese herbal medicine in the treatment of mild to moderate COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One
Enmozhi, Raja, Sebastine, Joseph, Andrographolide as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: an in silico approach, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Filardo, Di Pietro, Mastromarino, Sessa, erapeutic potential of resveratrol against emerging respiratory viral infections, Pharmacology & erapeutics
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in infection and inflammation, Nutrients
Gammoh, Rink, Zinc in infection and inflammation, Nutrients
Guillin, Vindry, Ohlmann, Chavatte, Selenium, selenoproteins and viral infection, Nutrients
Hawkes, Kelley, Taylor, e effects of dietary selenium on the immune system in healthy men, Biological Trace Element Research
Hong-Zhi, Xiao-Ying, Yu-Huan, Huang, Da-Hui, Traditional Chinese Medicine: an effective treatment for 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP), Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines
Hu, Wu, Logue, Andrographis paniculata (Chu� an X � in Lián) for symptomatic relief of acute respiratory tract infections in adults and children: a systematic review and meta-analysis, PLoS One
Jiang, Xia, Ying, Lu, A novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) causing pneumonia-associated respiratory syndrome, Cellular and Molecular Immunology
Jothimani, Kailasam, Danielraj, COVID-19: poor outcomes in patients with Zinc deficiency, International Journal of Infectious Diseases
Kedzierski, Linossi, Kolesnik, Suppressor of cytokine signaling 4 (SOCS4) protects against severe cytokine storm and enhances viral clearance during influenza infection, PLoS Pathogens
Kieliszek, Lipinski, Selenium supplementation in the prevention of coronavirus infections (COVID-19), Medical Hypotheses
Kim, Marks, Clemens, Looking beyond COVID-19 vaccine phase 3 trials, Nature Medicine
Kopansky-Giles, Vernon, Boon, Steiman, Kelly et al., Inclusion of a CAM therapy (chiropractic care) for the management of musculoskeletal pain in an integrative, inner city, hospital-based primary care setting, Journal of Alternative Medicine Research
Kumar, Sinha, Cardiovascular disease in India: a 360 degree overview, Medical Journal Armed Forces India
Liu, Ying, e inhibitory effect of curcumin on virus-induced cytokine storm and its potential use in the associated severe pneumonia, Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology
Majedi, Majedi, Existing drugs as treatment options for COVID-19: a brief survey of some recent results, Journal of Chemistry Letters
Majeed, Nagabhushanam, Gowda, Mundkur, An exploratory study of selenium status in healthy individuals and in patients with COVID-19 in a south Indian population: the case for adequate selenium status, Nutrition
Maurya, Kumar, Prasad, Bhatt, Saxena, Structure-based drug designing for potential antiviral activity of selected natural products from Ayurveda against SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein and its cellular receptor, Virus Disease
Nayebi, Esteghamati, Meysamie, e effects of a Melissa officinalis L. based product on metabolic parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized double-blinded controlled clinical trial, Journal of Complementary & Integrative Medicine
Pormohammad, Monych, Turner, Zinc and SARS-CoV-2: a molecular modeling study of Zn interactions with RNA-dependent RNA-polymerase and 3C-like proteinase enzymes, International Journal of Molecular Medicine
Ramdani, Bachari, Potential therapeutic effects of Resveratrol against SARS-CoV-2, Acta Virologica
Rayman, Selenium and human health, e Lancet
Saydah, Eberhardt, Use of complementary and alternative medicine among adults with chronic diseases: United States 2002, Journal of Alternative & Complementary Medicine
Seifert, Jeitler, Stange, e relevance of complementary and integrative medicine in the COVID-19 pandemic: a qualitative review of the literature, Frontiers of Medicine
Shagufta, Asim, Qamar, Antihyperlipidemic effect of seeds of jamun (eugenia jambolana) in subjects of intermediate hyperglycemia: a pilot study, Traditional and Integrative Medicine
Shi, Huang, Chen, Andrographolide and its fluorescent derivative inhibit the main proteases of 2019-nCoV and SARS-CoV through covalent linkage, Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications
Singer, Adams, Integrating complementary and alternative medicine into mainstream healthcare services: the perspectives of health service managers, BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Singh, Malik, Raina, Computational investigation for identification of potential phytochemicals and antiviral drugs as potential inhibitors for RNA-dependent RNA polymerase of COVID-19, Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics
Soni, Mehta, Ratre, Curcumin, a traditional spice component, can hold the promise against COVID-19?, European Journal of Pharmacology
Verity, Okell, Dorigatti, Estimates of the severity of coronavirus disease 2019: a model-based analysis, e Lancet Infectious Diseases
Wessels, Rolles, Rink, e potential impact of zinc supplementation on COVID-19 pathogenesis, Frontiers in Immunology
Who, R&D Blueprint Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 erapeutic Trial Synopsis
Who, WHO Lists Two Additional COVID-19 Vaccines for Emergency Use and COVAX Roll-Out
Wintergerst, Maggini, Hornig, Immuneenhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions, Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism
Yang, Wei, Huang, Resveratrol inhibits the replication of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in cultured Vero cells, Phytotherapy Research
Zahedipour, Hosseini, Sathyapalan, Potential effects of curcumin in the treatment of COVID-19 infection, Phytotherapy Research
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2021/8447545",
"ISSN": [
"1741-4288",
