Evaluation of Acebilustat, a Selective Inhibitor of Leukotriene B4 Biosynthesis, for Treatment of Outpatients With Mild-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial
et al., Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad187, NCT04662060, Mar 2023
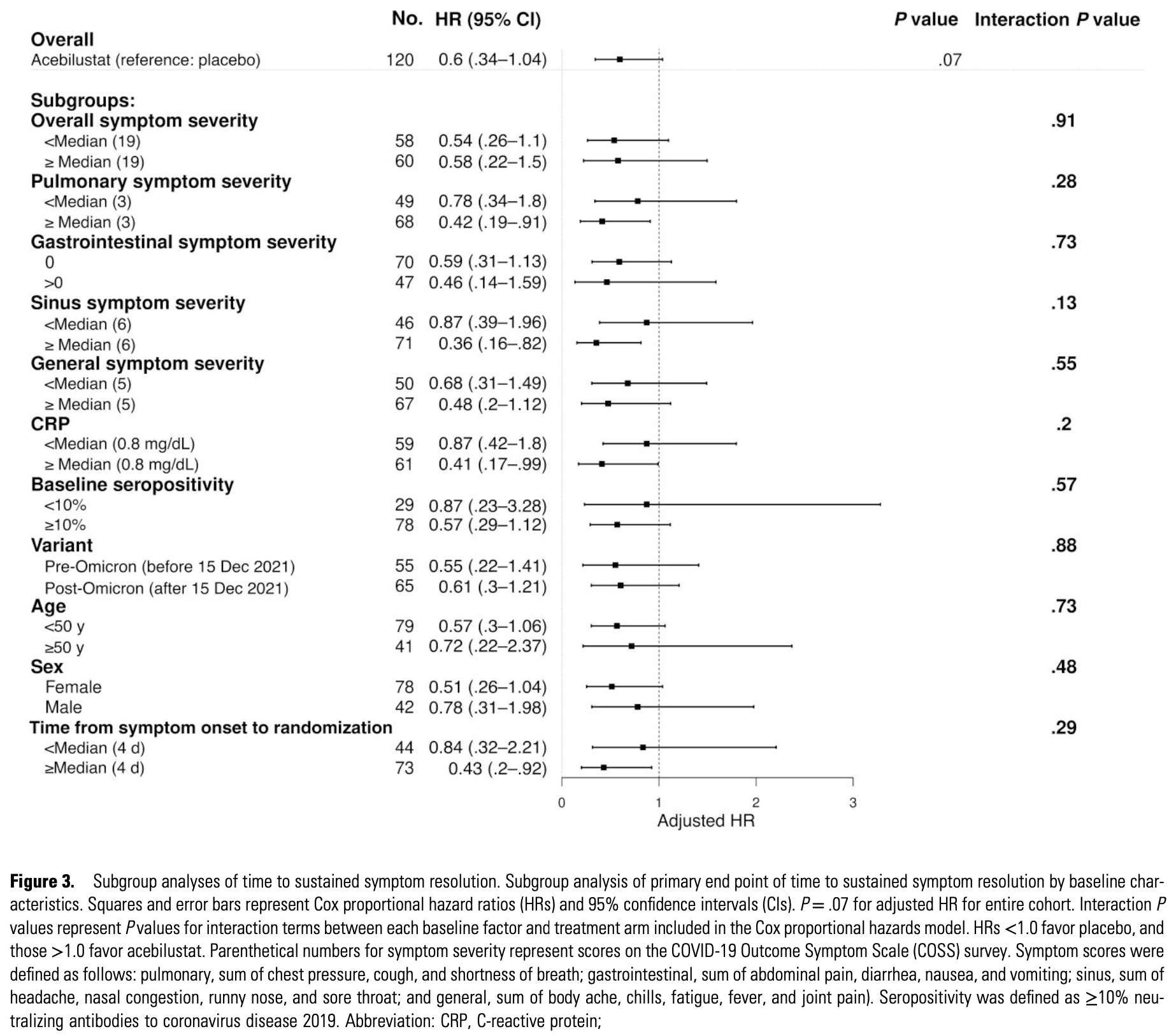
RCT 120 outpatients showing no significant difference in time to sustained symptom resolution or viral clearance with acebilustat treatment. Subgroup analyses showed consistent patterns of longer symptom duration in treated participants.
