The effects of colchicine on hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
et al., Journal of Investigative Medicine, doi:10.1177/10815589221141815, IRCT20190804044429N5, Jan 2023
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
Very late treatment (10 days from onset) RCT 110 patients in Iran, showing no significant difference in outcomes with colchicine. Colchicine 2mg loading dose followed by 0.5mg bid for 7 days.
|
risk of death, 7.3% lower, RR 0.93, p = 1.00, treatment 6 of 55 (10.9%), control 6 of 51 (11.8%), NNT 117.
|
|
risk of mechanical ventilation, 7.3% lower, RR 0.93, p = 1.00, treatment 6 of 55 (10.9%), control 6 of 51 (11.8%), NNT 117.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 23.6% higher, RR 1.24, p = 0.63, treatment 12 of 55 (21.8%), control 9 of 51 (17.6%).
|
|
risk of no recovery, 27.9% lower, RR 0.72, p = 0.59, treatment 7 of 55 (12.7%), control 9 of 51 (17.6%), NNT 20, day 14.
|
|
risk of no recovery, 11.7% lower, RR 0.88, p = 0.69, treatment 20 of 55 (36.4%), control 21 of 51 (41.2%), NNT 21, day 7.
|
|
recovery time, 14.3% lower, relative time 0.86, p = 0.06, treatment 55, control 51.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Kasiri et al., 16 Jan 2023, Double Blind Randomized Controlled Trial, placebo-controlled, Iran, peer-reviewed, mean age 54.6, 6 authors, study period February 2021 - May 2021, average treatment delay 10.0 days, trial IRCT20190804044429N5.
Contact: ghazaeianm@gmail.com.
The effects of colchicine on hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
Journal of Investigative Medicine, doi:10.1177/10815589221141815
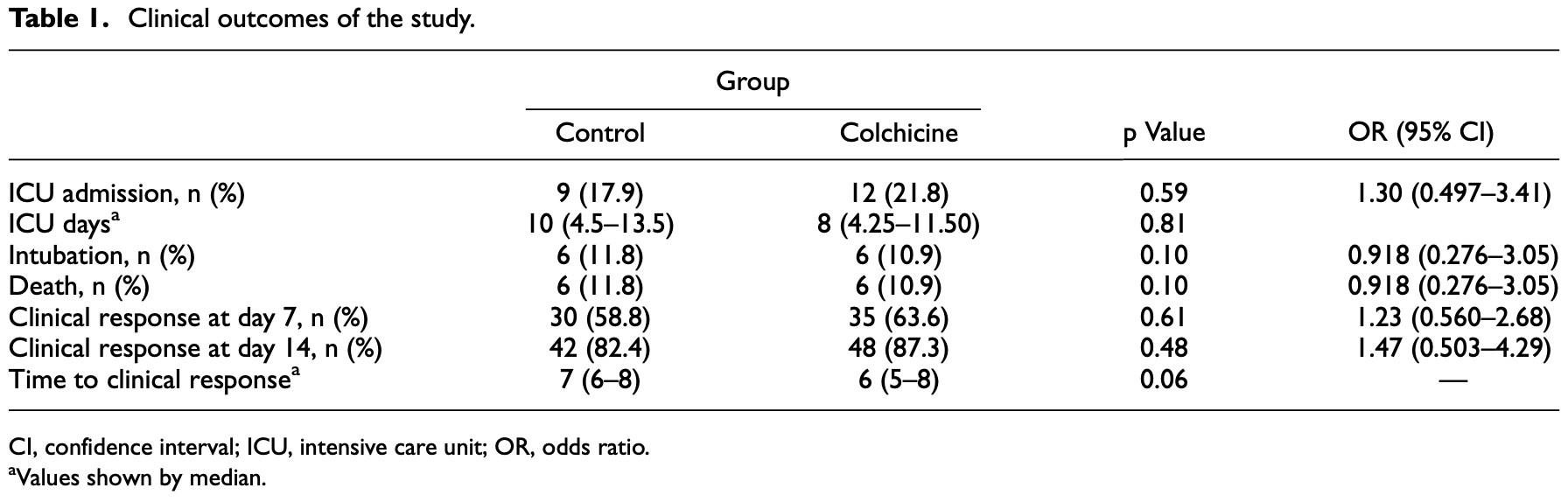
This study was designed to evaluate the effects of colchicine in the improvement of clinical outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. This prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted on adult patients (.18 years) with severe COVID-19. The included patients were randomly (1:1) assigned to the colchicine (2 mg loading dose followed by 0.5 mg twice daily for 7 days) or placebo group. Both groups received remdesivir and interferon beta-1b. The primary outcome of the study was to receive clinical response as ordinal scale of 1 or 2. Secondary outcomes were hospital complications and 28-day mortality. Between February and May 2021, 110 patients were included and 106 of them were analyzed. Baseline clinical characteristics and demographics were not significantly different. According to the ordinal scale, 30 patients in the control group (58.8%) responded to treatment within 7 days, while 35 patients (63.6%) in the colchicine group showed the same response (p = 0.61, odds ratio (OR) = 1.23, 95% CI [0.560-2.68]). On the 14th day, 87.3% of the colchicine group (n = 48) and 82.4% of the control group (n = 42) responded (p = 0.48, OR = 1.47, 95% CI [0.50.3-4.29]. In addition, 28-day mortality, intensive care unit admission, and hospital duration were not different between the groups (p = 0.99, 0.59, 0.06). Diarrhea and nausea were the major side effects dominant in the colchicine group. Colchicine showed no beneficial effects on clinical improvement and hospital complications in patients with COVID-19. Moreover, in case of prescription, the safety concerns of colchicine, specially gastrointestinal side effects, should be taken into account.
