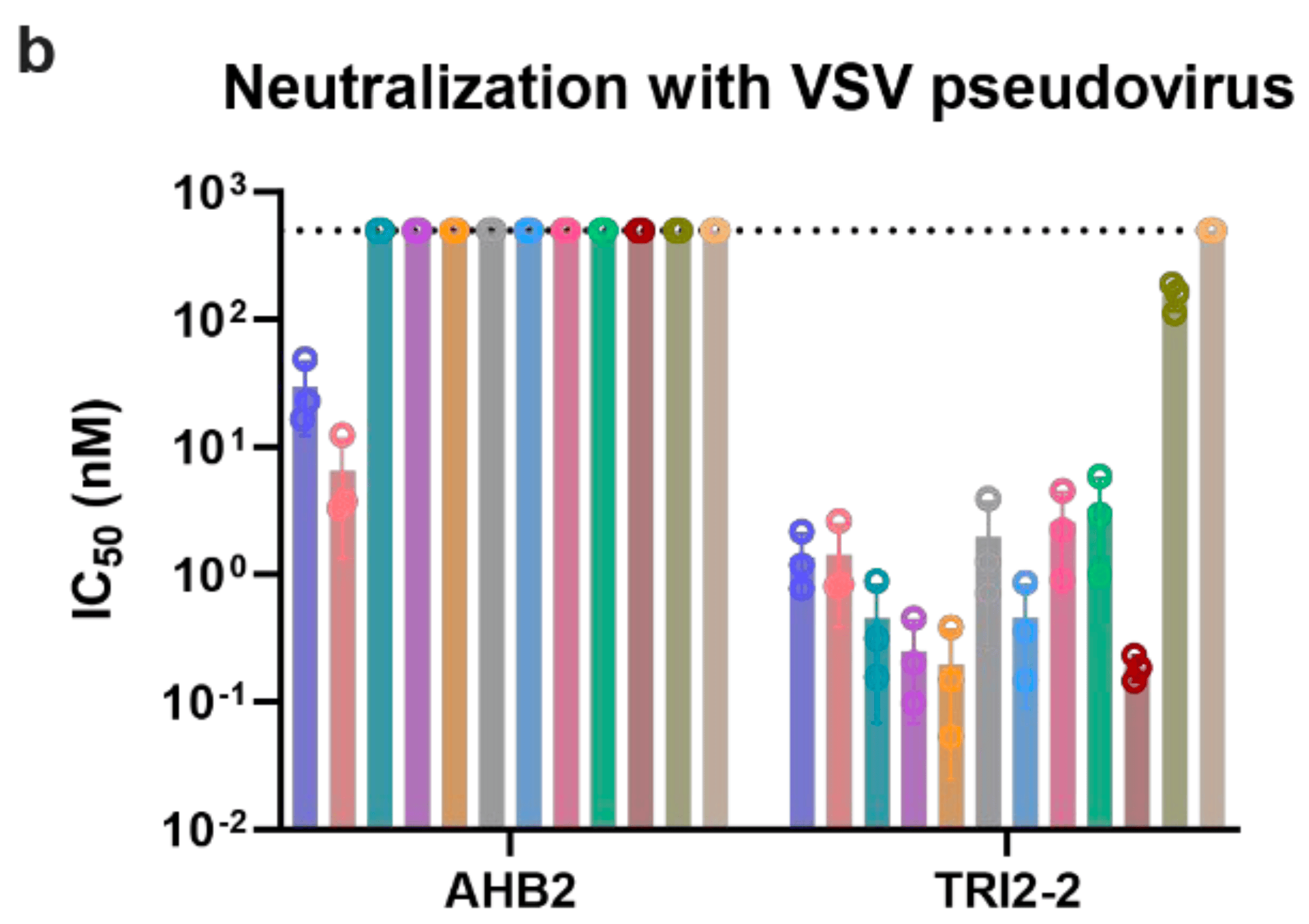
The computationally designed TRI2-2 miniprotein inhibitor protects against multiple SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
et al., Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-025-09499-2, Jan 2026
In vitro and mouse study showing broad neutralizing activity and protective efficacy with TRI2-2, a computationally-designed homotrimeric miniprotein inhibitor against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants.
