Oral corticoid, aspirin, anticoagulant, colchicine, and furosemide to improve the outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients - the COCAA-COLA cohort study
et al., Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008, Jun 2021
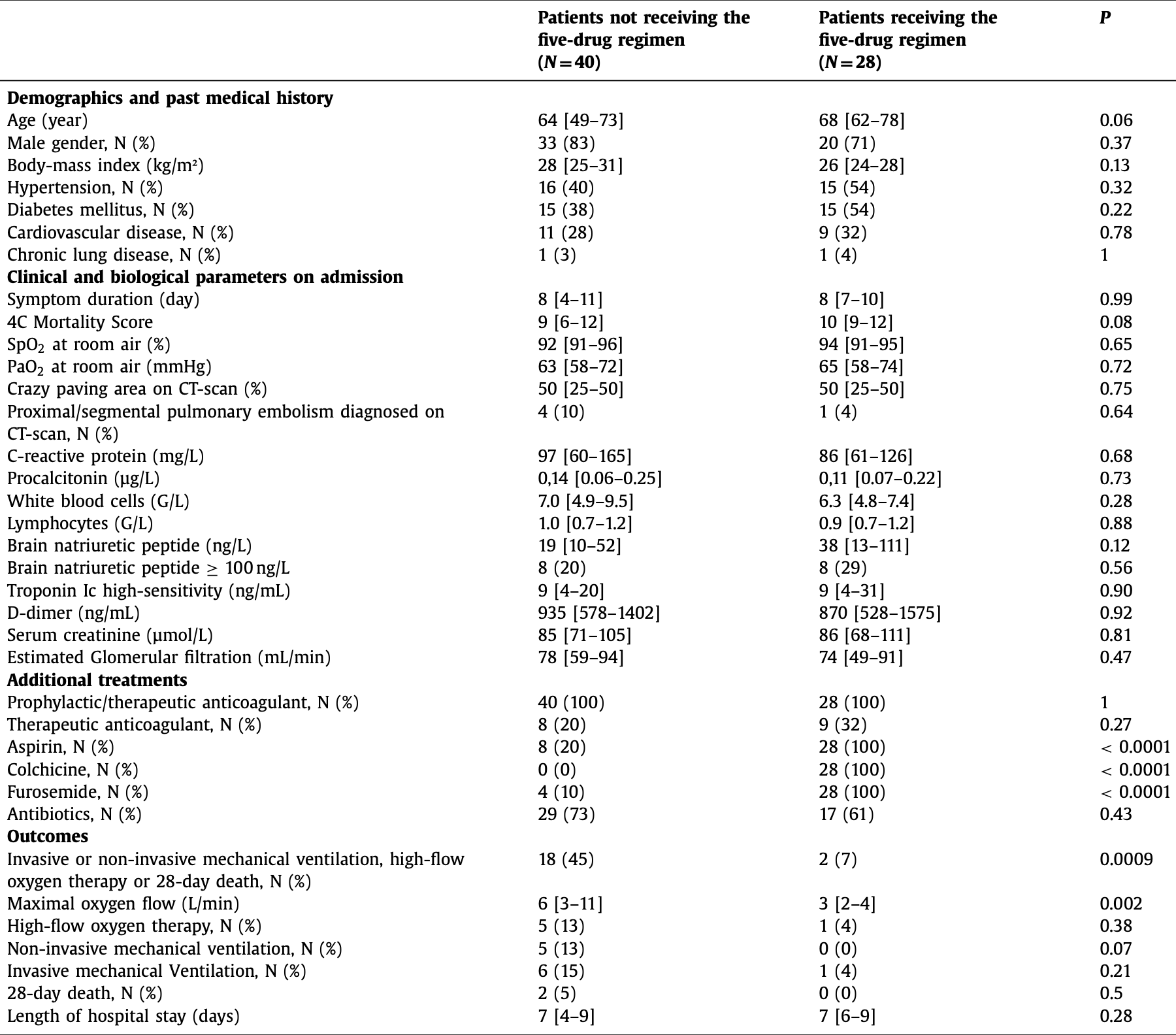
Observational study in France with 28 hospitalized patients treated with prednisone/furosemide/colchicine/salicylate/direct anti-Xa inhibitor, and 40 control patients, showing lower combined mortality, ventilation, or high-flow oxygen therapy with treatment.
