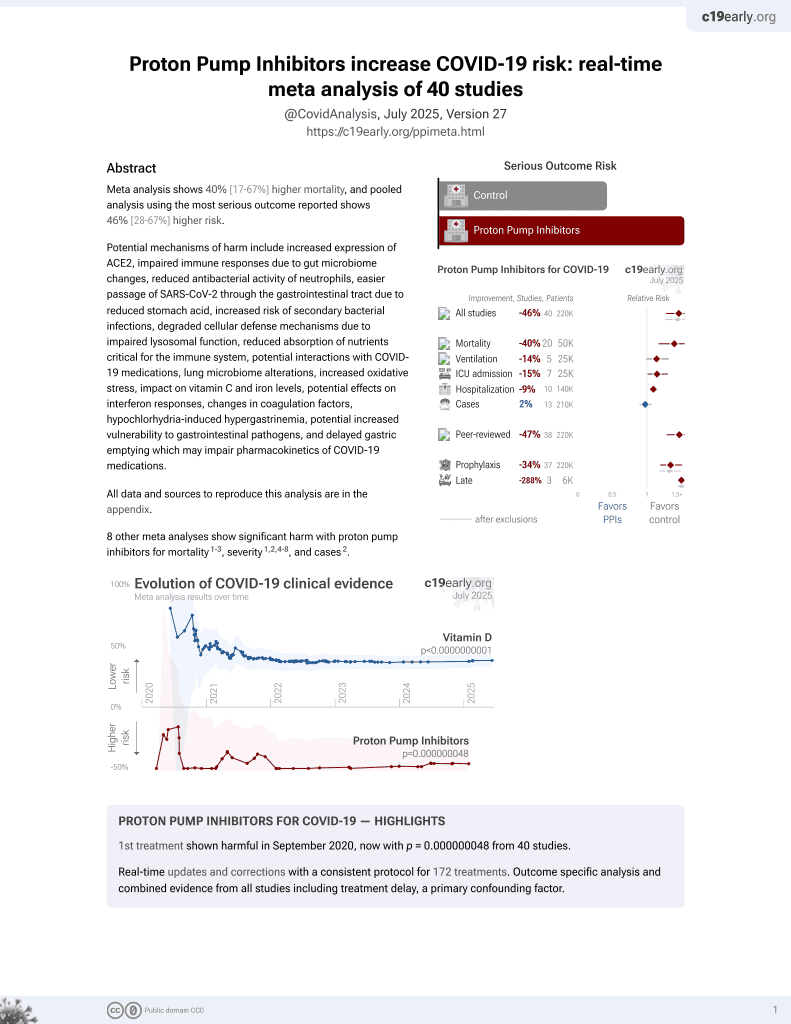
Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching
et al., Gut, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248, Jul 2020
PPIs for COVID-19
1st treatment shown to increase risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.000000048 from 40 studies.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
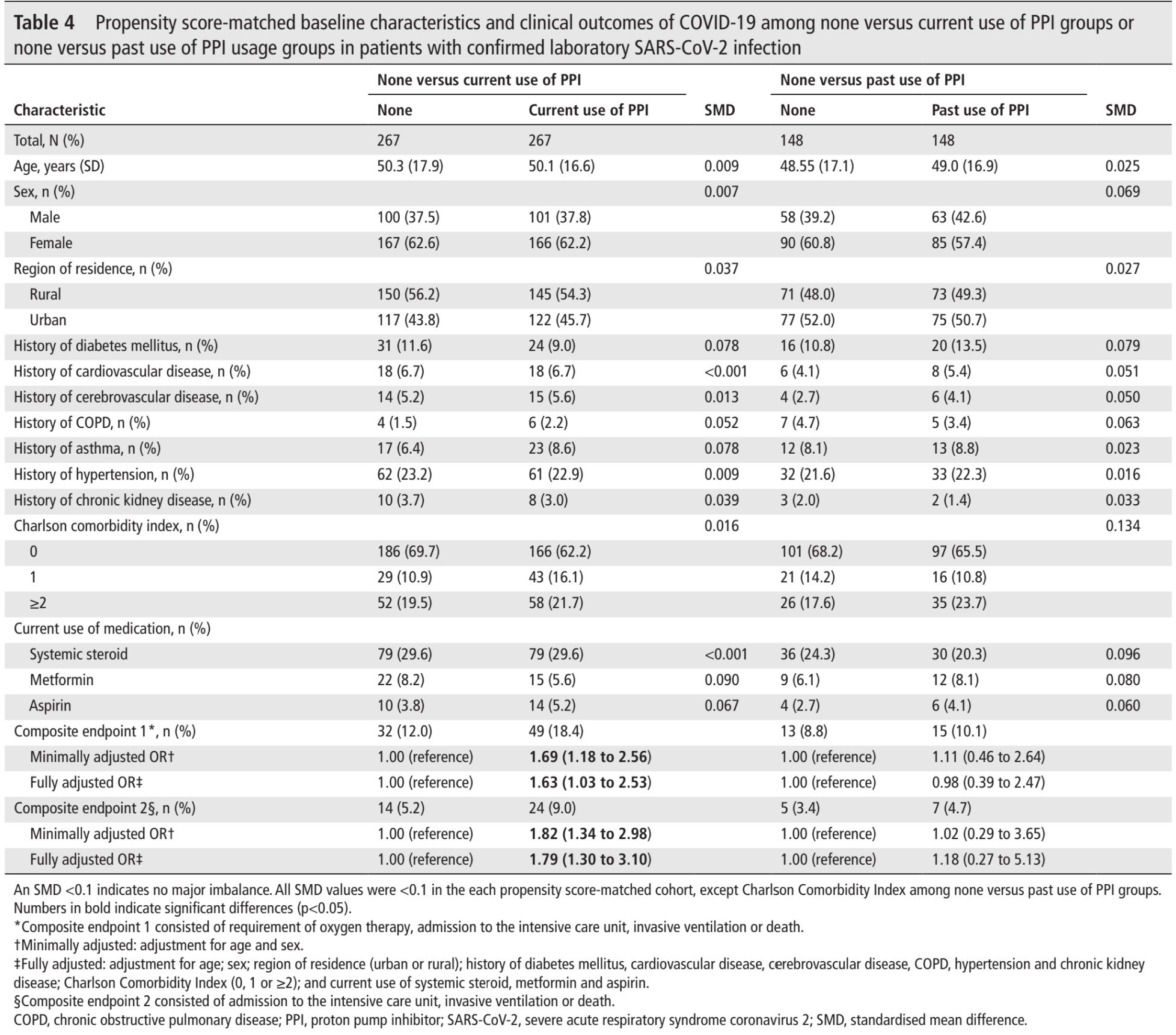
PSM retrospective 132,316 patients in South Korea, showing significantly higher risk of severe COVID-19 with PPI use, but no significant difference in cases.
|
risk of severe case, 79.0% higher, OR 1.79, p = 0.009, treatment 267, control 267, adjusted per study, ICU, mechanical ventilation, death, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of severe case, 63.0% higher, OR 1.63, p = 0.03, treatment 267, control 267, adjusted per study, oxygen, ICU, mechanical ventilation, death, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 10.0% lower, OR 0.90, p = 0.11, treatment 13,873, control 13,873, adjusted per study, propensity score matching, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Lee et al., 30 Jul 2020, retrospective, South Korea, peer-reviewed, 12 authors, study period 1 January, 2020 - 15 May, 2020.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"ISSN": [
"0017-5749",
"1468-3288"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"abstract": "<jats:sec><jats:title>Objective</jats:title><jats:p>The adverse effects of proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) have been documented for pneumonia; however, there is no consensus regarding whether the use of PPIs might be harmful regarding the risk of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection. In this regard, we aimed to measure the potential associations of the current use of PPIs with the infection rates of COVID-19 among patients who underwent SARS-CoV-2 testing.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Design</jats:title><jats:p>Data were derived from a Korean nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching. We included 132 316 patients older than 18 years who tested for SARS-CoV-2 between 1 January and 15 May 2020. Endpoints were SARS-CoV-2 positivity (primary) and severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 (secondary: admission to intensive care unit, administration of invasive ventilation or death).</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Results</jats:title><jats:p>In the entire cohort, there were 111 911 non-users, 14 163 current PPI users and 6242 past PPI users. After propensity score matching, the SARS-CoV-2 test positivity rate was not associated with the current or past use of PPIs. Among patients with confirmed COVID-19, the current use of PPIs conferred a 79% greater risk of severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19, while the relationship with the past use of PPIs remained insignificant. Current PPI use starting within the previous 30 days was associated with a 90% increased risk of severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19.</jats:p></jats:sec><jats:sec><jats:title>Conclusion</jats:title><jats:p>Patients taking PPIs are at increased risk for severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 but not susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection. This suggests that physicians need to assess benefit–risk assessments in the management of acid-related diseases amid the COVID-19 pandemic.</jats:p></jats:sec>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lee",
"given": "Seung Won",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ha",
"given": "Eun Kyo",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yeniova",
"given": "Abdullah Özgür",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "Sung Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kim",
"given": "So Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Koh",
"given": "Hyun Yong",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yang",
"given": "Jee Myung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jeong",
"given": "Su Jin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Moon",
