Bioinformatics analysis of the proteome in the pathway of complement and coagulation cascades in COVID-19: discovering potential biomarkers of FGB and SERPINA5
et al., BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8, Oct 2025
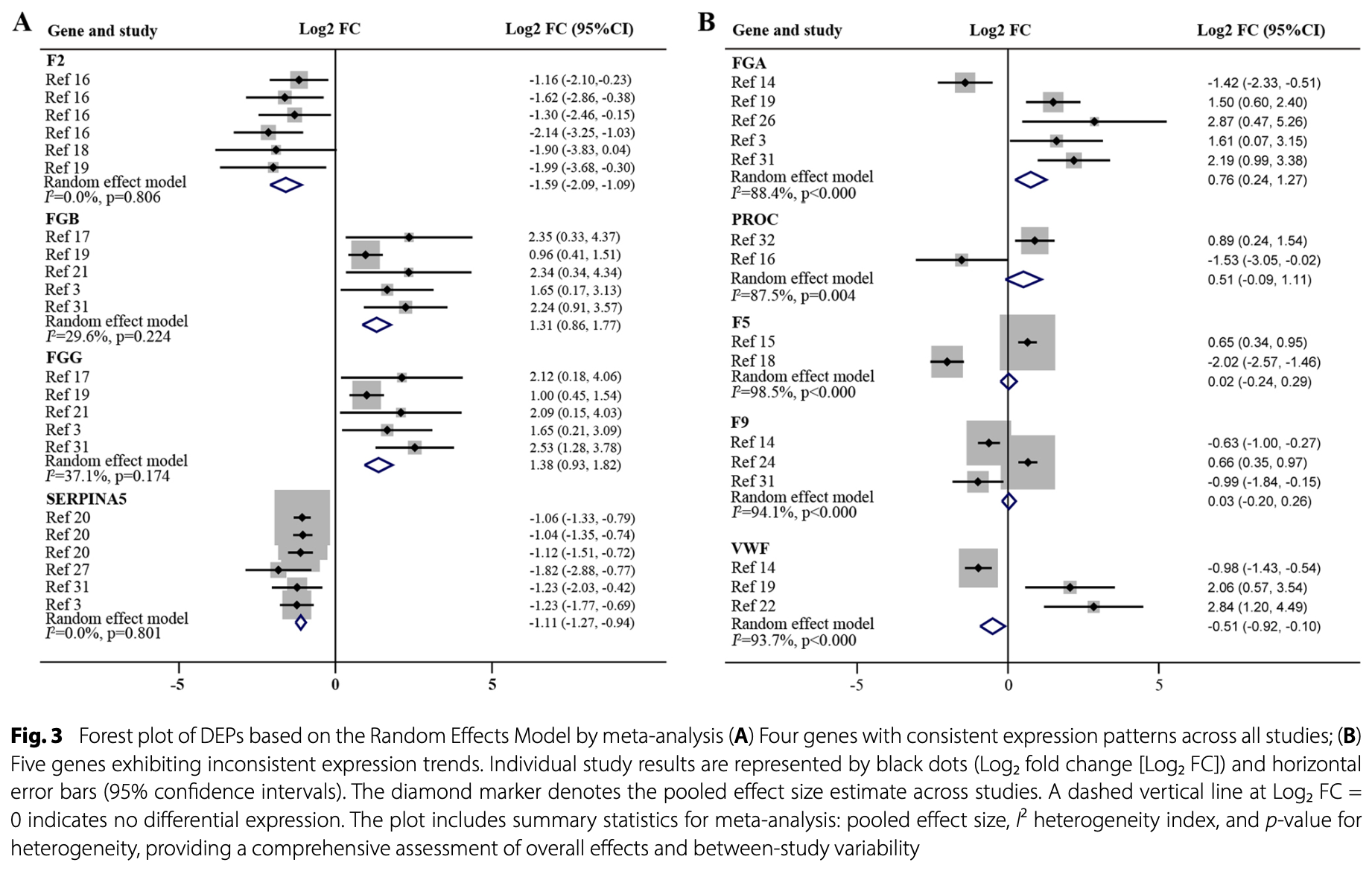
Bioinformatics and immunohistochemistry study identifying dysregulation in the coagulation pathway in COVID-19, highlighting FGB and FGG (upregulated) and F2 (thrombin) and SERPINA5 (downregulated) as key hub genes. The findings support using existing anticoagulants targeting F2 and suggest FGB and SERPINA5 are potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
Liu et al., 8 Oct 2025, peer-reviewed, 8 authors.