This study is excluded in meta-analysis:
combined treatments may contribute more to the effect seen.
Study covers aspirin and colchicine.
|
risk of mortality, ventilation, or high-flow oxygen therapy, 95.7% lower, OR 0.04, p < 0.001, treatment 28, control 40, adjusted per study, multivariable, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kevorkian et al., 30 Jun 2021, retrospective, France, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, study period 9 January, 2020 - 30 November, 2020, this trial uses multiple treatments in the treatment arm (combined with prednisone, furosemide, salicylate, direct anti-Xa inhibitor) - results of individual treatments may vary.
Short durations of corticosteroids for hospitalised COVID-19 patients are associated with a high readmission rate
Journal of Infection, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.03.002
Oral corticoid, aspirin, anticoagulant, colchicine, and furosemide to improve the outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients -the COCAA-COLA cohort study Dear Editor,
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.03.002 .
Author contributions Haiyan
Ethical statement Patient screening and case reviews were undertaken as part of routine infection control in the hospital.
Ethics Ethical approval was not required for this service evaluation and audit of practice.
Authors' contributions SD, AR and NM designed the study methodology. SD, TE and XG collated the data. SD drafted the initial manuscript with all authors contributing significantly to revising this for submission. All authors agreed on the final version for submission to the journal.
Supplementary materials Supplementary material associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.011 .
Appendix
List of the SEMI-COVID-19 network members Coordinator of the SEMI- COVID-19
Consent for publication All the authors agree to publish.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Declaration of Competing Interest The authors declare no conflict of interest
Rapid whole-genome sequencing to inform COVID-19 outbreak response in Vietnam Dear Editor, The emergence of new SARS-CoV-2 variants, especially those of concerns, and their rapid dispersal emphasize the importance of active surveillance for SARS-CoV-2 variants worldwide. 1 , 2 In the morning of 28th January 2021, after 55 days..
References
Adrielle, Santos, Filho, Silva, Santos et al., Recurrent COVID-19 including evidence of reinfection and enhanced severity in thirty Brazilian healthcare workers, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.020
Ahmed, Hall, Robinson, Verhoef, Premkumar et al., Global prevalence of norovirus in cases of gastroenteritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis, The Lancet Infect Dis
Amy, Ellyn, Ko Jean, Chevinsky, Desisto et al., Characteristics of hospitalized COVID-19 patients discharged and experiencing same-hospital readmission -United States, March-August 2020, MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep
Anderson, May, Infectious diseases of humans: dynamics and control
Angus, Derde, Al-Beidh, Annane, Arabi et al., Effect of hydrocortisone on mortality and organ support in patients with severe COVID-19: the REMAP-CAP COVID-19 corticosteroid domain randomized clinical trial, JAMA, doi:10.1001/jama.2020.17022
Arnold, Hamilton, Milne, Morley, Viner et al., Patient outcomes after hospitalisation with COVID-19 and implications for followup: results from a prospective UK cohort, Thorax, doi:10.1136/thoraxjnl-2020-216086
Bansal, Grenfell, Meyers, When individual behaviour matters: homogeneous and network models in epidemiology, J R Soc Interface
Banyai, Estes, Martella, Parashar, Viral gastroenteritis, Lancet
Barberino, Silva, Rebouças, Barreiro, Alcântara et al., Evaluation of blood stream infections by Candida in three tertiary hospitals in Salvador, Brazil: a case-control study, Braz J Infect Dis
Bartsch, Lopman, Ozawa, Hall, Lee, Global economic burden of norovirus gastroenteritis, PLoS ONE
Batchelor, Revealed: The hospitals facing the most pressure to meet coronavirus demand
Bilaloglu, Aphinyanaphongs, Jones, Iturrate, Hochman et al., Thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a New York city health system, JAMA
Biswas, Rahaman, Biswas, Haque, Ibrahim, Association of sex, age, and comorbidities with mortality in COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Intervirology
