Public health impact of poor sleep on COVID-19, influenza and upper respiratory infections
et al., Sleep Medicine, doi:10.1016/j.sleep.2022.05.369, Jul 2022
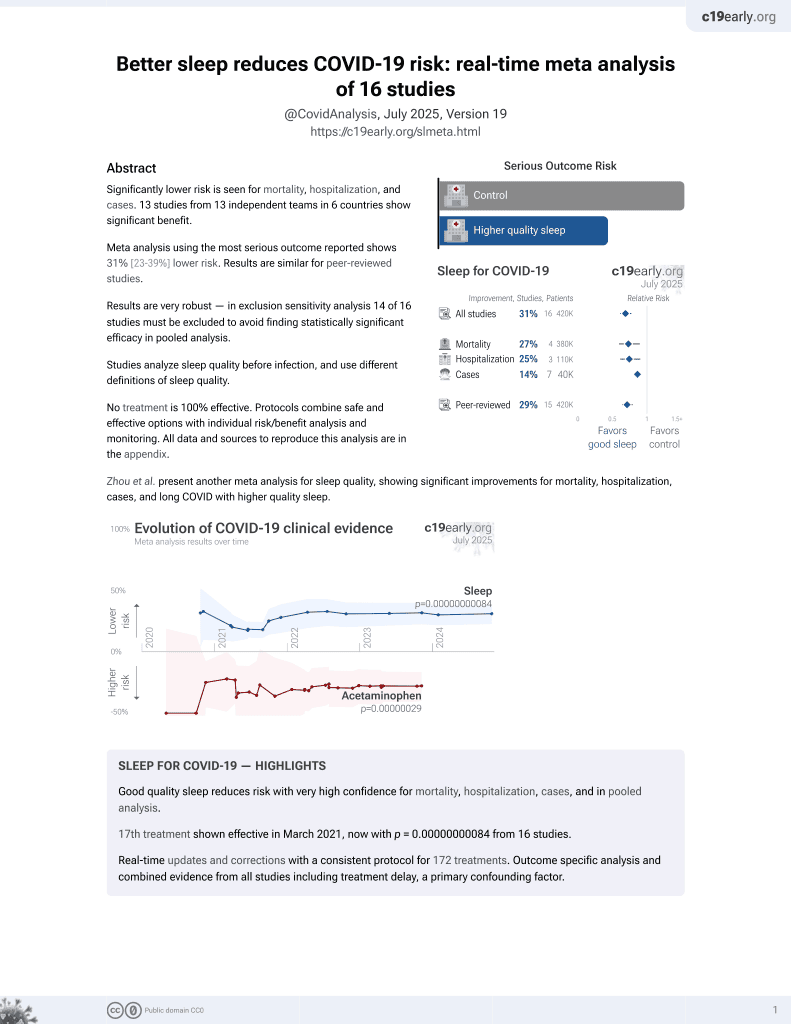
Sleep for COVID-19
18th treatment shown to reduce risk in
March 2021, now with p = 0.00000000084 from 16 studies.
No treatment is 100% effective. Protocols
combine treatments.