"1741-427X"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1155/2021/8447545",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Background. SARS-CoV-2 has emerged as a global threat due to its infectivity and rapid transmission. We evaluated the safety and efficacy of herbal and mineral formulation (ImmuActive) as an adjunct therapy in COVID-19 patients. Methods. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study was conducted in 100 COVID-19 patients in three centers in Southern India, and 92 subjects completed the study. Subjects were followed up until they were discharged from the hospital or for a maximum of 28 days, whichever was earlier. The primary outcome parameters were the mean change and time required to change the ordinal scale of disease severity by one unit. The secondary outcomes were the time required to turn RT-PCR negative or get discharged from the hospital, change in modified Jackson’s Symptom Severity score, and COVID-19 quality of life questionnaire. Results. The ordinal scale at the end of the study was significantly lower in COVID-19 patients supplemented with ImmuActive (0.57) than placebo (1.0), with a <jats:inline-formula>\n <math xmlns=\"http://www.w3.org/1998/Math/MathML\" id=\"M1\">\n <mi>p</mi>\n </math>\n </jats:inline-formula> value of 0.0043. The ordinal scale decreased by one unit within 2.35 days in ImmuActive-supplemented patients, while it took 3.36 days in placebo-supplemented patients. Days of hospitalization and time required to turn RT-PCR negative were comparatively lower in the ImmuActive arm than the placebo arm. Change in modified Jackson’s Symptom Severity Score and COVID-19 QOL were significant from screening to the end of the study in both ImmuActive and placebo arms. There were no adverse events observed during the study period. Conclusion. The study results suggest that ImmuActive could be a beneficial and safe adjunct treatment for effectively managing COVID-19 infection symptoms.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"8447545",
"8447545"
],
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-1690-7470",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sami-Sabinsa Group Limited, 19/1, 19/2, I Main, II Phase, Peenya Industrial Area, Bangalore, Karnataka 560 058, India"
},
{
"name": "Sabinsa Corporation, 20 Lake Drive, East Windsor, Piscataway, NJ 08520, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Majeed",
"given": "Muhammed",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-9470-4110",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sabinsa Corporation, 20 Lake Drive, East Windsor, Piscataway, NJ 08520, USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Nagabhushanam",
"given": "Kalyanam",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0002-7983-9153",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sami-Sabinsa Group Limited, 19/1, 19/2, I Main, II Phase, Peenya Industrial Area, Bangalore, Karnataka 560 058, India"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Shah",
"given": "Kalpesh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2928-1726",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Sami-Sabinsa Group Limited, 19/1, 19/2, I Main, II Phase, Peenya Industrial Area, Bangalore, Karnataka 560 058, India"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": true,
"family": "Mundkur",
"given": "Lakshmi",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-11T17:41:12Z",
"timestamp": 1633974072000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-11T17:41:33Z",
"timestamp": 1633974093000
},
"editor": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Hu",
"given": "Changmin",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
4,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2024-04-08T23:14:29Z",
"timestamp": 1712618069858
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 8,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2021-10-11T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1633910400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/8447545.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/8447545.xml",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://downloads.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/8447545.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "98",
"original-title": [],
"page": "1-9",
"prefix": "10.1155",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
10,
11
]
]
},
"publisher": "Hindawi Limited",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.26355/eurrev_202004_20871",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "1"
},
{
"article-title": "Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)–symptoms",
"author": "Center for Disease Control and Prevention",
"key": "2"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1017/dmp.2020.149",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "3"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41423-020-0372-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "4"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s1473-3099(20)30243-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "5"
},
{
"article-title": "Existing drugs as treatment options for COVID-19: a brief survey of some recent results",
"author": "S. Majedi",
"first-page": "2",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Chemistry Letters",
"key": "6",
"volume": "1",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "7",
"volume-title": "WHO Lists Two Additional COVID-19 Vaccines for Emergency Use and COVAX Roll-Out",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01230-y",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "8"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1037/e623942009-001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1472-6882-14-167",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "10"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ctim.2019.08.017",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "11"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2011/983792",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "12"
},
{
"article-title": "Inclusion of a CAM therapy (chiropractic care) for the management of musculoskeletal pain in an integrative, inner city, hospital-based primary care setting",
"author": "D. Kopansky-Giles",