Bono, Delfino, Furfaro, Mikulska, Nicco et al., Clinical performance of the (1, 3)-β-D -glucan assay in early diagnosis of nosocomial Candida bloodstream infections, Clin Vaccine Immunol
Brinkmann, Reichard, Goosmann, Fauler, Uhlemann et al., Neutrophil extracellular traps kill bacteria, Science, doi:10.1126/science.1092385
Bugembe, Phan, Ssewanyana, Semanda, Nansumba et al., lineage A variant (A.23.1) with altered spike has emerged and is dominating the current Uganda epidemic, doi:10.1101/2021.02.08.21251393
Bullard, Dust, Funk, Strong, Alexander et al., Predicting infectious SARS-CoV-2 from diagnostic samples, Clin Infect Dis
Cao, Wang, Wen, Liu, Jingli, A trial of lopinavir-ritonavir in adults hospitalized with severe covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2001282
Carmona-Bayonas, Jimenez-Fonseca, Castañón, A trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/nejmc2008043
Casas-Rojo, Antón-Santos, Millán-Núñez-Cortés, Lumbreras-Bermejo, Ramos-Rincón et al., Clinical characteristics of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 in Spain: results from the SEMI-COVID-19 registry, Rev Clin Esp, doi:10.1016/j.rce.2020.07.003
Centre, Prevention, Control: Rapid increase of a SARS-CoV-2 variant with multiple spike protein mutations observed in the United Kingdom
Cevik, Kuppalli, Kindrachuk, Peiris, Virology, transmission, and pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2, BMJ
Chandan, Milon, Islam Muhammad, Miquel, Docea et al., Potential therapeutic options for COVID-19: current status, challenges, and future perspectives, Front Pharmacol, doi:10.3389/fphar.2020.572870
Chau, Lam, Dung, Yen, Minh et al., None
Chow, Khanna, Kethireddy, Yamane, Levine et al., Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, Anesth Analg, doi:10.1213/ANE.0000000000005292
Chowdhury, Moores, Connors, Anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19, N Engl J Med
Chowell, Nishiura, Characterizing the transmission dynamics and control of ebola virus disease, PLOS Biol
Cook, Kursumovic, Lennane, Exclusive: deaths of NHS staff from covid-19 analysed
Corman, Landt, Kaiser, Molenkamp, Meijer et al., Detection of 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) by real-time RT-PCR, Euro Surveill
Cornely, Bassetti, Calandra, Garbino, Kullberg et al., ESCMID * guideline for the diagnosis and management of Candida diseases 2012: non-neutropenic adult patients, Clin Microbiol Infect
Crozier, Rajan, Buchan, Mckee, Put to the test: use of rapid testing technologies for Covid-19, BMJ
Davis, Assaf, Mccorkell, Wei, Low et al., Characterizing long COVID in an international Cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2020.12.24.20248802
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Siasos, Giotaki et al., Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Development, Team, R: A language and environment for statistical computing
Diallo, Rabilloud, Ayouba, Touré, Thaurignac et al., Prevalence of infection among asymptomatic and paucisymptomatic contact persons exposed to Ebola virus in Guinea: a retrospective, cross-sectional observational study, Lancet Infect Dis
Digital, NHS workforce
Dixon, Taylor, Dee, Hakim, Cantey et al., Contact tracing activities during the Ebola virus disease epidemic in Kindia and Faranah, Guinea, 2014, Emerg Infect Dis
Donald, Multiple Imputation for Nonresponse in Surveys John Wiley
Downs, Eyre, O'donnell, Jeffery, Home-based SARS-CoV-2 lateral flow antigen testing in hospital workers, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.008
Elise, Sonia, Gilles, Stéphane, Minh et al., Early administration of ritonavir-boosted lopinavir could prevent severe COVID-19, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.05.039
Elsayed, Reddy, Murthy, Gupta, Valiuskyte et al., The Possibility and Cause of Relapse After Previously Recovering From COVID-19: a Systematic Review, Cureus, doi:10.7759/cureus.10264
Esposito, Principi, Norovirus vaccine: priorities for future research and development, Front Immunol
Etard, Ibrahima Camara Centre de Recherche et de Formation en Infectiologie de Guinée, Conakry, Guinée. Cécé Kpamou Centre de Recherche et de Formation en Infectiologie de Guinée
Eyre, Lumley, O'donnell, Campbell, Sims et al., Differential occupational risks to healthcare workers from SARS-CoV-2 observed during a prospective observational study, Elife
Faria, Claro, Candido, Franco, Andrade et al., Genomic characterisation of an emergent SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus: preliminary findings, Virological