Contact: mitenike@sjtu.edu.cn, songshu@shaphc.org, zhanglijun@shaphc.org.
In silico studies are an important part of preclinical research, however results may be very different in vivo.
Bioinformatics analysis of the proteome in the pathway of complement and coagulation cascades in COVID-19: discovering potential biomarkers of FGB and SERPINA5
BMC Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8
The complement system, a key innate immunity component, is implicated in COVID-19 pathogenesis. Proteomic studies reveal dysregulated complement and coagulation cascades (CCC) proteins in COVID-19, yet comprehensive analyses remain limited. This bioinformatics study analyzed proteomic data (from inception to January 13, 2025) across Web of Science, PubMed, EMBASE, and Wiley Online Library using keywords "complement and coagulation cascades", "COVID-19", and "proteomics". Included studies compared differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) in COVID-19 patients versus healthy controls. Two reviewers independently extracted data. DEPs were analyzed via R (v4.4.2), Stata (v14), and STRING (v12.0). Twenty studies identified 3,018 DEPs, including 58 CCC-related genes (e.g., FGB, SERPINA5, FGG, F2). Hub genes were identified using MCODE and cytohubba in Cytoscape, and 16 hub genes (e.g., FGB, SERPINA5) were found. Stata confirmed consistent expression of FGB, SERPINA5, FGG, and F2. All of them are the biomarkers of diseases, and are the drug targets except SERPINA5 according to the reports from OpenTargets database. Immunohistochemistry validated FGB upregulation and SERPINA5 downregulation. In summary, CCC pathway proteins are extensively dysregulated in COVID-19. FGB and SERPINA5 are potential diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets, offering insights into severe COVID-19 mechanisms and guiding novel treatment strategies.
Abbreviations
Declarations Ethics approval and consent to participate The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (Protocol No. 2023-S077-01, approved on July 4, 2023). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their legal next of kin involved in the study.
Consent for publication Not applicable.
Competing interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Publisher's Note Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
Alghanem, Mansour, Shaibah, Quantitative proteomics analysis of COVID-19 patients: Fetuin-A and tetranectin as potential modulators of innate immune responses, Heliyon
Asanuma, Yoshikawa, Hayashi, Protein C inhibitor inhibits breast cancer cell growth, metastasis and angiogenesis independently of its protease inhibitory activity, Int J Cancer
Ayass, Cao, Zhang, Noninvasive nasopharyngeal proteomics of COVID-19 patient identify abnormalities related to complement and coagulation cascade and mucosal immune system, PLoS ONE
Bader, Hogue, An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks, BMC Bioinformatics
Bijsmans, Smits, De Graeff, Loss of SerpinA5 protein expression is associated with advanced-stage serous ovarian tumors, Mod Pathol
Blangy-Letheule, Vergnaud, Dupas, Value of a secretomic approach for distinguishing patients with COVID-19 viral pneumonia among patients with respiratory distress admitted to intensive care unit, J Med Virol
Cantrell, Feldman, Rosenfeldt, Prothrombin prevents fatal T cell-dependent anemia during chronic virus infection of mice, JCI Insight
Chin, Chen, Wu, CytoHubba: identifying hub objects and subnetworks from complex interactome, BMC Syst Biol
Chung, Lam, Tan, Comprehensive review of COVID-19: epidemiology, pathogenesis, advancement in diagnostic and detection techniques, and Post-Pandemic treatment strategies, Int J Mol Sci
Erickson, Huang, Allen, SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung epithelial cells induces TMPRSS-mediated acute fibrin deposition, Nat Commun
Fodil, Annane, Complement Inhibition and COVID-19: the story so Far, Immunotargets Ther
Geervliet, Bansal, Matrix metalloproteinases as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases, Cells
Geyer, Arend, Doll, High-resolution serum proteome trajectories in COVID-19 reveal patient-specific seroconversion, EMBO Mol Med
Guo, Han, Han, Bioinformation analysis of differential expression proteins in different processes of COVID-19, Viral Immunol
Hendaus, Jomha, From COVID-19 to clot: the involvement of the complement system, J Biomol Struct Dyn
Hirdman, Boden, Kjellstrom, Proteomic characteristics and diagnostic potential of exhaled breath particles in patients with COVID-19, Clin Proteomics
Jing, Jia, Wong, SERPINA5 inhibits tumor cell migration by modulating the fibronectin-integrin beta1 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma, Mol Oncol
Kaiser, Leunig, Pekayvaz, Self-sustaining IL-8 loops drive a prothrombotic neutrophil phenotype in severe COVID-19, JCI Insight
Lasalle, Gonye, Freeman, Longitudinal characterization of Circulating neutrophils uncovers phenotypes associated with severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Cell Rep Med