Authors' contributions Hossein Kasiri and Mobin Ghazaiean: Data Curation, Investigation. Nima Rouhani: Project Administration. Fahimeh Nader-behdani: Writing-original draft. Monireh Ghazaeian: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Writing-review & editing. Robabeh Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi: Formal analysis and Data Curation.
Declaration of conflicting interests The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Ethics approval This study abides by the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Ethics Committee of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences (IR.MAZUMS.REC.1399.914).
Supplemental material Supplemental material for this article is available online.
References
Ali, Baloch, Ahmed, The outbreak of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)-an emerging global health threat, J Infect Public Health
Beigel, Tomashek, Dodd, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Buonaguro, Puzanov, Ascierto, Anti-IL6R role in treatment of COVID-19-related ARDS, J Transl Med
Cao, Li, COVID-19: towards understanding of pathogenesis, Cell Res
Deftereos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Effect of colchicine vs standard care on cardiac and inflammatory biomarkers and clinical outcomes in patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019: the GRECCO-19 randomized clinical trial, JAMA Netw Open
Garcı´a, Mancilla-Galindo, Paredes-Paredes, Mechanisms of infection by SARS-CoV-2, inflammation and potential links with the microbiome, Future Virol
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial, RMD Open
Madsen, Remdesivir for the treatment of COVID-19-final report, N Engl J Med
Manenti, Maggiore, Fiaccadori, Reduced mortality in COVID-19 patients treated with colchicine: results from a retrospective, observational study, PLoS One
Montealegre-Go´mez, Garavito, Go´mez-Lo´pez, Colchicine: a potential therapeutic tool against COVID-19. Experience of 5 patients, Reumatol Clin
Nasiripour, Zamani, Farasatinasab, Can colchicine as an old anti-inflammatory agent be effective in COVID-19?, J Clin Pharmacol
Nuki, Colchicine: its mechanism of action and efficacy in crystal-induced inflammation, Curr Rheumatol Reports
Papadopoulos, Patoulias, Teperikidis, Colchicine as a potential therapeutic agent against cardiovascular complications of COVID-19: an exploratory review, SN Compr Clin Med
Salehzadeh, Pourfarzi, Ataei, The impact of colchicine on the COVID-19 patients: a clinical trial study, Mediterr J Rheumatol
Scarsi, Piantoni, Colombo, Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Rheum Dis
Schlesinger, Firestein, Brunetti, Colchicine in COVID-19: an old drug, new use, Curr Pharmacol Rep
Shi, Wang, Shao, COVID-19 infection: the perspectives on immune responses, Cell Death Differ
Soy, Keser, Atagu¨ndu¨z, Cytokine storm in COVID-19: pathogenesis and overview of antiinflammatory agents used in treatment, Clin Rheumatol
Stewart, Yang, Atkins, Adverse events during oral colchicine use: a systematic review and metaanalysis of randomised controlled trials, Arthritis Res Ther
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, Pl, Geen plaats voor colchicine in de behandeling van COVID-19, Respir Med
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1177/10815589221141815",
"ISSN": [
"1081-5589",
"1708-8267"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/10815589221141815",
"abstract": "<jats:p> This study was designed to evaluate the effects of colchicine in the improvement of clinical outcomes of hospitalized COVID-19 patients. This prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial was conducted on adult patients (>18 years) with severe COVID-19. The included patients were randomly (1:1) assigned to the colchicine (2 mg loading dose followed by 0.5 mg twice daily for 7 days) or placebo group. Both groups received remdesivir and interferon beta-1b. The primary outcome of the study was to receive clinical response as ordinal scale of 1 or 2. Secondary outcomes were hospital complications and 28-day mortality. Between February and May 2021, 110 patients were included and 106 of them were analyzed. Baseline clinical characteristics and demographics were not significantly different. According to the ordinal scale, 30 patients in the control group (58.8%) responded to treatment within 7 days, while 35 patients (63.6%) in the colchicine group showed the same response (p = 0.61, odds ratio (OR) = 1.23, 95% CI [0.560–2.68]). On the 14th day, 87.3% of the colchicine group (n = 48) and 82.4% of the control group (n = 42) responded (p = 0.48, OR = 1.47, 95% CI [0.50.3–4.29]. In addition, 28-day mortality, intensive care unit admission, and hospital duration were not different between the groups (p = 0.99, 0.59, 0.06). Diarrhea and nausea were the major side effects dominant in the colchicine group. Colchicine showed no beneficial effects on clinical improvement and hospital complications in patients with COVID-19. Moreover, in case of prescription, the safety concerns of colchicine, specially gastrointestinal side effects, should be taken into account. </jats:p>",
"alternative-id": [
"10.1177/10815589221141815"
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Kasiri",
"given": "Hossein",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "School of Medicine, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghazaiean",