"given": "Sun Joon",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cho",
"given": "Joo Young",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Yoo",
"given": "In Kyung",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"ORCID": "http://orcid.org/0000-0003-1628-9948",
"affiliation": [],
"authenticated-orcid": false,
"family": "Yon",
"given": "Dong Keon",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Gut",
"container-title-short": "Gut",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"bmj.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-30T21:33:51Z",
"timestamp": 1596144831000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
11,
5
]
],
"date-time": "2022-11-05T06:34:13Z",
"timestamp": 1667630053000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100003725",
"award": [
"NRF2019R1G1A109977912"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"name": "National Research Foundation of Korea"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2024,
7,
19
]
],
"date-time": "2024-07-19T14:27:08Z",
"timestamp": 1721399228595
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 163,
"issue": "1",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
30
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "1",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
12,
9
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://bmj.com/coronavirus/usage",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
30
]
],
"date-time": "2020-07-30T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1596067200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://syndication.highwire.org/content/doi/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "239",
"original-title": [],
"page": "76-84",
"prefix": "10.1136",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
30
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2020,
7,
30
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
1
]
]
},
"publisher": "BMJ",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.5394",
"article-title": "Baseline characteristics and outcomes of 1591 patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 admitted to ICUs of the Lombardy region, Italy",
"author": "Grasselli",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1574",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.1",
"volume": "323",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3345/cep.2020.00493",
"article-title": "Epidemiology, virology, and clinical features of severe acute respiratory syndrome -coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2; coronavirus Disease-19)",
"author": "Park",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "119",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pediatr",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.2",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1183/13993003.00547-2020",
"article-title": "Comorbidity and its impact on 1590 patients with COVID-19 in China: a nationwide analysis",
"author": "Guan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2000547",
"journal-title": "Eur Respir J",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.3",
"volume": "55",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3345/cep.2020.00535",
"article-title": "Epidemiology and clinical features of coronavirus disease 2019 in children",
"author": "Choi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "125",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pediatr",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.4",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1093/cid/ciaa415",
"article-title": "Obesity in patients younger than 60 years is a risk factor for Covid-19 hospital admission",
"author": "Lighter",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.5",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0422",
"article-title": "Patients with cancer appear more vulnerable to SARS-CoV-2: a multicenter study during the COVID-19 outbreak",
"author": "Dai",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "783",