Fernandez, Erstad, Petty, Nix, Time to positive culture and identification for Candida blood stream infections, Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis
Fowler, Armson, Gonzales, A highly effective reverse-transcription loop-mediated isothermal amplification (RT-LAMP) assay for the rapid detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection, J Infect Jan
Francesco, Poiesi, Gargiulo, Bonfanti, Pollara et al., Co-infection of Chlamydia pneumoniae and Mycoplasma pneumoniae with SARS-CoV-2 is associated with more severe features, J Infect
Fred, Frederick, Dolin Raphael Principles and practice of infectious diseases, Princ. Pract. Infect
Fricke, Glockner, Dreier, Lange, Impact of non-pharmaceutical interventions targeted at COVID-19 pandemic on influenza burden -a systematic review, J Infect
Fröhlich, Jeschke, Eichler, Thiele, Alhariri et al., Impact of oral anticoagulation on clinical outcomes of COVID-19: a nationwide cohort study of hospitalized patients in Germany, Clin Res Cardiol, doi:10.1007/s00392-020-01783-x
Garcia-Pachon, Grau-Delgado Maria, Soler-Sempere, Zamora-Molina, Baeza-Martinez et al., Respiratory Medicine
Garcia-Pachon, Zamora-Molina, Soler-Sempere, Baeza-Martinez, Grau-Delgado et al., Asthma and COPD in hospitalized COVID-19 patients, Arch Bronconeumol, doi:10.1016/j.arbres.2020.05.007
Garg, Arora, Kumar, The, post-COVID" syndrome: how deep is the damage?, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26465
Gidari, Nofri, Saccarelli, Bastianelli, Sabbatini et al., Is recurrence possible in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)? Case series and systematic review of literature, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, doi:10.1007/s10096-020-04057-6
Gil, Weller, Rokadiya, Mirfenderesky, Ahmed et al., Letter in response to 'Modelling SARS-CoV2 spread in London: approaches to lift the lockdown' local experience, national questions. How local is local enough, J Infect
Grant, Wilmore, Mccann, Donnelly, Lai et al., Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in healthcare workers at a London NHS Trust, Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol
Grasselli, Greco, Zanella, Albano, Antonelli et al., Risk factors associated with mortality among patients with COVID-19 in intensive care units in Lombardy, Italy, JAMA Intern. Med
Graziani, Soriano, Del Rio-Bermudez, Morena, Diaz et al., Characteristics and prognosis of COVID-19 in patients with COPD, J. Clin. Med
Green, Merzon, Vinker, Golan-Cohen, Magen, COVID-19 susceptibility in bronchial asthma, J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, doi:10.1016/j.jaip.2020.11.020
Hagau, Slavcovici, Gonganau, Oltean, Dirzu et al., Clinical aspects and cytokine response in severe H1N1 influenza a virus infection, Crit Care, doi:10.1186/cc9324
Hall, Foulkes, Saei, Andrews, Oguti et al., Effectiveness of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against infection and COVID-19 vaccine coverage in healthcare workers in England, multicentre prospective cohort study (the SIREN study), Prepr Lancet
Halpin, Mcivor, Whyatt, Adams, Harvey et al., Postdischarge symptoms and rehabilitation needs in survivors of COVID-19 infection: a cross-sectional evaluation, J Med Virol, doi:10.1002/jmv.26368
Hanrath, Payne, Duncan, Prior SARS-CoV-2 infection is associated with protection against symptomatic reinfection, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.023
Hansen, Michlmayr, Gubbels, Mølbak, Ethelberg, Assessment of protection against reinfection with SARS-CoV-2 among 4 million PCR-tested individuals in Denmark in 2020: a population-level observational study, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(21)00575-4
Heesterbeek, Anderson, Andreasen, Bansal, De Angelis et al., Modeling infectious disease dynamics in the complex landscape of global health, Science, doi:10.1126/science.aaa4339
Hirotsu, Maejima, Shibusawa, Amemiya, Nagakubo et al., Prospective study of 1,308 nasopharyngeal swabs from 1,033 patients using the LUMIPULSE SARS-CoV-2 antigen test: comparison with RT-qPCR, doi:10.1093/infdis/jir865
Hirotsu, Maejima, Shibusawa, Nagakubo, Hosaka et al., Pooling RT-qPCR testing for SARS-CoV-2 in 10 0 0 individuals of healthy and infection-suspected patients, Sci. Rep
Hogan, Jewell, Sherrard-Smith, Vesga, Watson et al., Potential impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on HIV, tuberculosis, and malaria in low-income and middle-income countries: a modelling study, Lancet Glob Heal, doi:10.1016/S2214-109X(20)30288-6