Standard of Care (SOC) for COVID-19 in the study country,
the USA, is very poor with very low average efficacy for approved treatments1.
Only expensive, high-profit treatments were approved for early treatment. Low-cost treatments were excluded, reducing the probability of early treatment due to access and cost barriers, and eliminating complementary and synergistic benefits seen with many low-cost treatments.
|
risk of hospitalization, no change, RR 1.00, p = 1.00, treatment 1 of 60 (1.7%), control 1 of 60 (1.7%).
|
|
ER visit, 80.0% lower, RR 0.20, p = 0.21, treatment 1 of 60 (1.7%), control 5 of 60 (8.3%), NNT 15.
|
|
sustained symptom resolution, 66.7% higher, HR 1.67, p = 0.07, treatment 60, control 60, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
first symptom resolution, 61.3% higher, HR 1.61, p = 0.05, treatment 60, control 60, adjusted per study, inverted to make HR<1 favor treatment, multivariable, Cox proportional hazards.
|
|
risk of no viral clearance, 5.9% lower, RR 0.94, treatment 60, control 60.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Levitt et al., 30 Mar 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, USA, peer-reviewed, median age 41.0, 20 authors, study period 22 April, 2021 - 5 April, 2022, average treatment delay 4.0 days, trial NCT04662060 (history).
Contact: jlevitt@stanford.edu.
Evaluation of Acebilustat, a Selective Inhibitor of Leukotriene B4 Biosynthesis, for Treatment of Outpatients With Mild-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial
Clinical Infectious Diseases, doi:10.1093/cid/ciad187
Background. The vast majority of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) disease occurs in outpatients where treatment is limited to antivirals for high-risk subgroups. Acebilustat, a leukotriene B4 inhibitor, has potential to reduce inflammation and symptom duration. Methods. In a single-center trial spanning Delta and Omicron variants, outpatients were randomized to 100 mg/d of oral acebilustat or placebo for 28 days. Patients reported daily symptoms via electronic query through day 28 with phone follow-up on day 120 and collected nasal swab samples on days 1-10. The primary outcome was sustained symptom resolution to day 28. Secondary 28-day outcomes included time to first symptom resolution, area under the curve (AUC) for longitudinal daily symptom scores, duration of viral shedding through day 10, and symptoms on day 120. Results. Sixty participants were randomized to each study arm. At enrollment, the median duration was 4 days (interquartile range, 3-5 days), and the median number of symptoms was 9 (7-11). Most patients (90%) were vaccinated, with 73% having neutralizing antibodies. A minority of participants (44%; 35% in the acebilustat arm and 53% in placebo) had sustained symptom resolution at day 28 (hazard ratio, 0.6 [95% confidence interval, .34-1.04]; P = .07 favoring placebo). There was no difference in the mean AUC for symptom scores over 28 days (difference in mean AUC, 9.4 [95% confidence interval, -42.1 to 60.9]; P = .72). Acebilustat did not affect viral shedding or symptoms at day 120. Conclusions. Sustained symptoms through day 28 were common in this low-risk population. Despite this, leukotriene B4 antagonism with acebilustat did not shorten symptom duration in outpatients with COVID-19. Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04662060.
Supplementary Data Supplementary materials are available at Clinical Infectious Diseases online. Consisting of data provided by the authors to benefit the reader, the posted materials are not copyedited and are the sole responsibility of the authors, so questions or comments should be addressed to the corresponding author.
