Reducing length of hospital stay with colchicine
et al., The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, doi:10.3855/jidc.14924, Jan 2022
Colchicine for COVID-19
5th treatment shown to reduce risk in
September 2020, now with p = 0.0000049 from 54 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
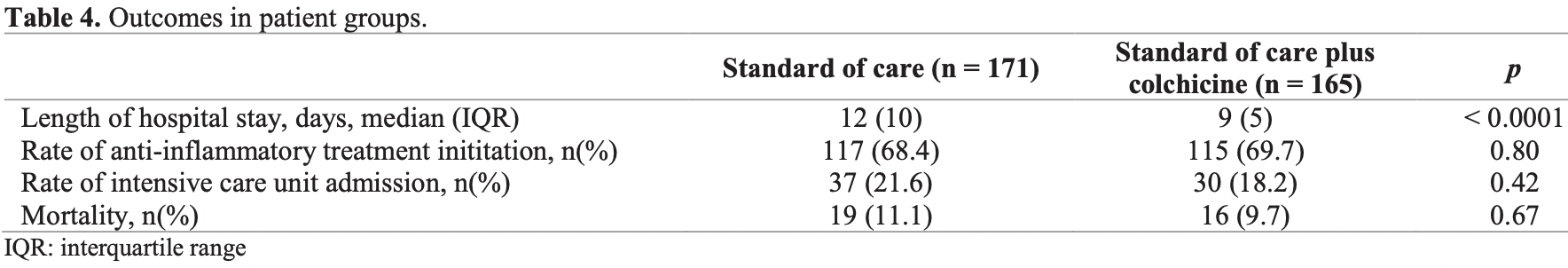
Retrospective 356 hospitalized COVID-19 patients, shorter hospitalization time with colchicine treatment. There were no statistically significant differences for mortality or ICU admission. Significantly lower mortality was seen with higher dosage (1mg/day vs 0.5mg/day). More control patients were on oxygen at baseline (65% vs. 54%).
This study is excluded in the after exclusion results of meta-analysis:
excessive unadjusted differences between groups.
|
risk of death, 12.7% lower, RR 0.87, p = 0.72, treatment 16 of 165 (9.7%), control 19 of 171 (11.1%), NNT 71.
|
|
risk of ICU admission, 16.0% lower, RR 0.84, p = 0.50, treatment 30 of 165 (18.2%), control 37 of 171 (21.6%), NNT 29.
|
|
hospitalization time, 25.0% lower, relative time 0.75, p < 0.001, treatment 165, control 171.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Karakaş et al., 31 Jan 2022, retrospective, Turkey, peer-reviewed, 11 authors, dosage 1mg daily, 0.5mg for 37 patients.
Reducing length of hospital stay with colchicine
The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries, doi:10.3855/jidc.14924
Introduction: Colchicine is an ancient agent with well-known anti-inflammatory effects and commonly used in treatment of hyperinflammatory conditions. It has been argued that colchicine could be an appropriate treatment option in COVID-19 to control hyperinflammatory response. Here in this study, we aimed to investigate the impact of colchicine on outcomes of COVID-19 in our inpatient cohort. Methodology: In this retrospective cohort study, hospitalized COVID-19 patients were investigated. Demographics, comorbidities, COVID-19 symptoms, laboratory findings on admission and discharge, baseline and seventh day oxygenation status, rates of mortality, intensive care unit admission, administration of other anti-inflammatory treatments and length of hospital stay were compared between patients who received standard of care medications and who received colchicine additionally. Results: Three hundred and thirty-six patients were included in the study (171 standard of care, 165 standard of care plus colchicine). The median length of hospital stay in colchicine group was significantly shorter. Rates of admission to intensive care unit, anti-inflammatory treatment administration and mortality did not differentiate between standard of care and colchicine groups. However, reduced rates of mortality and ICU admission were observed in patients who received colchicine with a dose of 1 mg/day when compared to patients who received 0.5 mg/day. Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that COVID-19 patients who received colchicine in addition to standard of care had shorter hospital stay. Our results further support the use of colchicine in treatment of COVID-19, particularly with a dose of 1 mg/day.
Authors
Conflict of interests: No conflict of interests is declared.