Hongchao, Richard, Henao-Restrepo Ana-Maria, Marie-Pierre, Vasee, WHO Solidarity Trial Consortium Repurposed antiviral drugs for Covid-19 -interim WHO solidarity trial results, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2023184
Horby, Lim, Emberson, Mafham, Bell, RECOVERY Collaborative Group Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 -preliminary report, N Engl J Med
Hughes, Troise, Donaldson, Mughal, Moore, Bacterial and fungal coinfection among hospitalized patients with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort study in a UK secondary-care setting, Clin Microbiol Infect
Jaafar, Aherfi, Wurtz, Grimaldier, Hoang et al., Correlation between 3790 qPCR positives samples and positive cell cultures including 1941 SARS-CoV-2 isolates, Clin Infect Dis
Jeffs, Williman, Brunton, Gullam, Walls, The epidemiology of listeriosis in pregnant women and children in New Zealand from 1997 to 2016: an observational study, BMC Public Health
Johansson, Quandelacy, Kada, Prasad, Steele et al., SARS-CoV-2 Transmission From People Without COVID-19 Symptoms, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.35057
Kawai, Ikematsu, Iwaki, Maeda, Satoh et al., A comparison of the effectiveness of oseltamivir for the treatment of influenza A and influenza B: a Japanese multicenter study of the 20 03-20 04 and 20 04-20 05 influenza seasons, Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am, doi:10.1086/505868
Kevorkian, Riveline, Vandiedonck, Girard, Galland et al., Early short-course corticosteroids and furosemide combination to treat non-critically ill COVID-19 patients: an observational cohort study, J Infect
Khaled, Hundley, Almilaji, Koeppen, Tsofliou, A priori and a posteriori dietary patterns in women of childbearing age in the UK, Nutrients, doi:10.3390/nu12102921
Knight, Ho, Pius, Buchan, Carson et al., Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol: development and validation of the 4C Mortality Score, BMJ
Korber, Fischer, Gnanakaran, Yoon, Theiler et al., Tracking Changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: evidence that D614G Increases Infectivity of the COVID-19 Virus, Cell
Kowalzik, Binder, Zoller, Riera-Montes, Clemens et al., Norovirus gastroenteritis among hospitalized patients, Germany, 2007-2012, Emerg Infect Dis
Kurt, A trial of Lopinavir-Ritonavir in Covid-19, N Engl J Med, doi:10.1056/NEJMc2008043
Lee, Hui, Zuo, Ngai, Lui et al., A prospective intervention study on higher-dose oseltamivir treatment in adults hospitalized with influenza a and B infections, Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am, doi:10.1093/cid/cit597
Liang, Shi, Wang, Xiao, Duan et al., The association of hypertension with the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients: evidence based on adjusted effect estimates, J. Infect
Lim, Kim, Chang, Choi, Kim, Machine learning prediction for mortality of patients diagnosed with COVID-19: a nationwide Korean cohort study, Sci. Rep
Logue, Franko, Mcculloch, Mcdonald, Magedson et al., Sequelae in adults at 6 months after COVID-19 infection, JAMA Netw Open, doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.0830
Mahase, Covid-19: ethnic minority doctors feel more pressured and less protected than white colleagues, survey finds, BMJ
Majra, Benson, Pitts, Stebbing, SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19) superspreader events, J Infect, doi:10.1098/j.jinf.2020.11.021
Martin, Marshall, Patel, Goss, Jenkins et al., Association of demographic and occupational factors with SARS-CoV-2 vaccine uptake in a multi-ethnic UK healthcare workforce: a rapid real-world analysis, MedRxiv
Mastrangelo, Germinario, Ferrante, Frangi, Voti et al., Study Group. Candidemia in COVID-19 patients: incidence and characteristics in a prospective cohort compared to historical non-COVID-19 controls, Clin Infect Dis
Matsuyama, Kawase, Nao, Shirato, Ujike et al., The inhaled steroid ciclesonide blocks SARS-CoV-2 RNA replication by targeting the viral replication-transcription complex in cultured cells, J Virol, doi:10.1128/JVI.01648-20
Mayer, Vidal-Alaball, Puigdellivol-Sanchez, Gomez, Leis et al., Clinical characterization of patients with COVID-19 in primary care in catalonia: retrospective observational study, JMIR Public Health Surveill
Mcbride, Eickhoff, Wald, Impact of Covid-19 quarantine and school cancelation on other common infectious diseases, Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J
Mook, Grant, Little, Kafatos, Gillespie, Emergence of pregnancy-related listeriosis amongst ethnic minorities in England and Wales, Euro Surveill