Notes Acknowledgments. We
References
Askari, Sahebkar, Soleimani, The efficacy of curcumin-piperine cosupplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial, Trials
Auner, Geiger, Henrich, Lehnert, Marzi et al., Circulating leukotriene B4 identifies respiratory complications after trauma, Mediators Inflamm
Brennan, Nadella, Zhao, Oral famotidine versus placebo in nonhospitalised patients with COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, data-intense, phase 2 clinical trial, Gut
Bunning, Hedlin, Purington, The COVID-19 Outpatient Pragmatic Platform Study (COPPS): study design of a multi-center pragmatic platform trial, Contemp Clin Trials
Clemency, Varughese, Gonzalez-Rojas, Efficacy of inhaled ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of adolescents and adults with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA Intern Med
Duvignaud, Lhomme, Onaisi, Inhaled ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in adults at risk of adverse outcomes: a randomised controlled trial (COVERAGE), Clin Microbiol Infect
Elborn, Bhatt, Grosswald, Ahuja, Springman, Phase I studies of acebilustat: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, food effect, and CY:3A induction, Clin Transl Sci
Elborn, Horsley, Macgregor, Phase I studies of acebilustat: biomarker response and safety in patients with cystic fibrosis, Clin Transl Sci
Elborn, Konstan, Taylor-Cousar, Empire-CF study: a phase 2 clinical trial of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor acebilustat in adult subjects with cystic fibrosis, J Cyst Fibros
Ford-Hutchinson, Bray, Doig, Shipley, Smith, Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes, Nature
Goodarzi, Goodarzi, Tager, Luster, Von Andrian, Leukotriene B4 and BLT1 control cytotoxic effector T cell recruitment to inflamed tissues, Nat Immunol
Group, Rogers, Wentworth, The association of baseline plasma SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen level and outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19, Ann Intern Med
Group; Horby, Lim, Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Haeggstrom, Funk, Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease, Chem Rev
Han, Enas, Mcentegart, Randomization by minimization for unbalanced treatment allocation, Stat Med
Hinks, Cureton, Knight, Azithromycin versus standard care in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 (ATOMIC2): an open-label, randomised trial, Lancet Respir Med
Holubar, Subramanian, Purington, Favipiravir for treatment of outpatients with asymptomatic or uncomplicated coronavirus disease 2019: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial, Clin Infect Dis
Investigators, Gordon, Mouncey, Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Jagannathan, Andrews, Bonilla, Peginterferon lambda-1a for treatment of outpatients with uncomplicated COVID-19: a randomized placebocontrolled trial, Nat Commun
Kalil, Patterson, Mehta, Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19, N Engl J Med
Kuppalli, Rasmussen, A glimpse into the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm, EBioMedicine
Lenze, Mattar, Zorumski, Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Mccarthy, Naggie, Boulware, Fluvoxamine for outpatient treatment of COVID-19: a decentralized, placebo-controlled, randomized, platform clinical trial, doi:10.1101/2022.10.17.22281178
Monteiro, Pinheiro, Luna-Gomes, Leukotriene B4 mediates neutrophil migration induced by heme, J Immunol
Oldenburg, Pinsky, Brogdon, Effect of oral azithromycin vs placebo on COVID-19 symptoms in outpatients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomized clinical trial, JAMA
Partrick, Moore, Moore, Barnett, Jr et al., Neutrophil priming and activation in the pathogenesis of postinjury multiple organ failure, New Horiz
Peters-Golden, Leukotrienes, N Engl J Med
Ramakrishnan, Nicolau, Jr, Langford, Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial, Lancet Respir Med
Reis, Moreira-Silva, Silva, Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial, Lancet Glob Health
Roltgen, Powell, Wirz, Defining the features and duration of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with disease severity and outcome, Sci Immunol
Sahoo, Huang, Sibai, Solis, Pinsky, Harmonization of SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription quantitative PCR tests to the first WHO international standard for SARS-CoV-2 RNA, J Clin Virol
Sibai, Wang, Yeung, Development and evaluation of an RT-qPCR for the identification of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant, J Clin Virol
Stephenson, Lonigro, Hyers, Webster, Fowler, Increased concentrations of leukotrienes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with ARDS or at risk for ARDS, Am Rev Respir Dis
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, Allier, Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, doubleblinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial, Lancet Respir Med
Tian, Rockson, Jiang, Leukotriene B 4 antagonism ameliorates experimental lymphedema, Sci Transl Med
Wang, Miller, Verghese, Multiplex SARS-CoV-2 genotyping reverse transcriptase PCR for population-level variant screening and epidemiologic surveillance, J Clin Microbiol
Yeung, Wang, Sibai, Evaluation of a rapid and accessible reverse transcription-quantitative PCR approach for SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern identification, J Clin Microbiol
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciad187",
"ISSN": [
"1058-4838",
"1537-6591"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1093/cid/ciad187",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Background</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The vast majority of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) disease occurs in outpatients where treatment is limited to antivirals for high-risk subgroups. Acebilustat, a leukotriene B4 inhibitor, has potential to reduce inflammation and symptom duration.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Methods</jats:title>\n <jats:p>In a single-center trial spanning Delta and Omicron variants, outpatients were randomized to 100 mg/d of oral acebilustat or placebo for 28 days. Patients reported daily symptoms via electronic query through day 28 with phone follow-up on day 120 and collected nasal swab samples on days 1–10. The primary outcome was sustained symptom resolution to day 28. Secondary 28-day outcomes included time to first symptom resolution, area under the curve (AUC) for longitudinal daily symptom scores, duration of viral shedding through day 10, and symptoms on day 120.