Mastaglio, Ruggeri, Risitano, The first case of COVID-19 treated with the complement C3 inhibitor AMY-101, Clin Immunol
Moraes, Martins-Gonçalves, Da Silva Lr, Proteomic profile of procoagulant extracellular vesicles reflects complement system activation and platelet hyperreactivity of patients with severe COVID-19, Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology
Ochoa, Hercules, Carmona, The next-generation open targets platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt, Nucleic Acids Res
Page, Mckenzie, Bossuyt, The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews, Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed)
Pushalkar, Wu, Maity, Complex changes in serum protein levels in COVID-19 convalescents, Sci Rep
Ray, Winter, Naik, Prognostic significance of the coagulation and complement systems in critical COVID-19 infection, Prague Med Rep
Rudnik, Hukara, Kocherova, Elevated fibronectin levels in profibrotic CD14(+) monocytes and CD14(+) macrophages in systemic sclerosis, Front Immunol
Sahin, Yurtseven, Dadmand, Plasma proteomics identify potential severity biomarkers from COVID-19 associated network, Proteom -Clin Appl
Schachtrup, Ryu, Helmrick, Fibrinogen triggers astrocyte Scar formation by promoting the availability of active TGF-beta after vascular damage, J Neurosci
Schweizer, Schaller, Zwiebel, Quantitative multiorgan proteomics of fatal COVID-19 uncovers tissue-specific effects beyond inflammation, EMBO Mol Med
Shannon, Markiel, Ozier, Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks, Genome Res
Song, Zeng, Xu, Proteomic lung analysis revealed hyper-activation of neutrophil extracellular trap formation in cases of fatal COVID-19, Heliyon
Soy, Keser, Atagunduz, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment, Clin Rheumatol
Subramanian, Nirantharakumar, Hughes, Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults, Nat Med
Thomas, Dzieciatkowska, Serum proteomics in COVID-19 patients: altered coagulation and complement status as a function of IL-6 level, J Proteome Res
Urwyler, Moser, Charitos, Treatment of COVID-19 with conestat alfa, a regulator of the complement, contact activation and Kallikrein-Kinin system, Front Immunol
Viode, Smolen, Van Zalm, Longitudinal plasma proteomic analysis of 1117 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 identifies features associated with severity and outcomes, Sci Adv
Wang, Liu, Liu, IFN-Inducible SerpinA5 triggers antiviral immunity by regulating STAT1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation, Int J Mol Sci
Wang, Yang, Tong, Integrative proteomics and metabolomics study reveal enhanced immune responses by COVID-19 vaccine booster shot against Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Med Virol
Wei, Gu, Ma, Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of plasma uncovers immune responses in patients with long COVID-19, Front Microbiol
Wu, Xu, Zhang, Longitudinal serum proteome characterization of COVID-19 patients with different severities revealed potential therapeutic strategies, Front Immunol
Xu, Lei, Ren, SOD1 is a possible predictor of COVID-19 progression as revealed by plasma proteomics, ACS Omega
Yang, Lin, Xue, Deciphering the Omicron variant: integrated omics analysis reveals critical biomarkers and pathophysiological pathways, J Translational Med
Yazdanifar, Mashkour, Bertaina, Making a case for using γδ T cells against SARS-CoV-2, Crit Rev Microbiol
Zhang, Lin, Liu, Proteomic profiling reveals a distinctive molecular signature for critically ill COVID-19 patients compared with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Int J Infect Diseases: IJID : Official Publication Int Soc Infect Dis
Zhang, Wang, Liu, The proteomic characteristics of airway mucus from critical ill COVID-19 patients, Life Sci
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8",
"ISSN": [
"1471-2334"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8",
"alternative-id": [
"11598"
],
"article-number": "1252",
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "5 May 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "28 August 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "8 October 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Declarations",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Ethics approval and consent to participate",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 2,
"value": "The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by Ethics Committee of Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center (Protocol No. 2023-S077-01, approved on July 4, 2023). Informed consent was obtained from all subjects or their legal next of kin involved in the study."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Consent for publication",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 3,
"value": "Not applicable."