Moreno-Pérez, Merino, Leon-Ramirez, Andres, Ramos et al., Post-acute COVID-19 Syndrome. Incidence and risk factors: a Mediterranean cohort study, J Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2021.01.004
Morrell, Fraser, Kollef, Delaying the empiric treatment of Candida bloodstream infection until positive blood culture results are obtained: a potential risk factor for hospital mortality, Antimicrob Agents Chemother
Naveca, Nascimento, Souza, Corado, Nascimento et al., Phylogenetic relationship of SARS-CoV-2 sequences from Amazonas with emerging Brazilian variants harboring mutations E484K and N501Y in the Spike protein
Ncov, Vietnamese Ministry of Health providing update information about COVID-19
Painset, Björkman, Kiil, Guiller, Marlet et al., LiSEQ -whole-genome sequencing of a cross-sectional survey of Listeria monocytogenes in ready-to-eat foods and human clinical cases in Europe, Microb Genom, doi:10.1099/mgen.0.000257
Perrone, Plowden, Garcia-Sastre, Katz, Tumpey, H5N1 and 1918 pandemic influenza virus infection results in early and excessive infiltration of macrophages and neutrophils in the lungs of mice, PLoS Pathog, doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000115
Peter, Mafham Marion, Jennifer, Linsell Louise, Natalie et al., Lopinavir-ritonavir in patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 (RECOVERY): a randomised, controlled, open-label, platform trial, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)32013-4
Peto, Covid, -19 Lateral Flow Oversight Team. COVID-19: rapid antigen detection for SARS-CoV-@ by lateral flow assay: a national systemic evaluation for mass-testing, medRxiv, doi:10.1101/2021.01.13.21249563
Pohl, Pouillot, Bazaco, Wolpert, Healy et al., Differences among incidence rates of invasive listeriosis in the US FoodNet population by age, sex, race/ethnicity, and pregnancy status, 2008-2016, Foodborne Pathog Dis
Rambaut, Holmes, O'toole, Hill, Mccrone et al., A dynamic nomenclature proposal for SARS-CoV-2 lineages to assist genomic epidemiology, Nat Microbiol
Richette, Doherty, Pascual, Barskova, Becce et al., updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout, Ann Rheum Dis
Rose, Adams, Whitehead, Wickham, O'brien et al., Neighbourhood unemployment and other socio-demographic predictors of emergency hospitalisation for infectious intestinal disease in England: a longitudinal ecological study, J Infect
Rosenthal, Cao, Gundrum, Sianis, Safo, Risk factors associated with in-hospital mortality in a US national sample of patients with COVID-19, JAMA Netw. Open
Roy, Hans, Don, Hollingsworth, Déirdre, How will country-based mitigation measures influence the course of the COVID-19 epidemic?, Lancet, doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30567-5
Scobie, Kanagarajah, Harris, Byrne, Amar et al., Mortality risk factors for listeriosis -a 10 year review of non-pregnancy associated cases in England 2006-2015, J Infect
Stasinopoulos, Rigby, Generalized additive models for location scale and shape (GAMLSS) in R, J Stat Softw
Stephen, Antonia, Riinu, Iain, Gail et al., Angiotensin converting enzyme genotypes and mortality from COVID-19: an ecological study, J. Infect
Sterne, Murthy, Diaz, Slutsky, Villar, WHO Rapid Evidence Appraisal for COVID-19 Therapies (REACT) Working Group Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis, JAMA
Su, Chaves, Perez, D'mello, Kirley et al., Comparing clinical characteristics between hospitalized adults with laboratoryconfirmed influenza A and B virus infection, Clin Infect Dis: Off Publ Infect Dis Soc Am, doi:10.1093/cid/ciu269
Tang, Toovey, Harvey, Hui, Introduction of the South African SARS-CoV-2 variant 501Y.V2 into the UK, J. Infect
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, L'allier, Gaudet, Shah et al., Efficacy of colchicine in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19, doi:10.1101/2021.01.26.21250494v1
Tegally, Wilkinson, Giovanetti, Iranzadeh, Fonseca et al., Emergence and rapid spread of a new severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) lineage with multiple spike mutations in South Africa, medRxiv
Toovey, Harvey, Bird, Tang, Introduction of Brazilian SARS-CoV-2 484 K.V2 related variants into the UK, J Infect
Tran, Vaudry, Moore, Bettinger, Scheifele, Hospitalization for Influenza A Versus B, Pediatrics, doi:10.1542/peds.2015-4643
Tu, Geskus, Thanh, Truong, Binh et al., The natural history and transmission potential of asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection, Clin Infect Dis