"given": "Mobin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Infectious Disease, Ibn Sina Medical and Educational Center, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Rouhani",
"given": "Nima",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Naderi-behdani",
"given": "Fahimeh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Pharmaceutical Research Center, Department of Clinical Pharmacy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences, Sari, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghazaeian",
"given": "Monireh",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [
{
"name": "Department of Biostatistics, School of Medical Sciences, Tarbiat Modares University, Tehran, Iran"
}
],
"family": "Ghodssi-Ghassemabadi",
"given": "Robabeh",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Journal of Investigative Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Journal of Investigative Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"journals.sagepub.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-17T10:42:57Z",
"timestamp": 1673952177000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
17
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-17T10:43:02Z",
"timestamp": 1673952182000
},
"funder": [
{
"DOI": "10.13039/501100004160",
"award": [
"IRMAZUMS8653"
],
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"name": "mazandaran university of medical sciences"
}
],
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
18
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-18T05:55:37Z",
"timestamp": 1674021337689
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/page/policies/text-and-data-mining-license",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
],
"date-time": "2023-01-16T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1673827200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/10815589221141815",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/full-xml/10.1177/10815589221141815",
"content-type": "application/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/pdf/10.1177/10815589221141815",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "179",
"original-title": [],
"page": "108155892211418",
"prefix": "10.1177",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2023,
1,
16
]
]
},
"publisher": "SAGE Publications",
"reference": [
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.jiph.2020.02.033",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr1-10815589221141815"
},
{
"author": "Madsen LW.",
"first-page": "1813",
"issue": "19",
"journal-title": "N Engl J Med",
"key": "bibr2-10815589221141815",
"volume": "338",
"year": "2020"
},
{
"DOI": "10.31138/mjr.33.2.232",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr3-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s40495-020-00225-6",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr4-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.13136",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr5-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s11926-008-0036-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr6-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1002/jcph.1645",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr7-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1056/NEJMoa2007764",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr8-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/annrheumdis-2020-217712",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr9-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s10067-020-05190-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr10-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s12967-020-02333-9",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr11-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.2217/fvl-2020-0310",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr12-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41418-020-0530-3",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr13-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1038/s41422-020-0327-4",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr14-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001455",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr15-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1371/journal.pone.0248276",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr16-10815589221141815"
},
{
"author": "Tardif JC",
"first-page": "924",
"journal-title": "Respir Med",
"key": "bibr17-10815589221141815",
"volume": "9",
"year": "2021"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/S2213-2600(21)00435-5",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr18-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.reuma.2020.05.001",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr19-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1186/s13075-020-2120-7",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr20-10815589221141815"
},
{
"DOI": "10.1007/s42399-020-00421-x",
"doi-asserted-by": "publisher",
"key": "bibr21-10815589221141815"
}
],
"reference-count": 21,
"references-count": 21,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "http://journals.sagepub.com/doi/10.1177/10815589221141815"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Biochemistry, Genetics and Molecular Biology",
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "The effects of colchicine on hospitalized COVID-19 patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1177/sage-journals-update-policy"
}