Lee et al., 10 Jan 2026, USA, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
Contact: dveesler@uw.edu, mdiamond@wustl.edu.
The computationally designed TRI2-2 miniprotein inhibitor protects against multiple SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants
Communications Biology, doi:10.1038/s42003-025-09499-2
The continued evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has compromised neutralizing antibody responses elicited by prior infection or vaccination and abolished the utility of most monoclonal antibody therapeutics. We previously described a computationally-designed, homotrimeric miniprotein inhibitor, designated TRI2-2, that protects mice against pre-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we show that TRI2-2 exhibits broadly near pan-neutralizing activity of SARS-CoV-2 variants that evolved during the 5 years since the emergence of and protects mice against BQ.1.1, XBB.1.5 and BA.2.86 challenge when administered intranasally post-exposure. The resistance of TRI2-2 to viral escape by most variants and the ability to deliver it directly to the upper airways highlight the potential of the multivalent miniprotein inhibitor as an alternative therapeutic modality.
Competing interests J.B.C., Y.J.P., R.R., D.B., M.S.D. and D.V. are co-inventors on a patent application that incorporates discoveries described in this article (application no.: PCT/US2021/034069, title: SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors). M.S.D. is a consultant or advisor for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology, IntegerBio, Akagera Medicines, Moderna, Merck, and GlaxoSmithKline. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Vir Biotechnology, Moderna, Emergent BioSolutions, and IntegerBio. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Author Contributions J.L., J.B.C., M.S.D., and D.V. designed the experiments; R.R. recombinantly expressed and purified TRI2-2. L.C. provided reagents for the experiments. J.L. performed binding assays and neutralization assays. J.L. carried out fusion assays with help from M.A.T.. J.L. vitrified the specimen and carried out cryoEM data collection. J.L, and Y.J.P., processed the cryoEM data with help from D.A. and D.V.. J.L and D.V. built and refined the atomic models. J.B.C. carried out the mice challenge study with assistance from S.S.. J.L., J.B.C., and D.V. analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript with input from all authors; D.B., M.S.D., and D.V. supervised the project.
References
Bowen, Omicron spike function and neutralizing activity elicited by a comprehensive panel of vaccines, Science eabq
Bussani, Persistence of viral RNA, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology, EBioMedicine
Cameroni, Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift, Nature
Cao, De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors, Science
Cao, Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone, Nature
Cao, Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent Omicron RBD evolution, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-022-05644-7
Cao, Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents, Cell Rep
Chen, Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and
Crawford, Protocol and Reagents for Pseudotyping Lentiviral Particles with SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein for Neutralization Assays, Viruses
Dauparas, Robust deep learning-based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN, Science
De Vries, Intranasal fusion inhibitory lipopeptide prevents direct-contact SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets, Science
Hassan, A single intranasal dose of chimpanzee adenovirus-vectored vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques, Cell Rep Med
Hoffmann, SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor, Cell
Hunt, Multivalent designed proteins neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and confer protection against infection in mice, Sci. Transl. Med
Kodaka, A new cell-based assay to evaluate myogenesis in mouse myoblast C2C12 cells, Exp. Cell Res
Langel, Adenovirus type 5 SARS-CoV-2 vaccines delivered orally or intranasally reduced disease severity and transmission in a hamster model, Sci. Transl. Med. eabn
Letko, Marzi, Munster, Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses, Nat Microbiol
Mao, Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses, Science
Oh, Intranasal priming induces local lung-resident B cell populations that secrete protective mucosal antiviral IgA, Science Immunology
Pacesa, BindCraft: one-shot design of functional protein binders, bioRxivorg, doi:10.1101/2024.09.30.615802
Park, Imprinted antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages, Science eadc
Robert, Gouet, Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server, Nucleic Acids Res