"journal-title": "Cancer Discov",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.6",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2352-3018(20)30111-9",
"article-title": "COVID-19 in patients with HIV: clinical case series",
"author": "Blanco",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e314",
"journal-title": "Lancet HIV",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.7",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2008975",
"article-title": "Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of Covid-19",
"author": "Reynolds",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2441",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.8",
"volume": "382",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.l1580",
"article-title": "Estimates of all cause mortality and cause specific mortality associated with proton pump inhibitors among US veterans: cohort study",
"author": "Xie",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "l1580",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.9",
"volume": "365",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1053/j.gastro.2019.10.023",
"article-title": "Interpreting reported risks associated with use of proton pump inhibitors: residual confounding in a 10-year analysis of national ambulatory data",
"author": "Ma",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "780",
"journal-title": "Gastroenterology",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.10",
"volume": "158",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Effects of daily treatment with acid suppressants for stress ulcer prophylaxis on risk of ventilator-associated events",
"author": "Li",
"first-page": "187",
"journal-title": "Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.11",
"volume": "41",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Incidence of cancer after asthma development: 2 independent population-based cohort studies",
"author": "Woo",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.12",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1111/pai.13233",
"article-title": "Exposure to humidifier disinfectants is associated with upper and lower airway diseases",
"author": "Yon",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Pediatr Allergy Immunol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.13",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3345/cep.2019.01291",
"article-title": "Ten-Year trends and prevalence of asthma, allergic rhinitis, and atopic dermatitis among the Korean population, 2008-2017",
"author": "Ha",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Clin Exp Pediatr",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.14",
"volume": "63",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jaip.2019.05.015",
"article-title": "Serum heavy metal levels are associated with asthma, allergic rhinitis, atopic dermatitis, allergic multimorbidity, and airflow obstruction",
"author": "Koh",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "2912",
"journal-title": "J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.15",
"volume": "7",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"article-title": "Association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors with COVID-19-related outcomes in Korea: a nationwide population-based cohort study",
"author": "Jung",
"journal-title": "Clin Infect Dis",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.16",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.7326/0003-4819-149-6-200809160-00005",
"article-title": "Proton-Pump inhibitor use and the risk for community-acquired pneumonia",
"author": "Sarkar",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "391",
"journal-title": "Ann Intern Med",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.17",
"volume": "149",
"year": "2008"
},
{
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.18",
"unstructured": "Mehta N , Kalra A , Nowacki AS , et al . Association of use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin II receptor blockers with testing positive for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA cardiology."