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Results</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Sixty participants were randomized to each study arm. At enrollment, the median duration was 4 days (interquartile range, 3–5 days), and the median number of symptoms was 9 (7–11). Most patients (90%) were vaccinated, with 73% having neutralizing antibodies. A minority of participants (44%; 35% in the acebilustat arm and 53% in placebo) had sustained symptom resolution at day 28 (hazard ratio, 0.6 [95% confidence interval, .34–1.04]; P = .07 favoring placebo). There was no difference in the mean AUC for symptom scores over 28 days (difference in mean AUC, 9.4 [95% confidence interval, −42.1 to 60.9]; P = .72). Acebilustat did not affect viral shedding or symptoms at day 120.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>\n <jats:sec>\n <jats:title>Conclusions</jats:title>\n <jats:p>Sustained symptoms through day 28 were common in this low-risk population. Despite this, leukotriene B4 antagonism with acebilustat did not shorten symptom duration in outpatients with COVID-19.</jats:p>\n <jats:p>Clinical Trials Registration. NCT04662060.</jats:p>\n </jats:sec>",
"author": [
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5316-4971",
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Levitt",
"given": "Joseph E",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantitative Sciences Unit, Division of Biomedical Informatics Research, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Hedlin",
"given": "Haley",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Center for Clinical Research , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Duong",
"given": "Sophie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantitative Sciences Unit, Division of Biomedical Informatics Research, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Lu",
"given": "Di",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantitative Sciences Unit, Division of Biomedical Informatics Research, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Justin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantitative Sciences Unit, Division of Biomedical Informatics Research, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bunning",
"given": "Bryan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Center for Clinical Research , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Elkarra",
"given": "Nadia",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Pathology Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
},
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Pinsky",
"given": "Benjamin A",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Celltaxis LLC , Atlanta, GA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Heffernan",
"given": "Eileen",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Celltaxis LLC , Atlanta, GA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Springman",
"given": "Eric",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pediatrics (Pulmonary Medicine), Center for Excellence in Pulmonary Biology, Department of Pediatrics, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Moss",
"given": "Richard B",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bonilla",
"given": "Hector F",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Medicine, Division of Infectious Diseases and Geographic Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Parsonnet",
"given": "Julie",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Zamanian",
"given": "Roham T",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Center for Clinical Research , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Langguth",
"given": "Jamison J",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Innovative Medicines Accelerator , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Bollyky",
"given": "Jenna",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Stanford Innovative Medicines Accelerator , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Khosla",
"given": "Chaitan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Nicolls",
"given": "Mark R",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Quantitative Sciences Unit, Division of Biomedical Informatics Research, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Desai",
"given": "Manisha",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Division of Pulmonary, Allergy, and Critical Medicine, Department of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine , Stanford, CA , USA"
}
],
"family": "Rogers",
"given": "Angela J",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Clinical Infectious Diseases",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-31T02:01:43Z",
"timestamp": 1680228103000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
9,
23
]
],
"date-time": "2023-09-23T04:12:58Z",
"timestamp": 1695442378000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100005492",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "Stanford University"
},
{
"name": "Celltaxis"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100016220",
"award": [
"UL1 TR003142"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "CTSA"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "NIH"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
12,
7
]
],
"date-time": "2023-12-07T08:37:20Z",
"timestamp": 1701938240401
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 1,
"issue": "2",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "2",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
26
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/pages/standard-publication-reuse-rights",
"content-version": "vor",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2023-03-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1680134400000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/advance-article-pdf/doi/10.1093/cid/ciad187/50310958/ciad187.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "am",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/77/2/186/51728055/ciad187.pdf",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "syndication"
},
{
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article-pdf/77/2/186/51728055/ciad187.pdf",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "286",
"original-title": [],
"page": "186-193",
"prefix": "10.1093",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
3,
30
]
]
},
"published-other": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
15
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
7,
26
]
]
},
"publisher": "Oxford University Press (OUP)",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2021436",