Rosen, A potent pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody resilient to epitope diversification, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.026
Song, Post-exposure prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-SARS-COV-2 monoclonal antibody) nasal spray for the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in healthy adult workers: a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study, Emerg. Microbes Infect
Tang, Respiratory mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 after mRNA vaccination, Sci Immunol
Tegally, Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages BA.4 and BA.5 in South Africa, Nat. Med
Viana, Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in southern Africa, Nature, doi:10.1038/d41586-021-03832-5
Walls, SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections elicit potent, broad, and durable neutralizing antibody responses, Cell, doi:10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.011
Walls, Structure, Function, and Antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 Spike Glycoprotein, Cell
Watson, De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion, Nature
Winkler, SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function, Nat. Immunol
Ying, Author Correction: Mucosal vaccine-induced cross-reactive CD8+ T cells protect against SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5 respiratory tract infection, Nat. Immunol
Yisimayi, Repeated Omicron exposures override ancestral SARS-CoV-2 immune imprinting, Nature
Zambaldi, De novo design of high-affinity protein binders with AlphaProteo
Zhou, A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin, Nature, doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s42003-025-09499-2",
"ISSN": [
"2399-3642"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s42003-025-09499-2",
"abstract": "<jats:title>Abstract</jats:title>\n <jats:p>The continued evolution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) has compromised neutralizing antibody responses elicited by prior infection or vaccination and abolished the utility of most monoclonal antibody therapeutics. We previously described a computationally-designed, homotrimeric miniprotein inhibitor, designated TRI2-2, that protects mice against pre-Omicron SARS-CoV-2 variants. Here, we show that TRI2-2 exhibits broadly neutralizing activity of SARS-CoV-2 variants and protects mice against BQ.1.1, XBB.1.5 and BA.2.86 challenge when administered intranasally post-exposure. The resistance of TRI2-2 to viral escape by most variants and the ability to deliver it directly to the upper airways highlight the potential of the multivalent miniprotein inhibitor as an alternative therapeutic modality.</jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"9499"
],
"assertion": [
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Received",
"name": "received",
"order": 1,
"value": "4 March 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "Accepted",
"name": "accepted",
"order": 2,
"value": "29 December 2025"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Article History",
"name": "ArticleHistory"
},
"label": "First Online",
"name": "first_online",
"order": 3,
"value": "10 January 2026"
},
{
"group": {
"label": "Competing interests",
"name": "EthicsHeading"
},
"name": "Ethics",
"order": 1,
"value": "J.B.C., Y.J.P., R.R., D.B., M.S.D., and D.V. are co-inventors on a patent application that incorporates discoveries described in this article (application no.: PCT/US2021/034069, title: SARS-CoV-2 inhibitors). M.S.D. is a consultant or advisor for Inbios, Vir Biotechnology, IntegerBio, Akagera Medicines, Moderna, Merck, and GlaxoSmithKline. The Diamond laboratory has received unrelated funding support in sponsored research agreements from Vir Biotechnology, Moderna, Emergent BioSolutions, and IntegerBio. All other authors declare no competing interests."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Jimin",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7331-5511",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Case",
"given": "James Brett",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0003-2901-6949",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Park",
"given": "Young-Jun",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ravichandran",
"given": "Rashmi",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7870-5308",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Asarnow",
"given": "Daniel",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-2260-2577",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Tortorici",
"given": "M. Alejandra",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Brown",
"given": "Jack T.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sanapala",
"given": "Shilpa",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Carter",