"first-page": "61",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Journal of Alternative Medicine Research",
"key": "13",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1515/jcim-2018-0088",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "14"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/acm.2006.12.805",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "15"
},
{
"article-title": "Antihyperlipidemic effect of seeds of jamun (eugenia jambolana) in subjects of intermediate hyperglycemia: a pilot study",
"author": "P. Shagufta",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Traditional and Integrative Medicine",
"key": "16",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmed.2020.587749",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "17"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.07.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "18"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S1875-5364(20)30022-4",
"article-title": "Traditional Chinese Medicine: an effective treatment for 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia (NCP)",
"author": "D. Hong-Zhi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "206",
"issue": "3",
"journal-title": "Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines",
"key": "19",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0256429",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "20"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fphar.2020.01189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "21"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6738",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "22"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s13337-020-00598-8",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "23"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173551",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "24"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcell.2020.00479",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "25"
},
{
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata in the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections: a systematic review of safety and efficacy",
"author": "J. T. Coon",
"first-page": "293",
"issue": "4",
"journal-title": "Planta Medica",
"key": "26",
"volume": "70",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"article-title": "Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects",
"author": "S. Akbar",
"first-page": "66",
"issue": "1",
"journal-title": "Alternative Medicine Review: A Journal of Clinical Therapeutic",
"key": "27",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1042/bj3380107",
"article-title": "Inhibition of proprotein convertases-1, -7 and furin by diterpines of Andrographis paniculata and their succinoyl esters",
"author": "A. Basak",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "107",
"issue": "Pt 1",
"journal-title": "Biochemical Journal",
"key": "28",
"volume": "338",
"year": "1999"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9060624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "29"
},
{
"article-title": "Andrographolide as a potential inhibitor of SARS-CoV-2 main protease: an in silico approach",
"author": "S. K. Enmozhi",
"first-page": "1",
"issue": "9",
"journal-title": "Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics",
"key": "30",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.08.086",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "31"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4149/av_2020_309",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "32"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ptr.6916",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "33"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/s0140-6736(11)61452-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "34"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu11092101",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "35"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mehy.2020.109878",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "36"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/nu9060624",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "37"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3892/ijmm.2020.4790",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "38"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.mjafi.2019.12.005",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "39"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.01712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "40"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1847688",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "41"
},
{
"author": "WHO",
"key": "42",
"volume-title": "R&D Blueprint Novel Coronavirus COVID-19 Therapeutic Trial Synopsis",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.ppat.1004134",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "43"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0181780",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "44"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107613",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "45"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1385/bter:81:3:189",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "46"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.nut.2020.111053",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "47"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1159/000090495",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "48"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ijid.2020.09.014",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "49"
}
],
"reference-count": 49,
"references-count": 49,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.hindawi.com/journals/ecam/2021/8447545/"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Complementary and alternative medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Assess the Efficacy and Safety of a Nutritional Supplement (ImmuActiveTM) for COVID-19 Patients",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "2021"
}
majeed