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with Covid-19",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "693",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B1",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1021/cr200246d",
"article-title": "Lipoxygenase and leukotriene pathways: biochemistry, biology, and roles in disease",
"author": "Haeggstrom",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5866",
"journal-title": "Chem Rev",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B2",
"volume": "111",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMra071371",
"article-title": "Leukotrienes",
"author": "Peters-Golden",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1841",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B3",
"volume": "357",
"year": "2007"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/286264a0",
"article-title": "Leukotriene B, a potent chemokinetic and aggregating substance released from polymorphonuclear leukocytes",
"author": "Ford-Hutchinson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "264",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B4",
"volume": "286",
"year": "1980"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/ni972",
"article-title": "Leukotriene B4 and BLT1 control cytotoxic effector T cell recruitment to inflamed tissues",
"author": "Goodarzi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "965",
"journal-title": "Nat Immunol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B5",
"volume": "4",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.4049/jimmunol.1002400",
"article-title": "Leukotriene B4 mediates neutrophil migration induced by heme",
"author": "Monteiro",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6562",
"journal-title": "J Immunol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B6",
"volume": "186",
"year": "2011"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1155/2012/536156",
"article-title": "Circulating leukotriene B4 identifies respiratory complications after trauma",
"author": "Auner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Mediators Inflamm",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B7",
"volume": "2012",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1164/ajrccm/138.3.714",
"article-title": "Increased concentrations of leukotrienes in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of patients with ARDS or at risk for ARDS",
"author": "Stephenson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "714",
"journal-title": "Am Rev Respir Dis",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B8",
"volume": "138",
"year": "1988"
},
{
"article-title": "Neutrophil priming and activation in the pathogenesis of postinjury multiple organ failure",
"author": "Partrick",
"first-page": "194",
"journal-title": "New Horiz",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B9",
"volume": "4",
"year": "1996"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102789",
"article-title": "A glimpse into the eye of the COVID-19 cytokine storm",
"author": "Kuppalli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B10",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12428",
"article-title": "Phase I studies of acebilustat: biomarker response and safety in patients with cystic fibrosis",
"author": "Elborn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "28",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B11",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcf.2021.08.007",
"article-title": "Empire-CF study: a phase 2 clinical trial of leukotriene A4 hydrolase inhibitor acebilustat in adult subjects with cystic fibrosis",
"author": "Elborn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1026",
"journal-title": "J Cyst Fibros",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B12",
"volume": "20",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/cts.12426",
"article-title": "Phase I studies of acebilustat: pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, food effect, and CY:3A induction",
"author": "Elborn",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "20",
"journal-title": "Clin Transl Sci",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B13",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cct.2021.106509",
"article-title": "The COVID-19 Outpatient Pragmatic Platform Study (COPPS): study design of a multi-center pragmatic platform trial",
"author": "Bunning",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Contemp Clin Trials",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B14",
"volume": "108",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/sim.3710",
"article-title": "Randomization by minimization for unbalanced treatment allocation",
"author": "Han",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "3329",
"journal-title": "Stat Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B15",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2009"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciimmunol.abe0240",
"article-title": "Defining the features and duration of antibody responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection associated with disease severity and outcome",
"author": "Roltgen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Immunol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B16",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105242",
"article-title": "Harmonization of SARS-CoV-2 reverse transcription quantitative PCR tests to the first WHO international standard for SARS-CoV-2 RNA",
"author": "Sahoo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B17",
"volume": "154",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105101",
"article-title": "Development and evaluation of an RT-qPCR for the identification of the SARS-CoV-2 omicron variant",
"author": "Sibai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Virol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B18",
"volume": "148",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/JCM.00859-21",
"article-title": "Multiplex SARS-CoV-2 genotyping reverse transcriptase PCR for population-level variant screening and epidemiologic surveillance",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B19",
"volume": "59",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1128/jcm.00178-22",
"article-title": "Evaluation of a rapid and accessible reverse transcription-quantitative PCR approach for SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern identification",
"author": "Yeung",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "J Clin Microbiol",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B20",
"volume": "60",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciac312",
"article-title": "Favipiravir for treatment of outpatients with asymptomatic or uncomplicated coronavirus disease 2019: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial",