"given": "Lauren",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0001-7896-6217",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Baker",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-8791-3165",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Diamond",
"given": "Michael S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "https://orcid.org/0000-0002-6019-8675",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Veesler",
"given": "David",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Communications Biology",
"container-title-short": "Commun Biol",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": [
"link.springer.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T22:13:17Z",
"timestamp": 1768083197000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T22:13:23Z",
"timestamp": 1768083203000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000011",
"award": [
"N/A"
],
"award-info": [
{
"award-number": [
"N/A"
]
}
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": [
{
"asserted-by": "publisher",
"id": "10.13039/100000011",
"id-type": "DOI"
}
],
"name": "Howard Hughes Medical Institute"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
11
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-11T22:22:57Z",
"timestamp": 1768170177631,
"version": "3.49.0"
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768003200000
}
},
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "am",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
],
"date-time": "2026-01-10T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1768003200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-09499-2",
"content-type": "text/html",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "297",
"original-title": [],
"prefix": "10.1038",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2026,
1,
10
]
]
},
"publisher": "Springer Science and Business Media LLC",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.058",
"author": "AC Walls",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "281",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "9499_CR1",
"unstructured": "Walls, A. C. et al. Structure, function, and antigenicity of the SARS-CoV-2 spike glycoprotein. Cell 181, 281–292.e6 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9499_CR2",
"unstructured": "Zhou, P. et al. A pneumonia outbreak associated with a new coronavirus of probable bat origin. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2012-7 (2020)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"author": "M Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "9499_CR3",
"unstructured": "Hoffmann, M. et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 181, 271–280.e8 (2020).",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41564-020-0688-y",
"author": "M Letko",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "562",
"journal-title": "Nat. Microbiol.",
"key": "9499_CR4",
"unstructured": "Letko, M., Marzi, A. & Munster, V. Functional assessment of cell entry and receptor usage for SARS-CoV-2 and other lineage B betacoronaviruses. Nat. Microbiol. 5, 562–569 (2020).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.011",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9499_CR5",
"unstructured": "Walls, A. C. et al. SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infections elicit potent, broad, and durable neutralizing antibody responses. Cell https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2022.01.011. (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abq0203",
"author": "JE Bowen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "890",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR6",
"unstructured": "Bowen, J. E. et al. Omicron spike function and neutralizing activity elicited by a comprehensive panel of vaccines. Science 377, 890–894 (2022).",
"volume": "377",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-021-04386-2",
"author": "E Cameroni",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "664",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR7",
"unstructured": "Cameroni, E. et al. Broadly neutralizing antibodies overcome SARS-CoV-2 Omicron antigenic shift. Nature 602, 664–670 (2022).",
"volume": "602",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/d41586-021-03832-5",
"author": "R Viana",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR8",
"unstructured": "Viana, R. et al. Rapid epidemic expansion of the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant in southern Africa. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-021-03832-5 (2022).",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-022-01911-2",
"author": "H Tegally",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1785",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "9499_CR9",