Van Dorp, Richard, Tan, Shaw, Acman et al., No evidence for increased transmissibility from recurrent mutations in SARS-CoV-2, Nat. Commun
Van Tan, COVID-19 control in Vietnam, Nat Immunol
Wake, Morgan, Choi, Winn, Reducing nosocomial transmission of COVID-19: implementation of a COVID-19 triage system, Clin Med (Lond), doi:10.7861/clinmed.2020-0411
Wang, Schmidt, Weisblum, Muecksch, Barnes et al., mRNA vaccine-elicited antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 and circulating variants, Nature
Wieler, Rexroth, Gottschalk, Emerging COVID-19 success story: Germany's strong enabling environment
Woolhouse, Dye, Etard, Smith, Charlwood et al., Heterogeneities in the transmission of infectious agents: implications for the design of control programs, Proc Natl Acad Sci
Yang, Xu, Liang, Shi, Wang et al., Disparities in the excess risk of mortality in the first wave of COVID-19: cross sectional study of the English sentinel network, J. Infect, doi:10.1016/j.jinf.2020.12.025
Yapar, Pullukcu, Avkan-Oguz, Sayin-Kutlu, Ertugrul et al., Evaluation of species distribution and risk factors of candidemia: a multicenter case-control study, Med Mycol
Zhang, Zhu, Zhang, Zhou, Song et al., Circulating rather than alveolar extracellular deoxyribonucleic acid levels predict outcomes in Influenza, J Infect Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jiaa241
Zhu, Liu, Zhang, Pu, Liu et al., High level of neutrophil extracellular traps correlates with poor prognosis of severe Influenza A infection, J. Infect. Dis, doi:10.1093/infdis/jix475
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008",
"ISSN": [
"0163-4453"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008",
"alternative-id": [
"S016344532100058X"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Oral corticoid, aspirin, anticoagulant, colchicine, and furosemide to improve the outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients - the COCAA-COLA cohort study"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Journal of Infection"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "© 2021 The British Infection Association. Published by Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kevorkian",
"given": "Jean-Philippe",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lopes",
"given": "Amanda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sène",
"given": "Damien",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Riveline",
"given": "Jean-Pierre",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Vandiedonck",
"given": "Claire",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Féron",
"given": "Florine",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Nassarmadji",
"given": "Kladoum",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mouly",
"given": "Stéphane",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mauvais-Jarvis",
"given": "Franck",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gautier",
"given": "Jean-François",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Mégarbane",
"given": "Bruno",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"Journal of Infection"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.jp",
"journalofinfection.com",
"clinicalkey.com",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
2,
9
]
],
"date-time": "2021-02-09T20:11:38Z",
"timestamp": 1612901498000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
12,
28
]
],
"date-time": "2021-12-28T02:15:35Z",
"timestamp": 1640657735000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000041",
"award": [
"7–20-COVID-051"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "American Diabetes Association"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000738",
"award": [
"BX003725"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs"
},
{
"DOI": "10.13039/100000002",
"award": [
"DK074970",
"DK107444"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "National Institutes of Health"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
2
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-02T11:47:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643802420690
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 7,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "print",
"value": "0163-4453"
}
],
"issue": "6",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "6",
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
}