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 4,
"value": "The authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Liu",
"given": "Siyuan",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Shi",
"given": "Huichun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Yuexiang",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhu",
"given": "Cuisong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Zhou",
"given": "Jing",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jin",
"given": "Wenzhong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Song",
"given": "Shu",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "zhang",
"given": "Lijun",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "BMC Infectious Diseases",
"container-title-short": "BMC Infect Dis",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-08T10:56:45Z",
"timestamp": 1759921005000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-08T10:56:50Z",
"timestamp": 1759921010000
},
"funder": [
{
"award": [
"KY-GW-2024-05"
],
"name": "Shanghai Public Health Clinical Center"
},
{
"award": [
"2022C03189"
],
"name": "Science and Technology Plan Project of Zhejiang Province"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-09T00:45:10Z",
"timestamp": 1759970710868,
"version": "build-2065373602"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
12
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1759881600000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
],
"date-time": "2025-10-08T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1759881600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/article/10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8/fulltext.html",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://link.springer.com/content/pdf/10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1186",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2025,
10,
8
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms25158155",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR1",
"unstructured": "Chung YS, Lam CY, Tan PH et al. Comprehensive review of COVID-19: epidemiology, pathogenesis, advancement in diagnostic and detection techniques, and Post-Pandemic treatment strategies. Int J Mol Sci. 2024; 25:8155."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01909-w",
"author": "A Subramanian",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1706",
"journal-title": "Nat Med",
"key": "11598_CR2",
"unstructured": "Subramanian A, Nirantharakumar K, Hughes S, et al. Symptoms and risk factors for long COVID in non-hospitalized adults. Nat Med. 2022;28:1706–14.",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31878",
"author": "S Song",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e31878",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "11598_CR3",
"unstructured": "Song S, Zeng L, Xu J, et al. Proteomic lung analysis revealed hyper-activation of neutrophil extracellular trap formation in cases of fatal COVID-19. Heliyon. 2024;10:e31878.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/07391102.2020.1832919",
"author": "MA Hendaus",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1909",
"journal-title": "J Biomol Struct Dyn",
"key": "11598_CR4",
"unstructured": "Hendaus MA, Jomha FA. From COVID-19 to clot: the involvement of the complement system. J Biomol Struct Dyn. 2022;40:1909–14.",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5",
"author": "M Soy",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2085",
"journal-title": "Clin Rheumatol",
"key": "11598_CR5",
"unstructured": "Soy M, Keser G, Atagunduz P, et al. Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of anti-inflammatory agents used in treatment. Clin Rheumatol. 2020;39:2085–94.",
"volume": "39",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.14712/23362936.2023.7",
"author": "A Ray",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "77",
"journal-title": "Prague Med Rep",
"key": "11598_CR6",
"unstructured": "Ray A, Winter KAK, Naik DSL, et al. Prognostic significance of the coagulation and complement systems in critical COVID-19 infection. Prague Med Rep. 2023;124:77–93.",
"volume": "124",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.recesp.2021.06.016",
"author": "MJ Page",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "790",
"journal-title": "Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed)",
"key": "11598_CR7",
"unstructured": "Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: an updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2021;74:790–9.",
"volume": "74",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1101/gr.1239303",
"author": "P Shannon",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2498",
"journal-title": "Genome Res",
"key": "11598_CR8",