"unstructured": "Tegally, H. et al. Emergence of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron lineages BA.4 and BA.5 in South Africa. Nat. Med. 28, 1785–1790 (2022).",
"volume": "28",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-05644-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9499_CR10",
"unstructured": "Cao, Y. et al. Imprinted SARS-CoV-2 humoral immunity induces convergent Omicron RBD evolution. Nature https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05644-7 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abd9909",
"author": "L Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "426",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR11",
"unstructured": "Cao, L. et al. De novo design of picomolar SARS-CoV-2 miniprotein inhibitors. Science 370, 426–431 (2020).",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"key": "9499_CR12",
"unstructured": "Hunt, A. C. et al. Multivalent designed proteins neutralize SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern and confer protection against infection in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 14, eabn1252 (2022)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.3390/v12050513",
"author": "KHD Crawford",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "513",
"journal-title": "Viruses",
"key": "9499_CR13",
"unstructured": "Crawford, K. H. D. et al. Protocol and reagents for pseudotyping lentiviral particles with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein for neutralization assays. Viruses 12, 513 (2020).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.yexcr.2015.06.015",
"author": "M Kodaka",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "171",
"journal-title": "Exp. Cell Res.",
"key": "9499_CR14",
"unstructured": "Kodaka, M. et al. A new cell-based assay to evaluate myogenesis in mouse myoblast C2C12 cells. Exp. Cell Res. 336, 171–181 (2015).",
"volume": "336",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.103104",
"author": "R Bussani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "EBioMedicine",
"key": "9499_CR15",
"unstructured": "Bussani, R. et al. Persistence of viral RNA, pneumocyte syncytia and thrombosis are hallmarks of advanced COVID-19 pathology. EBioMedicine 61, 103104 (2020).",
"volume": "61",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-020-0778-2",
"author": "ES Winkler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1327",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "9499_CR16",
"unstructured": "Winkler, E. S. et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection of human ACE2-transgenic mice causes severe lung inflammation and impaired function. Nat. Immunol. 21, 1327–1335 (2020).",
"volume": "21",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-022-04654-9",
"author": "L Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "551",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR17",
"unstructured": "Cao, L. et al. Design of protein-binding proteins from the target structure alone. Nature 605, 551–560 (2022).",
"volume": "605",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.adc9127",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9499_CR18",
"unstructured": "Park, Y.-J. et al. Imprinted antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages. Science 378, 619–627 (2022)."
},
{
"author": "J Tang",
"journal-title": "Sci. Immunol.",
"key": "9499_CR19",
"unstructured": "Tang, J. et al. Respiratory mucosal immunity against SARS-CoV-2 after mRNA vaccination. Sci. Immunol. 7, eadd4853 (2022).",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06753-7",
"author": "A Yisimayi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "148",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR20",
"unstructured": "Yisimayi, A. et al. Repeated Omicron exposures override ancestral SARS-CoV-2 immune imprinting. Nature 625, 148–156 (2024).",
"volume": "625",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"author": "T Mao",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR21",
"unstructured": "Mao, T. et al. Unadjuvanted intranasal spike vaccine elicits protective mucosal immunity against sarbecoviruses. Science 378, eabo2523 (2022).",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"author": "JE Oh",
"journal-title": "Sci. Immunol.",
"key": "9499_CR22",
"unstructured": "Oh, J. E. et al. Intranasal priming induces local lung-resident B cell populations that secrete protective mucosal antiviral IgA. Sci. Immunol. 6, eabj5129 (2021).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/scitranslmed.abn6868",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9499_CR23",
"unstructured": "Langel, S. N. et al. Adenovirus type 5 SARS-CoV-2 vaccines delivered orally or intranasally reduced disease severity and transmission in a hamster model. Sci. Transl. Med. 14, eabn6868 (2022)."
