Correlation of Vitamin D Levels with COVID-19 Severity and Outcome
et al., Indian Journal of Clinical Practice, 32:6, Nov 2021
Vitamin D for COVID-19
8th treatment shown to reduce risk in
October 2020, now with p < 0.00000000001 from 136 studies, recognized in 18 countries.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
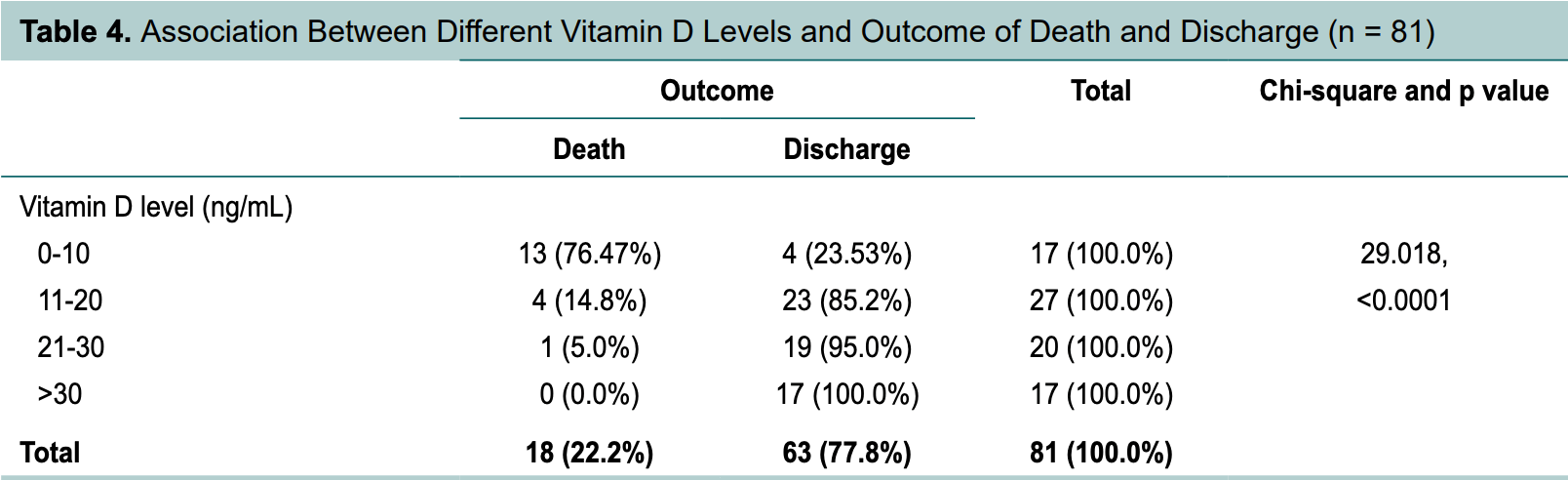
Prospective study of 81 hospitalized COVID+ patients in India, showing low vitamin D levels associated with COVID-19 severity and mortality.
This is the 108th of 228 COVID-19 sufficiency studies for vitamin D, which collectively show higher levels reduce risk with p<0.0000000001.
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
unadjusted results with no group details.
|
risk of death, 89.8% lower, RR 0.10, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥10ng/mL) 5 of 64 (7.8%), low D levels (<10ng/mL) 13 of 17 (76.5%), NNT 1.5.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 90.3% lower, RR 0.10, p < 0.001, high D levels (≥10ng/mL) 4 of 64 (6.2%), low D levels (<10ng/mL) 11 of 17 (64.7%), NNT 1.7.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kaur et al., 30 Nov 2021, prospective, India, peer-reviewed, 5 authors.
ClInICal Study
Background and aims: Low vitamin D levels have been associated with an increase in inflammatory cytokines and a significantly increased risk of pneumonia and viral upper respiratory tract infections. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increase in thrombotic episodes, which are frequently observed in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). These conditions are reported to carry a higher mortality in COVID-19. So, we conducted a study to prove the correlation of vitamin D levels with COVID-19 infection and severity. Material and methods: The present study was conducted at RNT Medical College, Udaipur, Rajasthan. This study was done over a period of 2 months after getting approval from Institutional Ethics Committee. Written and informed consent was obtained from patients. In this study, 81 patients admitted in COVID wards and ICU, with COVID reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) positive reports were included. Results: Out of a total 81 patients, 37 (45.7%) were in the 41-60 years age group, 29 (35.8%) were more than 60 years of age and 15 (18.5%) were less than 40 years of age. Seventeen patients had severe vitamin D deficiency, 27 patients had moderate vitamin D deficiency, 20 patients had mild vitamin D deficiency and 17 patients had normal vitamin D level. Out of 17 patients who had severe vitamin D deficiency, 11 (64.7%) patients required invasive mechanical ventilation and out of these 17 patients, 13 (76.47%) patients died. Out of 17 patients who had normal level of vitamin D, 16 (94.1%) maintained SpO 2 at room air and only 1 patient required invasive mechanical ventilation. As the level of vitamin D increased from severely low to normal level, requirement of high oxygen support decreased and SpO 2 at room air increased. Mean of vitamin D among the patients who died was 10.4963 while mean of vitamin D level among patients who survived and were discharged was 27.2362. All 17 patients who had normal level of vitamin D were discharged from the hospital. Mean of serum ferritin and mean of interleukin (IL)-6 was high in patients who died and low in patients who were discharged. Conclusions: Vitamin D level plays an important role in COVID-19 disease. Vitamin D have significant role in protection from severe form of disease.
References
Chen, Wu, Guo, Cao, Huang et al., Clinical and immunological features of severe and moderate coronavirus disease 2019, J Clin Invest
Fisher, Rahimzadeh, Brierley, Gration, Doree et al., The role of vitamin D in increasing circulating T regulatory cell numbers and modulating T regulatory cell phenotypes in patients with inflammatory disease or in healthy volunteers: A systematic review, PLoS One
Johnstone, Parsons, Botelho, Millar, Mcneil et al., Immune biomarkers predictive of respiratory viral infection in elderly nursing home residents, PLoS One
Lu, Zhang, Ma, Yue, Zou et al., Link between community-acquired pneumonia and vitamin D levels in older patients, Z Gerontol Geriatr
Manion, Hullsiek, Wilson, Rhame, Kojic et al., Study to Understand the Natural History of HIV/AIDS in the Era of Effective Antiretroviral Therapy (the 'SUN Study') Investigators. Vitamin D deficiency is associated with IL-6 levels and monocyte activation in HIV-infected persons, PLoS One
Mohammed, Mirshafiey, Vahedi, Hemmasi, Nasl Khameneh et al., None
Peterson, Heffernan, Serum tumor necrosis factoralpha concentrations are negatively correlated with serum 25(OH)D concentrations in healthy women, J Inflamm (Lond)
Prietl, Treiber, Mader, Hoeller, Wolf et al., High-dose cholecalciferol supplementation significantly increases peripheral CD4⁺ Tregs in healthy adults without negatively affecting the frequency of other immune cells, Eur J Nutr
Science, Maguire, Russell, Smieja, Walter et al., Low serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D level and risk of upper respiratory tract infection in children and adolescents, Clin Infect Dis
Weir, Thenappan, Bhargava, Chen, Does vitamin D deficiency increase the severity of COVID-19?, Clin Med (Lond)