"unstructured": "Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, et al. Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 2003;13:2498–504.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1471-2105-4-2",
"author": "GD Bader",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2",
"journal-title": "BMC Bioinformatics",
"key": "11598_CR9",
"unstructured": "Bader GD, Hogue CW. An automated method for finding molecular complexes in large protein interaction networks. BMC Bioinformatics. 2003;4:2.",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/1752-0509-8-S4-S11",
"author": "CH Chin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "S11",
"issue": "Suppl 4",
"journal-title": "BMC Syst Biol",
"key": "11598_CR10",
"unstructured": "Chin CH, Chen SH, Wu HH, et al. CytoHubba: identifying hub objects and sub-networks from complex interactome. BMC Syst Biol. 2014;8(Suppl 4):S11.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gkac1046",
"author": "D Ochoa",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "D1353",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res",
"key": "11598_CR11",
"unstructured": "Ochoa D, Hercules A, Carmona M, et al. The next-generation open targets platform: reimagined, redesigned, rebuilt. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023;51:D1353–9.",
"volume": "51",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.xcrm.2022.100779",
"author": "TJ LaSalle",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "100779",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep Med",
"key": "11598_CR12",
"unstructured": "LaSalle TJ, Gonye ALK, Freeman SS, et al. Longitudinal characterization of Circulating neutrophils uncovers phenotypes associated with severity in hospitalized COVID-19 patients. Cell Rep Med. 2022;3:100779.",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.adl5762",
"author": "A Viode",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "eadl5762",
"journal-title": "Sci Adv",
"key": "11598_CR13",
"unstructured": "Viode A, Smolen KK, van Zalm P, et al. Longitudinal plasma proteomic analysis of 1117 hospitalized patients with COVID-19 identifies features associated with severity and outcomes. Sci Adv. 2024;10:eadl5762.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acs.jproteome.0c00365",
"author": "A D’Alessandro",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "4417",
"journal-title": "J Proteome Res",
"key": "11598_CR14",
"unstructured": "D’Alessandro A, Thomas T, Dzieciatkowska M, et al. Serum proteomics in COVID-19 patients: altered coagulation and complement status as a function of IL-6 level. J Proteome Res. 2020;19:4417–27.",
"volume": "19",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202114167",
"author": "PE Geyer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e14167",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "11598_CR15",
"unstructured": "Geyer PE, Arend FM, Doll S, et al. High-resolution serum proteome trajectories in COVID-19 reveal patient-specific seroconversion. EMBO Mol Med. 2021;13:e14167.",
"volume": "13",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/acsomega.1c01375",
"author": "B Xu",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "16826",
"journal-title": "ACS Omega",
"key": "11598_CR16",
"unstructured": "Xu B, Lei Y, Ren X, et al. SOD1 is a possible predictor of COVID-19 progression as revealed by plasma proteomics. ACS Omega. 2021;6:16826–36.",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.lfs.2021.119046",
"author": "Z Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "119046",
"journal-title": "Life Sci",
"key": "11598_CR17",
"unstructured": "Zhang Z, Wang T, Liu F, et al. The proteomic characteristics of airway mucus from critical ill COVID-19 patients. Life Sci. 2021;269:119046.",
"volume": "269",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0274228",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR18",
"unstructured": "Ayass MA, Cao W, Zhang J et al. Noninvasive nasopharyngeal proteomics of COVID-19 patient identify abnormalities related to complement and coagulation cascade and mucosal immune system. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0274228."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fcimb.2022.926352",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR19",
"unstructured": "Moraes E, Martins-Gonçalves R, da Silva LR et al. Proteomic profile of procoagulant extracellular vesicles reflects complement system activation and platelet hyperreactivity of patients with severe COVID-19. Frontiers in cellular and infection microbiology. 2022;12:926352."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2022.893943",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR20",
"unstructured": "Wu S, Xu Y, Zhang J et al. Longitudinal serum proteome characterization of COVID-19 patients with different severities revealed potential therapeutic strategies. Front Immunol. 2022;13:893943."