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2021-06-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1622505600000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S016344532100058X?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S016344532100058X?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "276-316",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2021,
6
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.17023",
"article-title": "Association between administration of systemic corticosteroids and mortality among critically Ill patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis",
"author": "Sterne",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1330",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0001",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jinf.2020.08.045",
"article-title": "Early short-course corticosteroids and furosemide combination to treat non-critically ill COVID-19 patients: an observational cohort study",
"author": "Kevorkian",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "e22",
"journal-title": "J Infect",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0002",
"volume": "82",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"article-title": "Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial",
"author": "Deftereos",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"journal-title": "JAMA Netw Open",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0003",
"volume": "3",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Aspirin use is associated with decreased mechanical ventilation, ICU admission, and in-hospital mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Chow",
"journal-title": "Anesth Analg",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0004",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Impact of oral anticoagulation on clinical outcomes of COVID-19: a nationwide cohort study of hospitalized patients in Germany",
"author": "Fröhlich",
"first-page": "1",
"journal-title": "Clin Res Cardiol",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0005",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMclde2028217",
"article-title": "Anticoagulation in hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Chowdhury",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "1675",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0006",
"volume": "383",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209707",
"article-title": "2016 updated EULAR evidence-based recommendations for the management of gout",
"author": "Richette",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "29",
"journal-title": "Ann Rheum Dis",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0007",
"volume": "76",
"year": "2017"
},
{
"article-title": "Dexamethasone in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 - preliminary report",
"author": "Horby",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0008",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jama.2020.13372",
"article-title": "Thrombosis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19 in a New York city health system",
"author": "Bilaloglu",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "799",
"journal-title": "JAMA",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0009",
"volume": "324",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/bmj.m3339",
"article-title": "Risk stratification of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19 using the ISARIC WHO Clinical Characterization Protocol: development and validation of the 4C Mortality Score",
"author": "Knight",
"doi-asserted-by": "crossref",
"first-page": "m3339",
"journal-title": "BMJ",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0010",
"volume": "370",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"article-title": "Efficacy of colchicine in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19",
"author": "Tardif",
"journal-title": "Medrxiv",
"key": "10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.008_bib0011",
"year": "2021"
}
],
"reference-count": 11,
"references-count": 11,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"Journal of Infection"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Infectious Diseases",
"Microbiology (medical)"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Oral corticoid, aspirin, anticoagulant, colchicine, and furosemide to improve the outcome of hospitalized COVID-19 patients - the COCAA-COLA cohort study"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "82"
}
kevorkian