References
Abu-Fanne, Stepanova, Litvinov, Abdeen, Bdeir et al., Neutrophil α-defensins promote thrombosis in vivo by altering fibrin formation, structure, and stability, Am J Hematol
Angelidis, Kotsialou, Kossyvakis, Vrettou, Zacharoulis et al., Colchicine pharmacokinetics and mechanism of action, Curr Pharm Des
Cicco, Cicco, Racanelli, Vacca, Neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs): two potential targets for COVID-19 treatment, Mediat Inflamm
Cunningham, Goh, Koh, Treatment of COVID-19: old tricks for new challenges, Crit Care
Dai, Zhang, Xia, Zhang, Shang et al., High-resolution chest CT features and clinical characteristics of patients infected with COVID-19 in Jiangsu, China, Int J Infect Dis
Deftereos, Siasos, Giannopoulos, Vrachatis, Angelidis et al., The Greek study in the effects of colchicine in COVID-19 complications prevention (GRECCO-19 study): rationale and study design, Hellenic J Cardiol
Dupuis, Sirois, Rhéaume, Nguyen, Clavet-Lanthier et al., Colchicine reduces lung injury in experimental acute respiratory distress syndrome, PloS One
Elshafei, Khalil, El-Bardissy, Danjuma, Ahmed et al., The efficacy of colchicine in the management of coronavirus disease 2019: a protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis, Medicine
Grailer, Canning, Kalbitz, Haggadone, Dhond et al., Critical role for the NLRP3 inflammasome during acute lung injury, J Immunol
Hemkens, Ewald, Gloy, Arpagaus, Olu et al., Cardiovascular effects and safety of long-term colchicine treatment: cochrane review and meta-analysis, Heart
Karakas, Md Division Of, Rheumatology, Corresponding author
Karamanou, Tsoucalas, Pantos, Androutsos, Isolating colchicine in 19th century: an old drug revisited, Curr Pharm Des
Lazaros, Imazio, Brucato, Vlachopoulos, Lazarou et al., The role of colchicine in pericardial syndromes, Curr Pharm Des
Lopes, Bonjorno, Giannini, Amaral, Menezes et al., Beneficial effects of colchicine for moderate to severe COVID-19: a randomised, double-blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial, RMD Open
Mehta, Mcauley, Brown, Sanchez, Tattersall et al., COVID-19: consider cytokine storm syndromes and immunosuppression, Lancet
Menche, Israel, Karpatkin, Platelets and microtubules: effect of colchicine and D2O on platelet aggregation and release induced by calcium ionophore A23187, J Clin Investig
Misawa, Takahama, Kozaki, Lee, Zou et al., Microtubule-driven spatial arrangement of mitochondria promotes activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, Nat Immunol
Mousavizadeh, Ghasemi, Genotype and phenotype of COVID-19: their roles in pathogenesis, J Microbiol Immunol Infect
Pope, Tschopp, The role of interleukin-1 and the inflammasome in gout: implications for therapy, Arthritis Rheum
Sandhu, Tieng, Chilimuri, Franchin, A case control study to evaluate the impact of colchicine on patients admitted to the hospital with moderate to severe COVID-19 infection, Can J Infect Dis Med Microbiol
Scarsi, Piantoni, Colombo, Airó, Richini et al., Association between treatment with colchicine and improved survival in a single-centre cohort of adult hospitalised patients with COVID-19 pneumonia and acute respiratory distress syndrome, Ann Rheum Dis
Spoto, Valeriani, Locorriere, Anguissola, Pantano et al., Influenza B virus infection complicated by lifethreatening pericarditis: a unique case-report and literature review, BMC Infect Dis
Tardif, Bouabdallaoui, Allier, Gaudet, Shah et al., Efficacy of colchicine in non-hospitalized patients with COVID-19
Vounotrypidis, COVID-19: an archetype innate immunity reaction and modes of treatment, Mediterr J Rheumatol
White, Chicca, Cooper, Milward, Chapple, Neutrophil extracellular traps in periodontitis: a web of intrigue, J Dent Res
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.3855/jidc.14924",
"ISSN": [
"1972-2680"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.3855/jidc.14924",
"abstract": "<jats:p>Introduction: Colchicine is an ancient agent with well-known anti-inflammatory effects and commonly used in treatment of hyperinflammatory conditions. It has been argued that colchicine could be an appropriate treatment option in COVID-19 to control hyperinflammatory response. Here in this study, we aimed to investigate the impact of colchicine on outcomes of COVID-19 in our inpatient cohort.
\nMethodology: In this retrospective cohort study, hospitalized COVID-19 patients were investigated. Demographics, comorbidities, COVID-19 symptoms, laboratory findings on admission and discharge, baseline and seventh day oxygenation status, rates of mortality, intensive care unit admission, administration of other anti-inflammatory treatments and length of hospital stay were compared between patients who received standard of care medications and who received colchicine additionally.
\nResults: Three hundred and thirty-six patients were included in the study (171 standard of care, 165 standard of care plus colchicine). The median length of hospital stay in colchicine group was significantly shorter. Rates of admission to intensive care unit, anti-inflammatory treatment administration and mortality did not differentiate between standard of care and colchicine groups. However, reduced rates of mortality and ICU admission were observed in patients who received colchicine with a dose of 1 mg/day when compared to patients who received 0.5 mg/day.
\nConclusions: Our study demonstrated that COVID-19 patients who received colchicine in addition to standard of care had shorter hospital stay. Our results further support the use of colchicine in treatment of COVID-19, particularly with a dose of 1 mg/day.</jats:p>",
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Karakaş",
"given": "Özlem",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Erden",
"given": "Abdulsamet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Güven",
"given": "Serdar Can",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Armağan",
"given": "Berkan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Sahiner",
"given": "Enes Seyda",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Kurtipek",
"given": "Ali Can",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Inan",
"given": "Osman",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Gemcioglu",
"given": "Emin",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ateş",
"given": "İhsan",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Omma",
"given": "Ahmet",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Küçüksahin",
"given": "Orhan",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": [
"The Journal of Infection in Developing Countries"
],
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": false,
"domain": []
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-21T20:42:43Z",
"timestamp": 1645476163000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-21T20:44:45Z",
"timestamp": 1645476285000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
2,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-02-21T21:15:33Z",
"timestamp": 1645478133507
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issn-type": [
{
"type": "electronic",
"value": "1972-2680"
}
],
"issue": "01",
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
]
},
"journal-issue": {
"issue": "01",
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
]
}
},
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0",
"content-version": "unspecified",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
],
"date-time": "2022-01-31T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1643587200000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://jidc.org/index.php/journal/article/download/14924/2721",
"content-type": "application/pdf",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://jidc.org/index.php/journal/article/download/14924/2721",
"content-type": "unspecified",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "similarity-checking"
}
],
"member": "2222",
"original-title": [],
"page": "57-62",
"prefix": "10.3855",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
]
},
"published-online": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
1,
31
]
]
},
"publisher": "Journal of Infection in Developing Countries",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"score": 1,
"short-container-title": [
"J Infect Dev Ctries"
],
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"Virology",
"Infectious Diseases",
"General Medicine",
"Microbiology",
"Parasitology"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": [
"Reducing length of hospital stay with colchicine"
],
"type": "journal-article",
"volume": "16"
}