},
{
"author": "Z Zhang",
"first-page": "258",
"journal-title": "Int J Infect Diseases: IJID : Official Publication Int Soc Infect Dis",
"key": "11598_CR21",
"unstructured": "Zhang Z, Lin F, Liu F, et al. Proteomic profiling reveals a distinctive molecular signature for critically ill COVID-19 patients compared with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int J Infect Diseases: IJID : Official Publication Int Soc Infect Dis. 2022;116:258–67.",
"volume": "116",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e15224",
"author": "B Alghanem",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e15224",
"journal-title": "Heliyon",
"key": "11598_CR22",
"unstructured": "Alghanem B, Mansour FA, Shaibah H, et al. Quantitative proteomics analysis of COVID-19 patients: Fetuin-A and tetranectin as potential modulators of innate immune responses. Heliyon. 2023;9:e15224.",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/prca.202200070",
"author": "AT Sahin",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2200070",
"journal-title": "Proteom – Clin Appl",
"key": "11598_CR23",
"unstructured": "Sahin AT, Yurtseven A, Dadmand S, et al. Plasma proteomics identify potential severity biomarkers from COVID-19 associated network. Proteom – Clin Appl. 2023;17:2200070.",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29219",
"author": "B Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e29219",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "11598_CR24",
"unstructured": "Wang B, Yang W, Tong Y, et al. Integrative proteomics and metabolomics study reveal enhanced immune responses by COVID-19 vaccine booster shot against Omicron SARS-CoV-2 infection. J Med Virol. 2023;95:e29219.",
"volume": "95",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jmv.29756",
"author": "A Blangy-Letheule",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e29756",
"journal-title": "J Med Virol",
"key": "11598_CR25",
"unstructured": "Blangy-Letheule A, Vergnaud A, Dupas T, et al. Value of a secretomic approach for distinguishing patients with COVID-19 viral pneumonia among patients with respiratory distress admitted to intensive care unit. J Med Virol. 2024;96:e29756.",
"volume": "96",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1089/vim.2023.0094",
"author": "N Guo",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "Viral Immunol",
"key": "11598_CR26",
"unstructured": "Guo N, Han X, Han G, et al. Bioinformation analysis of differential expression proteins in different processes of COVID-19. Viral Immunol. 2024;37:194–201.",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41598-024-54534-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR27",
"unstructured": "Pushalkar S, Wu S, Maity S et al. Complex changes in serum protein levels in COVID-19 convalescents. Sci Rep. 2024;14:4479."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-024-05022-z",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR28",
"unstructured": "Yang Q, Lin Z, Xue M et al. Deciphering the Omicron variant: integrated omics analysis reveals critical biomarkers and pathophysiological pathways. J Translational Med 2024;22:219."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12014-023-09403-2",
"author": "G Hirdman",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "13",
"journal-title": "Clin Proteomics",
"key": "11598_CR29",
"unstructured": "Hirdman G, Boden E, Kjellstrom S, et al. Proteomic characteristics and diagnostic potential of exhaled breath particles in patients with COVID-19. Clin Proteomics. 2023;20:13.",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.150862",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR30",
"unstructured": "Kaiser R, Leunig A, Pekayvaz K et al. Self-sustaining IL-8 loops drive a prothrombotic neutrophil phenotype in severe COVID-19. JCI Insight 2021;6:e150862."