},
{
"author": "AO Hassan",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep. Med.",
"key": "9499_CR24",
"unstructured": "Hassan, A. O. et al. A single intranasal dose of chimpanzee adenovirus-vectored vaccine protects against SARS-CoV-2 infection in rhesus macaques. Cell Rep. Med. 2, 100230 (2021).",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41590-024-01781-5",
"author": "B Ying",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "578",
"journal-title": "Nat. Immunol.",
"key": "9499_CR25",
"unstructured": "Ying, B. et al. Author correction: mucosal vaccine-induced cross-reactive CD8+ T cells protect against SARS-CoV-2 XBB.1.5 respiratory tract infection. Nat. Immunol. 25, 578 (2024).",
"volume": "25",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.abf4896",
"author": "RD de Vries",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1379",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR26",
"unstructured": "de Vries, R. D. et al. Intranasal fusion inhibitory lipopeptide prevents direct-contact SARS-CoV-2 transmission in ferrets. Science 371, 1379–1382 (2021).",
"volume": "371",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"author": "R Song",
"journal-title": "Emerg. Microbes Infect.",
"key": "9499_CR27",
"unstructured": "Song, R. et al. Post-exposure prophylaxis with SA58 (anti-SARS-COV-2 monoclonal antibody) nasal spray for the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19 in healthy adult workers: a randomized, single-blind, placebo-controlled clinical study. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 12, 2212806 (2023).",
"volume": "12",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.026",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9499_CR28",
"unstructured": "Rosen, L. E. et al. A potent pan-sarbecovirus neutralizing antibody resilient to epitope diversification. Cell https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.09.026 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.celrep.2022.111845",
"author": "Y Cao",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "111845",
"journal-title": "Cell Rep.",
"key": "9499_CR29",
"unstructured": "Cao, Y. et al. Rational identification of potent and broad sarbecovirus-neutralizing antibody cocktails from SARS convalescents. Cell Rep. 41, 111845 (2022).",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-023-06415-8",
"author": "JL Watson",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1089",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR30",
"unstructured": "Watson, J. L. et al. De novo design of protein structure and function with RFdiffusion. Nature 620, 1089–1100 (2023).",
"volume": "620",
"year": "2023"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-025-09429-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"key": "9499_CR31",
"unstructured": "Pacesa, M. et al. One-shot design of functional protein binders with BindCraft. Nature 646, 483–492 (2025)."
},
{
"key": "9499_CR32",
"unstructured": "Zambaldi, V. et al. De novo design of high-affinity protein binders with AlphaProteo. Preprint at https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.08022 (2024)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.add2187",
"author": "J Dauparas",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "49",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR33",
"unstructured": "Dauparas, J. et al. Robust deep learning–based protein sequence design using ProteinMPNN. Science 378, 49–56 (2022).",
"volume": "378",
"year": "2022"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41591-021-01294-w",
"author": "RE Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "717",
"journal-title": "Nat. Med.",
"key": "9499_CR34",
"unstructured": "Chen, R. E. et al. Resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants to neutralization by monoclonal and serum-derived polyclonal antibodies. Nat. Med. 27, 717–726 (2021).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/science.1259530",
"author": "CJ Russo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1377",
"journal-title": "Science",
"key": "9499_CR35",
"unstructured": "Russo, C. J. & Passmore, L. A. Electron microscopy: ultrastable gold substrates for electron cryomicroscopy. Science 346, 1377–1380 (2014).",
"volume": "346",
"year": "2014"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jsb.2005.07.007",
"author": "DN Mastronarde",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "36",
"journal-title": "J. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "9499_CR36",
"unstructured": "Mastronarde, D. N. Automated electron microscope tomography using robust prediction of specimen movements. J. Struct. Biol. 152, 36–51 (2005).",
"volume": "152",
"year": "2005"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nmeth.4169",
"author": "A Punjani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "290",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "9499_CR37",
"unstructured": "Punjani, A., Rubinstein, J. L., Fleet, D. J. & Brubaker, M. A. cryoSPARC: algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat. Methods 14, 290–296 (2017).",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-019-0575-8",
"author": "T Bepler",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1153",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "9499_CR38",
"unstructured": "Bepler, T. et al. Positive-unlabeled convolutional neural networks for particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs. Nat. Methods 16, 1153–1160 (2019).",
"volume": "16",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41592-020-00990-8",