"author": "Holubar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1883",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B21",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41467-021-22177-1",
"article-title": "Peginterferon lambda-1a for treatment of outpatients with uncomplicated COVID-19: a randomized placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Jagannathan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1967",
"journal-title": "Nat Commun",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B22",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00160-0",
"article-title": "Inhaled budesonide in the treatment of early COVID-19 (STOIC): a phase 2, open-label, randomised controlled trial",
"author": "Ramakrishnan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "763",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B23",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamainternmed.2021.6759",
"article-title": "Efficacy of inhaled ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of adolescents and adults with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Clemency",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "42",
"journal-title": "JAMA Intern Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B24",
"volume": "182",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cmi.2022.02.031",
"article-title": "Inhaled ciclesonide for outpatient treatment of COVID-19 in adults at risk of adverse outcomes: a randomised controlled trial (COVERAGE)",
"author": "Duvignaud",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"journal-title": "Clin Microbiol Infect",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B25",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.22760",
"article-title": "Fluvoxamine vs placebo and clinical deterioration in outpatients with symptomatic COVID-19: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Lenze",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2292",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B26",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2214-109X(21)00448-4",
"article-title": "Effect of early treatment with fluvoxamine on risk of emergency care and hospitalisation among patients with COVID-19: the TOGETHER randomised, platform clinical trial",
"author": "Reis",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e42",
"journal-title": "Lancet Glob Health",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B27",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "McCarthy",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B28",
"year": "1 2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00222-8",
"article-title": "Colchicine for community-treated patients with COVID-19 (COLCORONA): a phase 3, randomised, double-blinded, adaptive, placebo-controlled, multicentre trial",
"author": "Tardif",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B29",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00263-0",
"article-title": "Azithromycin versus standard care in patients with mild-to-moderate COVID-19 (ATOMIC2): an open-label, randomised trial",
"author": "Hinks",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1130",
"journal-title": "Lancet Respir Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B30",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2021.11517",
"article-title": "Effect of oral azithromycin vs placebo on COVID-19 symptoms in outpatients with SARS-CoV-2 infection: a randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Oldenburg",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "490",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B31",
"volume": "326",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2022-326952",
"article-title": "Oral famotidine versus placebo in non-hospitalised patients with COVID-19: a randomised, double-blind, data-intense, phase 2 clinical trial",
"author": "Brennan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "879",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B32",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13063-022-06375-w",
"article-title": "The efficacy of curcumin-piperine co-supplementation on clinical symptoms, duration, severity, and inflammatory factors in COVID-19 outpatients: a randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial",
"author": "Askari",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "472",
"journal-title": "Trials",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B33",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.aal3920",
"article-title": "Leukotriene B4 antagonism ameliorates experimental lymphedema",
"author": "Tian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Sci Transl Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B34",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00676-0",
"article-title": "Tocilizumab in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial",
"author": "RECOVERY Collaborative Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1637",
"journal-title": "Lancet",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B35",
"volume": "397",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2100433",
"article-title": "Interleukin-6 receptor antagonists in critically ill patients with Covid-19",
"author": "REMAP-CAP Investigators",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1491",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B36",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2031994",
"article-title": "Baricitinib plus remdesivir for hospitalized adults with Covid-19",
"author": "Kalil",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "795",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B37",
"volume": "384",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/M22-0924",
"article-title": "The association of baseline plasma SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antigen level and outcomes in patients hospitalized with COVID-19",
"author": "ACTIV-3/TICO Study Group",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1401",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2023092304121090100_ciad187-B38",
"volume": "175",
"year": "2022"
}
],
"reference-count": 38,
"references-count": 38,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://academic.oup.com/cid/article/77/2/186/7095671"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Evaluation of Acebilustat, a Selective Inhibitor of Leukotriene B4 Biosynthesis, for Treatment of Outpatients With Mild-Moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 2 Trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "77"
}