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.292.16.1955",
"article-title": "Risk of community-acquired pneumonia and use of gastric acid-suppressive drugs",
"author": "Laheij",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1955",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.19",
"volume": "292",
"year": "2004"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3748/wjg.v23.i35.6500",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors therapy and risk of Clostridium difficile infection: systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Trifan",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "6500",
"journal-title": "World J Gastroenterol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.20",
"volume": "23",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1080/14740338.2019.1577820",
"article-title": "Proton pump inhibitors therapy and the risk of pneumonia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials and observational studies",
"author": "Wang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "163",
"journal-title": "Expert Opin Drug Saf",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.21",
"volume": "18",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1124/pr.118.017129",
"article-title": "Novel therapeutic approaches targeting the renin-angiotensin system and associated peptides in hypertension and heart failure",
"author": "Arendse",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "539",
"journal-title": "Pharmacol Rev",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.22",
"volume": "71",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321388",
"article-title": "Faecal calprotectin indicates intestinal inflammation in COVID-19",
"author": "Effenberger",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1543",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.23",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-320953",
"article-title": "Digestive system is a potential route of COVID-19: an analysis of single-cell coexpression pattern of key proteins in viral entry process",
"author": "Zhang",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1010",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.24",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/gutjnl-2020-321013",
"article-title": "Gastrointestinal symptoms of 95 cases with SARS-CoV-2 infection",
"author": "Lin",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "997",
"journal-title": "Gut",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.25",
"volume": "69",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052",
"article-title": "SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor",
"author": "Hoffmann",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "271",
"journal-title": "Cell",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.26",
"volume": "181",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30092-8",
"article-title": "Preventing COVID-19-induced pneumonia with anticytokine therapy",
"author": "Monteleone",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e255",
"journal-title": "Lancet Rheumatol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.27",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1126/sciadv.aao4966",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.28"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0128004",
"article-title": "Risk of community-acquired pneumonia with outpatient proton-pump inhibitor therapy: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Lambert",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "PLoS One",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.29",
"volume": "10",
"year": "2015"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1586/ecp.12.20",
"article-title": "Are proton pump inhibitors associated with the development of community-acquired pneumonia? A meta-analysis",
"author": "Giuliano",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "337",
"journal-title": "Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.30",
"volume": "5",
"year": "2012"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jns.2019.02.041",
"article-title": "Acid-suppressive medications and risk of pneumonia in acute stroke patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis",
"author": "Marchina",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "122",
"journal-title": "J Neurol Sci",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.31",
"volume": "400",
"year": "2019"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198005",
"article-title": "Co-Infection with respiratory pathogens among COVID-2019 cases",
"author": "Zhu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "Virus Res",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.32",
"volume": "285",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.23876/j.krcp.2018.37.1.59",
"article-title": "Association of proton pump inhibitor use with renal outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease",
"author": "Cho",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "59",
"journal-title": "Kidney Res Clin Pract",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.33",
"volume": "37",
"year": "2018"
},
{
"DOI": "10.3343/alm.2020.40.5.351",
"article-title": "Guidelines for laboratory diagnosis of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Korea",
"author": "Hong",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "351",
"journal-title": "Ann Lab Med",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.34",
"volume": "40",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1046/j.1365-2036.2000.00840.x",
"article-title": "CYP2C19 genotype status and intragastric pH during dosing with lansoprazole or rabeprazole",
"author": "Adachi",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1259",
"journal-title": "Aliment Pharmacol Ther",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.35",
"volume": "14",
"year": "2000"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sapharm.2005.12.001",
"article-title": "Addressing the issue of channeling bias in observational studies with propensity scores analysis",
"author": "Lobo",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "143",
"journal-title": "Res Social Adm Pharm",
"key": "2021021905401457000_70.1.76.36",
"volume": "2",
"year": "2006"
}
],
"reference-count": 36,
"references-count": 36,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://gut.bmj.com/lookup/doi/10.1136/gutjnl-2020-322248"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19 associated with proton pump inhibitors: a nationwide cohort study with propensity score matching",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/crossmarkpolicy",
"volume": "70"
}