"author": "A Punjani",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1214",
"journal-title": "Nat. Methods",
"key": "9499_CR39",
"unstructured": "Punjani, A., Zhang, H. & Fleet, D. J. Non-uniform refinement: adaptive regularization improves single-particle cryo-EM reconstruction. Nat. Methods 17, 1214–1221 (2020).",
"volume": "17",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.5281/zenodo.3576629",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "9499_CR40",
"unstructured": "Asarnow, D., Palovcak, E. & Cheng, Y. UCSF pyem v0.5. Zenodo https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.3576629 (2019)."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S205225251801463X",
"author": "J Zivanov",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "5",
"journal-title": "IUCrJ",
"key": "9499_CR41",
"unstructured": "Zivanov, J., Nakane, T. & Scheres, S. H. W. A Bayesian approach to beam-induced motion correction in cryo-EM single-particle analysis. IUCrJ 6, 5–17 (2019).",
"volume": "6",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jmb.2003.07.013",
"author": "PB Rosenthal",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "721",
"journal-title": "J. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "9499_CR42",
"unstructured": "Rosenthal, P. B. & Henderson, R. Optimal determination of particle orientation, absolute hand, and contrast loss in single-particle electron cryomicroscopy. J. Mol. Biol. 333, 721–745 (2003).",
"volume": "333",
"year": "2003"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.ultramic.2013.06.004",
"author": "S Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "24",
"journal-title": "Ultramicroscopy",
"key": "9499_CR43",
"unstructured": "Chen, S. et al. High-resolution noise substitution to measure overfitting and validate resolution in 3D structure determination by single particle electron cryomicroscopy. Ultramicroscopy 135, 24–35 (2013).",
"volume": "135",
"year": "2013"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41586-024-07215-4",
"author": "K Jamali",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "450",
"journal-title": "Nature",
"key": "9499_CR44",
"unstructured": "Jamali, K. et al. Automated model building and protein identification in cryo-EM maps. Nature 628, 450–457 (2024).",
"volume": "628",
"year": "2024"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.str.2018.09.006",
"author": "B Frenz",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "134",
"journal-title": "Structure",
"key": "9499_CR45",
"unstructured": "Frenz, B. et al. Automatically fixing errors in glycoprotein structures with Rosetta. Structure 27, 134–139.e3 (2019).",
"volume": "27",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7554/eLife.17219",
"author": "RY Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e17219",
"journal-title": "Elife",
"key": "9499_CR46",
"unstructured": "Wang, R. Y. Automated structure refinement of macromolecular assemblies from cryo-EM maps using Rosetta. Elife 5, e17219 (2016).",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2016"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S2059798319011471",
"author": "D Liebschner",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "861",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol.",
"key": "9499_CR47",
"unstructured": "Liebschner, D. et al. Macromolecular structure determination using X-rays, neutrons and electrons: recent developments in Phenix. Acta Crystallogr. D. Struct. Biol. 75, 861–877 (2019).",
"volume": "75",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1107/S0907444909042073",
"author": "VB Chen",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "12",
"journal-title": "Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr.",
"key": "9499_CR48",
"unstructured": "Chen, V. B. et al. MolProbity: all-atom structure validation for macromolecular crystallography. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 66, 12–21 (2010).",
"volume": "66",
"year": "2010"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/nsmb.3115",
"author": "J Agirre",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "833",
"journal-title": "Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol.",
"key": "9499_CR49",
"unstructured": "Agirre, J. et al. Privateer: software for the conformational validation of carbohydrate structures. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 22, 833–834 (2015).",
"volume": "22",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virol.2020.05.015",
"author": "JB Case",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "39",
"journal-title": "Virology",
"key": "9499_CR50",
"unstructured": "Case, J. B., Bailey, A. L., Kim, A. S., Chen, R. E. & Diamond, M. S. Growth, detection, quantification, and inactivation of SARS-CoV-2. Virology 548, 39–48 (2020).",
"volume": "548",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/nar/gku316",
"author": "X Robert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "W320",
"journal-title": "Nucleic Acids Res.",
"key": "9499_CR51",
"unstructured": "Robert, X. & Gouet, P. Deciphering key features in protein structures with the new ENDscript server. Nucleic Acids Res. 42, W320–W324 (2014).",
"volume": "42",
"year": "2014"
}
],
"reference-count": 51,
"references-count": 51,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://www.nature.com/articles/s42003-025-09499-2"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The computationally designed TRI2-2 miniprotein inhibitor protects against multiple SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variants",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "https://doi.org/10.1007/springer_crossmark_policy"
}