6,400+ studies for
210+ treatments. c19early.org
|
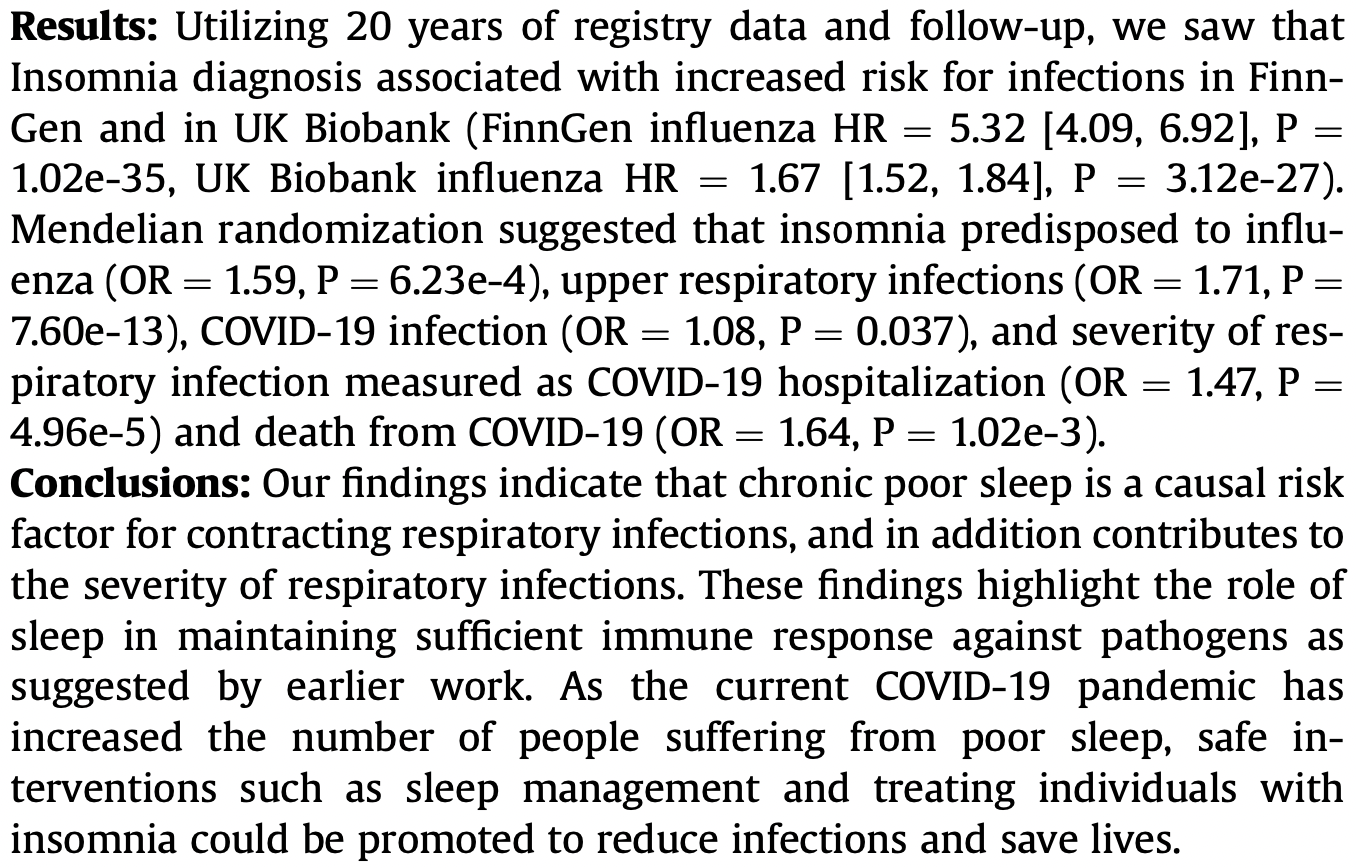
FinnGen Mendelian randomization study showing higher risk of COVID-19 mortality, hospitalization, and infection with insomnia.
|
risk of death, 39.0% lower, OR 0.61, p = 0.001, inverted to make OR<1 favor improved sleep, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of hospitalization, 32.0% lower, OR 0.68, p < 0.001, inverted to make OR<1 favor improved sleep, RR approximated with OR.
|
|
risk of case, 7.4% lower, OR 0.93, p = 0.04, inverted to make OR<1 favor improved sleep, RR approximated with OR.
|
| Effect extraction follows pre-specified rules prioritizing more serious outcomes. Submit updates |
Jones et al., 21 Jul 2022, retrospective, multiple countries, peer-reviewed, 12 authors.