},
{
"DOI": "10.15252/emmm.202317459",
"author": "L Schweizer",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "e17459",
"journal-title": "EMBO Mol Med",
"key": "11598_CR31",
"unstructured": "Schweizer L, Schaller T, Zwiebel M, et al. Quantitative multiorgan proteomics of fatal COVID-19 uncovers tissue-specific effects beyond inflammation. EMBO Mol Med. 2023;15:e17459.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fmicb.2024.1470193",
"author": "Y Wei",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "1470193",
"journal-title": "Front Microbiol",
"key": "11598_CR32",
"unstructured": "Wei Y, Gu H, Ma J, et al. Proteomic and metabolomic profiling of plasma uncovers immune responses in patients with long COVID-19. Front Microbiol. 2024;15:1470193.",
"volume": "15",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2147/ITT.S284830",
"author": "S Fodil",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "273",
"journal-title": "Immunotargets Ther",
"key": "11598_CR33",
"unstructured": "Fodil S, Annane D. Complement Inhibition and COVID-19: the story so Far. Immunotargets Ther. 2021;10:273–84.",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2020.02072",
"author": "P Urwyler",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "2072",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "11598_CR34",
"unstructured": "Urwyler P, Moser S, Charitos P, et al. Treatment of COVID-19 with conestat alfa, a regulator of the complement, contact activation and Kallikrein-Kinin system. Front Immunol. 2020;11:2072.",
"volume": "11",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.clim.2020.108450",
"author": "S Mastaglio",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "108450",
"journal-title": "Clin Immunol",
"key": "11598_CR35",
"unstructured": "Mastaglio S, Ruggeri A, Risitano AM, et al. The first case of COVID-19 treated with the complement C3 inhibitor AMY-101. Clin Immunol. 2020;215:108450.",
"volume": "215",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0137-10.2010",
"author": "C Schachtrup",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "5843",
"journal-title": "J Neurosci",
"key": "11598_CR36",
"unstructured": "Schachtrup C, Ryu JK, Helmrick MJ, et al. Fibrinogen triggers astrocyte Scar formation by promoting the availability of active TGF-beta after vascular damage. J Neurosci. 2010;30:5843–54.",
"volume": "30",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/cells9051212",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR37",
"unstructured": "Geervliet E, Bansal R. Matrix metalloproteinases as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets in liver diseases. Cells 2020;9:1212."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3389/fimmu.2021.642891",
"author": "M Rudnik",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "642891",
"journal-title": "Front Immunol",
"key": "11598_CR38",
"unstructured": "Rudnik M, Hukara A, Kocherova I, et al. Elevated fibronectin levels in profibrotic CD14(+) monocytes and CD14(+) macrophages in systemic sclerosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:642891.",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-023-42140-6",
"author": "R Erickson",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "6380",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "11598_CR39",
"unstructured": "Erickson R, Huang C, Allen C, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of human lung epithelial cells induces TMPRSS-mediated acute fibrin deposition. Nat Commun. 2023;14:6380.",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1172/jci.insight.181063",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR40",
"unstructured": "Cantrell R, Feldman HA, Rosenfeldt L et al. Prothrombin prevents fatal T cell-dependent anemia during chronic virus infection of mice. JCI Insight. 2025;10:e18106."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/ijms24065458",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "11598_CR41",
"unstructured": "Wang C, Liu Y, Liu X et al. IFN-Inducible SerpinA5 triggers antiviral immunity by regulating STAT1 phosphorylation and nuclear translocation. Int J Mol Sci 2023;24:5458."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/1040841X.2020.1822279",
"author": "M Yazdanifar",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "689",
"journal-title": "Crit Rev Microbiol",
"key": "11598_CR42",
"unstructured": "Yazdanifar M, Mashkour N, Bertaina A. Making a case for using γδ T cells against SARS-CoV-2. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2020;46:689–702.",
"volume": "46",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.molonc.2013.12.003",
"author": "Y Jing",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "366",
"journal-title": "Mol Oncol",
"key": "11598_CR43",
"unstructured": "Jing Y, Jia D, Wong CM, et al. SERPINA5 inhibits tumor cell migration by modulating the fibronectin-integrin beta1 signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Oncol. 2014;8:366–77.",
"volume": "8",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/modpathol.2010.214",
"author": "IT Bijsmans",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "463",
"journal-title": "Mod Pathol",
"key": "11598_CR44",
"unstructured": "Bijsmans IT, Smits KM, de Graeff P, et al. Loss of SerpinA5 protein expression is associated with advanced-stage serous ovarian tumors. Mod Pathol. 2011;24:463–70.",
"volume": "24",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/ijc.22773",
"author": "K Asanuma",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"first-page": "955",
"journal-title": "Int J Cancer",
"key": "11598_CR45",
"unstructured": "Asanuma K, Yoshikawa T, Hayashi T, et al. Protein C inhibitor inhibits breast cancer cell growth, metastasis and angiogenesis independently of its protease inhibitory activity. Int J Cancer. 2007;121:955–65.",
"volume": "121",
"year": "2007"
}
],
"reference-count": 45,
"references-count": 45,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://bmcinfectdis.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12879-025-11598-8"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Bioinformatics analysis of the proteome in the pathway of complement and coagulation cascades in COVID-19: discovering potential biomarkers of FGB and SERPINA5",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy",
"volume": "25"
}