PUBLIC HEALTH IMPACT OF POOR SLEEP ON COVID-19, INFLUENZA AND UPPER RESPIRATORY INFECTIONS
there were significant differences in the ASRS (t¼-6.175, p<0.001), WURS (t¼-6.087, p<0.01), p<0.001), p<0.001), p<0.01). Psychological characteristics differed significantly in ASRS (F¼22.517, p<0.001, aIn comparison of the insomnia-positive group to the insomnia-negative group, the OR was 4.088 in the PHQ-9 positive group (95% CI: 2.02-8.28) and 2.286 in the MDQ positive group (95% CI: 1.38-2.86). Conclusions: Insomnia was associated with a variety of mental symptoms, and the psychological symptoms were shown to be severe according to the severity of insomnia. Therefore, adequate intervention is needed to improve the symptoms of insomnia.
DOI record:
{
"DOI": "10.1016/j.sleep.2022.05.369",
"ISSN": [
"1389-9457"
],
"URL": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2022.05.369",
"alternative-id": [
"S1389945722005536"
],
"assertion": [
{
"label": "This article is maintained by",
"name": "publisher",
"value": "Elsevier"
},
{
"label": "Article Title",
"name": "articletitle",
"value": "Public health impact of poor sleep on COVID-19, influenza and upper respiratory infections"
},
{
"label": "Journal Title",
"name": "journaltitle",
"value": "Sleep Medicine"
},
{
"label": "CrossRef DOI link to publisher maintained version",
"name": "articlelink",
"value": "https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2022.05.369"
},
{
"label": "Content Type",
"name": "content_type",
"value": "simple-article"
},
{
"label": "Copyright",
"name": "copyright",
"value": "Copyright © 2022 Published by Elsevier B.V."
}
],
"author": [
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Jones",
"given": "S.E.",
"sequence": "first"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Maisha",
"given": "F.I.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Strausz",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Cade",
"given": "B.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Tervi",
"given": "A.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Helaakoski",
"given": "V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Broberg",
"given": "M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lammi",
"given": "V.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Lane",
"given": "J.M.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Redline",
"given": "S.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Saxena",
"given": "R.",
"sequence": "additional"
},
{
"affiliation": [],
"family": "Ollila",
"given": "H.M.",
"sequence": "additional"
}
],
"container-title": "Sleep Medicine",
"container-title-short": "Sleep Medicine",
"content-domain": {
"crossmark-restriction": true,
"domain": [
"clinicalkey.fr",
"clinicalkey.jp",
"clinicalkey.es",
"clinicalkey.com.au",
"clinicalkey.com",
"elsevier.com",
"sciencedirect.com"
]
},
"created": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-21T03:49:28Z",
"timestamp": 1658375368000
},
"deposited": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
21
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-21T17:52:13Z",
"timestamp": 1658425933000
},
"indexed": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
7,
22
]
],
"date-time": "2022-07-22T04:40:05Z",
"timestamp": 1658464805706
},
"is-referenced-by-count": 0,
"issued": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"language": "en",
"license": [
{
"URL": "https://www.elsevier.com/tdm/userlicense/1.0/",
"content-version": "tdm",
"delay-in-days": 0,
"start": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12,
1
]
],
"date-time": "2022-12-01T00:00:00Z",
"timestamp": 1669852800000
}
}
],
"link": [
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1389945722005536?httpAccept=text/xml",
"content-type": "text/xml",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
},
{
"URL": "https://api.elsevier.com/content/article/PII:S1389945722005536?httpAccept=text/plain",
"content-type": "text/plain",
"content-version": "vor",
"intended-application": "text-mining"
}
],
"member": "78",
"original-title": [],
"page": "S135",
"prefix": "10.1016",
"published": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"published-print": {
"date-parts": [
[
2022,
12
]
]
},
"publisher": "Elsevier BV",
"reference-count": 0,
"references-count": 0,
"relation": {},
"resource": {
"primary": {
"URL": "https://linkinghub.elsevier.com/retrieve/pii/S1389945722005536"
}
},
"score": 1,
"short-title": [],
"source": "Crossref",
"subject": [
"General Medicine"
],
"subtitle": [],
"title": "Public health impact of poor sleep on COVID-19, influenza and upper respiratory infections",
"type": "journal-article",
"update-policy": "http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/elsevier_cm_policy",
"volume": "100"
}